修回日期: 2005-03-11
接受日期: 2005-03-22
在线出版日期: 2005-05-01
目的: 研究MMP-1, TIMP-1在肝纤维化发生发展中的作用.
方法: ♀SD大鼠48只, 体质量120-150 g, 随机分成正常对照组8只和肝纤维化组40只. 肝纤维化动物模型制备按Blackwell方法 稍加改进, 予HSA致敏大鼠后再予尾静脉攻击注射. 在攻击注射0, 2, 4, 6, 8 wk后取肝. 应用肝组织羟脯氨酸(HYP)的测定和HE, 嗜银及VG染色监测肝纤维组织增生情况, ELISA方法测定MMP-1, TIMP-1的蛋白表达, 半定量RT-PCR 方法测定MMP-1, TIMP-1基因表达.
结果: HYP随着HSA的不断注射逐渐升高, 纤维组织增生逐渐加重, 显示HSA所致的免疫性肝纤维化逐步形成. 正常肝组织有MMP-1蛋白表达, 在肝纤维化发展过程中以及肝硬化阶段, 其蛋白表达没有显著性变化(P>0.05); 而TIMP-1蛋白表达水平逐渐增加(4 wk后, 与0 wk比较有统计学差别: P<0.01), 到肝硬化阶段达到高峰(8 wk时接近0 wk的4倍). 在肝纤维化形成的进展中, MMP-1mRNA表达无明显变化(P>0.05), 而TIMP-1mRNA表达随着时间的推移而逐渐增高(4 wk后与0 wk比较, P<0.01). 在肝纤维化发生发展中, MMP-1/TIMP-1蛋白表达比值逐渐降低, 尤其是4 wk以后, 分别与0 wk比较有显著差异(P<0.01). 按肝纤维化增生程度分组, 随着肝纤维化程度的加重, TIMP-1的表达逐渐升高, MMP-1/TIMP-1比值逐渐减小.
结论: 在大鼠免疫性肝纤维化进程中, TIMP-1进行性升高, 使MMP-1活性受到抑制. MMP-1及TIMP-1比例逐渐失调并持续存在, 加速了肝纤维化的进程.
引文著录: 段志军, 胡祥, 高志红, 谭晨, 袁宏, 李士军. 大鼠免疫性肝纤维化形成中MMP-1和TIMP-1表达的动态变化. 世界华人消化杂志 2005; 13(9): 1106-1110
Revised: March 11, 2005
Accepted: March 22, 2005
Published online: May 1, 2005
AIM: To evaluate the roles of matrix metalloproteinase-1/ tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinse-1 (MMP-1/TIMP-1) in the course of formation and progression of liver fibrosis.
METHODS: Forty-eight female SD rats, 120-150 g in weight, were divided randomly into 2 groups, 8 rats in normal control group and 40 rats in fibrosis group. The fibrotic animal model was established according to the method of Blackwell with some modifications. Human serum albumin (HSA)-sensitized rats were further attacked by i. v. injection of HSA through the coccygeal vein. Liver tissues were obtained 0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 weeks after the attack. Liver hydroxyproline (HYP) content was determined, and HE, argentophilic as well as Van Gieson's (VG) stainings were performed to monitor the process of fibroproliferation. The protein and RNA of MMP-1/TIMP-1 were analyzed using ELISA and semi-quantitative RT-PCR, respectively.
RESULTS: Gradual formation of hepatic fibrosis was detected in the rats, which indicated an ideal model to study the process of generation and development of fibrosis. MMP-1 protein was present in the normal liver, with no significant change in fibrosis and cirrhosis (P>0.05). In contrast, TIMP-1 protein was increased progressively (P<0.01, after 4 weeks), reaching the peak in the stage of cirrhosis (the value after 8 wks was increased by 4 folds). In consistence with the changes of the proteins, MMP-1 mRNA expression did not alter significantly during the fibrosis process (P>0.05), while TIMP-1 mRNA expression was increased gradually (P<0.01, after 4 weeks). MMP-1/TIMP-1 ratio tended to decrease in this process. The change was more profound after 4 weeks (P<0.01). Moreover, the extent of the increase of TIMP-1 and the decrease of MMP-1/TIMP-1 ratio was well correlated with the extent of fibrosis, as revealed by the study of rats in different groups with different grades of fibroproliferation.
