修回日期: 2003-08-10
接受日期: 2003-08-25
在线出版日期: 2004-02-15
目的: 从水液代谢来研究慢性浅表性胃炎脾胃湿热证与AQP4表达的关系.
方法: 慢性浅表性胃炎患者32例, 其中脾胃湿热证20例, 脾气虚证12 例; 另10例正常人为对照. 胃镜下取胃体上部黏膜, 观察黏膜炎症情况, 免疫组化法、图像分析系统半定量AQP4的蛋白表达量.
结果: 脾胃湿热证胃黏膜的炎症明显要重于脾虚证和正常人组(中重度比17/20 vs 6/12, 0/10, P<0.05, P<0.01); 脾胃湿热证AQP4蛋白表达量强于脾虚证组(209±59 vs 127±61, P<0.01)和正常人组(vs 164±32, P<0.05); 脾虚证蛋白表达量低于正常人组, 但两组无显著性差异(127±61 vs 164±32, P>0.05).
结论: AQP与水液代谢密切相关, AQP的异常表达可能是脾胃湿热证的发生机制之一.
引文著录: 周正, 劳绍贤, 黄志新, 张向菊, 黄烈平, 匡忠生. 慢性浅表性胃炎脾胃湿热证与水通道蛋白4蛋白表达的关系. 世界华人消化杂志 2004; 12(2): 379-381
Revised: August 10, 2003
Accepted: August 25, 2003
Published online: February 15, 2004
AIM: To study the relationship between piwei damp-heat syndrome and aquaporin 4 (AQP4) from fluid metabolism in patients with chronic superficial gastritis.
METHODS: A total of 32 patients with chronic superficial gastritis were composed of 20 cases of piwei damp-heat syndrome and 12 of pi-qi deficiency syndrome, while 10 cases of healthy people were taken as control. The mucosa of upper stomach was obtained by gastroscopic biopsy. The mucosal inflammation was observed and the protein expression of AQP4 was semiquantitated by the immunohistochemistry and image assay system.
RESULTS: The mucosal inflammation of piwei damp-heat syndrome group was more severe than that of the other two groups significantly (moderate or severe rate 17/20 vs 6/12, 0/10, P < 0.05, P < 0.01, respectively), and the protein expression of AQP4 in piwei damp-heat syndrome group was also higher than that of the other two groups significantly (209±59 vs 127±61 and 164±32, P < 0.01, P < 0.05, respectively).
CONCLUSION: AQP has a close connection with water metabolism. The abnormal expression of AQP may be one of the pathogenesis of piwei damp-heat syndrome.
- Citation: Zhou Z, Lao SX, Huang ZX, Zhang XJ, Huang LP, Kuang ZS. Relationship between piwei damp-heat syndrome of chronic superficial gastritis and aquaporin 4 protein expression. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi 2004; 12(2): 379-381
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1009-3079/full/v12/i2/379.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.11569/wcjd.v12.i2.379
中医的脾(胃)是以消化系统为主的多系统的功能综合单位, 包括了消化、水电解质代谢、能量代谢、神经内分泌等多系统的功能; 近年关于脾实质的研究, 证型上集中在脾虚证的研究, 功能上集中在"脾主运化、尤其脾主运化水谷"的研究, 而关于脾胃实证和"脾主运化水液"的研究较少[1-3]. 现代医学认为[4-11], 水通道蛋白(aquaporin, AQP)是生物膜上特异性转运水的整合蛋白质, 是水通过生物膜的主要方式, 其作用是参与调节水平衡; AQP目前已成功分离出10个亚型, 在胃黏膜中主要是AQP4的表达. 我们以水液代谢为切入点, 研究脾胃湿热证与AQP4之间的关系.
