修回日期: 2019-04-30
接受日期: 2019-06-17
在线出版日期: 2019-07-08
miR-183在胃癌、乳腺癌、膀胱癌等多种肿瘤组织中低表达, 发挥抑癌基因的作用, 但其在胃癌中作用机制目前尚不十分清楚. 研究表明, miR-183可以通过调节Wnt/β-catenin信号通路抑制骨肉瘤细胞的生长、迁移和侵袭, 而Wnt/β-catenin信号通路在胃癌中高度激活与胃癌的发生和转移密切相关. 但miR-183是否调节Wnt/β-catenin信号通路影响胃癌细胞生物学特性尚不清楚.
探讨miR-183调控Wnt/β-catenin信号通路对胃癌细胞生物学特性的影响.
采用qRT-PCR检测miR-183在不同胃癌细胞株中的表达情况, 在胃癌细胞SGC-7901中转染miR-183 mimics或mimics对照, 分别设为miR-183组和miR-NC组, qRT-PCR检测转染效率, 噻唑蓝增殖实验检测SGC-7901细胞增殖变化, 流式细胞仪检测SGC-7901细胞凋亡情况, Transwell实验检测SGC-7901细胞侵袭和迁移能力, Western blot法检测凋亡相关及Wnt/β-catenin信号通路相关蛋白表达水平. 使用Wnt/β-catenin信号通路激动剂氯化锂处理过表达miR-183的SGC-7901细胞, 观察SGC-7901细胞生物学特性的变化.
与正常胃黏膜上皮GES-1细胞相比, 4株胃癌细胞中miR-183的表达水平明显降低(P<0.05). 转染miR-183 mimics后SGC-7901细胞中miR-183的表达水平显著升高(P<0.05). 过表达miR-183后SGC-7901细胞OD值降低(P<0.05), 凋亡率、Bax和Cleaved Caspase-3蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.05), 侵袭和迁移细胞数减少(P<0.05), β-catenin、p-GSK-3β和Cyclin D1蛋白表达水平下调(P<0.05), GSK-3β蛋白表达水平上调(P<0.05). 激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路部分逆转了过表达miR-183对SGC-7901细胞增殖、侵袭和迁移的抑制作用及凋亡促进作用(P<0.05).
miR-183可能通过抑制Wnt/β-catenin信号通路阻碍人胃癌SGC-7901细胞增殖、侵袭和迁移能力, 促进细胞凋亡.
核心提要: miR-183可能通过抑制Wnt/β-catenin信号通路阻碍人胃癌SGC-7901细胞增殖、侵袭和迁移能力, 促进细胞凋亡.
引文著录: 张希成, 沈金根, 贾正我, 钱丽芬, 孙元龙. miR-183调控Wnt/β-catenin信号通路影响胃癌SGC-7901细胞生物学特性的研究. 世界华人消化杂志 2019; 27(13): 798-806
Revised: April 30, 2019
Accepted: June 17, 2019
Published online: July 8, 2019
MiR-183 is lowly expressed in various tumor tissues such as gastric cancer, breast cancer, and bladder cancer, and plays a role as a tumor suppressor gene. However, its mechanism of action in gastric cancer is still not fully understood. Studies have shown that miR-183 can inhibit the growth, migration, and invasion of osteosarcoma cells by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, and the high activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway is closely related to the occurrence and metastasis of gastric cancer. However, it is still unclear whether miR-183 affects the biological behaviors of gastric cancer cells by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
To investigate the effect of miR-183 on the biological behaviors of gastric cancer cells and the possible mechanism involved.
qRT-PCR was used to detect the expression of miR-183 in different gastric cancer cell lines. After gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells were transfected with miR-183 mimic or miR-NC, the transfection efficiency was detected by qRT-PCR, the proliferation of SGC-7901 cells was detected by MTT proliferation assay, the apoptosis of SGC-7901 cells was detected by flow cytometry, and the invasion and migration of SGC-7901 cells were detected by Transwell assay. Western blot was used to detect the expression of apoptosis-related and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway-related proteins. The SRC-7901 cells overexpressing miR-183 were treated with Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway agonist lithium chloride to observe the changes in biological behaviors of SGC-7901 cells.
Compared with normal gastric mucosal epithelial GES-1 cells, the expression of miR-183 was significantly decreased in the four gastric cancer cell lines (P < 0.05). The expression level of miR-183 was significantly increased in SGC-7901 cells transfected with miR-183 mimic (P < 0.05). After overexpression of miR-183, the proliferation of SGC-7901 cells decreased (P < 0.05), the apoptosis rate and the protein expression of Bax and cleaved Caspase-3 increased (P < 0.05), and cell migration and invasion decreased (P < 0.05). The expression levels of β-catenin, p-GSK-3β, and cyclin D1 proteins were down-regulated (P < 0.05), and the expression level of GSK-3β protein was up-regulated (P < 0.05). Activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway partially reversed the inhibitory effect of miR-183 overexpression on the proliferation, invasion, and migration of SGC-7901 cells and the promotive effect on cell apoptosis (P < 0.05).
MiR-183 inhibits the proliferation, invasion, and migration of human gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells and promotes cell apoptosis possibly by inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
- Citation: Zhang XC, Shen JG, Jia ZW, Qian LF, Sun YL. MiR-183 affects biological behaviors of gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi 2019; 27(13): 798-806
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1009-3079/full/v27/i13/798.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.11569/wcjd.v27.i13.798
胃癌是全球第四大常见癌症, 也是全球癌症死亡的第三大原因. 在中国, 统计数据表明, 就发病率(每10万人中有679.1人)和死亡率(每10万人中有498.0人)而言, 胃癌是第二大常见癌症[1]. 近年来, 随着胃镜检查和手术技术的发展, 早期胃癌的5年死亡率显著降低, 然而, 对于晚期胃癌, 5年死亡率仍为30%-50%[2]. 晚期胃癌死亡率与腹膜播散, 血行播散和淋巴结转移有关. 因此, 有必要探讨胃癌进展的机制, 如增殖, 生长, 凋亡, 迁移和侵袭. 大量研究表明, 微小RNA(microRNA, miRNA)在胃癌进展中起重要作用[3-5]. miRNA是高度保守的非编码序列, 其长度通常为18至24个核苷酸, 通过与靶基因mRNA的3'UTR结合, 以抑制靶基因翻译或诱导其降解. 迄今为止, 已经鉴定了超过2500种miRNA(miRbase数据库), 并且它们的异位表达与肿瘤生长, 侵袭, 转移, 肿瘤细胞增殖和凋亡相关[6]. miR-183是一种在不同物种中高度保守的miRNA, 最近的证据表明, 其在乳腺癌、膀胱癌和子宫内膜癌等多种肿瘤中异常表达, 参与肿瘤的形成和进展[7-9]. 已有报道表明miR-183在胃癌组织中表达水平降低, 发挥抑癌基因的作用, 但其作用机制目前尚不完全清楚[10]. Wnt/β-catenin信号通路普遍存在于动物体, 在调控机体生长发育、细胞增殖分化、肿瘤发生等多种生理病理中扮演重要角色[11,12]. 目前研究显示, Wnt/β-catenin信号通路在胃癌中高度激活, 且与胃癌的发生和转移密切相关[13]. 目前关于miR-183是否通过调控Wnt/β-catenin信号通路影响胃癌细胞生物学特性的研究尚无报道, 因此本实验以胃癌SGC-7901细胞为研究对象, 探究miR-183影响胃癌细胞增殖、凋亡、侵袭和迁移可能的机制.
