修回日期: 2023-01-04
接受日期: 2023-01-17
在线出版日期: 2023-02-08
环状RNA是通过反向剪接形成的一大类单链共价闭合的非编码RNA, 广泛存在于多个细胞系和不同物种中, 具有高度保守的序列, 在特定组织或发育阶段特异性表达, 并极其稳定. 新近证据表明, 环状RNA与各类肿瘤密切相关, 可作为微小RNA及蛋白质"海绵"、转录调节因子、蛋白质翻译模板等角色, 在胃癌发生发展机制中发挥着多种重要作用. 本文就环状RNA的生物发生、特性、生物学功能、介导胃癌发生发展的潜在作用等方面研究现状进行了综述.
核心提要: circRNA作为分子调控机制可能是胃癌癌变的关键中介, 控制着许多涉及基因和信号分子的级联反应. 本文综述了circRNA参与胃癌的发生和进展及其对胃癌早期诊断和治疗的贡献.
引文著录: 吴雨林, 楼晓军, 范依静. circRNA影响胃癌发生发展及其机制的研究进展. 世界华人消化杂志 2023; 31(3): 85-91
Revised: January 4, 2023
Accepted: January 17, 2023
Published online: February 8, 2023
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are a large class of non-coding RNAs with single-strand covalently closed loops, formed by reverse splicing, which widely exist in many cell lines and diverse species. Some circRNAs have highly evolutionarily conserved sequences, or tissue-specific or cell-specific expression patterns, and many circRNAs are extremely stable. In the past decades, accumulating evidence has indicated that circRNAs participate in the mechanisms associated with the development of many kinds of tumors, exert important biological functions by acting as microRNA or protein ‘sponges’, transcriptional regulatory factors, and protein translation templates, and play key roles in the occurrence and development of gastric cancer. This review comprehensively summarizes the biogenesis, characteristics, and biological functions of circRNAs, and the molecular mechanisms underlying the role of circRNAs in the carcinogenesis and progression of gastric cancer.
- Citation: Wu YL, Lou XJ, Fan YJ. Role of circRNAs in gastric cancer. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi 2023; 31(3): 85-91
