修回日期: 2005-07-01
接受日期: 2005-07-06
在线出版日期: 2005-08-28
目的: 检测survivin和caspase-3蛋白在胃癌前病变及胃癌组织中的表达情况, 探讨其与胃黏膜癌变的关系及作用机制.
方法: 采用Envision免疫组化学二步法检测不同胃黏膜病变组织131例(包括慢性炎症44例、单纯肠化生31例, 异型增生40例和胃癌16例)中survivin和caspase-3蛋白的表达情况.
结果: 慢性炎症, 单纯肠化生, 异型增生和胃癌中的survivin蛋白阳性表达率分别为4.5%(2/44), 51.6%(15/31), 100.0%(40/40)和93.8%(15/16).胃癌组织和异型增生组 survivin蛋白表达显著高于单纯肠化生组(P<0.05). 胃癌survivin蛋白表达阳性组caspase-3蛋白表达(3/13, 23.1%)显著低于survivin蛋白表达阴性组(2/3, 66.7%, P<0.05).
结论: 胃癌survivin蛋白表达水平与异型增生相当, 高于单纯肠化生, survivin可能通过阻抑caspase-3促进胃癌的演进.
引文著录: 吕晓君, 吴东瑛, 杨琳, 张淑敏, 辛彦. 胃癌前病变及胃癌组织中survivin和caspase-3蛋白表达的意义. 世界华人消化杂志 2005; 13(16): 1951-1955
Revised: July 1, 2005
Accepted: July 6, 2005
Published online: August 28, 2005
AIM: To detect the expression survivin and caspase-3 in the tissues of gastric cancer and precancerous lesion, and to explore their roles in the carcinogenesis gastric cancer.
METHODS: The expression of survivin and caspase-3 protein were detected by Envision immunohistochemistry in 131 cases of paraffin-embedded specimens from different gastric mucosa, including 44 cases of chronic gastritis, 31 cases of intestinal metaplasia, 40 cases of dysplasia and 16 cases of gastric cancer.
RESULTS: The positive rates of survivin expression in chronic gastritis, intestinal metaplasia, dysplasia and gastric cancer were 4.5%(2/44), 51.6%(15/31), 100.0%(40/40) and 93.8%(15/16) respectively. The positive rates of survivin protein in gastric cancer and dysplasia were significantly higher than that in intestinal metaplasia(P<0.05). The level of caspase-3 expression in positive survivin groups was significantly lower than in negative survivin group(23.1% vs 66.7%, P<0.05).
CONCLUSION: The positive rate of survivin protein in gastric cancer is similar to that in dysplasia, and higher than that in intestinal metaplasia. Survivin may promote the progression of gastric cancer by inhibiting the expression of caspase-3.
- Citation: Lv XJ, Wu DY, Yang L, Zhang SM, Xin Y. Significance of survivin and caspase-3 protein expression in gastric precancerous lesions and gastric cancer tissue. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi 2005; 13(16): 1951-1955
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1009-3079/full/v13/i16/1951.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.11569/wcjd.v13.i16.1951
细胞凋亡受抑制是恶性肿瘤细胞自主性增殖的主要原因, 其与恶性肿瘤的发生发展密切相关[1-3].survivin为一种凋亡抑制蛋白, 是迄今发现最强的凋亡抑制因子[4-6].其表达可能与胃癌的发生和演进有关[7-9], 但对于survivin是否参与胃癌早期发生, 即其在胃黏膜肠上皮化生和异型增生等癌前病变中的表达情况目前研究得并不十分清楚.caspase3是凋亡发生信号通路下游最主要的执行蛋白[10-11], 研究发现survivin蛋白能够抑制Fas、Bax及caspase-3/7诱导的细胞凋亡[12-13], 那么survivin对凋亡的抑制作用多大程度依赖于caspase-3通路而起作用以及这种作用是否在整个癌的转化和演进中起作用?我们利用免疫组织化学方法检测survivin和caspase-3的表达情况, 探讨survivin蛋白在胃黏膜癌变过程中所起的作用及其表达与凋亡效应蛋白caspase-3的关系.
中国医科大学附属一院胃黏膜活检标本131例, 其中: 不伴有肠上皮化生(IM)和异型增生(Dys)之胃黏膜慢性炎症(SGC)44例、不伴异型增生之单纯肠上皮化生31例, 中重度异型增生40例, 胃癌(GC)16例.兔抗人survivin多克隆抗体和caspase-3多克隆抗体购自于福建迈新公司, 工作浓度为1∶80; PV9000试剂盒购自北京中山公司.