人正常胃黏膜上皮GES-1细胞及4株胃癌SGC-7901、NCI-N87、MKN-28和MKN-45细胞购自美国ATCC细胞库; 胎牛血清、胰蛋白酶购自美国HyClone公司; 青霉素、链霉素购自北京鼎国昌盛生物技术有限公司; PRIM-1640培养基购自美国Gibco公司; miR-183 mimics及mimis Control购自广州市锐博生物科技有限公司; Lipofectamine 2000转染试剂购自美国Invitogen公司; MTT试剂购自美国Sigma公司; AnnexinⅤ-FITC/PI细胞凋亡测定试剂盒购自日本TaKaRa公司; TRIzol试剂、逆转录试剂盒、荧光定量PCR测定试剂盒购自北京康为世纪生物科技有限公司; BCA蛋白浓度测定试剂盒、ECL化学发光试剂购自碧云天生物科技研究所; 兔抗Bax一抗和兔抗Cleaved Caspase-3一抗和辣根过氧化物酶标记的山羊抗兔IgG购自美国Abcam公司; 兔抗β-catenin、GSK-3β、p-GSK-3β和Cyclin D1抗体购自美国CST公司.
1.2.1 细胞培养和转染: 人正常胃黏膜上皮GES-1细胞及胃癌SGC-7901、NCI-N87、MKN-28和MKN-45细胞培养于含10%胎牛血清、1×105U/L青霉素、100 mg/L链霉素的PRIM-1640培养基中, 置于5%CO2、相对湿度95%、37 ℃培养箱内培养, 及时观察细胞生长状态并更换新鲜培养液, 待细胞生长汇合率在80%以上时, 使用0.25%的胰蛋白酶消化细胞, 进行传代培养.
选择SGC-7901细胞为转染对象, 转染前1 d, 将处于对数生长期的SGC-7901细胞种植到6孔板中, 置37 ℃培养箱过夜培养, 采用Lipofectamine 2000分别将miR-183 mimics和对照mimics Control转染至SGC-7901细胞, 分别记为miR-183组和miR-NC组, 同时设置空白对照, 即未转染的SGC-7901细胞记为Blank组. 具体操作步骤参考Lipofectamine 2000试剂说明书, 转染后6 h更换为完全培养液.
1.2.2 qRT-PCR检测各细胞中miR-183的表达水平: 分别收集对数生长期的GES-1、SGC-7901、NCI-N87、MKN-28、MKN-45及转染48 h后各组SGC-7901细胞, 使用TRIzol试剂提取细胞总RNA, 使用逆转录试剂盒以总RNA为模板合成cDNA, 测定cDNA浓度, 以cDNA为模板使用荧光定量PCR试剂盒扩增目的产物, 扩增条件设置为: 94 ℃预变性3 min, 94 ℃变性20 s, 60 ℃退火20 s, 72 ℃延伸10 s, 共设40个循环. 以U6为内参, 使用2-△△Ct法计算各细胞系及各组SGC-7901细胞中miR-183相对表达水平.
1.2.3 MTT法检测SGC-7901细胞增殖能力: 收集转染48 h后各组SGC-7901细胞接种于96孔板中, 每孔5×103个, 待细胞贴壁后按照方法1.2进行转染和分组, 分别在转染12、24、48、72 h时, 向每孔细胞中加入10 μL浓度为5 mg/mL的MTT, 于37 ℃下孵育4 h, 弃上清后每孔细胞中加入150 μL二甲基亚砜, 避光反应10 min, 使用酶标仪测定各孔细胞在490 nm处OD值, 每组细胞每个时间点设置3个复孔, 实验重复3次.
1.2.4 流式细胞仪检测细胞凋亡情况: 收集转染48 h后各组SGC-7901细胞, 用预冷PBS洗涤2次, 收集约1×106个细胞, 加入100 μL结合缓冲液重悬细胞, 再向细胞中分别加入5 μL FITC-AnnexinⅤ和5 μL PI染液, 轻轻混匀, 避光孵育30 min, 立即上流式细胞仪检测细胞凋亡情况, 实验重复3次.
1.2.5 Transwell实验检测细胞侵袭和迁移能力: 使用RPMI-1640培养液稀释Matrigel基质胶, 稀释的Matrigel胶包被Transwell小室的上室面, 风干待用. 分别收集转染24 h各组SGC-7901细胞, 以无血清培养液重悬细胞, 制成2×105个/mL的细胞悬液, 取200 μL细胞悬液加入到Transwell小室的上室(Transwell迁移实验上室不以Matrigel胶包被), 在下室中加入500 μL含10%胎牛血清的RPMI-1640培养液, 置培养箱中常规培养24 h. 取出小室, 用棉签擦去上室细胞, PBS洗涤小室3次, 以多聚甲醛固定20 min, 结晶紫染色20 min, PBS洗涤数次, 风干后在倒置显微镜下随机选取5个视野, 观察并记录穿膜细胞数, 实验重复3次.
1.2.6 Western blot检测各组SGC-7901细胞中蛋白表达水平: 转染48 h后, 收集各组SGC-7901细胞, 加入细胞裂解液在冰上提取总蛋白. BCA蛋白浓度测定试剂盒检测总蛋白浓度, 取30 μg蛋白样品经10%十二烷基硫酸钠-聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳分离蛋白, 将凝胶上的蛋白电转至PVDF膜上, 将膜置5%脱脂奶粉中封闭1 h, 分别加入一抗4 ℃过夜孵育, Bax一抗(1:1000), Cleaved Caspase-3一抗(1:1000), β-catenin一抗(1:1000), GSK-3β一抗(1:1000), p-GSK-3β一抗(1:1000), Cyclin D1一抗(1:1000). PBST洗涤3次, 每次10 min, 加入辣根过氧化物酶标记的二抗(1:3000), 室温孵育2 h. PBST洗涤3次, 每次10 min, 加入ECL化学发光试剂显影, 以GAPDH为内参, 使用Image J软件分析各条带灰度值, 计算各组SGC-7901细胞中目的蛋白相对表达水平.
1.2.7 激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路对SGC-7901细胞的影响: 为进一步探究miR-183通过调控Wnt/β-catenin信号通路影响胃癌细胞增殖、凋亡侵袭和迁移的生物学特性, 本实验在过表达miR-183的SGC-7901细胞添加20 mmol/L的Wnt/β-catenin信号通路激动剂LiCl, 分别采用MTT、流式细胞仪、Transwell实验检测细胞增殖、凋亡、侵袭和迁移能力的变化.
