修回日期: 2006-01-05
接受日期: 2006-01-26
在线出版日期: 2006-03-08
目的: 观察胃癌及正常胃黏膜Maspin, uPA, MMP-7表达的意义.
方法: 应用免疫组化SP法检测胃管状腺癌30例, 胃印戒细胞癌30例, 正常胃黏膜组织20例中Maspin, uPA, MMP-7的表达情况.
结果: 在胃管状腺癌中Maspin, uPA, MMP-7阳性表达率分别为50%, 70%和80%; 胃印戒细胞癌中阳性表达率分别为46.7%, 76.7%和90%; 正常胃黏膜组织中阳性表达率分别为90%, 35%和30%. Maspin的表达与浸润深度、淋巴结转移相关, 而与肿块的大小和TNM分期无关. uPA和MMP-7的表达与浸润深度、淋巴结转移、TNM分期相关, 而与肿块的大小无关. Maspin的表达与uPA和MMP-7的表达呈负相关(P = 0.012, r = -0.322; P = 0.008, r = -0.341); uPA的表达与MMP-7的表达呈正相关(P = 0.034, r = 0.274).
结论: Maspin在胃癌中表达下调, uPA和MMP-7在胃癌中过表达, 他们在胃癌的浸润转移中起重要作用, 可作为反应胃癌病理生物学行为的有效指标.
引文著录: 邓玮, 易永芬, 刘丹丹. 胃癌组织Maspin, uPA, MMP-7表达的意义. 世界华人消化杂志 2006; 14(7): 660-665
Revised: January 5, 2006
Accepted: January 26, 2006
Published online: March 8, 2006
AIM: To investigate the expression of Maspin, urokinase-type plasrninogen activator (uPA) uPA and Matrix metalloproteinase-7 (MMP-7) and their roles in the tumorigenesis and progre-ssion of gastric cancer.
METHODS: Immunohistochemistry SP method was used to detect the expression of Maspin, uPA and MMP-7 in tissues from gastric adenocarcinoma (n = 30), signet-ring cell carcinoma (n = 30), and normal gastric mucosa (n = 20).
RESULTS: The positive rates of Maspin, uPA and MMP-7 were 50%, 70% and 80%, respectively, in gastric adenocarcinoma, and they were 46.7%, 76.7% and 90%, respectively, in signet-ring cell carcinoma. However, the positive rates of Maspin, uPA, and MMP-7 were 90%, 35%, and 30%, respectively, in normal gastric mucosa. Maspin, uPA, and MMP-7 expression were significantly different between tissues from carcinoma and normal mucosa (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01). Maspin expression was significantly related to the depth of invasion and lymph node metastasis, but not to tumor size and TNM staging. The expression of uPA and MMP-7 were markedly related to the depth of invasion, lymph node metastasis and TNM staging, but not to tumor size. Maspin expression had a negative correlation with uPA and MMP-7 (P = 0.012, r = -0.322; P = 0.008, r = -0.341), while uPA expression had a positive correlation with MMP-7 (P = 0.034, r = 0.274).
CONCLUSION: Down-regulated expression of Maspin and up-regulated expression of uPA and MMP-7 play important roles in the invasion and metastasis of gastric carcinoma. They may serve as effective markers of reflecting the biopathological behaviors of gastric carcinoma.
- Citation: Deng W, Yi YF, Liu DD. Significance of Maspin, uPA and MMP-7 expression in human gastric carcinoma. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi 2006; 14(7): 660-665
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1009-3079/full/v14/i7/660.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.11569/wcjd.v14.i7.660
胃癌是常见的消化系统恶性肿瘤之一, 许多基因在胃癌的浸润转移中发挥重要作用. Maspin基因是丝氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂超家族中的一种, 分子质量为42 ku, 具有肿瘤抑制活性. 大量研究表明, 在多种肿瘤比如乳腺癌、口腔鳞癌中, Maspin的表达与其预后有关. 而Maspin基因的缺失会导致肿瘤浸润转移能力的增强. MMP-7和uPA分别属于金属蛋白酶类和丝氨酸蛋白酶类, 他们能有效地降解细胞外基质, 与恶性肿瘤发生和发展密切相关. 但是, 联合检测Maspin, uPA, MMP-7与胃癌的生物学特性的关系尚未见报道. 我们应用免疫组化SP染色法, 检测Maspin, uPA, MMP-7在胃管状腺癌、胃印戒细胞癌及正常胃黏膜组织中的表达, 并探讨他们之间的关系及其在胃癌浸润转移中的作用.