慢性浅表性胃炎的诊断标准参照中华医学会消化病学分会2000年井冈山会议制定的标准(中华消化杂志 2000; 20: 199-201), 中医辨证脾胃湿热证和脾气虚证的诊断标准参照2002年国家药品监督管理局颁布的《中药新药临床研究指导原则》[12], 10例正常人为本校学生志愿者, 诊断标准为无心、肝、脾、肺、肾等系疾病、常规实验室检查正常、胃黏膜胃镜征象和病理组织学基本正常、舌脉正常. 结合症状、体征、胃镜检查和病理组织学结果, 参照上述慢性浅表性胃炎的诊断标准, 所有患者均确诊为慢性浅表性胃炎, 病例来源于广州中医药大学第一附属医院, 其中辨证脾胃湿热证者20例, 脾气虚证者12例. 所有受试对象均签订知情同意书.
日本Olympus GIF-240XQ型电子胃镜检查, 胃体距EG线2 cm的大、小弯处分别钳取胃黏膜组织4块, 每块0.5×0.5 cm大小, 组织放入40g/L多聚甲醛中固定组织、常规包埋切片、HE染色, 3位病理专科医师在未知诊断、同一设定条件下分析胃黏膜的炎症程度(轻度、中度、重度)(炎症分级标准参考中华消化杂志 2000; 20: 199-201). 组织经包埋切片后, H2O2封闭, 微波法热修复抗原, 血清封闭液封闭, 分别滴加羊抗人AQP4的多克隆抗体(美国Santa Cruz公司)、生物化兔抗羊二抗(武汉博士德公司)和SABC, DAB显色, 苏木素衬染, 透明封片. 显微境下观察, 北航图像分析系统3 000进行病理图像分析, 以阳染光密度值×染面积比值(%)作为观察指标.
统计学处理 等级资料用Ridit分析和K independent sample test, 计量资料用方差分析.
慢性浅表性胃炎患者胃镜下胃黏膜不同程度的充血水肿, 黏液附着, 甚至有少许浅糜烂灶, 显微镜下示炎性细胞和淋巴细胞浸润. 和脾虚证相比, 脾胃湿热证患者胃镜下胃黏膜充血水肿明显, 黏液增多, 显微镜下也发现炎性细胞浸润的面积和深度要严重(P<0.05, 表1).
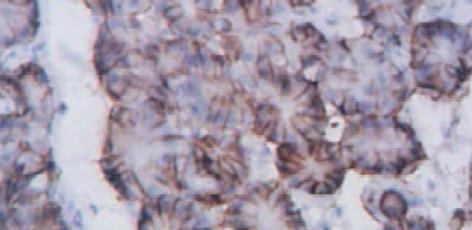
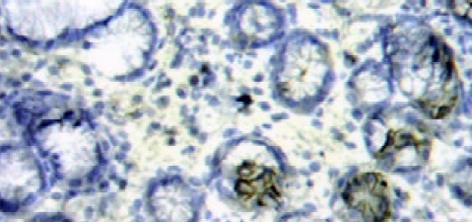
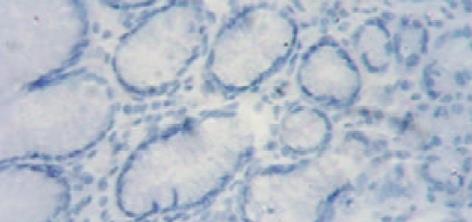
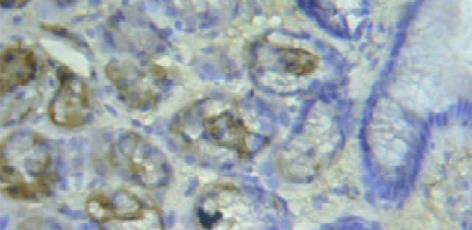
显微下观察, AQP4主要表达在黏膜固有层中, 分布在胃腺主细胞膜和壁细胞膜的基侧面. 脾胃湿热证组阳染呈深棕黄色, 阳染面积比例大(图1). 脾虚证组阳染色呈浅棕色, 阳染面积小, 或无阳染(图2, 图3). 正常人组阳染强度中等, 阳染面积也较广(图4). 阳染结果经全自动图像分析后: 脾胃湿热证AQP4蛋白表达量强于脾虚证组(209±59 vs 127±61, P<0.01)和正常人组(vs 164±32, P<0.05); 脾虚证蛋白表达量虽低于正常人组, 但两组无显著性差异(127±61 vs 164±32, P>0.05).