统计学处理 使用SPSS 21.0软件分析数据, 所得数据均以mean±SD表示, 两组间差异比较采用t检验, 多组间差异比较采用单因素方差分析, 两两组间差异比较采用SNK-q检验分析, 以P<0.05表示差异有统计学意义.
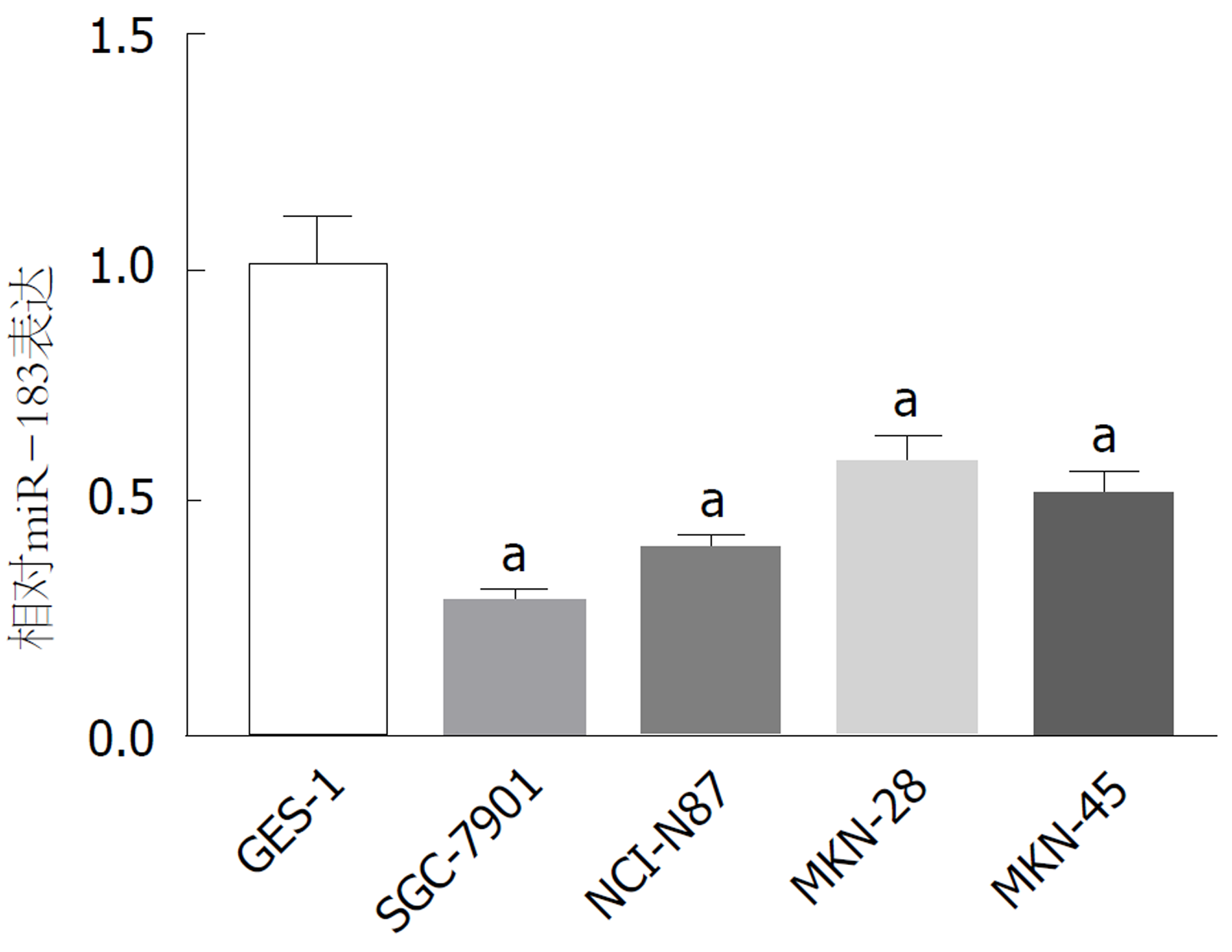
qRT-PCR检测结果表明, 与人正常胃黏膜上皮GES-1细胞相比, 4株胃癌SGC-7901、NCI-N87、MKN-28和MKN-45细胞中miR-183的表达水平明显降低(P<0.05). 见图1. 提示miR-183在胃癌细胞中呈低表达, 尤其在SGC-7901细胞中表达水平最低, 后续选取SGC-7901细胞株进行miR-183过表达的功能研究.
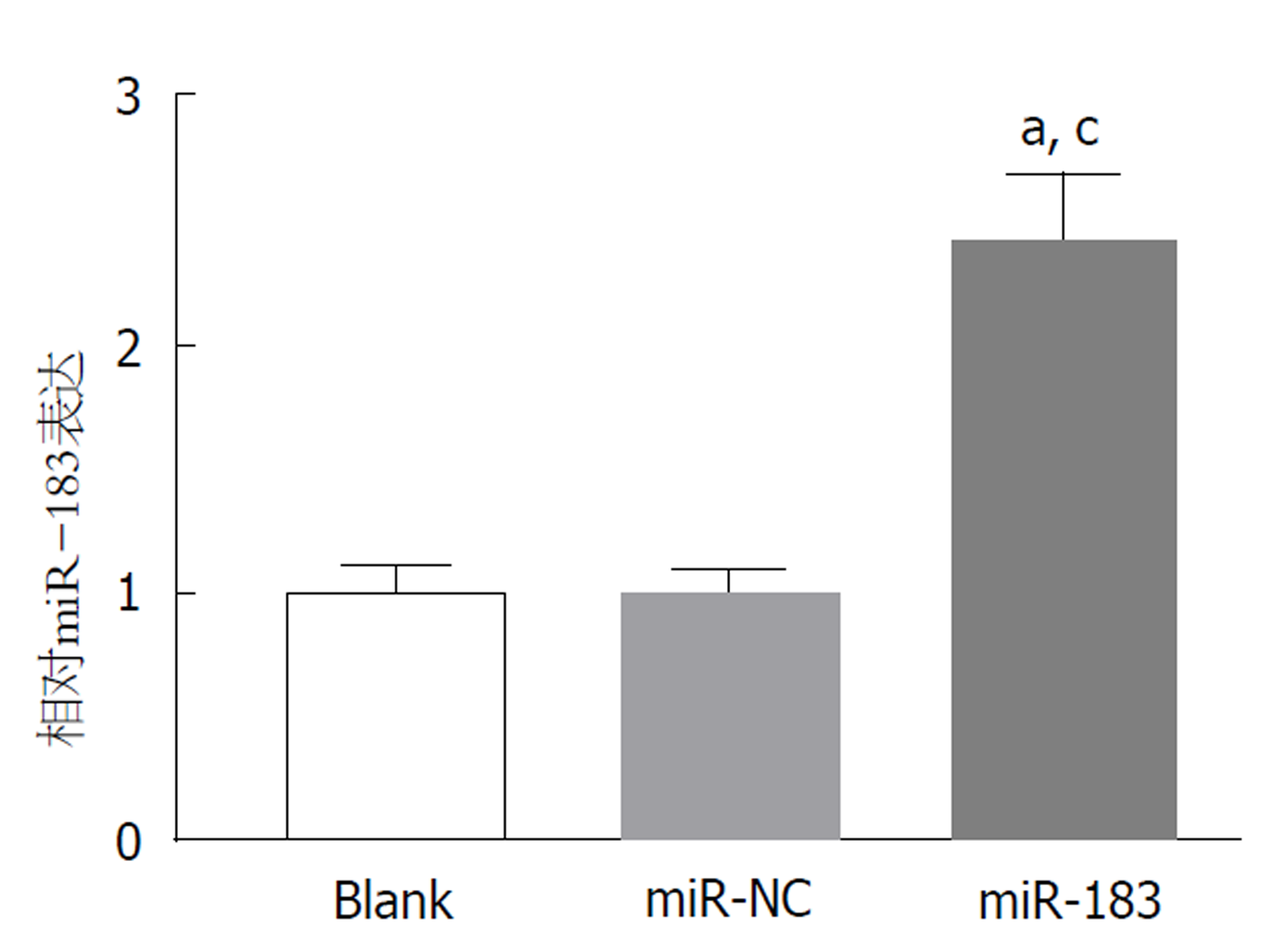
qRT-PCR检测结果显示, 与Blank组和miR-NC组比, miR-183组SGC-7901细胞中miR-183表达水平明显升高(P<0.05). Blank组与miR-NC组比, SGC-7901细胞中miR-183表达水平差异无明显变化(P>0.05). 见图2. 结果表明miR-183 mimis转染胃癌SGC-7901细胞能够上调miR-183的表达, 可满足后续miR-183过表达的功能研究.