采用Envision免疫组织化学方法对各种胃黏膜病变进行免疫组化染色.免疫组化步骤简述如下, 用3 mL/L H2O2灭活内源性过氧化物酶20 min, 抗原暴露采用EDTA热修复结合胃蛋白酶消化法(37℃, 40 min); 正常山羊血清封闭15 min, 然后滴加一抗150 μL于37℃孵育2 h; PV9000孵育30 min, DAB显色, 苏木素复染.利用PBS代替一抗作为阴性对照, 用已知阳性切片作阳性对照.survivin蛋白和caspase-3蛋白阳性表达定位于胃黏膜上皮及胃癌细胞质.在组织切片中不显色为阴性(-), 胞核或胞质显示为淡黄至黄棕色者为阳性细胞标志, 将阳性细胞按其数量及显色强度分为3级: 表达弱阳性(+), 即阳性细胞数<10%, 显色强度为淡黄色或仅个别细胞呈黄至棕黄色染色; 表达中度阳性(++), 即阳性细胞数及显色强度介于弱阳性与强阳性之间.表达强阳性(+++), 即阳性细胞数>60%, 多数细胞呈黄至棕黄色染色.
统计学处理 采用χ2检验分析比较不同胃黏膜病变组织中survivin和caspase-3蛋白的阳性表达率的差别, P<0.05有统计学意义, P<0.01有显著性差异.
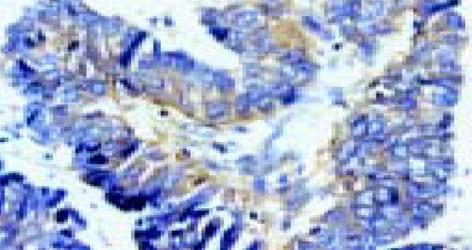
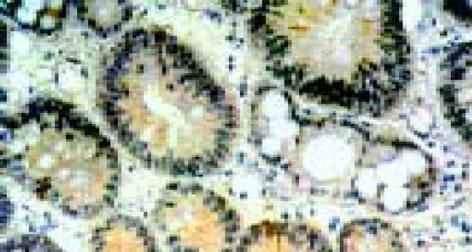
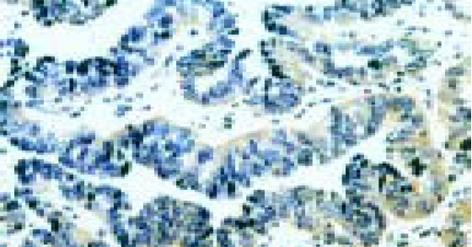
慢性炎症组survivin表达阳性率为4.5%(2/44), 均为弱阳性表达, 阳性细胞主要分布在胃黏膜组织的腺颈部增殖区; 不伴异型增生的单纯IM组survivin阳性表达率为51.6%(15/31), 显著高于慢性炎症组而低于异型增生组(100.0%, 40/40, P<0.01).13/16例(81.3%)胃癌组织survivin蛋白表达阳性, 显著高于单纯IM组(P<0.05).survivin蛋白表达在胃癌组和不典型增生组间无统计学差异, 且与不同胃癌组织学类型无关(P>0.05,表1和图1, 2).将伴有和不伴有异型增生的IM分型, 结果发现, III型IM中survivin蛋白表达阳性率(35/35, 100%)显著高于I型IM(1/5, 20%)和II型IM(14/36, 61.1%), P<0.01; 而I型和II型IM之间survivin阳性表达率无明显差异(P>0.05, 表1和图3).将40例胃黏膜异型增生组按组织学类型分型, 腺瘤型19例(占47.5%), 隐窝型13例(32.5%), 再生型8例(20%), 所有异型增生病例均可检测到survivin蛋白表达, 阳性率100%(40/40), 各型之间survivin蛋白表达程度无统计学差异(P>0.05, 表1和图4).