CONCLUSION: The main cause responsible for the deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM) during fibrosis might not be a gradual decrease in MMP-1 level, but a progressing increase in TIMP-1 level, which suppresses the activity of MMP-1 so as to diminish matrix degradation. A gradual decrease of MMP-1/TIMP-1 ratio during this process indicates a progressing disproportion between MMP-1 and TIMP-1, which accelerates the fibrosis process. TIMP-1 expression and MMP-1/TIMP-1 ratio are two useful indexes to reflect the fibrotic extent.
- Citation: Duan ZJ, Hu X, Gao ZH, Tan C, Yuan H, Li SJ. Dynamic change of MMP-1/TIMP-1 expression in experimental immune hepatic fibrosis. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi 2005; 13(9): 1106-1110
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1009-3079/full/v13/i9/1106.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.11569/wcjd.v13.i9.1106
肝纤维化的发生不仅是由于肝脏细胞外基质(extrace-llular matrix, ECM)合成过多, 而且与ECM降解水平的变化有着密切关系[1]. 基质金属蛋白酶(matrix metalloproteinases, MMPs)可降解多种ECM成分. 正常情况下, 肝脏ECM合成和降解维持着动态平衡, MMPs和金属蛋白酶组织抑制因子(tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinses, TIMPs)在调节这种平衡中起重要作用[2]. 慢性肝损伤时MMPs/TIMPs比值发生变化, 导致ECM合成增多, 降解减少, 最终沉积形成肝纤维化. 参与肝纤维化形成的主要胶原是I, III型胶原, 参与降解I, III型胶原的基质金属蛋白酶主要是MMP-1[3], 他的抑制因子为TIMP-1[4-5], 当MMP-1和TIMP-1比例失调时, I, III型胶原降解减少而沉积. 我们以人血清白蛋白所致的大鼠免疫性肝纤维化模型为基础, 在肝纤维化形成的不同时期同步测定肝组织MMP-1, TIMP-1蛋白和基因水平的表达, 旨在进一步了解MMP-1/TIMP-1在肝纤维化发生发展中的作用及其与肝纤维化程度的关系.
♀Sprague-Dawley大鼠48只, 体质量120-150 g, 由大连医科大学实验动物中心提供, 随机分成正常对照组8只和肝纤维化组40只(死亡动物未计算在内).200 g/L人血清白蛋白(human serum albumin, HSA); 大鼠MMP-1及TIMP-1测定(ELISA)试剂盒; RT-PCR扩增试剂盒, 引物序列来自文献[6-8].
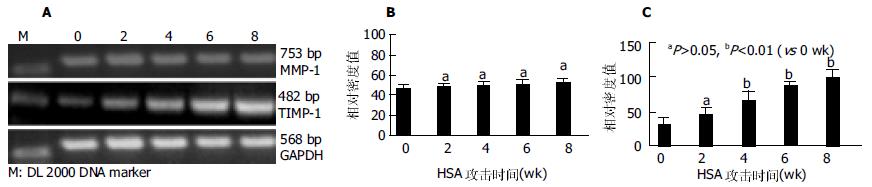
大鼠免疫性肝纤维化动物模型的制备按Blackwell方法[9]稍加改进. 末次致敏后10 d予尾静脉攻击注射HSA, 每次0.3-0.5 mL(2.5-4 mg, 逐渐增加), 2次/wk, 共8 wk. 正常对照组, 予相应量的生理盐水注射. 在HSA攻击注射前(0 wk)以及攻击2, 4, 6, 8 wk末分别取8只大鼠去头取肝, 一部分迅速投入液氮, 之后转入-70℃保存, 再用生理盐水制备100 g/L肝匀浆, 或提取总RNA(每组任取3只鼠肝组织), 均置于-20℃保存. 另一部分置入10 g/L中性甲醛中固定, 制备病理切片. 肝组织羟脯氨酸(HYP)的测定: 离心取上清液加浓盐酸在高温中水解, 再与对二甲氨基苯甲醛呈色反应测定含量. HE染色观察肝纤维组织增生程度与分布情况: "-"-"+++"; 嗜银染色观察III型胶原增生程度: "-"-"+++"; VG染色观察I型胶原增生程度: "-"-"+++"[10]. MMP-1和TIMP-1蛋白表达的测定: ELISA方法, 分别根据试剂盒说明测定并计算出二者蛋白表达数值. MMP-1, TIMP-1基因表达的测定: RT-PCR方法, 按照扩增试剂盒操作. 取HSA攻击 0, 2, 4, 6, 8 wk末的肝组织称质量后匀浆, 采用异硫氰酸胍法并参照Chomczynski et al方法提取总RNA, 判定RNA的质量和浓度, 通过逆转录反应及PCR反应后, 取扩增产物加入2%的琼脂糖凝胶孔中, TAE缓冲液, 50 V电压, 电泳1 h, 照相记录结果经扫描, 通过计算机QuantiScan分析软件处理, 与内参照(GAPDH)对比, 以%代表目的基因的相对表达值.
