修回日期: 2018-11-10
接受日期: 2018-12-11
在线出版日期: 2019-03-28
胃癌(gastric cancer, GC)是消化道最常见的恶性肿瘤之一, 其发病率和死亡率在所有癌症中均位列第二位, 且中晚期GC患者所占比例较高, 有不断上升的趋势, 治疗疗效极差. 近年来, 大量的研究证明, miR-200c在GC患者血清中的含量明显升高, 并且miR-200c的水平与上皮间质转化及淋巴结转移密切相关. 因此, 深入揭示miR-200c在GC诊断中的作用不仅有助于GC的早期诊断, 还可以用来制定新的有效治疗策略以及判断GC患者的预后. 本文就miR-200c在GC早期诊断中的作用研究进展进行综述, 并对其应用前景进行展望.
核心提要: 胃癌(gastric cancer, GC)是消化道最常见的恶性肿瘤之一, 其发病率和死亡率在所有癌症中均位列第二位, 在所有就诊的患者中, 晚期GC患者所占比例较高, 有不断上升的趋势. 如何提高GC患者的早期诊断水平并跟踪评估GC患者的治疗疗效对提高GC患者的治疗效果具有重要意义. 长期以来, 癌胚抗原CEA已经成为胃肠道肿瘤的较好标志物, 但仍无法精准的预测GC患者的发病情况. 有关miR-200c在GC患者血清中的表达对进一步提高GC的早期诊断率可能具有重要意义.
引文著录: 张玲倩, 卢宁. miR-200c在胃癌早期诊断中的作用研究现状及展望. 世界华人消化杂志 2019; 27(6): 382-388
Revised: November 10, 2018
Accepted: December 11, 2018
Published online: March 28, 2019
Gastric cancer (GC) is one of the most common malignant tumors of the digestive tract, and its morbidity and mortality still rank the second among all cancers. The proportion of patients with advanced GC is higher, and their therapeutic effect is extremely poor. In recent years, numerous studies have shown that the content of miR-200c in GC patients is significantly increased, and the level of miR-200c is closely related to epithelial-mesenchymal transition and lymph node metastasis. Therefore, in-depth disclosure of the role of miR-200c in the diagnosis of GC will not only contribute to the early diagnosis of GC, but also help develop new effective treatment strategies and judge the prognosis of patients with GC. This article reviews the role of miR-200c in the early diagnosis of GC and discusses its application prospects.