胃黏膜异型增生组织中, caspase-3蛋白表达阳性率在survivin蛋白表达阳性组(29/35, 82.9%)和survivin蛋白表达减低组(3/5, 60.0%)两组间无统计学差异(P>0.05, 表2).胃癌组织中, survivin蛋白表达阳性组caspase-3蛋白表达(3/13, 23.1%)明显低于survivin蛋白表达阴性组(2/3, 66.7%, P<0.05, 表2和图5).
| 胃黏膜病变 | survivin表达 | n | caspase-3表达 | P | |
| - | -~+++(%) | ||||
| 异型增生 | + | 5 | 2 | 3(60.0) | >0.05 |
| ++~+++ | 35 | 6 | 29(82.9) | ||
| 胃癌 | - | 3 | 1 | 2(66.7) | <0.05 |
| +~+++ | 13 | 10 | 3(2 3.1) | ||
凋亡是肿瘤生长过程中的关键性事件, 在肿瘤细胞中, 凋亡信号转导途径常出现缺陷.survivin基因是由Ambrosini et al[14]于1997年发现并克隆的, 由约1.5×103个碱基对组成, 位于染色体17q25, 蛋白产物由142个氨基酸组成, Mr 16 500, 表达具有明显的细胞周期依赖性, 只在细胞周期的G2/M期表达, 定位于细胞有丝分裂的纺锤体.survivin蛋白是凋亡抑制蛋白(inhibitor of apoptosis protein, IAP)家族新成员, 具有抑制细胞凋亡和调节细胞分裂的双重功能, 其含一个杆状病毒凋亡抑制蛋白重复序列(baculovirus inhibition apoptosis protein repeat, BIR), BIR中含有对抑制凋亡有重要作用的氨基酸残基Pro33、Trp67和Cys84, survivin通过这些残基与caspase3和caspase7结合抑制caspase的活性, 阻止多种凋亡信号诱导的细胞凋亡[15-19].survivin蛋白调节细胞分裂是通过有丝分裂前期与纺锤体微管发生特异性结合反应, 使肿瘤细胞逃避细胞周期G2/M期检测点的监控, 抵抗因DNA损伤或突变自身诱导的细胞凋亡而发挥作用的, 从而导致肿瘤细胞异常分裂增殖[20-22].survivin蛋白广泛表达于胚胎和胎儿组织及多数恶性肿瘤组织, 但不见于发育成熟的正常终末分化组织, 而当组织发生恶变后, 会再次出现survivin的高表达, 提示survivin与各种组织的正常分化和自身稳定以及肿瘤的发生发展密切相关[23], 其与胃癌的形成和发展也有着较大的关系[24].Kania et al[25]发现, 在正常的胃黏膜中survivin mRNA有极低度表达, 但无survivin蛋白表达, 癌组织的表达显著高于癌旁组织; Sarela et al[26-27]认为, survivin蛋白在癌组织中的表达是一个渐进的过程, 随着癌前细胞向癌细胞转化survivin表达逐渐升高, 提示survivin表达水平的改变在正常胃黏膜向胃癌的转化过程中可能发挥重要作用.但亦有不同研究结果的报道, 倪仙荣et al[28]研究显示, survivin在46例正常胃黏膜和46例异型增生细胞内均无阳性表达.
本研究结果显示, 正常胃黏膜及慢性炎症胃黏膜survivin表达率极低或不表达, 从胃黏膜肠上皮化生开始survivin阳性表达率明显上调, 到胃黏膜异型增生达到最高, 胃黏膜癌变时survivin阳性表达率维持在高水平.survivin阳性表达在中重度异型增生与癌之间不存在显著性差异, 提示survivin蛋白在细胞向中重度异型细胞转化的过程中开始发挥作用, 暗示survivin蛋白有希望作为胃癌预警和早期发现的一个有用的标志物.Survivin的表达与不典型增生类型、胃癌组织学类型无关, 提示survivin表达可能主要与细胞癌变有关.其可能是胃癌相关致癌因子激活在正常胃黏膜组织中"关闭"的survivin基因, 通过抑制凋亡及干扰正常细胞周期调控机制等途径, 进而参与胃癌的发生发展, 其具体分子机制仍需进一步深入研究探索.我们还发现, 胃癌组织中survivin蛋白阳性表达组caspase-3表达显著低于survivin蛋白阴性表达组(P<0.05); 而在异型增生黏膜中二者无统计学差异, 提示在胃癌演进过程中survivin通过阻抑caspase-3发挥重要作用, 而在癌细胞转化过程中并非通过caspase-3来发挥作用, 分析原因可能有以下两点: 一是其可能通过其他效应caspase-6/7来发挥凋亡的抑制作用[29]; 二是通过其细胞周期调节作用, 使肿瘤细胞逃避细胞周期G2/M期检测点的监控, 抵抗因DNA损伤或突变自身诱导的细胞凋亡, 从而导致肿瘤细胞异常分裂增殖[30-31].