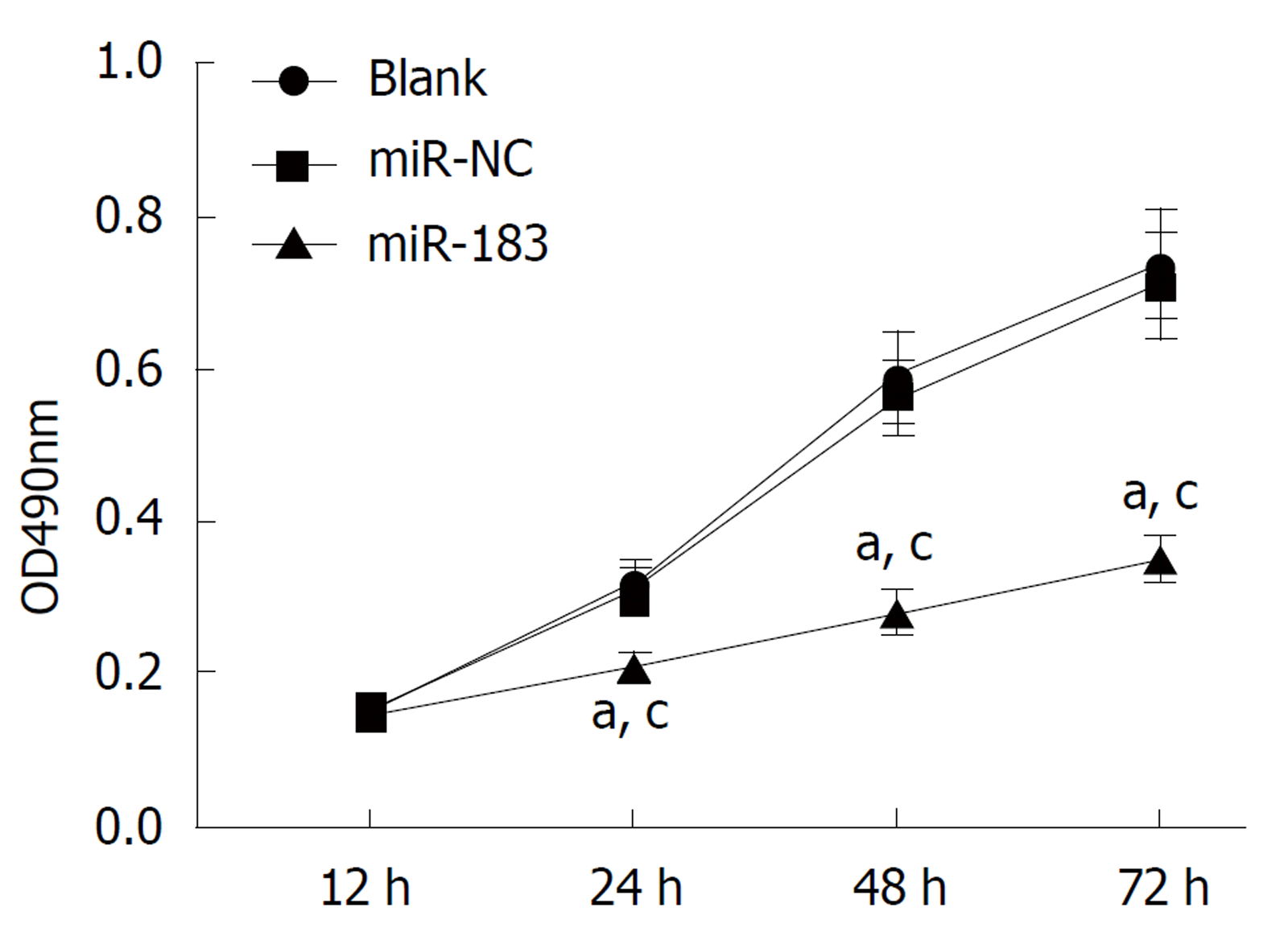
MTT实验检测结果表明, 与Blank组和miR-NC组比, miR-183组SGC-7901细胞增殖能力明显降低(P<0.05). Blank组与miR-NC组比, SGC-7901细胞增殖能力无明显改变(P>0.05). 见图3. 说明过表达miR-183能够抑制SGC-7901细胞体外增殖能力.