统计学处理 等级资料用秩和检验, 计量资料用方差分析.
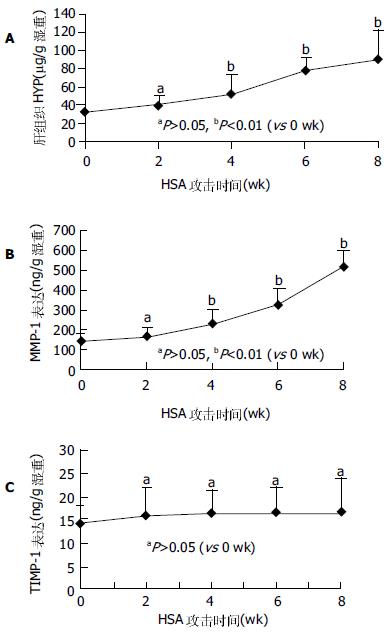
HSA攻击0, 2, 4, 6, 8 wk大鼠肝脏, 0-2 wk大多数基本正常, 表面光亮, 边缘规整, 触之质软, 切割易碎; 6-8 wk肝脏光亮度明显下降, 颜色变暗, 边缘不规整, 肝表面粗糙, 布满针尖大小的颗粒, 分布均匀紧密, 触之质较硬, 易切割, 不易碎; 4 wk鼠肝基本介于上述二者之间. 随着注射次数的增加及时间的推移, 肝纤维化逐渐形成, 而且肝纤维化程度逐渐加重(表1), 至4 wk以后, 肝纤维组织增生明显, 6-8 wk明显有假小叶形成, 提示大鼠免疫性肝纤维化模型是很好观察肝纤维化形成过程的模型(4 wk后与0 wk比较P<0.01). 随着HSA的不断注射, 肝组织HYP含量逐渐增多, 2 wk时与0 wk比较虽未显示显著变化(P>0.05), 但4 wk以后, 分别与0 wk比较均有统计学差异(P<0.01). 提示免疫性肝纤维化逐步形成的过程(图1A).
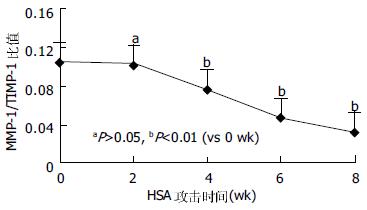
随着HSA的不断注射及肝纤维化的逐渐形成, 肝组织MMP-1的蛋白表达虽在2 wk时似有升高趋势, 但2 wk后趋于平稳, 各个时间点的表达分别与0 wk时的表达比较无统计学意义(P>0.05, 图1B). 可以看出, 随着HSA的攻击注射和纤维化的逐渐形成, 肝组织TIMP-1的蛋白表达持续升高(图1C), 自4 wk始, 与0 wk比较有明显统计学差别(P<0.01), 至8 wk时, 其升高接近0 wk的4倍. 半定量RT-PCR结果显示, 在大鼠免疫性肝纤维化形成的进展中, 在HSA攻击0, 2, 4, 6及8 wk末所检测的MMP-1mRNA表达无明显变化(P>0.05), 而同步检测的TIMP-1mRNA表达随着时间的推移而逐渐增高, 2 wk与0 wk比较虽未显示出统计学意义(P>0.05), 4、6和8 wk分别与0 wk比较, 却有显著差别(P<0.01, 图2). 在大鼠免疫性肝纤维化发生发展中, MMP-1/TIMP-1蛋白表达比值逐渐降低, 尤其是4 wk以后, 分别与0 wk比较有显著差异(P<0.01, 图3).