凋亡抑制因子survivin在正常胃黏膜-肠上皮化生-异型增生-胃癌的演变过程中起重要作用, 是癌变的早期事件, 可作为胃癌预警和早期诊断的联合应用分子指标.胃癌是一种多因素参与、发病机制复杂的疾病, 在其治疗过程中有两种方法是普遍应用的, 即控制细胞增殖和促进细胞凋亡.survivin参与了这两个过程, 是影响细胞周期、有丝分裂和细胞凋亡的关键分子, 且在胃癌组织中过度表达在正常成人终末分化组织(除胸腺、生殖腺及胎盘外)无表达, 将他作为靶点, 抑制其功能, 促进肿瘤细胞凋亡将是很好的抗肿瘤策略.
编辑: 潘伯荣 审读: 张海宁
| 1. | Kwon KB, Kim EK, Lim JG, Jeong ES, Shin BC, Jeon YS, Kim KS, Seo EA, Ryu DG. Molecular mechanisms of apoptosis induced by Scorpio water extract in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. World J Gastroenterol. 2005;11:943-947. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 2. | Jing Z, Nan KJ, Hu ML. Cell proliferation, apoptosis and the related regulators p27, p53 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2005;11:1910-1916. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 3. | Mao JD, Wu P, Xia XH, Hu JQ, Huang WB, Xu GQ. Correlation between expression of gastrin, somatostatin and cell apoptosis regulation gene bcl-2/bax in large intestine carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2005;11:721-725. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 4. | Tong QS, Zheng LD, Chen FM, Zeng FQ, Wang L, Dong JH, Lu GC. Selection of optimal antisense accessible sites of survivin and its application in treatment of gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2005;11:634-640. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 5. | Bokarewa M, Lindblad S, Bokarew D, Tarkowski A. Balance between survivin, a key member of the apoptosis inhibitor family, and its specific antibodies determines erosivity in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005;7:R349-358. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 6. | Wrzesien-Kus A, Smolewski P, Sobczak-Pluta A, Wierzbowska A, Robak T. The inhibitor of apoptosis protein family and its antagonists in acute leukemias. Apoptosis. 2004;9:705-715. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 7. | Miyachi K, Sasaki K, Onodera S, Taguchi T, Nagamachi M, Kaneko H, Sunagawa M. Correlation between survivin mRNA expression and lymph node metastasis in gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 2003;6:217-224. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 8. | Meng H, Lu CD, Sun YL, Dai DJ, Lee SW, Tanigawa N. Expression level of wild-type survivin in gastric cancer is an independent predictor of survival. World J Gastroenterol. 2004;10:3245-3250. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 9. | Tu SP, Jiang XH, Lin MC, Cui JT, Yang Y, Lum CT, Zou B, Zhu YB, Jiang SH, Wong WM. Suppression of survivin expression inhibits in vivo tumorigenicity and angiogenesis in gastric cancer. Cancer Res. 2003;63:7724-7732. [PubMed] |
| 10. | Fu YG, Qu YJ, Wu KC, Zhai HH, Liu ZG, Fan DM. Apoptosis-inducing effect of recombinant Caspase-3 expressed by constructed eukaryotic vector on gastric cancer cell line SGC7901. World J Gastroenterol. 2003;9:1935-1939. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 11. | Zheng HC, Sun JM, Wei ZL, Yang XF, Zhang YC, Xin Y. Expression of Fas ligand and caspase-3 contributes to formation of immune escape in gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2003;9:1415-1420. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 12. | Li YH, Wang C, Meng K, Chen LB, Zhou XJ. Influence of survivin and caspase-3 on cell apoptosis and prognosis in gastric carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2004;10:1984-1988. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 13. | Yang LQ, Fang DC, Wang RQ, Yang SM. Effect of NF-kappaB, survivin, Bcl-2 and Caspase3 on apoptosis of gastric cancer cells induced by tumor necrosis factor related apoptosis inducing ligand. World J Gastroenterol. 2004;10:22-25. [PubMed] |