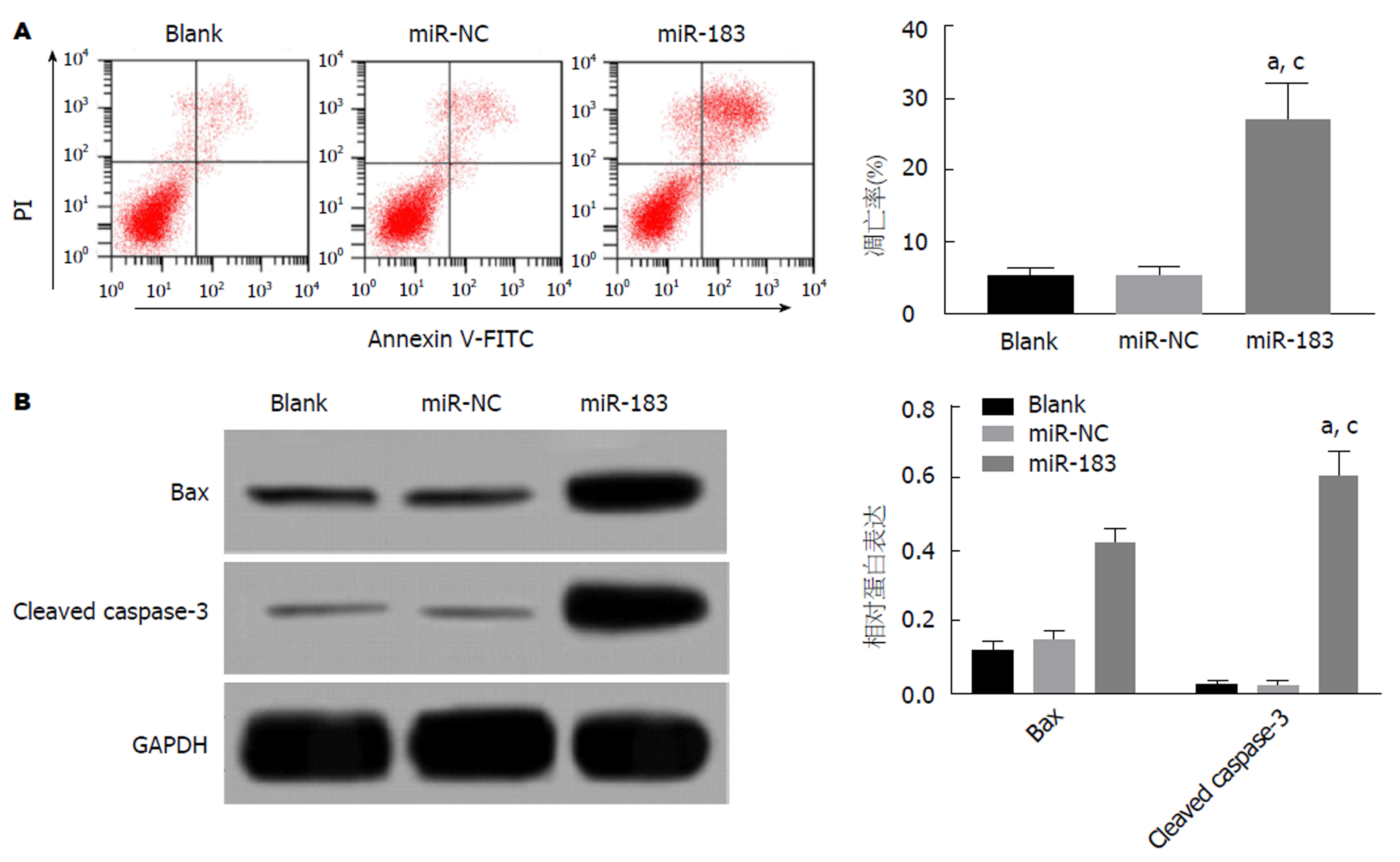
流式细胞仪和Western blot检测结果显示, 与Blank组和miR-NC组比, miR-183组SGC-7901细胞凋亡率、Bax和Cleaved Caspase-3蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.05). Blank组与miR-NC组比, SGC-7901细胞凋亡率、Bax和Cleaved Caspase-3蛋白表达水平均无明显改变(P>0.05). 见图4. 提示过表达miR-183能够促进SGC-7901细胞凋亡.
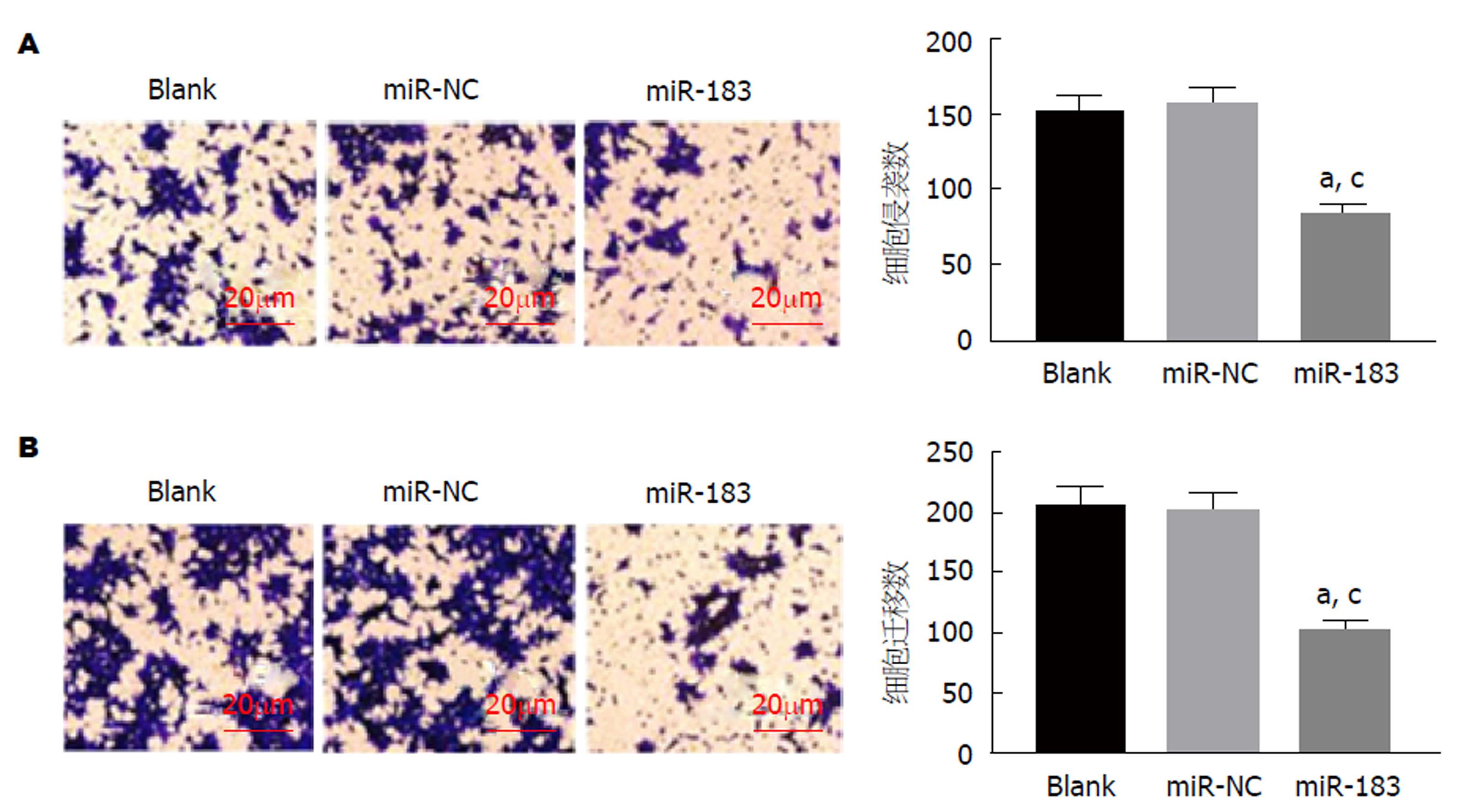
Transwell实验结果显示, 与Blank组和miR-NC组比, miR-183组侵袭和迁移细胞数均明显减少(P<0.05). Blank组与miR-NC组比, 侵袭和迁移细胞数均无明显改变(P>0.05). 见图5. 提示过表达miR-183能够抑制SGC-7901细胞侵袭和迁移能力.