- Citation: Zhang LQ, Lu N. Role of miR-200c in early diagnosis of gastric cancer: Current status and prospects. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi 2019; 27(6): 382-388
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1009-3079/full/v27/i6/382.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.11569/wcjd.v27.i6.382
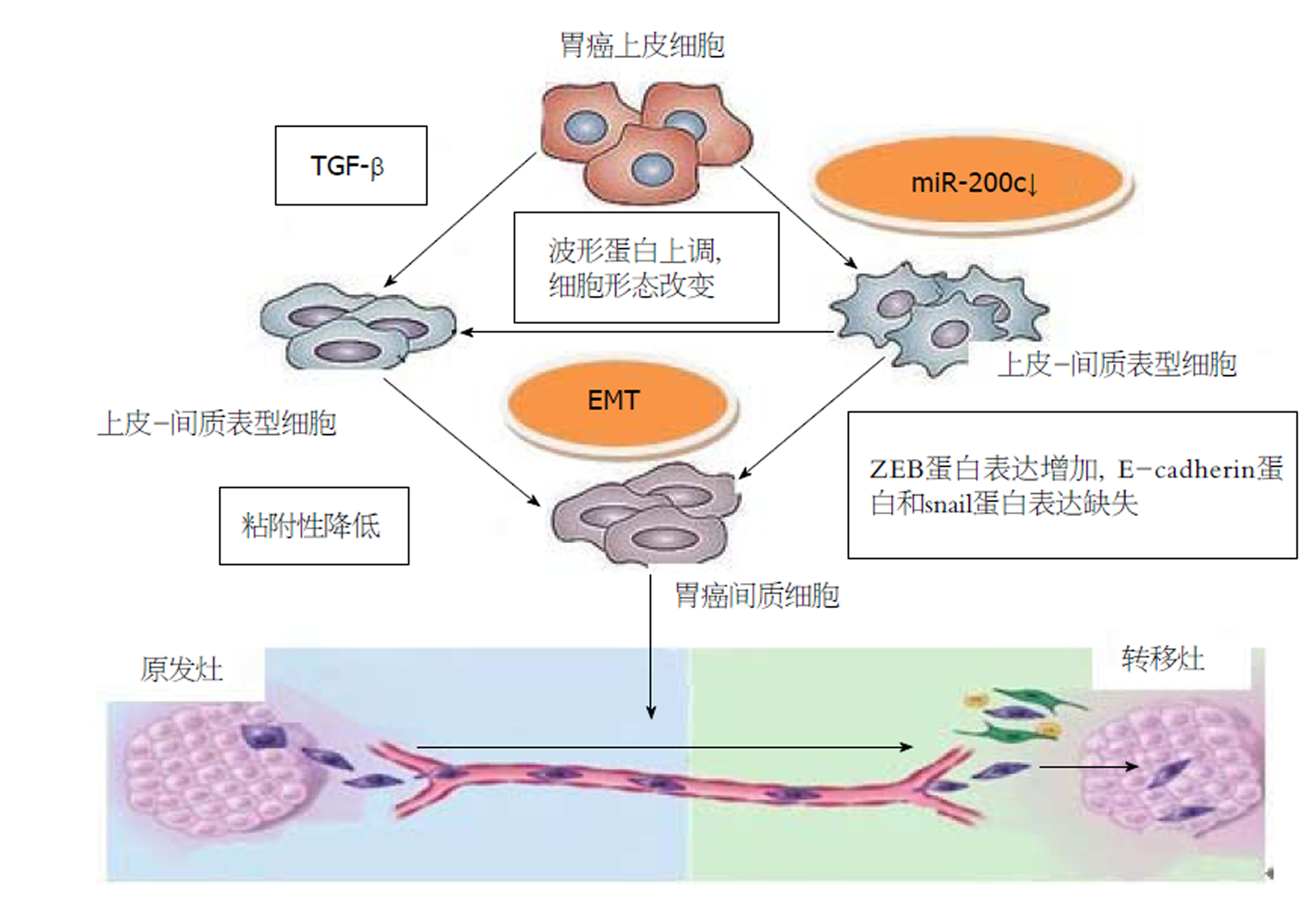
胃癌(gastric cancer, GC)是消化道最常见的恶性肿瘤之一, 严重威胁人类健康. 近年来随着检查和治疗手段的不断提高, 其发病率总体有所下降, 但仍居于消化道恶性肿瘤的首位[1]. 由于GC的发展规律和特点, 临床上有相当一部分患者在GC术后、化疗后仍出现局部复发和(或)远处转移, 严重影响了GC患者的预后[2-9]. 上皮间质转化(epithelial mesenchymal transition, EMT)的发生与肿瘤侵袭、转移、复发密切相关, 在肿瘤细胞获得EMT的过程中, 上皮源性的细胞失去极性, 导致肿瘤细胞的黏附能力下降、迁移运动能力增加[10,11]. 目前有研究证实GC细胞中miR-200c的表达下调, 导致与EMT密切相关的E-钙黏蛋白表达减少, 细胞间的黏附作用降低, 侵袭转移能力增加[12-15]. 因此, 有必要探讨miR-200c调控EMT阻止GC复发转移的作用机制.
microRNAs(简称miRNA或miR)是一类短小的单链非编码RNA, 一般由17-25 bp组成, 最早由Lee等[16]在1993年研究参与调控线虫时序发育时发现, 统称为小分子RNA或微小RNA(microRNA). miRNA不能翻译蛋白质, 主要在转录后水平调控其他编码基因, 即通过与其配对的特定靶信使RNA(mRNA)的3'-非翻译区(3'-UTR)来抑制翻译或诱导靶mRNA的降解, 参与细胞的增殖、凋亡与分化等多种重要生命活动的调控[17]. 近年来研究发现, miRNA参与多种恶性肿瘤的演进, 起抑癌基因或原癌基因的作用. miRNA曾经长期被视为转录的副产物, 然而越来越多的证据表明, miRNA参与正常生理活动与病理过程的调控[18]. miRNA参与调节几乎所有已知的癌变过程, 包括细胞生长、增殖、分化、血管生成、细胞凋亡以及侵袭和转移[19].