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1009-3079/full/v31/i3/85.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.11569/wcjd.v31.i3.85
胃癌(gastric cancer, GC)作为癌症相关死亡的第四大原因[1], 是全球目前所重视的主要公共卫生问题之一. 环状RNA(circular RNA, circRNA)在最初并未受到较多关注, 在长达三十余年时间内被认为是细胞内mRNA剪接错误导致的无功能副产物[2]. 随后, 由于分子生物学领域的不断进步和高通量测序等技术的广泛使用, circRNA的研究持续完善不断扩充, 许多数据支持circRNA在胃癌发生发展中的作用. 据报道, 多种circRNA在胃癌组织或细胞系中异常表达, 探索胃癌相关circRNA作为生物标志物或靶点的机制及潜能将为胃癌早期诊断、预后和有效治疗提供新的方向和可能性, 具有明确的临床意义.
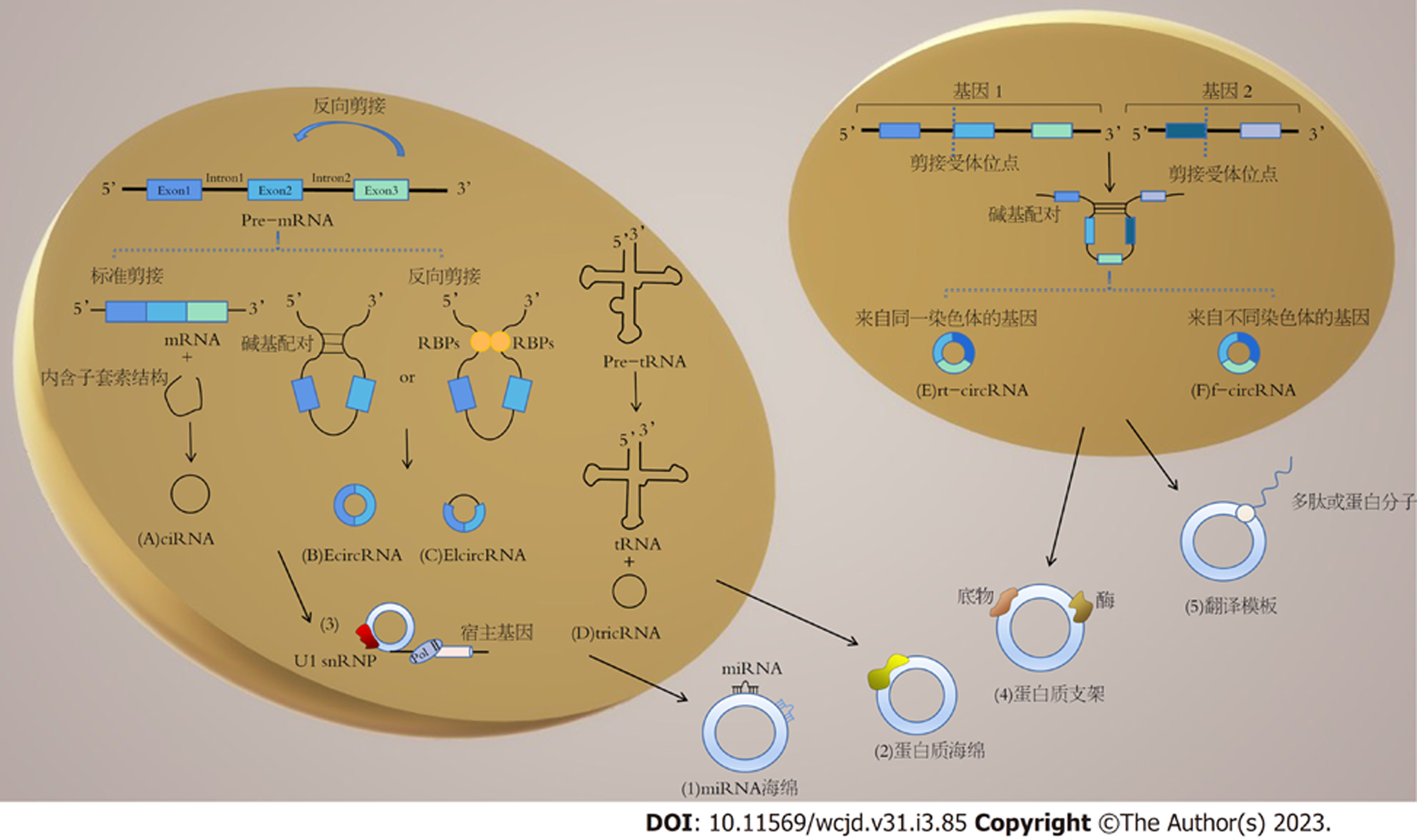
CircRNA作为一种缺少5′端和3′端的共价闭合环状结构的非编码RNA(non-coding RNA, ncRNA), 由一种称为反向剪接的非常规方式产生. 在反向剪接过程中, 下游的5'剪接供体部位与上游的3'剪接受体部位共价连接, 同时剪接体移除全部或部分内含子后其余序列再次连接, 形成单链共价闭合环[3]. 常规剪接点的突变或使用剪接体的通用抑制剂异银杏双黄酮, 均可一定程度上抑制反向剪接从而减少circRNA的产生[4], 这表明circRNA的反向剪接利用了常规剪接体或线性剪接相同的剪接位点. 具体circRNA类别及形成方式见图1.
既往有报道阐述了circRNA的4种可能形成机制[4,10]: (1)套索驱动的环化: 一个外显子的3′端与另一外显子的5′端通过核糖体蛋白的连续组装形成套索结构, 导致外显子跳读并驱动环化形成circRNA; (2)反向重复序列驱动的环化: 含有反向重复元件的两个内含子, 如Alu元件, 由互补的碱基配对, 使下游剪接位点与上游剪接位点紧密接近, 构成并排的双链, 推动环化反应从而形成circRNA; (3)RNA结合蛋白(RNA binding proteins, RBPs)驱动的环化: 内含子中RBPs的保守结合序列通过结合外显子侧翼的内含子, 引起下游内含子与上游内含子的相互作用而促进环化, 原理基本同(2); (4)tRNA前体剪接途径: tRNA剪接内切酶复合体(tRNA splicing endonuclease complex, TSEN)识别bulge-helix-bulge(BHB)序列, 再切除tRNA前体的内含子, 连接末端形成tRNA和tRNA内含子circRNA. 然而目前circRNA生成的具体机制尚未明确, 相关证据并不充分, 仍需要持续且更深入的研究.
circRNA以不同的角色发挥其功能(图1), 影响胃癌发生和进展. 在此, 我们讨论了circRNA主要的作用机制, 并通过特定的例子说明其与胃癌的关系.
miRNA作为另一类非编码RNA, 在翻译后水平上参与基因表达调控, 其失调与胃癌的发生有关[11]. circRNA具有多个miRNA反应元件(microRNA response elements, MER)[12], 可作为分子海绵以及内源竞争RNA(competing endogenous RNA, ceRNA)与相应的miRNA吸附结合. 其于胃癌的致癌或抑癌功能极其可能通过与miRNA的竞争性结合, 促使miRNA降解, 或降低 miRNA对mRNA的3′端非翻译区靶向结合的能力, 影响下游miRNA分子信号通路, 直接或间接调控胃癌细胞的增殖、侵袭和迁移等肿瘤活动[13,14].
