Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Hepatol. Jan 27, 2018; 10(1): 41-50
Published online Jan 27, 2018. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v10.i1.41
Published online Jan 27, 2018. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v10.i1.41
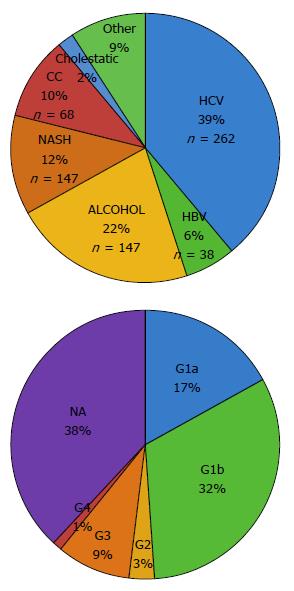
Figure 1 Etiologies oh hepatocellular carcinoma in the overall cohort and hepatitis C virus genotypes.
HCV was the main cause of liver disease related with hepatocellular carcinoma including cirrhotic and non-cirrhotic patients. Distribution of known HCV genotypes (G) showed that G1b was the most frequent (n = 88), followed by G1a (n = 47), G3 (n = 27), G2 (n = 8) and G4 (n = 2). HCV: Hepatitis C virus.
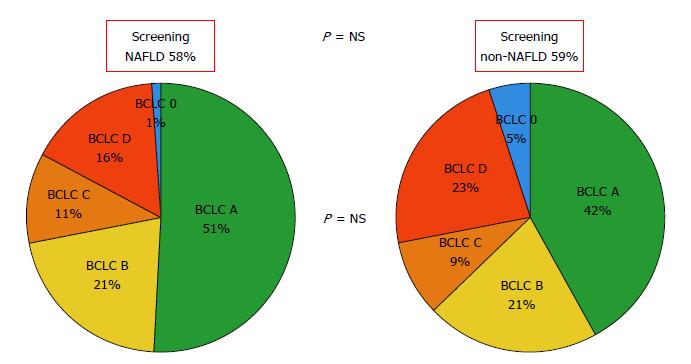
Figure 2 Comparative analysis regarding hepatocellular carcinoma previous surveillance and Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer staging at diagnosis between non alcoholic fatty liver disease and other etiologies of liver disease.
NAFLD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Non-NAFLD: Other than NAFLD (includes all other etiologies).
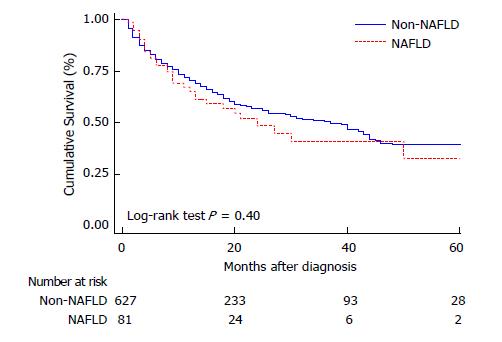
Figure 3 Comparative survival between non alcoholic fatty liver disease and other etiologies of liver disease.
NAFLD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; Non-NAFLD: Other than NAFLD (includes all other etiologies).
- Citation: Piñero F, Pages J, Marciano S, Fernández N, Silva J, Anders M, Zerega A, Ridruejo E, Ameigeiras B, D’Amico C, Gaite L, Bermúdez C, Cobos M, Rosales C, Romero G, McCormack L, Reggiardo V, Colombato L, Gadano A, Silva M. Fatty liver disease, an emerging etiology of hepatocellular carcinoma in Argentina. World J Hepatol 2018; 10(1): 41-50
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v10/i1/41.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v10.i1.41