很多研究显示, miRNA与肿瘤的发生发展密切相关, 采用基因芯片技术对多种肿瘤组织样本中的miRNA表达谱进行检测, 发现大多数miRNA在肿瘤样本中出现下调, 少部分miRNA表达水平上调[20]. 在各种人类实体肿瘤和恶性血液病研究中, 整个miRNA基因组的研究显示在肿瘤和正常组织间是有miRNA表达差异的, miRNA在细胞分化、增殖、迁移和凋亡中起重要的调控作用[21]. 因此, miRNA的功能失调可能导致人类各种疾病如肿瘤、肝脏疾病、免疫机能障碍和代谢紊乱的发生[22,23].
miRNA-200家族是miRNA家族的重要成员[17]. 最近的研究表明, 种子序列决定miRNA-200家族的区分, 并决定着各成员的功能差异. miRNA-200家族分为miRNA-200a、miRNA-141和miRNA-200b、miRNA-200c、miRNA-429两个亚家族[24]. 前者有相同的种子序列"AACACU"; 后者有共同种子序列"AAUACU". 作为miRNA-200家族中的一个成员, miRNA-200c基因簇定位于12号染色体p13.31上, 其基因序列为 5'-UAAUACUGCCGGGUAAUGAUGGA-3'. miR-200c的作用靶点是转录因子ZEB1和ZEB2(锌指E盒同源结合蛋白-1、2)[25,26].
目前已有相关实验证实miR-200c通过靶向多种蛋白影响GC细胞的增殖、侵袭能力, 且多数研究结果显示miR-200c可显著抑制人GC细胞增殖[27,28]. 伍菲菲等[29]采用MTT法检测miR-200c对人GCMGC-803细胞生长增殖能力的影响, 并通过荧光素酶报告载体系统证实miR-200c可抑制GC细胞增殖, 并进一步证实DNMT3B是miR-200c直接调控的靶基因, miR-200c通过靶向调控DNMT3B的表达而抑制GC细胞生长增殖能力.
李鹰飞等[30]通过CCK-8法、FCM、Transwell等方法检测了48例GC和相应癌旁组织的标本, 采用双荧光素酶实验验证miR-200c对EFNA1基因的靶向抑制作用, 并分析GC组织中EFNA1蛋白表达与患者性别、年龄、吸烟、饮酒、病理类型、浸润深度、淋巴结及远处转移、肿瘤部位间的关系, 结果显示与对照组相比, miR-200c可使GC细胞SGC7901的增殖能力明显降低(P<0.05), 总凋亡率升高(P<0.05), 侵袭能力降低(P<0.05), 并证实miR-200c可通过靶向EFNA1基因抑制GC细胞增殖及侵袭, 促进凋亡.
由此说明, 尽管miR-200c抑制GC细胞增殖的作用靶点不同, 作用机制也不同, 但是都能够通过不同的信号通路起到抑制GC细胞增殖的能力. 其确切的作用机制及靶点仍有待于进一步的实验加以补充完善.
ZEB-1是重要的非受体细胞核转录因子, 定位于人类10号染色体短臂上, 能抑制多种基因的表达[31]. 已有研究表明, miR-200c可通过与ZEB-1的3'-UTR结合, 抑制ZEB-1蛋白的表达[32], ZEB-1蛋白进一步与E-cadherin蛋白启动子上保守的E2-boxes结合, 使E-cadherin表达上调, 从而加强了细胞间的黏附作用, 抑制恶性肿瘤细胞的侵袭转移能力[33]. 除了miR-200c对ZEB1的抑制作用, 研究还发现ZEB1蛋白的表达上调后可以明显抑制miR-200c的表达, 这样在miR-200c和ZEB1之间就形成一个负反馈回路, 起到调节肿瘤细胞的侵袭转移能力[34].
目前已有研究证实miR-200c能够通过抑制ZEB-1蛋白的表达, 从而起到抑制肿瘤细胞的迁移及侵袭能力. 宋永站等[35]利用脂质体Lipofectamin2000将人工合成的miR-200c转染SGC-7901细胞, 转染24 h后RT-PCR检测各转染组中ZEB1基因的表达量, Transwell小室法检测各转染组细胞迁移和侵袭能力的变化. 结果表明转染miR-200c能明显抑制SGC-7901细胞ZEB1基因的表达及细胞迁移和侵袭能力. 且ZEB1基因的表达水平与肿瘤细胞的侵袭和迁移能力相关.