既往一些研究已经证明了circRNA在胃癌中的miRNA海绵作用. CIRS-7/CDR1as是第一批被指出可作为miRNA海绵从而起到调控作用的circRNA. Pan等人[15]随后研究发现并证实, CIRS-7/CDR1as的过表达可通过PTEN/PI3K/AKT信号通路拮抗miR-7诱导的抑癌作用, 并认为该circRNA的异常表达与细胞增殖、凋亡以及TNM分期和预后相关. 在Yang和Wang等人的研究[16,17]中, circHIPK3和circSMAD4均于胃癌组织中过度表达, 分别通过miR-637/AKT1轴、miR-1276/WNT/β-catenin轴促进胃癌细胞的生长和代谢. hsa_circ_0081143[13]被报道在体内发挥海绵作用, 从而下调miR-646, 进一步与miR-646靶点细胞周期蛋白依赖性蛋白6(cyclin-dependent kinase 6, CDK6)相互作用, 因而可能在胃癌进展过程中发挥调节癌基因的作用. circCOL1A2通过阻隔miR-1286来调节泛素特异性蛋白酶10(ubiquitin-specific protease 10, USP10), 进而诱导复制激活因子C2刺激胃癌细胞的迁移和侵袭[18]. 另外, circ_0063526被证明为miR-449a的分子海绵, 可通过调节miR-449a/SHMT2轴, 增强胃癌细胞对顺铂(cisplatin, CDDP)的耐药性[19], 为胃癌治疗策略提供了一种新思路.
一些circRNA以蛋白质"海绵"、调节因子或支架的身份, 通过调节下游信息通路, 影响肿瘤细胞的恶性行为[4,20].
Pereira团队[21]分析了54个circRNA中存在的RBP位点, 其中, IGF2BP2和MOV10能够与这项研究中的所有circRNA结合; 此外, LIN28A和LIN28B在11个circRNA中均有结合位点, 并且在一项Meta分析中被报道与胃癌相关[22]. 另一项研究[23]中, Y-box结合蛋白-1(Y-box binding protein 1, YBX1)也是一种可与circRNA互相作用的RBP, circFAT1能直接与其结合进而间接阻断胃癌细胞的发生发展. Yang等人[24]表明circ-HuR在胃癌组织中表达下调, 这种异常表达对胃癌细胞的生长、侵袭和转移均有抑制作用. 进一步分析机制发现, circ-HuR可与CCHC型锌指核酸结合蛋白(CCHC-type zinc finger nucleic acid binding protein, CNBP)相互作用, 抑制CNBP与人类抗原R(human antigen R, HuR)启动子的结合, 导致HuR下调, 起到抑制肿瘤进展的作用. 此外, 有关于HuR,circTHBS1还能与其互相作用提高由HuR介导的抑制素βA(inhibin subunit beta A, INHβA)癌基因mRNA的稳定性, 激活转化生长因子-β(transforming growth factor-β, TGF-β)途径增强胃癌恶性程度[25].
与此同时, 可在细胞核中富集的circRNA有机会参与基因表达的调控, 通过与U1核内小核糖核蛋白(small nuclear ribonucleic protein, snRNP)或参与转录的蛋白结合, 调节RNA聚合酶Ⅱ(RNA-polⅡ RNA polymerase Ⅱ, PolⅡ)的活性, 在转录水平上调控基因的表达[26]. Ding研究[27]发现, 沉默NURF复合体亚基BPTF、RBBP4或SNF2L可诱导细胞凋亡, 抑制细胞迁移和侵袭, 并认为NURF复合物也促进了胃癌的进展; 定位于细胞核的circ_DONSON则可招募NURF复合体至SOX4启动子并启动其转录从而抑制胃癌的生长.
circRNA还可作为蛋白质支架来增强酶反应动力学, 例如, circ_CEA[28]起到支架作用并增强抑癌基因p53和细胞周期蛋白依赖性蛋白1(cyclin-dependent kinase 1, CDK1)之间的相互作用, 由CDK1介导的p53于Ser315位点的磷酸化因此而强化, 导致p53的活性被抑制, 使胃癌细胞免受应激诱导的凋亡, 于是circ_CEA靶向药物与化疗药物联合应用可能增加胃癌细胞的凋亡率, 缩小肿瘤体积, 减轻化疗药物的副作用.
最初, circRNA被预计是一类没有蛋白质编码能力的ncRNA[29]. 然而有研究表明, 包含起始密码子(AUG)、开放阅读框(open reading frame, ORF)、m6A内部核糖体进入位点 (m6A internal ribosome entry site, MIRES)和内部核糖体进入位点(internal ribosome entry site, IRES)[30]的circRNA可以通过滚环扩增(rolling circle amplification, RCA)驱动翻译[31,32], 因此可编码特殊的多肽或蛋白并具备相关生物学功能, 例如, Qu等[33]研究者研发了一种具有编码Spike蛋白受体结合域(RBD)的circRNA疫苗, 可以有效增强对抗新冠病毒的能力.