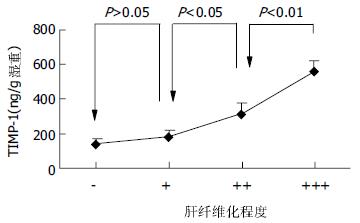
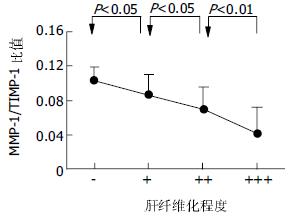
把0-8 wk 5组TIMP-1蛋白表达数值另按各大鼠的纤维化程度的不同重新分组: "-"组(n = 13), "+"组(n = 6), "++"组(n = 10), "+++"组(n = 11). 可以看出, 肝纤维化程度越重, 肝组织TIMP-1的蛋白表达也越高(图4). 把0-8 wk 5组MMP-1/TIMP-1比值也按各大鼠的纤维化程度的不同重新分组比较, 我们可以清楚地看到, 肝组织MMP-1/TIMP-1蛋白表达比值随着肝纤维化程度的加重反而逐渐减小(图5).
在肝纤维化形成过程中, ECM大量沉积, 尤以I型和III型胶原增生为主, 而正常肝组织中, 胶原纤维合成和溶解维持动态平衡, 只有当平衡失调时, 大量ECM沉积形成肝纤维化. MMP-1是肝脏中分解I型及III型胶原的主要胶原酶, TIMP-1是MMP-1的抑制因子, 通过与活化的MMP-1发生不可逆结合而发挥作用. 因此MMP-1和TIMP-1失衡, 在肝纤维化形成中起着重要的作用[11-12]. 我们用大鼠免疫性肝纤维化模型, 通过3种染色观察成纤维细胞、I型及III型胶原增生情况, 而肝组织羟脯氨酸含量测定又被认为是判定肝纤维化程度的良好指标, 在通过上述检查密切监测以证实人血清白蛋白攻击所致免疫性肝纤维化进展过程的同时, 分别用ELISA和RT-PCR方法监测肝纤维化形成不同时期肝组织MMP-1及TIMP-1的蛋白表达和基因表达的动态变化. 结果表明, MMP-1在正常肝组织有表达, 在肝纤维化发生、发展过程中(攻击后2-6 wk)及肝硬化阶段(6-8 wk), 其蛋白表达和基因表达水平没有显著性变化; 而在此过程中TIMP-1蛋白表达和基因表达水平逐渐增加, 到肝硬化阶段到达高峰. 这一结果与Benyon et al结果相似[13-15], 但这些学者未进一步观察他们的动态改变. 由此看来, 导致大鼠免疫性肝纤维化形成的主要原因可能并不是因为MMP-1的表达逐渐减少, 而是由于TIMP-1进行性升高, 使MMP-1活性受到抑制. 因此, 可以推测在肝纤维化形成过程中, 是TIMP-1在起主要调节作用.