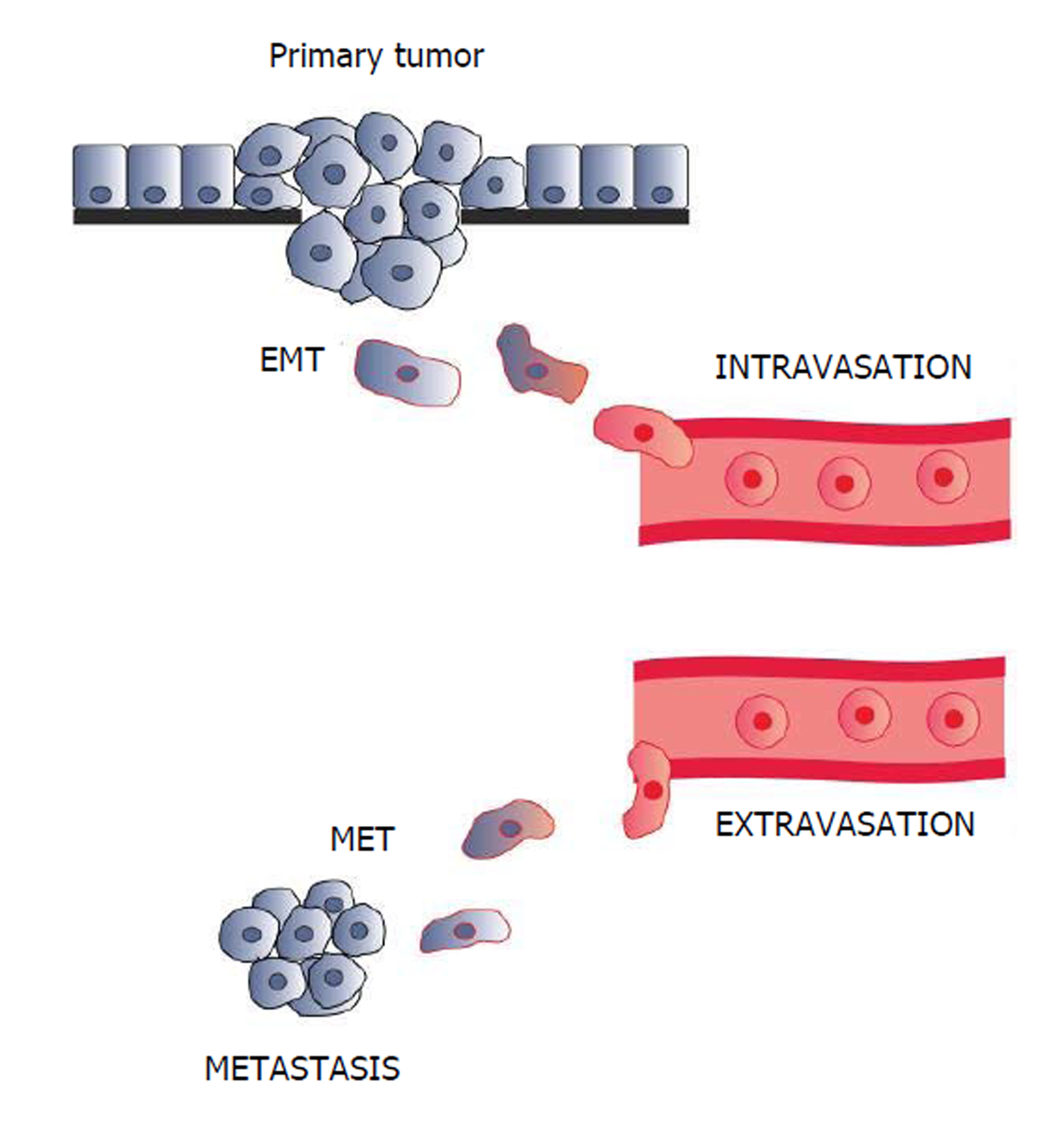
EMT是肿瘤重要的恶性生物学行为之一, 存在于人体多个病理生理过程中, 以上皮表型缺失和获得间质表型为主要特征[24], 研究表明肿瘤的侵袭转移机制中包含EMT这一过程[36]. EMT的发生与肿瘤侵袭、转移、复发密切相关, 在肿瘤细胞获得EMT的过程中, 上皮源性的细胞失去极性, 导致肿瘤细胞的黏附能力下降, 迁移运动能力增加[37]. 当发生EMT时, 上皮细胞失去顶-基底极性, 细胞间的黏附力减弱或者消失, 细胞骨架重塑, 获得纤维细胞样形态, 同时上皮表型标志物E-cadherin蛋白表达下调, 而间质型标志物N-钙黏蛋白(N-cadherin)、纤维黏连蛋白(fibronectin, FN)等表达上调, 同时特异性核转录因子ZEB-l表达也随之上调[38,39]. 这一系列的因素共同导致肿瘤细胞的侵袭转移能力增加(图1).