目前circRNA翻译功能在胃癌中的相关研究较少, 其中, circMAPK1被报道可编码新型抑癌蛋白MAPK1-109aa, 该蛋白通过竞争性结合MEK1并削弱MAPK1的磷酸化, 从而抑制MAPK1通路及其下游因子的激活, 削弱胃癌细胞增殖和侵袭的能力[34]. 在有关circGSPT1的研究中, Hu等人[35]发现该circRNA可由IRES驱动编码一个功能性多肽, 称为GSPT1-238aa, 其在体外可抑制胃癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭. 他们还证实GSPT1-238aa能与Vimentin/Beclin1/14-3-3复合体结合, 通过PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路调节胃癌细胞的自噬, 并认为该蛋白极有潜力作为胃癌治疗的新靶点.
根据生物信息学算法, 应有数千个起到编码蛋白质作用的circRNA. 然而, 到目前为止, 只有少数被证明具有翻译功能, 因而circRNA的翻译能力仍存在争议. 有研究认为[10], 这种翻译可能是无效的: 由于一个环状结构RNA的同一ORF的始末位置非常接近, 据此, 翻译过程的起始和终止将同时于同一位置发生, 该情况在目前已知条件下难以成立. 总而言之, circRNA翻译功能这一假设应考虑其他证据来源来支持, 有待进一步的全面研究.
胃癌发生发展涉及多个方面, 例如癌细胞的生长、死亡和肿瘤微环境等, 都共同决定了其生物学行为. 已有大量研究表明, circRNA在胃癌组织中高度特异性表达, 其表达水平与胃癌的恶性肿瘤生物学行为密切相关, 在影响胃癌发展方面发挥着重要作用.
研究发现许多在组织及细胞中异常表达的circRNA具有影响细胞周期或调节细胞增殖、死亡的能力. 例如, circFOXO3通过与细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶2(cyclin-dependent kinase 2, CDK2)和p21结合形成三元复合物circFOXO3-p21-CDK2, 该三元复合物阻断细胞周期蛋白E(cyclinE)/CDK2复合物的形成, 同时消除p21对细胞周期蛋白A(cyclinA)/CDK2复合物的抑制, 使细胞周期在G1期停滞, 抑制细胞增殖[36]. 在胃癌中, Xie等人[37]发现hsa_circ_0006470的过表达可显著诱导细胞周期阻滞而无法进入S期, 抑制胃癌细胞的增殖、迁移和活力以阻止胃癌的发生发展. 另外, Wang[38]认为circ_SKA3可能通过miR-520h/CDC42轴参与调节胃癌细胞增殖、细胞周期进程、集落形成、迁移、侵袭、凋亡. 近期, Xu等学者[39]还证明circST3GAL6通过调控FOXP2介导的转录抑制原癌基因MET, 而MET是经典自噬通路PI3K/Akt/mTOR的启动因素, circST3GAL6则可能诱导细胞凋亡和自噬抑制了胃癌细胞的恶性行为.
铁死亡是近期发现的一种有别于细胞凋亡、坏死和自噬的新型细胞死亡类型, 它涉及铁依赖的过氧化脂质和活性氧的积累从而诱导细胞死亡, 并被认为是胃癌的一种抑癌机制[40]. Jiang[41]的研究认为, circ_0000190在抑制胃癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭的同时, 还通过miR-382-5P/ZnRF3轴促进Erastin和ras选择性致死化合物(ras selective lethal 3, RSL3)诱导的铁死亡进而阻滞胃癌的发展. 而Li[42]发现circ_0008035通过调控miR-599及其靶基因EIF4A1减少铁蓄积和削弱脂质过氧化, 从而抑制细胞铁死亡, 导致胃癌的侵袭和进展.
上皮间充质转化(epithelial-mesenchymal transformation, EMT)即原有上皮表型的细胞的黏附性逐渐丢失, 分化为易侵袭、易迁移的间充质表型细胞的过程, 是肿瘤发展的重要途径, 伴随着大多数肿瘤细胞的转移. 在大多数EMT过程中, 上皮型钙黏蛋白(E-cad)含量减少, 而神经钙黏蛋白(N-cad)、Vimentin和EMT-TF因子等的表达水平逐渐增强[43]. 一项研究[44]中的体内外实验表明, circPTPN22可能通过与miRNA的竞争性结合靶向调控并促进EMT过程, 从而影响胃癌细胞的转移. 在另一项研究中, hsa_circ_0005230同样通过海绵作用影响miR-1299/RHOT1通路, 增强EMT途径并影响胃癌的生物学行为[45].