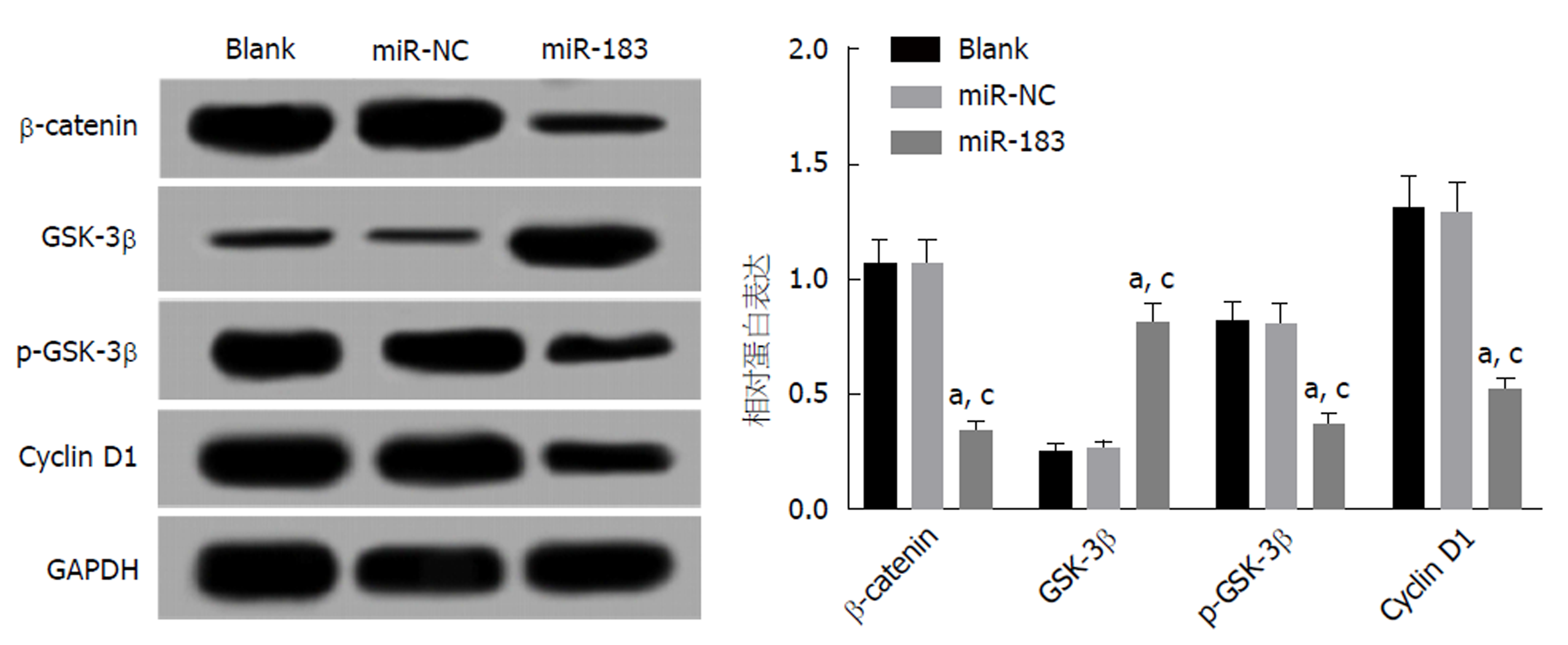
Western blot检测结果显示, 与Blank组和miR-NC组比, miR-183组SGC-7901细胞中β-catenin、p-GSK-3β和Cyclin D1蛋白表达水平下调(P<0.05), GSK-3β蛋白表达水平上调(P<0.05), Blank组与miR-NC组比, β-catenin、GSK-3β、p-GSK-3β和Cyclin D1表达水平无明显变化(P>0.05). 见图6. 提示过表达miR-183能够抑制Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的激活.
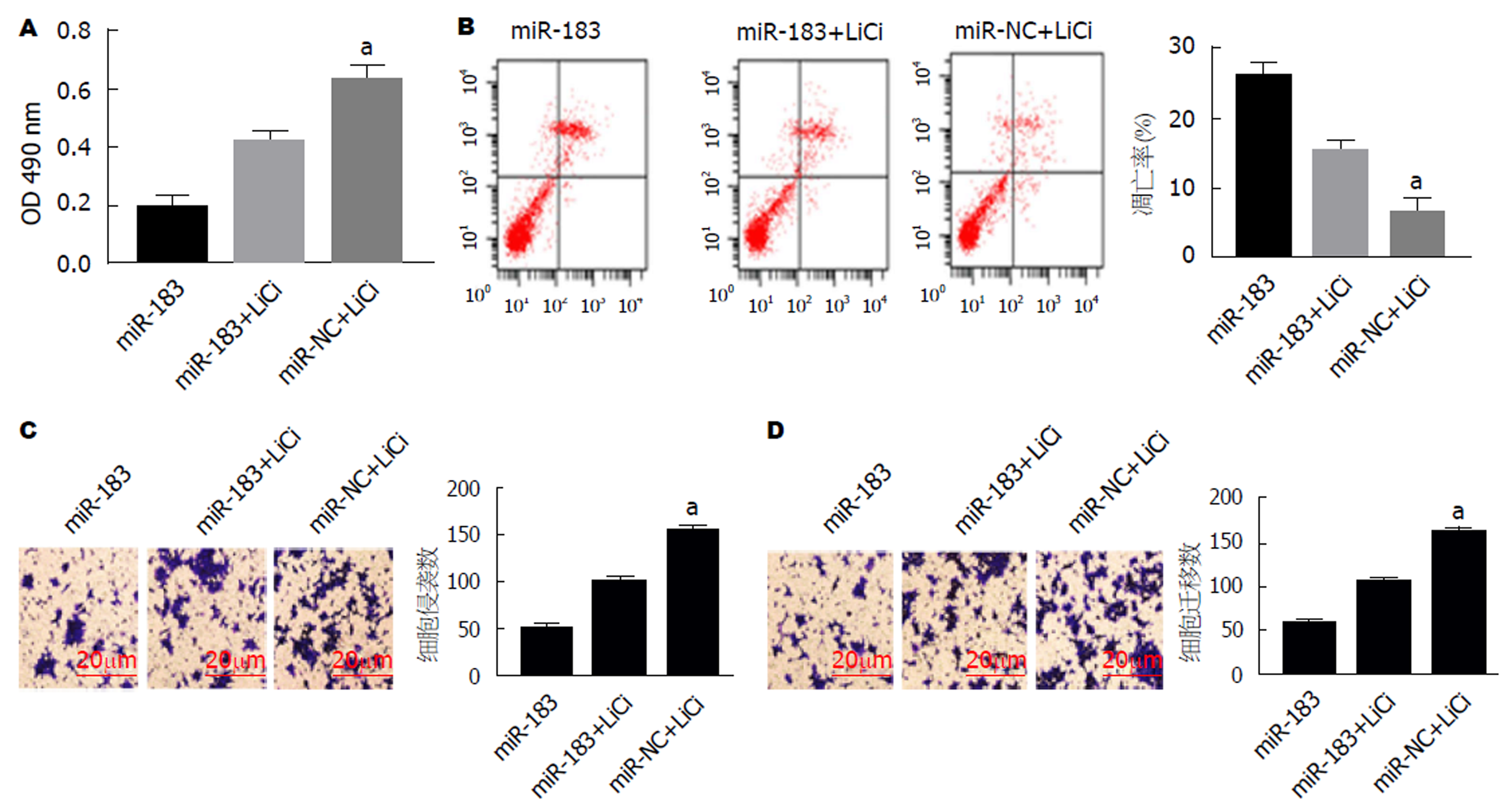
使用Wnt/β-catenin信号通路激动剂激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路后, MTT实验、流式细胞仪以及Transwell实验结果发现, 与miR-183组比, miR-183+LiCl组SGC-7901细胞增殖能力升高(t = 6.832, P<0.05), 凋亡率下降(t = 5.24, P<0.05), 侵袭和迁移细胞数增多[t(侵袭) = 7.281, t(迁移) = 7.564, P<0.05]. 见图7. 表明miR-183介导Wnt/β-catenin信号通路影响SGC-7901细胞增殖、凋亡、侵袭和迁移.