有研究指出肿瘤形成机制中包含肿瘤细胞EMT这一过程[41]. EMT使上皮细胞失去了细胞极性以及与基底膜的连接, 转换为具有较高迁移与侵袭、抗凋亡和降解细胞外基质的能力的间质表型. 然而这过程有赖于miR-200c对细胞的调控[42]. miR-200c是EMT过程中的重要调节基因, 除了在正常细胞的表型转换中起作用, 还在多种类型癌细胞的表型转换中起调节作用[43]. 大量研究证实, 在多种肿瘤组织中存在miR-200c的表达缺失[44]. DNA的甲基化、致癌基因的激活和肿瘤抑制基因p53的缺失导致的miR-200c的缺失和癌细胞的低分化和干细胞化存在着联系[45].
不少功能性研究表明, miR-200c是抑制EMT和不同类型的癌症侵袭转移的一个关键的因素[46]. 机制上, EMT表现为E-cadherin的表达缺失, 组成细胞骨架的角蛋白转化为波形蛋白, 从而引起细胞形态的改变, 促进了肿瘤细胞的运动和侵袭能力[47]. 目前, 研究最为热门的miR-200c的作用靶点是转录因子ZEB1和ZEB2, 而转录因子ZEB1/ZEB2可下调E-cadherin的表达, 降低细胞间黏附作用, 从而促进肿瘤细胞的侵袭转移[48](图2). miR-200c可通过直接抑制ZEBl/ZEB2的表达, 进而增加E-cadherin的表达, 阻止EMT的发生, 从而抑制GC侵袭和转移能力.
目前, 已有多个实验证实, miR-200c在GC组织中的含量与正常组织相比明显下调. 李小华等[49]通过采用实时荧光定量PCR分析了25例GC组织中miR-200家族的表达. 结果显示: 与癌旁正常组织相比, GC组织中miR-200家族有不同程度的表达下调(P<0.05), 在TNM Ⅲ期GC组织中miR-200b, miR-200c表达显著低于癌旁正常组织(P<0.05). GC组织中的miR-200家族表达与E-cadherin的表达下调呈正相关(P<0.05). 结果表明, GC组织中miR-200家族表达下调可能与GC侵袭转移有关. 周欣亮等[50]检测了GC组织中miR-200c的表达水平与GC患者临床病理特征的相关性, 结果表明: miR-200c在GC细胞中的表达下调促进了GC的复发与转移, 且miR-200c的表达水平显著降低; 且miR-200c的表达与肿瘤TNM分期、肿瘤浸润深度、无病生存期之间存在显著的负相关关系. 黄俊等[51]采用原位杂交法检测了40例正常人群胃黏膜组织以及121例GC患者组织中miR-200c的表达情况, 结果显示miR-200c在GC组织中表达显著下调, 且miR-200c的表达水平与GC临床分期和淋巴结转移情况显著相关(P<0.05). 由此可见, miR-200c在GC组织中的含量与正常组织相比明显下调, 且与GC患者的临床分期和淋巴结转移情况密切相关. 类似研究结果较多, 我们分别检索了中国知网、万方、Pubmed等数据库, 归纳出相关研究结果如下(表1).