1998-01/2004-01手术切除(术前未化疗)的胃癌组织石蜡块80例, 其中胃管状腺癌30例, 印戒细胞癌30例. 正常胃黏膜组织20例取自胃癌手术切除标本的正常切缘, 切缘经组织学证实无癌组织浸润. 胃癌中肿块≥4 cm 36例, <4 cm 24例. 侵及黏膜及黏膜下层者8例, 侵及固有肌层者13例, 侵及浆膜层者39例. 有局部淋巴结转移者36例, 无淋巴结转移者24例. TNM 0, Ⅰ期24例; Ⅱ, Ⅲ, Ⅳ期36例. Maspin即用型mAb(MS-1767-R7)购自美国Neomaker公司, uPA mAb购自武汉博士德公司, MMP-7 mAb购自福州迈新公司, SP-9000购自北京中杉生物公司.
采用免疫组化SP法, 切片常规脱蜡至水, 30 mL/L过氧化氢孵育10 min, pH 8.0的EDTA缓冲液微波修复5 min, 滴加正常山羊血清工作液孵育10 min, 一抗4℃过夜, 滴加二抗, 孵育15 min, 滴加三抗, 孵育15 min, DAB显色, 苏木素复染, 脱水, 透明, 封片. PBS代替一抗作阴性对照, 已知阳性切片作阳性对照. Maspin定位于细胞质内或细胞质细胞核同时着色. 依据染色强度及阳性细胞率来计算评分. 染色强度: 0为阴性, 1为弱阳性, 2为阳性, 3为强阳性; 阳性细胞数0, <1%, <10%, <1/3, <2/3, >2/3分别积分为0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5; 两项之和0-2分为阴性(-), 3-5分为阳性(+), 6-8分为强阳性(++). uPA定位于细胞质内, 细胞质呈棕黄色者为阳性细胞, 依据染色强度及阳性细胞率来计算评分. 染色强度: 0为阴性, 1为弱阳性, 2为阳性, 3为强阳性; 阳性细胞数0, 1%-25%, 25%-50%, >50%分别积分为0, 1, 2, 3; 两项之和为3-6分者评为免疫组织化学染色阳性. MMP-7定位于细胞质内, 取10个高倍视野1 000个细胞计数阳性细胞数, 阳性细胞<10%为阴性, ≥10%为阳性.
统计学处理 应用SPSS11.5统计软件进行统计分析. 采用χ2检验及Spearman等级相关分析. 检验水准为0.05.