目前研究已经证明miRNA是致癌过程中的关键调节剂, 例如肿瘤细胞增殖, 分化, 侵袭和转移, 起到肿瘤抑制剂或癌基因的作用[14,15]. 因此, 阐明miRNA在肿瘤发展中的潜在机制可为恶性肿瘤提供有价值的诊断和治疗策略. 本实验探究了miR-183在不同胃癌细胞株及正常胃黏膜上皮细胞中的表达, 结果发现miR-183在4种胃癌细胞株中的表达均显著低于正常胃黏膜上皮细胞, 其中miR-183在胃癌SGC-7901细胞中表明量降低最为明显. Cao等[16]研究发现, 胃癌组织中miR-183的表达明显低于其邻近正常组织, miR-183的下调与淋巴结转移和病理TNM分期密切相关, 体外细胞实验发现miR-183通过调节Ezrin在胃癌中起到肿瘤抑制剂的作用. 而Li等[17]实验表明, miR-183可能通过调节胃癌细胞增殖, 凋亡和转移而作为致癌基因起作用, 并且miR-183的致癌作用可能与直接靶向PDCD4有关. 提示miR-183在胃癌中的作用可能与肿瘤微环境下调控的不同靶基因有关. 本实验构建过表达miR-183的SGC-7901细胞, 结果发现过表达miR-183可抑制SGC-7901细胞体外增殖、侵袭和迁移能力, 且能够诱导细胞凋亡, 表明miR-183在胃癌SGC-7901细胞中发挥抑癌基因的作用.
Wnt/β-catenin信号通路在进化上高度保守, 在细胞增殖、分化及黏附等多种细胞生物学行为中发挥重要作用[18]. 多项研究表明, Wnt/β-catenin信号通路在肝癌、乳腺癌、肺癌等多种恶性肿瘤的发生和发展中起关键作用[19-21]. 目前研究已发现胃癌中Wnt/β-catenin信号通路异常激活, 且在胃癌发生和进展中发挥重要作用[22]. β-catenin是Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的关键效应因子, 被认为是肿瘤进展中有效的致癌基因. Wnt蛋白作为一种细胞生长信号因子, 诱导细胞内信号转导导致GSK-3β蛋白发生磷酸化, 进而阻碍β-catenin降解, 导致β-catenin累积. 当β-catenin转位至细胞核中, 将激活下游分子Cyclin D1等的转录, 调节细胞增殖、迁移等相应细胞学行为[23]. Leung等[24]研究发现, Wnt/β-catenin信号通路激活可促进高侵袭性肝细胞癌中miR-183/96/182的表达. 最近Yang等[25]研究发现miR-183通过调节Wnt/β-catenin信号通路抑制骨肉瘤细胞的生长、迁移和侵袭. 本研究中, 过表达miR-183后通过Western blot检测SGC-7901细胞中Wnt/β-catenin信号通路相关分子, 结果发现β-catenin、p-GSK-3β和Cyclin D1蛋白表达水平均明显下调, 而GSK-3β蛋白表达水平上调, 表明过表达miR-183能够抑制Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的激活, 提示miR-183对胃癌SGC-7901细胞生物学特性的影响可能与调控Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的激活有关. 为进一步探究miR-183通过调控Wnt/β-catenin信号通路发挥作用, 本实验在过表达miR-183的SGC-7901细胞中添加Wnt/β-catenin信号通路特异性激动剂LiCl激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路, 结果显示, LiCl激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路可部分逆转过表达miR-183导致的对SGC-7901细胞增殖、侵袭和迁移能力的抑制作用以及对细胞凋亡诱导作用. 以上实验结果表明miR-183通过抑制Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的激活抑制胃癌SGC-7901细胞增殖、侵袭和迁移, 促进细胞凋亡.
总之, 本研究表明miR-183可抑制胃癌SGC-7901细胞增殖、侵袭和迁移, 促进细胞凋亡, 该过程与抑制Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的激活有关. 了解miR-183在胃癌发病机制和Wnt/β-catenin信号通路中的确切作用有望增加我们对癌症发展的生物学基础的掌握, 且还可促进针对胃癌的新治疗策略的开发.
miR-183在胃癌、乳腺癌、膀胱癌等多种肿瘤组织中低表达, 发挥抑癌基因的作用, 但其在胃癌中作用机制目前尚不十分清楚. 研究表明, miR-183可以通过调节Wnt/β-catenin信号通路抑制骨肉瘤细胞的生长、迁移和侵袭, 而Wnt/β-catenin信号通路在胃癌中高度激活与胃癌的发生和转移密切相关. 但miR-183是否调节Wnt/β-catenin信号通路影响胃癌细胞生物学特性尚不清楚.
本研究探讨miR-183是否通过调控Wnt/β-catenin信号通路影响胃癌细胞增殖、凋亡、侵袭和迁移, 旨在阐明miR-183在胃癌中的抗癌机制.
本研究探讨miR-183是否通过调控Wnt/β-catenin信号通路影响胃癌细胞增殖、凋亡、侵袭和迁移, 旨在阐明miR-183在胃癌中的抗癌机制.
体外培养人正常胃黏膜细胞和4中胃癌细胞系, RT-qPCR检测miR-183在各细胞中的表达情况. 以胃癌SGC-7901细胞为研究对象, 构建过表达miR-183的胃癌细胞, MTT法、流式细胞术和Transwell实验分别检测过表达miR-183对胃癌细胞增殖、凋亡、迁移和侵袭的影响, Western blot实验检测过表达miR-183对胃癌细胞中Wnt/β-catenin通路相关蛋白表达的影响. 使用Wnt/β-catenin信号通路激动剂激活过表达miR-183的胃癌细胞中Wnt/β-catenin信号通路, 观察细胞增殖、凋亡、迁移和侵袭能力变化.
miR-183在4中胃癌细胞株中均表达下调. 过表达miR-183抑制胃癌SGC-7901细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭并诱导细胞凋亡, 抑制胃癌细胞中Wnt/β-catenin信号通路相关蛋白表达. Wnt/β-catenin信号通路激动剂处理过表达miR-183的胃癌细胞后, miR-183对胃癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭的抑制作用减弱, 对胃癌细胞凋亡的促进作用也减弱.