在胃癌的发展过程中, 癌细胞可以产生多种促进血管生成的蛋白质, 其中, 血管内皮生长因子(vascular endothelial growth factor, VEGF)被认为是一种经典的肿瘤血管形成分子, 诱导血管内皮细胞增殖, 促进肿瘤血管形成, 是肿瘤侵袭和转移的关键步骤, 与胃癌患者预后密切相关[46]. Lu等人[47]在研究circ-RanGAP1过程中发现其作为miR-877-3p的海绵, 上调VEGF的表达, 从而促进胃癌细胞的迁移和侵袭. 另外, HuR是VEGF信号通路中的重要元件, 通过与VEGF信使RNA受体结合并稳定其结构[48], circSHKBP1则通过上调HuR促进VEGF的翻译[49]. circ_0007099的表达在胃癌患者中下调, 其抗肿瘤功能可能通过介导miR-425-3p/GNG7轴抑制血管生成和葡萄糖代谢等胃癌细胞的恶性行为[50]. Du等[51]还发现EB病毒(Epstein-Barr virus, EBV)编码的circRNA, ebv-circLMP2A, 在调节EBV相关胃癌(EBV associated gastric carcinoma, EBVaGC)的肿瘤血管生成中是必需的, 并可能为EBVaGC提供有价值的治疗靶点.
糖酵解是机体相对缺氧时获得能量的主要途径, 是肿瘤生长和发展的主要能量来源, 同时癌细胞可在一定程度上增加缺氧诱导因子(hypoxia inducible factor-1 α, HIF-1α)的表达, 促进肿瘤组织处血管生成, 与肿瘤的侵袭、浸润和转移紧密关联[52], 是癌症恶变的重要始动因素. 一些circRNA已经显示出重编程细胞糖酵解的能力, 胃癌相关circRNA的下调可能会抑制胃癌细胞的糖酵解和其进展. Zhou等人[53]的研究提出, circ_0006089可能通过海绵化miR-3P增强胃癌细胞糖酵解能力并促进其生长、转移. circDNMT1是新近发现的一种用于肿瘤治疗的circRNA, Li等学者[54]研究发现circDNMT1可能是胃癌进展过程中糖酵解的重要贡献者, 认为circDNMT1的过表达抵消了miR-576-3P对葡萄糖摄取、丙酮酸产生、HIF-1α表达的抑制作用以及对葡萄糖摄取与乳酸生成比的升高作用, 提供胃癌进展的肿瘤微环境.
一些circRNA可以稳定地存在于人体体液中, 且丰度较高, 拥有较高的稳定性和重复性, 可作为液体活检的生物标志物[55].
Roy等人[56]认为血清circRNA指标可以有效识别早期胃癌患者, 并根据胃癌术后患者血清标本中多种circRNA的表达减少这一结果, 认为它们具有肿瘤特异性, 并极有可能起源于体循环. Reis-das-Mercês[57]发现5种circRNA(hsa_circ_0000211、hsa_circ_0000284、hsa_circ_0000524、hsa_circ_0001136和hsa_circ_0004771)在胃癌组织中的表达均显著上调, 其中, 有3种circRNA的qPCR表达谱在组织和血液两种类型的样本中相近, 也就是说, 这些circRNA作为侵袭性较小的胃癌血清学生物标志物具有巨大的临床应用潜力.
许多胃癌患者难以被早期诊断是由于其中相当一部分是由胃炎转化而来, 因此区分胃癌和胃炎也尤为重要. 为此, Ma等人[44]收集了104例健康者、70例胃炎患者和120例胃癌患者的血液样本, 以检测circPTPN22表达水平的差异. 研究结果表示, 血清circPTPN22水平在这三种人群中呈阶梯式升高, 在诊断胃癌的敏感性(78%)、特异性(84%)、总体准确率(80%)、阳性预测值(84%)和阴性预测值(76%)方面, circPTPN22均高于临床上常用的CEA和CA199.
在过去的十年中, circRNA已经成为一大类重要的非编码RNA, 其中许多circRNA通过不同的作用机制在胃癌的发生和发展中发挥关键作用, 这些分子作为胃癌诊断、预后的生物标记物以及治疗干预方面均具有明确的前景. 因此, 为了更好地指导、归纳和实验设计, 不同的研究团队已鉴定和记录了数以万计的circRNA, 特别是归纳了癌症特异性circRNA的综合数据库CSCD[58]. 然而, 对于这样一个相对年轻的研究领域, 目前还没有circRNA显示出在该领域临床实践中的适用性, 仍有复杂的争议亟待解决以及严峻的挑战需要面对, 这对推动未来胃癌诊断、预后监测生物学标志物以及治疗靶点至关重要.