| 14. | Ambrosini G, Adida C, Altieri DC. A novel anti-apoptosis gene, survivin, expressed in cancer and lymphoma. Nat Med. 1997;3:917-921. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 15. | Ma H, Nguyen C, Lee KS, Kahn M. Differential roles for the coactivators CBP and p300 on TCF/beta-catenin-mediated survivin gene expression. Oncogene. 2005;24:3619-3631. [DOI] |
| 16. | Sun C, Nettesheim D, Liu Z, Olejniczak ET. Solution structure of human survivin and its binding interface with Smac/Diablo. Biochemistry. 2005;44:11-17. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 17. | Li F. Role of survivin and its splice variants in tumorigenesis. Br J Cancer. 2005;92:212-216. |
| 18. | Johnson ME, Howerth EW. Survivin: a bifunctional inhibitor of apoptosis protein. Vet Pathol. 2004;41:599-607. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 19. | McNeish IA, Lopes R, Bell SJ, McKay TR, Fernandez M, Lockley M, Wheatley SP, Lemoine NR. Survivin interacts with Smac/DIABLO in ovarian carcinoma cells but is redundant in Smac-mediated apoptosis. Exp Cell Res. 2005;302:69-82. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 20. | Zangemeister-Wittke U, Simon HU. An IAP in action: the multiple roles of survivin in differentiation, immunity and malignancy. Cell Cycle. 2004;3:1121-1123. [DOI] |
| 21. | Cai Z, Bao HY, Lin MF. Correlation between survivin mRNA expression and homoharringtonine induced apoptosis of malignant hematopoietic cells. Chin Med J (Engl). 2005;118:548-554. [PubMed] |
| 22. | Sanna MG, da Silva Correia J, Ducrey O, Lee J, Nomoto K, Schrantz N, Deveraux QL, Ulevitch RJ. IAP suppression of apoptosis involves distinct mechanisms: the TAK1/JNK1 signaling cascade and caspase inhibition. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22:1754-1766. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 23. | Zhu HX, Wang YH, Zhou CQ, Zhang G, Bai JF, Quan LP, Liu ZH, Xu NZ. Expression of survivin and its significance in esophageal cancer. Zhonghua Zhongliu Zazhi. 2005;27:22-24. [PubMed] |
| 24. | Tsuburaya A, Noguchi Y, Yoshikawa T, Saito A, Doi C, Okamoto T, Fukuzawa K. An anti-apoptosis gene, survivin and telomerase expression in gastric cancer. Hepatogastroenterology. 2002;49:1150-1152. [PubMed] |
| 25. | Kania J, Konturek SJ, Marlicz K, Hahn EG, Konturek PC. Expression of survivin and caspase-3 in gastric cancer. Dig Dis Sci. 2003;48:266-271. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 26. | Sarela AI, Scott N, Ramsdale J, Markham AF, Guillou PJ. Immunohistochemical detection of the anti-apoptosis protein, survivin, predicts survival after curative resection of stage II colorectal carcinomas. A. nn Surg Oncol. 2001;8:305-310. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 27. | Sarela AI, Macadam RC, Farmery SM, Markham AF, Guillou PJ. Expression of the antiapoptosis gene, survivin, predicts death from recurrent colorectal carcinoma. Gut. 2000;46:645-650. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 28. | 倪 仙荣, 董 吉顺. 胃癌中survivin、PTEN、cyclinD1和p53基因的表达及其相关性. 临床与实验病理学杂志. 2003;19:396-400. |
| 29. | Liu T, Brouha B, Grossman D. Rapid induction of mitochondrial events and caspase-independent apoptosis in Survivin-targeted melanoma cells. Oncogene. 2004;23:39-48. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 30. | Chandele A, Prasad V, Jagtap JC, Shukla R, Shastry PR. Upregulation of survivin in G2/M cells and inhibition of caspase 9 activity enhances resistance in staurosporine-induced apoptosis. Neoplasia. 2004;6:29-40. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 31. | Ohashi H, Takagi H, Oh H, Suzuma K, Suzuma I, Miyamoto N, Uemura A, Watanabe D, Murakami T, Sugaya T. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt regulates angiotensin II-induced inhibition of apoptosis in microvascular endothelial cells by governing survivin expression and suppression of caspase-3 activity. Circ Res. 2004;94:785-793. [PubMed] [DOI] |