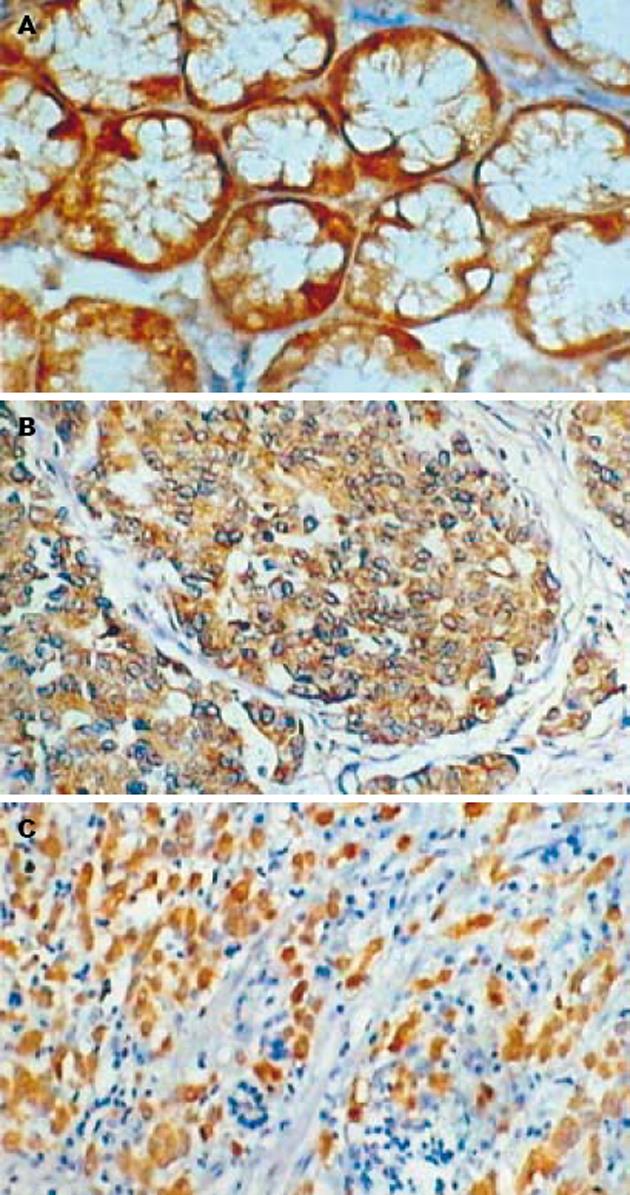
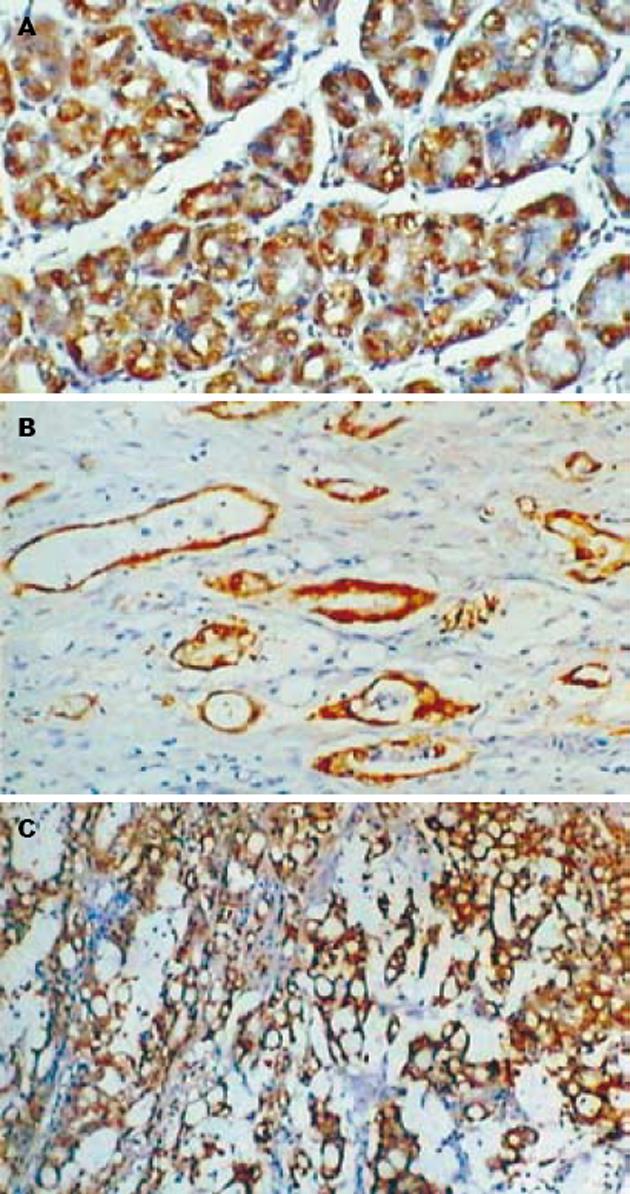
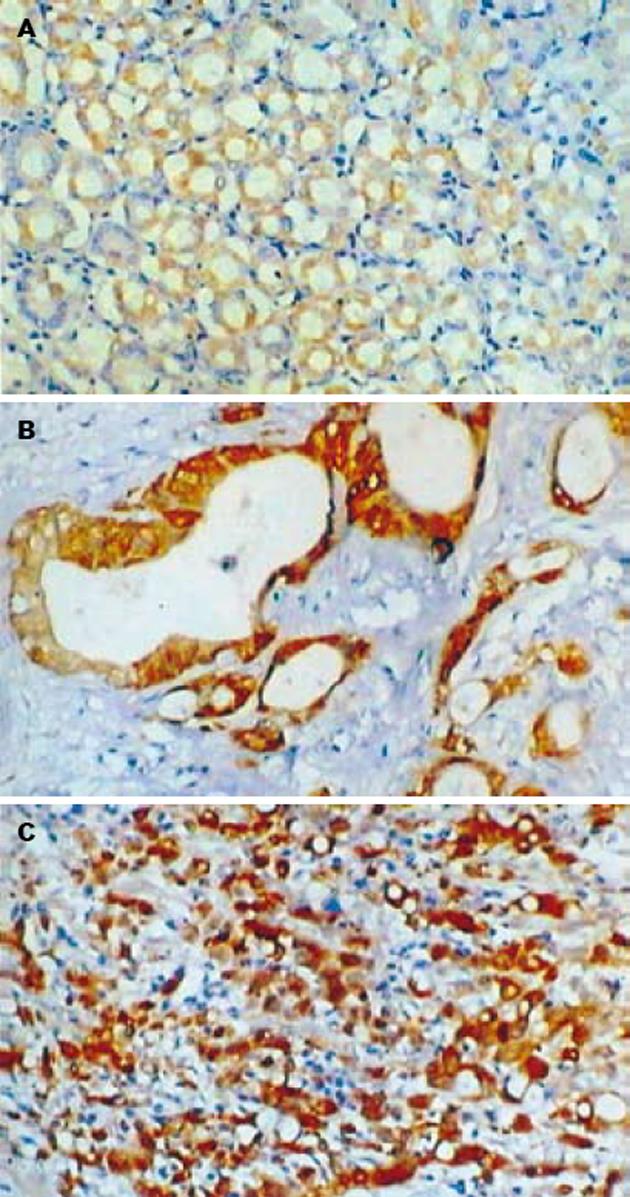
Maspin主要表达于正常胃黏膜的腺上皮细胞和胃癌细胞的细胞质(图1). 在胃管状腺癌中Maspin阳性表达率为50%(15/30), 9例为阳性(+), 6例为强阳性(++), 强阳性率为20%; 胃印戒细胞癌中Maspin阳性表达率为46.7%(14/30), 10例为阳性(+), 4例为强阳性(++), 强阳性率为13.3%; 正常胃黏膜组织中Maspin阳性表达率为90%(18/20), 5例为阳性(+), 13例为强阳性(++), 强阳性率为65%. 正常胃黏膜组织中Maspin阳性表达率和阳性表达强度明显高于胃管状腺癌和胃印戒细胞癌(P<0.05), 而胃管状腺癌和胃印戒细胞癌之间Maspin阳性表达率无明显差别(P>0.05). uPA阳性物质主要位于正常胃黏膜的腺上皮细胞和肿瘤细胞的胞质(图2), 30例胃管状腺癌中uPA阳性表达率为70%(21/30), 30例胃印戒细胞癌中uPA阳性表达率为76.7%(23/30), 20例正常胃黏膜组织中uPA阳性表达率为35%(7/20). 正常胃黏膜组织中uPA阳性表达率明显低于胃管状腺癌和胃印戒细胞癌(P<0.05), 而胃管状腺癌和胃印戒细胞癌之间无明显差别(P>0.05). 正常胃黏膜和肿瘤细胞MMP-7阳性者为胞质中出现棕黄色颗粒(图3). 30例胃管状腺癌中MMP-7阳性表达率为80%(24/30), 30例胃印戒细胞癌中阳性表达率90%(27/30), 20例正常胃黏膜组织中阳性表达率为30%(6/20). 正常胃黏膜组织中MMP-7阳性表达率明显低于胃管状腺癌和胃印戒细胞癌(P<0.05), 而胃管状腺癌和胃印戒细胞癌之间无明显差别(P>0.05, 表1).