脾主运化, 运化水液, 在水液代谢中起着重要作用, 可用"化"和"运"来概括: 通过"脾的化", 能够把水谷物的液态成分转化成水液, 能够把水液化生唾、汗、尿、消化液及其他生理性液体; 通过"脾的运", 能够把津液和多余的水液转输至肺、肾和全身. 脾主运化水液的功能健旺, 可防止体内水液不正常的停滞, 起到维持体内津液平衡的作用. 如脾(胃)运化水液失常, 易湿浊内生, 湿聚化热, 这也是脾胃湿热证的基本病机. 可见, 脾胃湿热证与"脾主运化水液"、水液代谢密切相关. 近年研究发现, 在多种器官组织的细胞膜上存在着一种整合蛋白质, 即水通道蛋白, 他能特异性地介导水转运, 是水通过生物膜的主要方式[4-8]. 1988年首次从哺乳动物红细胞膜上分离AQP1 (J Biol Chem 1988; 263: 15634), 目前已成功分离出10个亚型[5,13-17], AQP家族成员具有基因序列同源性, 有4个外显子和3个内含子, 一个大的外显子编码氨基端分子, 三个小的外显子编码羧基端分子, 编码的AQP蛋白分子是4个单体组成的四聚体结构, 每一单体结构相似, 具有独立功能. 在消化道已发现有7种AQP亚型 [18-27]; 在人胃体主要是AQP4表达, 且只表达胃底腺主细胞和壁细胞的膜上, 功能是参与胃液的分泌, 和/或维持壁细胞的正常容积[9]. AQP4的作用强度可能与以下因素有关: 蛋白表达量、细胞膜上的排列方式、单位膜面积的分布强度等. 胃黏膜AQP4表达在主细胞和壁细胞膜的基侧面, 在细胞膜的顶部及黏液上皮细胞未见表达. 脾胃湿热证组AQP4的蛋白表达要高于正常人组和脾虚证组(P<0.01, P<0.05), 而脾虚证组则低于正常人组(P>0.05); 同时还发现脾胃湿热证组胃黏膜的炎症程度要重于其他两组(P<0.01, P<0.05).
脾胃湿热证与水液代谢失衡密切相关. 脾胃湿热证的炎性介质增加(如组胺、5-羟色胺), 细胞代谢呈代偿性亢进状态, 胃泌素升高, 这些会引起胃黏膜炎症、胃液分泌增加; 我们发现, 脾胃湿热证胃黏膜的AQP4升高, 可能会引起组织间隙和微血管的水进入胃腺细胞或其他细胞, 引起局部水平衡紊乱, 参与炎症反应. 而脾虚证则有线粒体能量传递低下, 胃黏膜分泌功能障碍, 这可能是脾虚证AQP4表达低于脾胃湿热证和正常人的原因. 脾胃湿热证和脾虚证一实一虚, 与水液代谢失衡都相关, AQP表达也不同, 这提示AQP可以用来研究中医"脾主运化水液"的发生机制.