林国友等[54]采用逆转录荧光PCR方法检测50例GC患者和50例健康对照者静脉血清中miR-200c的表达情况, 结果显示GC患者中血清miR-200c水平明显高于健康对照组, ROC曲线分析显示miR-200c诊断GC的ROC曲线下面积为0.725(95%CI: 0.698-0.851), 敏感度和特异度分别为67.5%和78.5%. miR-200c水平与患者年龄、性别、肿瘤大小和TNM分期无关, 提示miR-200c水平可能成为GC独立诊断标志物. 唐锦莉等[55]应用实时荧光定量PCR技术(TaqMan探针法)研究了47例胃腺癌患者及50名健康对照者检测血清中miR-200c的表达水平, 分析其与年龄、性别、肿瘤定位、大小、分化程度、TNM分期、淋巴结转移等病理参数的关系, 并比较30例GC根治术前及术后6-8 d血浆中miR-200c的表达的变化情况, 结果显示miR-200c在GC患者血清中相对表达量为(15.15±3.02), 与对照组(3.39±0.87)相比, 显著升高(t = -2.854, P = 0.006). 且miR-200c在术后表达降低(t = 2.978, P = 0.006). ROC曲线分析表明血清miR-200c曲线下面积(AUC)分别是0.692、0.792、0.798; 敏感性和特异性分别是97%、54%. 证实了miR-200c对胃腺癌的联合检测具有较高的灵敏度和特异性. Zhang等[56]应用定量RT-PCR分析了98名GC患者血清样品中miR-200c表达水平, 并确定该表达与临床病理特征和存活之间的关系. 结果发现GC患者的相对血清miR-200c水平显著高于健康对照, 且GC患者血清miR-200c水平高的患者的总生存率显著低于低水平患者. 这表明GC患者中血清miR-200c的表达可能作为GC患者早期诊断的一个较好指标, 且由于其灵敏度和特异度均较好, 可用于评估GC患者的预后.
近年来, 虽然人们在GC的早期诊断方面做了很多有意义的探索, 但尚未取得长足的进展. 胃镜的广泛使用对GC患者的早期定位和定性诊断具有不可替代的作用, 但胃镜毕竟属于有创性检查, 目前尚未作为一个常规检查项目, 尤其的在农村边远地区, 胃镜远远没有达到普及的程度[57]. 血清癌胚抗原虽然对GC的诊断具有一定的指导意义, 但是由于其灵敏度和特异性均不高, 在GC的早期诊断中发挥的作用有限, 仅限于高度怀疑为GC的患者的常规筛查以及胃肠道肿瘤患者术后的定期随访[4]. 因此, 在GC的早期诊断和预后评估方面, 仍需进一步开发出其他指标. 目前关于miR-200c的研究尚不全面, 有关miR-200c在GC诊断中的作用和对GC患者预后的评估作用仍有待于大样本的临床试验加以研究证实. 但是, 随着对miR-200c研究的不断深入, 以及miR-200c作用的相关靶点的发现, 可以预测的是miR-200c将在GC的诊断和跟踪随访方面具有较大价值.
学科分类: 胃肠病学和肝病学
手稿来源地: 新疆维吾尔自治区
同行评议报告分类
A级 (优秀): 0
B级 (非常好): B
C级 (良好): C, C
D级 (一般): 0
E级 (差): 0
编辑: 崔丽君 电编:张砚梁
| 1. | Chen W, Zheng R, Zhang S, Zhao P, Zeng H, Zou X, He J. Annual report on status of cancer in China, 2010. Chin J Cancer Res. 2014;26:48-58. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 2. | Li H, Lu P, Lu Y, Liu C, Xu H, Wang S, Chen J. Predictive factors of lymph node metastasis in undifferentiated early gastric cancers and application of endoscopic mucosal resection. Surg Oncol. 2010;19:221-226. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 4. | Kumar S, Nag A, Mandal CC. A Comprehensive Review on miR-200c, A Promising Cancer Biomarker with Therapeutic Potential. Curr Drug Targets. 2015;16:1381-1403. [PubMed] |
| 6. | Zhou X, Wang Y, Shan B, Han J, Zhu H, Lv Y, Fan X, Sang M, Liu XD, Liu W. The downregulation of miR-200c/141 promotes ZEB1/2 expression and gastric cancer progression. Med Oncol. 2015;32:428. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 7. | Zhang HP, Sun FB, Li SJ. Serum miR-200c expression level as a prognostic biomarker for gastric cancer. Genet Mol Res. 2015;14:15913-15920. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 8. | Pan Q, Law COK, Yung MMH, Han KC, Pon YL, Lau TCK. Novel RNA aptamers targeting gastrointestinal cancer biomarkers CEA, CA50 and CA72-4 with superior affinity and specificity. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0198980. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 9. | Yang W, Hu R, Li GC, Zhou ML, Wang Y, Shen LJ, Liang LP, Zhang Z. Survival outcomes and patterns of failure after D2 dissection and adjuvant chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced gastric cancer: a retrospective study. Br J Radiol. 2018;91:20170594. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 10. | 王 智勇, 吴 继锋. 胃癌组织中zeb-1和c-jun蛋白的表达及意义. 临床与实验病理学杂志. 2015;1:48-51. [DOI] |
| 11. | Wellner U, Schubert J, Burk UC, Schmalhofer O, Zhu F, Sonntag A, Waldvogel B, Vannier C, Darling D, zur Hausen A, Brunton VG, Morton J, Sansom O, Schüler J, Stemmler MP, Herzberger C, Hopt U, Keck T, Brabletz S, Brabletz T. The EMT-activator ZEB1 promotes tumorigenicity by repressing stemness-inhibiting microRNAs. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11:1487-1495. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 13. | Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY, Nieto MA. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell. 2009;139:871-890. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 14. | Song F, Yang D, Liu B, Guo Y, Zheng H, Li L, Wang T, Yu J, Zhao Y, Niu R, Liang H, Winkler H, Zhang W, Hao X, Chen K. Integrated microRNA network analyses identify a poor-prognosis subtype of gastric cancer characterized by the miR-200 family. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20:878-889. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 15. | Hur K, Toiyama Y, Takahashi M, Balaguer F, Nagasaka T, Koike J, Hemmi H, Koi M, Boland CR, Goel A. MicroRNA-200c modulates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in human colorectal cancer metastasis. Gut. 2013;62:1315-1326. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 16. | Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993;75:843-854. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 17. | Yata K, Beder LB, Tamagawa S, Hotomi M, Hirohashi Y, Grenman R, Yamanaka N. MicroRNA expression profiles of cancer stem cells in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 2015;47:1249-1256. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 18. | Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ. Oncomirs - microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:259-269. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 19. | Castanotto D, Rossi JJ. The promises and pitfalls of RNA-interference-based therapeutics. Nature. 2009;457:426-433. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 20. | Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 2005;120:15-20. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 21. | Sun Z, Hu W, Xu J, Kaufmann AM, Albers AE. MicroRNA-34a regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell phenotype of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in vitro. Int J Oncol. 2015;47:1339-1350. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 22. | Tang H, Deng M, Tang Y, Xie X, Guo J, Kong Y, Ye F, Su Q, Xie X. miR-200b and miR-200c as prognostic factors and mediators of gastric cancer cell progression. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19:5602-5612. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 23. | Hwang J, Min BH, Jang J, Kang SY, Bae H, Jang SS, Kim JI, Kim KM. MicroRNA Expression Profiles in Gastric Carcinogenesis. Sci Rep. 2018;8:14393. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 24. | Snowdon J, Zhang X, Childs T, Tron VA, Feilotter H. The microRNA-200 family is upregulated in endometrial carcinoma. PLoS One. 2011;6:e22828. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 25. | Kurata A, Yamada M, Ohno SI, Inoue S, Hashimoto H, Fujita K, Takanashi M, Kuroda M. Expression level of microRNA-200c is associated with cell morphology in vitro and histological differentiation through regulation of ZEB1/2 and E-cadherin in gastric carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2018;39:91-100. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 26. | Li M, Gu K, Liu W, Xie X, Huang X. MicroRNA-200c as a prognostic and sensitivity marker for platinum chemotherapy in advanced gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8:51190-51199. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 27. | Chen Y, Zuo J, Liu Y, Gao H, Liu W. Inhibitory effects of miRNA-200c on chemotherapy-resistance and cell proliferation of gastric cancer SGC7901/DDP cells. Chin J Cancer. 2010;29:1006-1011. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 28. | Wei W, Shi L, Chen W, Hu L, Chen D, Shi X, Xiang H, Guo C, Wu Z. miR-200c regulates the proliferation, apoptosis and invasion of gastric carcinoma cells through the downregulation of EDNRA expression. Int J Mol Med. 2018;41:1619-1626. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 31. | Mongroo PS, Rustgi AK. The role of the miR-200 family in epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Biol Ther. 2010;10:219-222. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 32. | Paterson EL, Kazenwadel J, Bert AG, Khew-Goodall Y, Ruszkiewicz A, Goodall GJ. Down-regulation of the miRNA-200 family at the invasive front of colorectal cancers with degraded basement membrane indicates EMT is involved in cancer progression. Neoplasia. 2013;15:180-191. [PubMed] |