肿瘤的大小和TNM分期与Maspin的阳性表达率无明显关系(P>0.05). 而浸润深度与Maspin的阳性表达率有相关性, 侵及黏膜及黏膜下、侵及肌层和侵及浆膜层者阳性率分别为75%(6/8), 61.5%(8/13), 38.5%(15/39), 有统计学意义(P<0.05). 无淋巴结转移者Maspin的阳性表达率为66.6%(16/24), 有淋巴结转移者为36.1%(13/36), 前者明显高于后者(P<0.05). 肿瘤的大小与uPA和MMP-7的阳性表达率无明显关系(P>0.05). 60例胃癌组织中uPA的阳性表达与浸润深度有关, 侵及黏膜及黏膜下、侵及肌层和侵及浆膜层者阳性率分别为50%(4/8), 61.5%(8/13), 82.1%(32/39), 有统计学意义(P<0.05); 无淋巴结转移者阳性表达率为54.2%(13/24), 有淋巴结转移者阳性表达率86.1%(31/36), 差异有显著性; TNM分期中0, Ⅰ期和Ⅱ, Ⅲ, Ⅳ期胃癌组织阳性表达率分别为58.3%(14/24), 83.3%(30/36), 有统计学意义(P<0.05). 胃癌组织中MMP-7的阳性表达与浸润深度有关, 侵及黏膜及黏膜下、侵及肌层和侵及浆膜层者阳性率分别为62.5%(5/8), 76.9%(10/13), 92.3%(36/39), 有统计学意义(P<0.05); 无淋巴结转移者阳性表达率为70.8%(17/24), 有淋巴结转移者阳性表达率94.4%(34/36), 二者有显著差异; TNM分期中0, Ⅰ期和Ⅱ, Ⅲ, Ⅳ期胃癌组织阳性表达率分别为70.8%(17/24), 94.4%(34/36), 二者有显著差异(表2).
胃癌组织中17例Maspin与uPA同时阳性表达, 4例Maspin与uPA同时阴性表达, Maspin与uPA表达呈负相关(P<0.05). 21例Maspin与MMP-7同时阳性表达, 1例同时阴性表达, Maspin与MMP-7表达呈负相关(P<0.05). 40例uPA与MMP-7同时阳性表达, 9例uPA与MMP-7同时阴性表达, uPA与MMP-7表达呈正相关(P<0.05, 表3).