TIMP-1是一种糖蛋白, 可抑制大部分MMPs, 尤其是MMP-1活性. TIMPs是特异性地与MMPs催化活性中心的锌离子结合, 封闭其催化活性, 而对MMPs起抑制作用. 许多细胞因子参与调节TIMP-1的合成与分泌[16-17]. 一些调节MMPs的细胞因子也同样调节TIMPs的合成[18]. Kordula et al[19]体外实验表明, 转化生长因子β(transforming growth factor, TGF-β), 血小板衍生长因子(platelet derived growth factor, PDGF), 白介素-6(interleukin-6, IL-6)等均可以促进TIMP-1的合成, 可能为肝纤维化时TIMP-1水平升高的原因之一. 此外, 大量实验表明, HSC的活化与增多可能为TIMP-1在肝纤维化形成时升高的又一原因[20]. 活化的HSC不但产生大量的ECM, 还通过分泌MMPs及TIMPs参与调节ECM的合成和降解. MMP-1/TIMP-1比值的变化更能反映ECM合成和降解的平衡或失衡[21-22]. 本结果显示, 在肝纤维化发生发展中MMP-1/TIMP-1比值逐渐下降, 说明基质合成和降解的平衡随着肝纤维化的进展逐渐失调而且加速了肝纤维化形成的进程. 此外, TIMP-1蛋白表达与肝纤维化程度具有相关性, 随着肝纤维化程度的加重, 肝组织TIMP-1的蛋白表达也是增加的; 而且, MMP-1/TIMP-1比值与肝纤维化的程度呈负相关, 比值越小, 肝纤维化程度越重, 因此, 肝组织TIMP-1的蛋白表达和MMP-1/TIMP-1比值, 可以作为反映肝纤维化程度的指标. 以上结果表明, MMP-1/TIMP-1在大鼠免疫性肝纤维化形成过程中所起的作用, 可能并不是因为MMP-1本身的变化而导致了胶原降解减少, 而是因为TIMP-1增多而抑制了MMP-1的作用, 二者比例的失调, 使纤维组织降解减少而沉积, 且这一作用持续存在, 促使纤维化的不断形成及加重, 最终导致肝硬化. 另外, 肝组织TIMP-1蛋白表达及MMP-1/TIMP-1蛋白表达比值分别与肝纤维化轻重程度具有相关性, 其他学者的研究提示血清中MMP-1/TIMP-1的含量比也与肝纤维化程度有密切关系[23-27], 这为临床医生处理慢性肝病提供了又一诊断、疗效判断和预后判断的手段[28-31].
编辑: 张海宁 电编: 潘伯荣
| 1. | Friedman SL. The cellular basis of hepatic fibrosis: mechanisms and treatment strategies. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:1828-1835. [PubMed] |
| 2. | Matrisian LM. Metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in matrix remodeling. Trends Genet. 1990;6:121-125. [PubMed] |
| 4. | Iredale JP. Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in liver fibrosis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1997;29:43-54. [PubMed] |
| 5. | Murawaki Y, Ikuta Y, Idobe Y, Kitamura Y, Kawasaki H. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 in the liver of patients with chronic liver disease. J Hepatol. 1997;26:1213-1219. [PubMed] |
| 7. | Nie QH, Cheng YQ, Xie YM, Zhou YX, Cao YZ. Inhibiting effect of antisense oligonucleotides phosphorthioate on gene expression of TIMP-1 in rat liver fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol. 2001;7:363-369. [PubMed] |
| 8. | Akahoshi T, Hashizume M, Tanoue K, Shimabukuro R, Gotoh N, Tomikawa M, Sugimachi K. Role of the spleen in liver fibrosis in rats may be mediated by transforming growth factor b-1. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002;17:59-65. [PubMed] |
| 9. | Blackwell JB. Cirrhosis resulting from repeated injection of antigen. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1965;90:245-257. [PubMed] |
| 10. | 段 志军, 李 吉彦, 谭 晨, 周 仕壮, 王 冬梅, 马 晓凯, 杨 洪涛, 白 长川, 胡 祥. 益气软肝方与肝刺激因子对大鼠免疫性肝纤维化保护作用的对照研究. 中医杂志. 2003;44:374-376. |
| 11. | Takahara T, Furui K, Yata Y, Jin B, Zhang LP, Nambu S, Sato H, Seiki M, Watanabe A. Dual expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and membrane-type 1-matrix metalloproteinase in fibrotic human liver. Hepatology. 1997;26:1521-1529. [PubMed] |
| 12. | Milani S, Herbst H, Schuppan D, Grappone C, Pellegrini G, Pinzani M, Casini A, Calabro A, Ciancio G, Stefanini F. Differential expression of matrix-metalloproteinase-1 and 2 genes in normal and fibrotic human liver. Am J Pathol. 1994;144:528-537. [PubMed] |
| 14. | Benyon RC, Iredale JP, Goddard S, Winwood PJ, Arthur MJ. Expression of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1 and 2 is increased in fibrotic human liver. Gastroenterology. 1996;110:821-831. [PubMed] |
| 16. | Overall CM, Wrana JL, Sodek J. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of 72-kDa gelatinase/type IV collagenase by transforming growth factor-beta 1 in human fibroblasts. Comparisons with collagenase and tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:14064-14071. [PubMed] |