编辑: N/A
| 1. | 劳 绍贤. 加强脾胃实证的研究. 中国中西医结合脾胃杂志. 1997;5:65-66. |
| 4. | Reuss L, Hirst BH. Water transport controversies--an overview. J Physiol. 2002;542:1-2. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 5. | Agre P, King LS, Yasui M, Guggino WB, Ottersen OP, Fujiyoshi Y, Engel A, Nielsen S. Aquaporin water channels--from atomic structure to clinical medicine. J Physiol. 2002;542:3-16. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 6. | Péqueux C, Brilot F, Martens H, Geenen V, Legros JJ. [New players in the physiopathology of water metabolism: the aquaporins]. Rev Med Liege. 1999;54:867-874. [PubMed] |
| 7. | Verkman AS, Yang B, Song Y, Manley GT, Ma T. Role of water channels in fluid transport studied by phenotype analysis of aquaporin knockout mice. Exp Physiol. 2000;85 Spec No:233S-241S. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 8. | Verkman AS. Physiological importance of aquaporins: lessons from knockout mice. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2000;9:517-522. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 9. | Misaka T, Abe K, Iwabuchi K, Kusakabe Y, Ichinose M, Miki K, Emori Y, Arai S. A water channel closely related to rat brain aquaporin 4 is expressed in acid- and pepsinogen-secretory cells of human stomach. FEBS Lett. 1996;381:208-212. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 10. | Ma T, Verkman AS. Aquaporin water channels in gastrointestinal physiology. J Physiol. 1999;517:317-326. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 11. | Koyama Y, Yamamoto T, Tani T, Nihei K, Kondo D, Funaki H, Yaoita E, Kawasaki K, Sato N, Hatakeyama K. Expression and localization of aquaporins in rat gastrointestinal tract. Am J Physiol. 1999;276:C621-C627. [PubMed] |
| 12. | 郑 筱萸. 中药新药临床研究指导原则(试行). 北京: 中国医药科技出版社 2002; 362-371. |
| 13. | Verkman AS, Mitra AK. Structure and function of aquaporin water channels. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2000;278:F13-F28. [PubMed] |
| 14. | Moshelion M, Becker D, Biela A, Uehlein N, Hedrich R, Otto B, Levi H, Moran N, Kaldenhoff R. Plasma membrane aquaporins in the motor cells of Samanea saman: diurnal and circadian regulation. Plant Cell. 2002;14:727-739. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 15. | Hurley PT, Ferguson CJ, Kwon TH, Andersen ML, Norman AG, Steward MC, Nielsen S, Case RM. Expression and immunolocalization of aquaporin water channels in rat exocrine pancreas. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2001;280:G701-G709. [PubMed] |
| 16. | Kreda SM, Gynn MC, Fenstermacher DA, Boucher RC, Gabriel SE. Expression and localization of epithelial aquaporins in the adult human lung. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2001;24:224-234. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 17. | Verkman AS, Matthay MA, Song Y. Aquaporin water channels and lung physiology. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2000;278:L867-L879. [PubMed] |
| 19. | Talbot NC, Garrett WM, Caperna TJ. Analysis of the expression of aquaporin-1 and aquaporin-9 in pig liver tissue: comparison with rat liver tissue. Cells Tissues Organs. 2003;174:117-128. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 20. | Tsujikawa T, Itoh A, Fukunaga T, Satoh J, Yasuoka T, Fujiyama Y. Alteration of aquaporin mRNA expression after small bowel resection in the rat residual ileum and colon. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2003;18:803-808. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 21. | Mennone A, Verkman AS, Boyer JL. Unimpaired osmotic water permeability and fluid secretion in bile duct epithelia of AQP1 null mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2002;283:G739-G746. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 22. | Nicchia GP, Frigeri A, Nico B, Ribatti D, Svelto M. Tissue distribution and membrane localization of aquaporin-9 water channel: evidence for sex-linked differences in liver. J Histochem Cytochem. 2001;49:1547-1556. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 23. | Aoki M, Kaneko T, Katoh F, Hasegawa S, Tsutsui N, Aida K. Intestinal water absorption through aquaporin 1 expressed in the apical membrane of mucosal epithelial cells in seawater-adapted Japanese eel. J Exp Biol. 2003;206:3495-3505. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 24. | Gresz V, Kwon TH, Hurley PT, Varga G, Zelles T, Nielsen S, Case RM, Steward MC. Identification and localization of aquaporin water channels in human salivary glands. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2001;281:G247-G254. [PubMed] |
| 25. | Hurley PT, Ferguson CJ, Kwon TH, Andersen ML, Norman AG, Steward MC, Nielsen S, Case RM. Expression and immunolocalization of aquaporin water channels in rat exocrine pancreas. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2001;280:G701-G709. [PubMed] |
| 26. | Wang KS, Ma T, Filiz F, Verkman AS, Bastidas JA. Colon water transport in transgenic mice lacking aquaporin-4 water channels. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2000;279:G463-G470. [PubMed] |
| 27. | Lignot JH, Cutler CP, Hazon N, Cramb G. Immunolocalisation of aquaporin 3 in the gill and the gastrointestinal tract of the European eel Anguilla anguilla (L. ). J Exp Biol. 2002;205:2653-2663. [PubMed] |