| 项目 | Maspin | rs | P值 | uPA | rs | P值 | |||
| - | + | - | + | ||||||
| MMP-7 | - | 1 | 8 | 9 | 0 | ||||
| + | 30 | 21 | -0.341 | 0.008 | 11 | 40 | 0.274 | 0.034 | |
| uPA | - | 4 | 12 | ||||||
| + | 27 | 17 | -0.322 | 0.012 | |||||
Maspin是丝氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂超家族中的一种, 具有抑制肿瘤的活性. 目前研究表明Maspin在多种正常细胞如乳腺、阴道、前列腺、皮肤的上皮细胞中高表达[1-2], 而在癌细胞如口腔鳞癌、乳腺癌中表达下调或缺失[3-6]. 我们的研究也显示正常胃黏膜中Maspin的阳性表达率明显高于胃管状腺癌和胃印戒细胞癌, 而胃管状腺癌和胃印戒细胞癌之间的阳性表达率无显著差异. 此结果提示Maspin表达下调与胃癌的恶性演进有关. 有作者报道癌细胞中Maspin的启动子出现cytosine甲基化, 而用甲基化抑制剂后, Maspin重新表达, 且出现剂量依赖, 这提示Maspin基因表达的下调与甲基化有关[7-9]. 也有作者认为Maspin表达下调与转录因子Ets和Ap1的转录活性失活有关, 正常上皮细胞中Ets可和Ap1协同作用, 激活启动子转录, 而癌细胞中Ets和Ap1正调节作用减弱, Maspin表达降低[10]. 我们讨论了Maspin的表达与临床病理特征的关系, 发现Maspin的表达与浸润和转移有关. 即浸润越深、有转移者Maspin表达越低. 这提示Maspin作为肿瘤转移抑制基因在胃癌演进中起着重要的抑制作用, 这与Maspin在其他肿瘤演进中的表现是吻合的[11-15]. 大量研究表明, Maspin在肿瘤浸润转移的各个环节中起着重要的作用: Maspin能改变细胞表面整合素的结构, 增强细胞对细胞外基质的黏附能力, 影响细胞内的信号传导, 使细胞向更良性表型转化[16]; Maspin能有效阻止内皮细胞对血管生长因子的反应, 抑制内皮细胞的生长, 阻止其形成管道结构, 使肿瘤微血管的密度减少[17-19]. 最近的研究表明Maspin还可以通过调节小G蛋白Rac1和PAK1(p21-活性激酶)的活性来抑制细胞的运动, 通过磷酰肌醇-3激酶(PI3K)和细胞外信号调节激酶(ERK)途径来调节细胞的黏附[20].
uPA是一种丝氨酸蛋白酶, 与特异性受体(uPAR)结合后, 具有活性, 能启动纤溶酶原活化为纤溶酶, 后者能降解肿瘤细胞外基质, 促进肿瘤的浸润转移. 我们发现, 正常胃黏膜中uPA的阳性表达率明显低于胃管状腺癌和胃印戒细胞癌, 且胃癌中浸润越深、有转移者uPA阳性表达越高. 这与Okusa et al[21]发现uPA高活性与肿瘤浸润深度和转移相关是一致的. 我们还发现Maspin的表达与uPA呈负相关, Biliran et al[22]发现Maspin可特异抑制细胞表面相关的uPA, 从而降低体外细胞的浸润运动潜能. 且有作者发现重组Maspin的反应活性部位是RSL结构, 能特异地与单链纤维蛋白溶酶原激活物结合, 形成稳定的复合物, 从而抑制纤维蛋白溶酶原激活物的活性[23-25]. 此外, Maspin可与uPA结合形成一种抗SDS的蛋白酶复合物, 降低uPA的释放能力, 减少纤溶酶原活化为纤溶酶.
MMP-7是MMP家族的重要成员, 他能降解基底膜成分如Ⅳ型胶原和弹性蛋白. 有作者发现胃癌中MMP-7表达增强[26-28]. 本研究发现正常胃黏膜中MMP-7的阳性表达率明显低于胃腺癌和胃印戒细胞癌, 且胃癌中浸润越深、有转移者MMP-7阳性表达越高. 这与其他作者的发现是一致的. 此外, uPA与MMP-7表达呈正相关. 有研究表明: uPA可以激活MMP, 开启MMP对细胞外基质的降解机制, 主要是uPA通过细胞外信号通路酪氨酸激酶活性包括Src和磷酰肌醇-3激酶(PI3K), 与整合素β1结合, 激活pro-MMP, 从而调节MMP的活性[29-30]. Maspin与MMP-7表达呈负相关, 这提示Maspin对MMP-7可能有下调作用, 我们推测其机制可能是Maspin通过下调uPA的表达, 从而影响信号传导系统使MMP-7的表达下降, 但其具体作用机制有待进一步探讨.
总之, 我们的结果提示, Maspin表达的下调和uPA, MMP-7的过表达在胃癌的浸润转移中起重要作用, 他们可以作为反映胃癌病理生物学行为的指标. 但三者之间是如何调节的有待进一步研究.