过表达miR-183可能通过抑制Wnt/β-catenin信号通路, 抑制胃癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭并诱导细胞凋亡.
本研究仅初步证实miR-183在胃癌中的抑癌作用可能与调控Wnt/β-catenin信号通路有关, 后期将继续深入探讨miR-183具体与哪个分子靶向结合而调控Wnt/β-catenin通路, 在胃癌中发挥抗癌作用.
学科分类: 胃肠病学和肝病学
手稿来源地: 浙江省
同行评议报告分类
A级 (优秀): 0
B级 (非常好): 0
C级 (良好): 0
D级 (一般): D, D, D
E级 (差): 0
编辑: 崔丽君 电编:刘继红
| 1. | Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ, He J. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:115-132. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 2. | Ciesielski M, Kruszewski WJ, Walczak J, Szajewski M, Szefel J, Wydra J, Buczek T, Czerepko M. Analysis of postoperative morbidity and mortality following surgery for gastric cancer. Surgeon volume as the most significant prognostic factor. Prz Gastroenterol. 2017;12:215-221. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 3. | Alessandrini L, Manchi M, De Re V, Dolcetti R, Canzonieri V. Proposed Molecular and miRNA Classification of Gastric Cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 4. | Hao NB, He YF, Li XQ, Wang K, Wang RL. The role of miRNA and lncRNA in gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8:81572-81582. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 5. | Liao Y, Liao Y, Li J, Liu L, Li J, Wan Y, Peng L. Genetic variants in miRNA machinery genes associated with clinicopathological characteristics and outcomes of gastric cancer patients. Int J Biol Markers. 2018;33:301-307. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 6. | Franke KR, Schmidt SA, Park S, Jeong DH, Accerbi M, Green PJ. Analysis of Brachypodium miRNA targets: evidence for diverse control during stress and conservation in bioenergy crops. BMC Genomics. 2018;19:547. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 7. | Macedo T, Silva-Oliveira RJ, Silva VAO, Vidal DO, Evangelista AF, Marques MMC. Overexpression of mir-183 and mir-494 promotes proliferation and migration in human breast cancer cell lines. Oncol Lett. 2017;14:1054-1060. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 8. | Gao JM, Huang LZ, Huang ZG, He RQ. Clinical value and potential pathways of miR-183-5p in bladder cancer: A study based on miRNA-seq data and bioinformatics analysis. Oncol Lett. 2018;15:5056-5070. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 9. | Ruan H, Liang X, Zhao W, Ma L, Zhao Y. The effects of microRNA-183 promots cell proliferation and invasion by targeting MMP-9 in endometrial cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;89:812-818. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 11. | Nusse R, Clevers H. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling, Disease, and Emerging Therapeutic Modalities. Cell. 2017;169:985-999. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 12. | Janda CY, Dang LT, You C, Chang J, de Lau W, Zhong ZA, Yan KS, Marecic O, Siepe D, Li X, Moody JD, Williams BO, Clevers H, Piehler J, Baker D, Kuo CJ, Garcia KC. Surrogate Wnt agonists that phenocopy canonical Wnt and β-catenin signalling. Nature. 2017;545:234-237. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 13. | Dai H, Deng HB, Wang YH, Guo JJ. Resveratrol inhibits the growth of gastric cancer via the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Oncol Lett. 2018;16:1579-1583. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 14. | Xu J, Xiao X, Yang D. In Vitro Methods for Analyzing miRNA Roles in Cancer Cell Proliferation, Invasion, and Metastasis. Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1733:159-171. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 15. | Ganju A, Khan S, Hafeez BB, Behrman SW, Yallapu MM, Chauhan SC, Jaggi M. miRNA nanotherapeutics for cancer. Drug Discov Today. 2017;22:424-432. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 16. | Cao LL, Xie JW, Lin Y, Zheng CH, Li P, Wang JB, Lin JX, Lu J, Chen QY, Huang CM. miR-183 inhibits invasion of gastric cancer by targeting Ezrin. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7:5582-5594. [PubMed] |
| 17. | Li C, Deng L, Zhi Q, Meng Q, Qian A, Sang H, Li X, Xia J. MicroRNA-183 Functions As an Oncogene by Regulating PDCD4 in Gastric Cancer. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2016;16:447-455. [PubMed] |
| 18. | Liu X, Gao Q, Zhao N, Zhang X, Cui W, Sun J, Fu J, Hao J. Sohlh1 suppresses glioblastoma cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Mol Carcinog. 2018;57:494-502. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 19. | Debebe A, Medina V, Chen CY, Mahajan IM, Jia C, Fu D, He L, Zeng N, Stiles BW, Chen CL, Wang M, Aggarwal KR, Peng Z, Huang J, Chen J, Li M, Dong T, Atkins S, Borok Z, Yuan W, Machida K, Ju C, Kahn M, Johnson D, Stiles BL. Wnt/β-catenin activation and macrophage induction during liver cancer development following steatosis. Oncogene. 2017;36:6020-6029. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 20. | Xiao X, Ao M, Xu F, Li X, Hu JL, Wang Y, Li DX, Zhu XQ, Xin CL, Shi WD. Effect of matrine against breast cancer by downregulating the vascular endothelial growth factor via the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Oncol Lett. 2018;15:1691-1697. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 21. | Zhang Q, Zhang B, Sun L, Yan Q, Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Su Y, Wang C. MicroRNA-130b targets PTEN to induce resistance to cisplatin in lung cancer cells by activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Cell Biochem Funct. 2018;36:194-202. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 22. | Li G, Su Q, Liu H, Wang D, Zhang W, Lu Z, Chen Y, Huang X, Li W, Zhang C, He Y, Fu L, Bi J. Frizzled7 Promotes Epithelial-to-mesenchymal Transition and Stemness Via Activating Canonical Wnt/β-catenin Pathway in Gastric Cancer. Int J Biol Sci. 2018;14:280-293. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 23. | Zheng W, Lin P, Ma Y, Shao X, Chen H, Chen D, Liu X, Li X, Ye H. Psoralen promotes the expression of cyclin D1 in chondrocytes via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2017;40:1377-1384. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 24. | Leung WK, He M, Chan AW, Law PT, Wong N. Wnt/β-Catenin activates MiR-183/96/182 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma that promotes cell invasion. Cancer Lett. 2015;362:97-105. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 25. | Yang X, Wang L, Wang Q, Li L, Fu Y, Sun J. MiR-183 inhibits osteosarcoma cell growth and invasion by regulating LRP6-Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;496:1197-1203. [PubMed] [DOI] |