学科分类: 胃肠病学和肝病学
手稿来源地: 浙江省
同行评议报告学术质量分类
A级 (优秀): 0
B级 (非常好): B
C级 (良好): C, C
D级 (一般): D
E级 (差): 0
科学编辑: 张砚梁 制作编辑:张砚梁
| 1. | Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209-249. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 2. | Xu C, Zhang J. Mammalian circular RNAs result largely from splicing errors. Cell Rep. 2021;36:109439. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 3. | Kristensen LS, Andersen MS, Stagsted LVW, Ebbesen KK, Hansen TB, Kjems J. The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 2019;20:675-691. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 4. | Ward Z, Pearson J, Schmeier S, Cameron V, Pilbrow A. Insights into circular RNAs: their biogenesis, detection, and emerging role in cardiovascular disease. RNA Biol. 2021;18:2055-2072. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 5. | Tang X, Ren H, Guo M, Qian J, Yang Y, Gu C. Review on circular RNAs and new insights into their roles in cancer. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021;19:910-928. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 6. | Wu W, Ji P, Zhao F. CircAtlas: an integrated resource of one million highly accurate circular RNAs from 1070 vertebrate transcriptomes. Genome Biol. 2020;21:101. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 7. | Kristensen LS, Jakobsen T, Hager H, Kjems J. The emerging roles of circRNAs in cancer and oncology. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2022;19:188-206. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 8. | Schmidt CA, Giusto JD, Bao A, Hopper AK, Matera AG. Molecular determinants of metazoan tricRNA biogenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47:6452-6465. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 9. | Vidal AF. Read-through circular RNAs reveal the plasticity of RNA processing mechanisms in human cells. RNA Biol. 2020;17:1823-1826. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 10. | Li R, Jiang J, Shi H, Qian H, Zhang X, Xu W. CircRNA: a rising star in gastric cancer. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020;77:1661-1680. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 11. | Zeng X, Xiao J, Bai X, Liu Y, Zhang M, Liu J, Lin Z, Zhang Z. Research progress on the circRNA/lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA axis in gastric cancer. Pathol Res Pract. 2022;238:154030. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 12. | Chen LL. The biogenesis and emerging roles of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016;17:205-211. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 13. | Xue M, Li G, Fang X, Wang L, Jin Y, Zhou Q. hsa_circ_0081143 promotes cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer by targeting miR-646/CDK6 pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2019;19:25. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 14. | Wang KW, Dong M. Role of circular RNAs in gastric cancer: Recent advances and prospects. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2019;11:459-469. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 15. | Pan H, Li T, Jiang Y, Pan C, Ding Y, Huang Z, Yu H, Kong D. Overexpression of Circular RNA ciRS-7 Abrogates the Tumor Suppressive Effect of miR-7 on Gastric Cancer via PTEN/PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119:440-446. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 16. | Yang D, Hu Z, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Xu J, Fu H, Zhu Z, Feng D, Cai Q. CircHIPK3 Promotes the Tumorigenesis and Development of Gastric Cancer Through miR-637/AKT1 Pathway. Front Oncol. 2021;11:637761. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 17. | Wang L, Li B, Yi X, Xiao X, Zheng Q, Ma L. Circ_SMAD4 promotes gastric carcinogenesis by activating wnt/¦Â-catenin pathway. Cell Prolif. 2021;54:e12981. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 18. | Li H, Chai L, Ding Z, He H. CircCOL1A2 Sponges MiR-1286 to Promote Cell Invasion and Migration of Gastric Cancer by Elevating Expression of USP10 to Downregulate RFC2 Ubiquitination Level. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022;32:938-948. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 19. | Yang G, Tan J, Guo J, Wu Z, Zhan Q. Exosome-mediated transfer of circ_0063526 enhances cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer cells via regulating miR-449a/SHMT2 axis. Anticancer Drugs. 2022;33:1047-1057. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 20. | Barbagallo D, Caponnetto A, Brex D, Mirabella F, Barbagallo C, Lauretta G, Morrone A, Certo F, Broggi G, Caltabiano R, Barbagallo GM, Spina-Purrello V, Ragusa M, Di Pietro C, Hansen TB, Purrello M. CircSMARCA5 Regulates VEGFA mRNA Splicing and Angiogenesis in Glioblastoma Multiforme Through the Binding of SRSF1. Cancers (Basel). 2019;11:194. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 21. | Pereira AL, Magalhães L, Pantoja RP, Araújo G, Ribeiro-Dos-Santos Â, Vidal AF. The Biological Role of Sponge Circular RNAs in Gastric Cancer: Main Players or Coadjuvants? Cancers (Basel). 2020;12:1982. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 22. | Zhang J, Xu A, Miao C, Yang J, Gu M, Song N. Prognostic value of Lin28A and Lin28B in various human malignancies: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Cell Int. 2019;19:79. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 23. | Fang J, Hong H, Xue X, Zhu X, Jiang L, Qin M, Liang H, Gao L. A novel circular RNA, circFAT1(e2), inhibits gastric cancer progression by targeting miR-548g in the cytoplasm and interacting with YBX1 in the nucleus. Cancer Lett. 2019;442:222-232. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 24. | Yang F, Hu A, Li D, Wang J, Guo Y, Liu Y, Li H, Chen Y, Wang X, Huang K, Zheng L, Tong Q. Circ-HuR suppresses HuR expression and gastric cancer progression by inhibiting CNBP transactivation. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:158. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 25. | Qiu S, Li B, Xia Y, Xuan Z, Li Z, Xie L, Gu C, Lv J, Lu C, Jiang T, Fang L, Xu P, Yang J, Li Y, Chen Z, Zhang L, Wang L, Zhang D, Xu H, Wang W, Xu Z. CircTHBS1 drives gastric cancer progression by increasing INHBA mRNA expression and stability in a ceRNA- and RBP-dependent manner. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13:266. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 27. | Ding L, Zhao Y, Dang S, Wang Y, Li X, Yu X, Li Z, Wei J, Liu M, Li G. Circular RNA circ-DONSON facilitates gastric cancer growth and invasion via NURF complex dependent activation of transcription factor SOX4. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:45. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 28. | Yuan Y, Zhang X, Du K, Zhu X, Chang S, Chen Y, Xu Y, Sun J, Luo X, Deng S, Qin Y, Feng X, Wei Y, Fan X, Liu Z, Zheng B, Ashktorab H, Smoot D, Li S, Xie X, Jin Z, Peng Y. Circ_CEA promotes the interaction between the p53 and cyclin-dependent kinases 1 as a scaffold to inhibit the apoptosis of gastric cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13:827. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 30. | Zhao J, Li Y, Wang C, Zhang H, Zhang H, Jiang B, Guo X, Song X. IRESbase: A Comprehensive Database of Experimentally Validated Internal Ribosome Entry Sites. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2020;18:129-139. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 31. | Lu Y, Li K, Gao Y, Liang W, Wang X, Chen L. CircRNAs in gastric cancer: current research and potential clinical implications. FEBS Lett. 2021;595:2644-2654. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 32. | Wang Y, Wu C, Du Y, Li Z, Li M, Hou P, Shen Z, Chu S, Zheng J, Bai J. Expanding uncapped translation and emerging function of circular RNA in carcinomas and noncarcinomas. Mol Cancer. 2022;21:13. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 33. | Qu L, Yi Z, Shen Y, Lin L, Chen F, Xu Y, Wu Z, Tang H, Zhang X, Tian F, Wang C, Xiao X, Dong X, Guo L, Lu S, Yang C, Tang C, Yang Y, Yu W, Wang J, Zhou Y, Huang Q, Yisimayi A, Liu S, Huang W, Cao Y, Wang Y, Zhou Z, Peng X, Wang J, Xie XS, Wei W. Circular RNA vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 and emerging variants. Cell. 2022;185:1728-1744.e16. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 34. | Jiang T, Xia Y, Lv J, Li B, Li Y, Wang S, Xuan Z, Xie L, Qiu S, He Z, Wang L, Xu Z. A novel protein encoded by circMAPK1 inhibits progression of gastric cancer by suppressing activation of MAPK signaling. Mol Cancer. 2021;20:66. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 35. | Hu F, Peng Y, Chang S, Luo X, Yuan Y, Zhu X, Xu Y, Du K, Chen Y, Deng S, Yu F, Feng X, Fan X, Ashktorab H, Smoot D, Meltzer SJ, Li S, Wei Y, Zhang X, Jin Z. Vimentin binds to a novel tumor suppressor protein, GSPT1-238aa, encoded by circGSPT1 with a selective encoding priority to halt autophagy in gastric carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2022;545:215826. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 36. | Bivik Stadler C, Arefin B, Ekman H, Thor S. PIP degron-stabilized Dacapo/p21(Cip1) and mutations in ago act in an anti- versus pro-proliferative manner, yet both trigger an increase in Cyclin E levels. Development. 2019;146:dev175927. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 37. | Xie J, Ning Y, Zhang L, Lin Y, Guo R, Wang S. Overexpression of hsa_circ_0006470 inhibits the malignant behavior of gastric cancer cells via regulation of miR-1234/TP53I11 axis. Eur J Histochem. 2022;66:3477. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 38. | Wang C, Jiang H, Peng J, Weng D, Zhang Y, Zhou Y, Zhang Q. Circular RNA circ_SKA3 enhances gastric cancer development by targeting miR-520h. Histol Histopathol. 2022;18521. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 39. | Xu P, Zhang X, Cao J, Yang J, Chen Z, Wang W, Wang S, Zhang L, Xie L, Fang L, Xia Y, Xuan Z, Lv J, Xu H, Xu Z. The novel role of circular RNA ST3GAL6 on blocking gastric cancer malignant behaviours through autophagy regulated by the FOXP2/MET/mTOR axis. Clin Transl Med. 2022;12:e707. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 40. | Ma M, Kong P, Huang Y, Wang J, Liu X, Hu Y, Chen X, Du C, Yang H. Activation of MAT2A-ACSL3 pathway protects cells from ferroptosis in gastric cancer. Free Radic Biol Med. 2022;181:288-299. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 41. | Jiang M, Mo R, Liu C, Wu H. Circ_0000190 sponges miR-382-5p to suppress cell proliferation and motility and promote cell death by targeting ZNRF3 in gastric cancer. J Biochem. 2022. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 42. | Li C, Tian Y, Liang Y, Li Q. Circ_0008035 contributes to cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis and ferroptosis in gastric cancer via miR-599/EIF4A1 axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2020;20:84. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 43. | Shang BQ, Li ML, Quan HY, Hou PF, Li ZW, Chu SF, Zheng JN, Bai J. Functional roles of circular RNAs during epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:138. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 44. | Ma S, Kong S, Gu X, Xu Y, Tao M, Shen L, Shen X, Ju S. As a biomarker for gastric cancer, circPTPN22 regulates the progression of gastric cancer through the EMT pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2021;21:44. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 45. | Peng YY, Sun D, Xin Y. Hsa_circ_0005230 is up-regulated and promotes gastric cancer cell invasion and migration via regulating the miR-1299/RHOT1 axis. Bioengineered. 2022;13:5046-5063. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 46. | Mortara L, Benest AV, Derosa L, Chouaib S, Ribatti D. Editorial: The intricate innate immune-cancer cell relationship in the context of tumor angiogenesis, immunity and microbiota: The angiogenic switch in the tumor microenvironment as a key target for immunotherapies. Front Immunol. 2022;13:1045074. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 47. | Lu J, Wang YH, Yoon C, Huang XY, Xu Y, Xie JW, Wang JB, Lin JX, Chen QY, Cao LL, Zheng CH, Li P, Huang CM. Circular RNA circ-RanGAP1 regulates VEGFA expression by targeting miR-877-3p to facilitate gastric cancer invasion and metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2020;471:38-48. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 48. | Yang LQ, Yu SP, Yang YT, Zhao YS, Wang FY, Chen Y, Li QH, Tian P, Zhu YY, Zhang JG, Lin GQ. Muscone derivative ZM-32 inhibits breast tumor angiogenesis by suppressing HuR-mediated VEGF and MMP9 expression. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;136:111265. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 49. | Xie M, Yu T, Jing X, Ma L, Fan Y, Yang F, Ma P, Jiang H, Wu X, Shu Y, Xu T. Exosomal circSHKBP1 promotes gastric cancer progression via regulating the miR-582-3p/HUR/VEGF axis and suppressing HSP90 degradation. Mol Cancer. 2020;19:112. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 50. | Zhang Z, Zhou Y, Zhou N, Yin J, Kuang X. Circ_0007099 upregulates GNG7 to function as a tumor inhibitor in gastric carcinoma by interacting with miR-425-3p. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022;13:1626-1639. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 51. | Du Y, Zhang JY, Gong LP, Feng ZY, Wang D, Pan YH, Sun LP, Wen JY, Chen GF, Liang J, Chen JN, Shao CK. Hypoxia-induced ebv-circLMP2A promotes angiogenesis in EBV-associated gastric carcinoma through the KHSRP/VHL/HIF1¦Á/VEGFA pathway. Cancer Lett. 2022;526:259-272. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 52. | Ng WL, Mohd Mohidin TB, Shukla K. Functional role of circular RNAs in cancer development and progression. RNA Biol. 2018;15:995-1005. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 53. | Zhou Y, Zhang Q, Liao B, Qiu X, Hu S, Xu Q. circ_0006089 promotes gastric cancer growth, metastasis, glycolysis, and angiogenesis by regulating miR-361-3p/TGFB1. Cancer Sci. 2022;113:2044-2055. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 54. | Li H, Cao B, Zhao R, Li T, Xu X, Cui H, Deng H, Gao J, Wei B. circDNMT1 Promotes Malignant Progression of Gastric Cancer Through Targeting miR-576-3p/Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1 Alpha Axis. Front Oncol. 2022;12:817192. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 55. | 鲁 意迅, 陈 凛. 环状RNA在胃癌中的研究进展. 中国普外基础与临床杂志. 2022;29:255-263. |
| 56. | Roy S, Kanda M, Nomura S, Zhu Z, Toiyama Y, Taketomi A, Goldenring J, Baba H, Kodera Y, Goel A. Diagnostic efficacy of circular RNAs as noninvasive, liquid biopsy biomarkers for early detection of gastric cancer. Mol Cancer. 2022;21:42. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 57. | Reis-das-Mercês L, Vinasco-Sandoval T, Pompeu R, Ramos AC, Anaissi AKM, Demachki S, de Assumpção PP, Vidal AF, Ribeiro-Dos-Santos Â, Magalhães L. CircRNAs as Potential Blood Biomarkers and Key Elements in Regulatory Networks in Gastric Cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:650. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 58. | Feng J, Chen W, Dong X, Wang J, Mei X, Deng J, Yang S, Zhuo C, Huang X, Shao L, Zhang R, Guo J, Ma R, Liu J, Li F, Wu Y, Han L, He C. CSCD2: an integrated interactional database of cancer-specific circular RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50:D1179-D1183. [PubMed] [DOI] |