| 17. | Roeb E, Graeve L, Hoffmann R, Decker K, Edwards DR, Heinrich PC. Regulation of tissue inhibitor of metallo proteinases-1 gene expression by cytokines and dexamethasone in rat hepatocyte primary cultures. Hepatology. 1993;18:1437-1442. [PubMed] |
| 18. | Gomez DE, Alonso DF, Yoshiji H, Thorgeirsson UP. Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases: structure, regulation and biological functions. Eur J Cell Biol. 1997;74:111-122. [PubMed] |
| 19. | Kordula T, Guttgemann I, Rose-John S, Roeb E, Osthues A, Tschesche H, Koj A, Heinrich PC, Graeve L. Synthesis of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1) in human hepatoma cells (HepG2). Up-regulation by interlukin-6 and transforming growth factor beta1. Febs Lett. 1992;313:144-147. [PubMed] |
| 20. | Iredale JP, Benyon RC, Pickering J, McCullen M, Northrop M, Pawley S, Hovell C, Arthur MJ. Mechanisms of spontaneous resolution of rat liver fibrosis: Hepatic stellate cell apoptosis and reduced hepatic expression of metalloproteinase inhibitors. J Clin Invest. 1998;102:538-549. [PubMed] |
| 22. | Arthur M J, Mann DA, Iredale JP. Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases, hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1998;13:S33-38. [PubMed] |
| 23. | Iredale JP, Goddard S, Murphy G, Benyon RC, Arthur MJ. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 and interstitial collagenase expression in autoimmune chronic active hepatitis and activated human hepatic lipocytes. Clin Sci (Lond). 1995;89:75-81. [PubMed] |
| 24. | Lichtinghagen R, Huegel O, Seifert T, Haberkorn CI, Michels D, Flemming P, Bahr M, Boeker KH. Expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and 9 and their inhibitors in peripheral blood cells of patients with chronic hepatitis C. Clin Chem. 2000;46:183-192. [PubMed] |
| 25. | Holoman J, Glasa J, Galbavy S, Danis D, Molnarova A, Kazar J, Bednarova A, Misianik J. Serum markers of liver fibrogenesis, and liver histology findings in patients with chronic liver diseases. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2002;103:70-75. [PubMed] |
| 26. | Boeker KH, Haberkorn CI, Michels D, Flemming P, Manns MP, Lichtinghagen R. Diagnostic potential of circulating TIMP-1 and MMP-2 as markers of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Clin Chim Acta. 2002;316:71-81. [PubMed] |
| 27. | Murawaki Y, Ikuta Y, Kawasaki H. Clinical usefulness of serum tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases(TIMP-2)assay in patients with chronic liver disease in comparison with serum TIMP-1. Clin Chim Acta. 1999;281:109-120. [PubMed] |
| 28. | Zhang BB, Cai WM, Weng HL, Hu ZR, Lu J, Zheng M, Liu RH. Diagnosis value of platelet deriverd growth factor-BB, transforming growth factor-betal, matrix metalloproteinase-1, and tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-1 in serum and peripheral blood mononuclear cells for hepatic fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol. 2003;9:2490-2496. [PubMed] |
| 29. | Flisiak R, Al-Kadasi H, Jaroszewicz J, Prokopowicz D, Flisiak I. Effect of lamivudine treatment on plasma levels of transforming growth factor betal, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinses-1 and metalloproteinase-1 in patients with chronic hepatitis B. World J Gastroenterol. 2004;10:2661-2665. [PubMed] |
| 30. | Cai WM, Zhang BB, Weng HL, Hu ZR, Lv J, Zheng M, Liu RH. The diagnosis value of eight serum indices for liver fibrosis. Zhonghua Ganzangbing Zazhi. 2004;12:219-222. [PubMed] |
| 31. | Luo YJ, Yu JP, Shi ZH, Wang L. Ginkgo biloba extract reverses CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in rats. World J Gastroenterol. 2004;10:1037-1042. [PubMed] |