| 34. | Chen HB, Zheng HT. MicroRNA-200c represses migration and invasion of gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells by inhibiting expression of fibronectin 1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017;21:1753-1758. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 37. | Takei Y, Shen G, Morita-Kondo A, Hara T, Mihara K, Yanagihara K. MicroRNAs Associated with Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Can Be Targeted to Inhibit Peritoneal Dissemination of Human Scirrhous Gastric Cancers. Pathobiology. 2018;85:232-246. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 38. | Zhou X, Men X, Zhao R, Han J, Fan Z, Wang Y, Lv Y, Zuo J, Zhao L, Sang M, Liu XD, Shan B. miR-200c inhibits TGF-β-induced-EMT to restore trastuzumab sensitivity by targeting ZEB1 and ZEB2 in gastric cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 2018;25:68-76. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 39. | Weingarten C, Jenudi Y, Tshuva RY, Moskovich D, Alfandari A, Hercbergs A, Davis PJ, Ellis M, Ashur-Fabian O. The Interplay Between Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) and the Thyroid Hormones-αvβ3 Axis in Ovarian Cancer. Horm Cancer. 2018;9:22-32. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 40. | Samatov TR, Tonevitsky AG, Schumacher U. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: focus on metastatic cascade, alternative splicing, non-coding RNAs and modulating compounds. Mol Cancer. 2013;12:107. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 41. | 彭 璇. ZEB-1在胃癌组织中的表达及临床意义. 湖北民族学院学报(医学版). 2013;30:9-11. |
| 42. | Cong N, Du P, Zhang A, Shen F, Su J, Pu P, Wang T, Zjang J, Kang C, Zhang Q. Downregulated microRNA-200a promotes EMT and tumor growth through the wnt/β-catenin pathway by targeting the E-cadherin repressors ZEB1/ZEB2 in gastric adenocarcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2013;29:1579-1587. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 43. | Liu Y, Li Y, Xu Q, Yao W, Wu Q, Yuan J, Yan W, Xu T, Ji X, Ni C. Long non-coding RNA-ATB promotes EMT during silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis by competitively binding miR-200c. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018;1864:420-431. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 44. | Wang Y, Zeng J, Pan J, Geng X, Liu Y, Wu J, Song P, Wang Y, Jia J, Wang L. MicroRNA-200c is involved in proliferation of gastric cancer by directly repressing p27 Kip1. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2016;8:227-233. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 45. | Jiang T, Dong P, Li L, Ma X, Xu P, Zhu H, Wang Y, Yang B, Liu K, Liu J, Xue J, Lv R, Su P, Kong G, Chang Y, Zhao C, Wang L. MicroRNA-200c regulates cisplatin resistance by targeting ZEB2 in human gastric cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 2017;38:151-158. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 46. | Mutlu M, Raza U, Saatci Ö, Eyüpoğlu E, Yurdusev E, Şahin Ö. miR-200c: a versatile watchdog in cancer progression, EMT, and drug resistance. J Mol Med (Berl). 2016;94:629-644. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 47. | Chang L, Guo F, Wang Y, Lv Y, Huo B, Wang L, Liu W. MicroRNA-200c regulates the sensitivity of chemotherapy of gastric cancer SGC7901/DDP cells by directly targeting RhoE. Pathol Oncol Res. 2014;20:93-98. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 48. | Xie NN, Liu ZX, Wu C, Wang PL, Song GT, Chen Z. MicroRNA-200c suppresses tumor metastasis in oral squamous carcinoma by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22:3415-3422. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 50. | 周 欣亮, 张 璁, 袁 虎方, 王 玉栋, 赵 连梅, 桑 梅香, 单 保恩. miR-200c在胃癌中的表达水平与患者临床病理特征的关系. 中国肿瘤生物治疗杂志. 2017;24:538-543. [DOI] |
| 53. | 常 靓. microRNA-200c在胃癌组织和细胞中的表达及其靶基因RhoE的预测和验证. 第八届中国肿瘤内科大会、第三届中国肿瘤医师大会暨中国抗癌协会肿瘤临床化疗专业委员会2014年学术年会论文集. 2014;723-723. |
| 55. | 唐 锦莉, 严 枫, 王 晓明, 葛 梦圆, 桂 珍, 李 金昌, 竺 明晨. 血浆miR-199a-5p与miR-200c-3p在胃腺癌中的临床应用. 中华检验医学杂志. 2015;6:402-406. [DOI] |
| 56. | Zhang H, Sun Z, Li Y, Fan D, Jiang H. MicroRNA-200c binding to FN1 suppresses the proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;88:285-292. [PubMed] [DOI] |