Maspin是一种新发现的丝氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂, 已在多种肿瘤中证实其具有抑制肿瘤侵袭、转移的作用. 但有关Maspin在胃癌中的研究, 国内外报道很少. 我们对Maspin在胃癌组织的表达进行了研究, 探讨了其表达与临床病理的关系, 首次分析了胃癌组织Maspin, uPA, MMP-7表达的相关性及其意义, 初步探讨了Maspin可能的作用机制, 为以后更深入的研究打下基础.
我们对Maspin在胃癌组织的表达进行了研究, 探讨了其表达与临床病理的关系, 首次分析了胃癌组织Maspin, uPA, MMP-7表达的相关性及其意义, 初步探讨了Maspin可能的作用机制, 为以后更深入的研究打下基础.
电编: 张敏 编辑:潘伯荣
| 1. | Cao D, Wilentz RE, Abbruzzese JL, Ho L, Maitra A. Aberrant expression of Maspin in idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease is associated with disease activity and neoplastic transformation. Int J Gastrointest Cancer. 2005;36:39-46. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 2. | Marioni G, Blandamura S, Giacomelli L, Calgaro N, Segato P, Leo G, Fischetto D, Staffieri A, de Filippis C. Nuclear expression of Maspin is associated with a lower recurrence rate and a longer disease-free interval after surgery for squamous cell carcinoma of the larynx. Histopathology. 2005;46:576-582. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 3. | Xia W, Lau YK, Hu MC, Li L, Johnston DA, Sheng S, El-Naggar A, Hung MC. High tumoral Maspin expression is associated with improved survival of patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogene. 2000;19:2398-2403. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 4. | Umekita Y, Yoshida H. Expression of Maspin is up-regulated during the progression of mammary ductal carcinoma. Histopathology. 2003;42:541-545. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 5. | Friedrich MG, Toma MI, Petri S, Cheng JC, Hamm-erer P, Erbersdobler A, Huland H. Expression of Maspin in non-muscle invasive bladder carcinoma: correlation with tumor angiogenesis and prognosis. Eur Urol. 2004;45:737-743. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 6. | Chen Z, Fan Z, McNeal JE, Nolley R, Caldwell MC, Mahadevappa M, Zhang Z, Warrington JA, Stamey TA. Hepsin and Maspin are inversely expressed in laser capture microdissectioned prostate cancer. J Urol. 2003;169:1316-1319. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 7. | Futscher BW, Oshiro MM, Wozniak RJ, Holtan N, Hanigan CL, Duan H, Domann FE. Role for DNA methylation in the control of cell type specific Maspin expression. Nat Genet. 2002;31:175-179. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 8. | Ito R, Nakayama H, Yoshida K, Oda N, Yasui W. Loss of Maspin expression is associated with development and progression of gastric carcinoma with p53 abnormality. Oncol Rep. 2004;12:985-990. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 9. | Primeau M, Gagnon J, Momparler RL. Synergistic antineoplastic action of DNA methylation inhibitor 5-AZA-2'-deoxycytidine and histone deacetylase inhibitor depsipeptide on human breast carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer. 2003;103:177-184. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 10. | Zhang M, Magit D, Sager R. Expression of Maspin in prostate cells is regulated by a positive ets elem-ent and a negative hormonal responsive element site recognized by androgen receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:5673-5678. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 11. | Machtens S, Serth J, Bokemeyer C, Bathke W, Minssen A, Kollmannsberger C, Hartmann J, Knuchel R, Kondo M, Jonas U. Expre-ssion of the p53 and Maspin protein in primary prostate cancer: correlation with clinical features. Int J Cancer. 2001;95:337-342. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 12. | Yasumatsu R, Nakashima T, Hirakawa N, Kumamoto Y, Kuratomi Y, Tomita K, Komiyama S. Maspin expression in stage I and II oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck. 2001;23:962-966. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 13. | Maass N, Hojo T, Rosel F, Ikeda T, Jonat W, Nagasa-ki K. Down regulation of the tumor suppressor gene Maspin in breast carcinoma is associated with a higher risk of distant metastasis. Clin Biochem. 2001;34:303-307. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 14. | Reddy KB, McGowen R, Schuger L, Visscher D, Sheng S. Maspin expression inversely correlates with breast tumor progression in MMTV/TGF-alpha transgenic mouse model. Oncogene. 2001;20:6538-6543. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 15. | Domann FE, Rice JC, Hendrix MJ, Futscher BW. Epigenetic silencing of Maspin gene expression in human breast cancers. Int J Cancer. 2000;85:805-810. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 16. | Seftor RE, Seftor EA, Sheng S, Pemberton PA, Sager R, Hendrix MJ. Maspin suppresses the invasive phenotype of human breast carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1998;58:5681-5685. [PubMed] |
| 17. | Zhang M, Volpert O, Shi YH, Bouck N. Maspin is an angiogenesis inhibitor. Nat Med. 2000;6:196-199. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 18. | Shi HY, Zhang W, Liang R, Abraham S, Kittrell FS, Medina D, Zhang M. Blocking tumor growth, invasion, and metastasis by Maspin in a syngeneic breast cancer model. Cancer Res. 2001;61:6945-6951. [PubMed] |
| 19. | Wang MC, Yang YM, Li XH, Dong F, Li Y. Maspin expression and its clinicopathological significance in tumorigenesis and progression of gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2004;10:634-637. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 20. | Odero-Marah VA, Khalkhali-Ellis Z, Chunthapong J, Amir S, Seftor RE, Seftor EA, Hendrix MJ. Maspin regulates different signaling pathways for motility and adhesion in aggressive breast cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 2003;2:398-403. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 21. | Okusa Y, Ichikura T, Mochizuki H. Prognostic impact of stromal cell-derived urokinase-type plasminogen activator in gastric carcinoma. Cancer. 1999;85:1033-1038. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 22. | Biliran H Jr, Sheng S. Pleiotrophic inhibition of pericellular urokinase-type plasminogen activator system by endogenous tumor suppressive Maspin. Cancer Res. 2001;61:8676-8682. [PubMed] |
| 23. | Zhang W, Zhang M. Tissue microarray analysis of Maspin expression and its reverse correlation with mutant p53 in various tumors. Int J Oncol. 2002;20:1145-1150. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 24. | Cher ML, Biliran HR Jr, Bhagat S, Meng Y, Che M, Lockett J, Abrams J, Fridman R, Zachareas M, Sheng S. Maspin expression inhibits osteolysis, tumor growth, and angiogenesis in a model of prostate cancer bone metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:7847-7852. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 25. | Kitoh T, Yanai H, Saitoh Y, Nakamura Y, Matsubara Y, Kitoh H, Yoshida T, Okita K. Increased express-ion of matrix metalloproteinase-7 in invasive early gastric cancer. J Gastroenterol. 2004;39:434-440. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 26. | Ajisaka H, Yonemura Y, Miwa K. Correlation of lymph node metastases and expression of matrix metalloproteinase-7 in patients with gastric cancer. Hepatogastroenterology. 2004;51:900-905. [PubMed] |
| 27. | Chen JQ, Zhan WH, He YL, Peng JS, Wang JP, Cai SR, Ma JP. Expression of heparanase gene, CD44v6, MMP-7 and nm23 protein and their relationship with the invasion and metastasis of gastric carcino-mas. World J Gastroenterol. 2004;10:776-782. [PubMed] |
| 28. | Aihara R, Mochiki E, Nakabayashi T, Akazawa K, Asao T, Kuwano H. Clinical significance of mucin phenotype, beta-catenin and matrix metallopro-teinase 7 in early undifferentiated gastric carcinoma. Br J Surg. 2005;92:454-462. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 29. | Festuccia C, Angelucci A, Gravina G, Eleuterio E, Vicentini C, Bologna M. Bombesin-dependent pro-MMP-9 activation in prostatic cancer cells requires beta1 integrin engagement. Exp Cell Res. 2002;280:1-11. [PubMed] [DOI] |