修回日期: 2003-08-20
接受日期: 2003-09-24
在线出版日期: 2004-02-15
目的: 观察胃癌癌前病变p21ras, c-erbB-2, p53癌基因蛋白表达与中医证候的关系.
方法: 经胃镜及病理证实为胃癌癌前病变的病例共40例, 其中中度异型增生24例, 重度异型增生9例, 不完全性结肠化生7例; 中医辨证属脾胃气阴两虚兼气滞者10例, 兼胃热者12例, 兼血瘀者18例. 所有胃黏膜活检标本采用抗生蛋白链菌素-生物素免疫组织化学标记的方法作p21ras、c-erbB-2、p53表达的检测.
结果: p21ras, c-erbB-2, p53在胃癌癌前病变中有过表达, 且其表达随着病变的进展而升高, 但中、重度异型增生及不完全性结肠上皮化生胃黏膜之间的表达差异无显著性(P>0.05). 在不同的兼证中, p21ras, p53的表达兼血瘀者大于兼胃热、气滞者(P<0.01), c-erbB-2的表达兼血瘀、胃热者大于兼气滞者(P<0.05).
结论: p21ras, c-erbB-2, p53癌基因蛋白在胃癌癌前病变中有过表达, 其表达与不同中医兼证有关, 可能有一定的证候特异性.
引文著录: 胡玲, 劳绍贤. 胃癌前病变p21ras, c-erbB-2, p53表达与中医证候的关系. 世界华人消化杂志 2004; 12(2): 262-265
Revised: August 20, 2003
Accepted: September 24, 2003
Published online: February 15, 2004
AIM: To explore the relationship between p21ras, c-erbB-2, p53 protein expression and TCM syndrome in gastric precancerous lesions (GPL).
METHODS: Forty cases with endosmotically and pathologically confirmed GPL were studied, including 24 cases of moderate dysplasia of gastric mucosa, 9 cases of severe dysplasia, 7 cases of incomplete colonic intestinal metaplasia. By the differential diagnosis of TCM, pi-wei deficiency of Qi and Yin associated stagnation of Qi, stomach-heat, and blood stasis were 10,12 and 18 cases respectively. Expression of p21ras, c-erbB-2 and p53 proteins was detected by the LSAB immunohistochemical method.
RESULTS: Overexpression of p21ras, c-erbB-2 and p53 proteins was found in GPL, and gradually increased with the progress of lesions; but among gastric mucosa of the mederate, severe dysphasia and incomplete colonic intestinal metaplasia, there are no differences in the expression of the genes (P > 0.05). Among the differential associated symptoms and signs, the expression of p21ras and p53 oncogene proteins was the blood stasis > stomach-heat and Qi stagnation (P < 0.01), and the expression of c-erbB-2 oncogene protein was the blood stasis and stomach-heat > Qi stagnation(P < 0.05).
CONCLUSION: Overexpression of p21ras, c-erbB-2 and p53 proteins is found in GPL. The expression is related with the differentially associated symptoms and signs.
- Citation: Hu L, Lao SX. Relationship between expression of p21ras, c-erbB-2 and p53 and TCM syndrome in gastric precancerous lesions. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi 2004; 12(2): 262-265
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1009-3079/full/v12/i2/262.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.11569/wcjd.v12.i2.262
胃癌癌前病变(gastric precancerous lesions, GPL)指胃黏膜中重度异型增生和/或不完全性结肠化生, p21ras, c-erbB-2, p53等癌基因异常表达与GPL的发生密切相关[1-14]. 中药治疗不仅能使GPL患者的临床症状得到缓解, 而且也能在一定程度上下调GPL组织中相关癌基因蛋白的过表达[15-27]. 但不论是各基因蛋白在GPL组织中不同病理改变的异常表达, 还是中药对各相关癌基因蛋白的调控作用均存在着一定的差异. 中医认为GPL是以脾胃气阴两虚为本, 或兼气滞、血瘀、热毒为标虚实夹杂的综合征候群, 癌基因异常表达在GPL组织中存在着一定的差异是否提示GPL组织中相关癌基因蛋白的表达可能具有一定的证候特异性? 为此, 我们在临床治疗取得一定疗效的基础上, 对GPL组织中p21ras, c-erbB-2, p53癌基因蛋白表达与GPL证候的关系进行探讨.
所有病例均于胃镜下胃窦部活检取材, 采用四点法, 作HE病理染色确认属于胃黏膜中重度异型增生者, 若为肠上皮化生胃黏膜尚需进一步采用HID-ABpH2. 5-PAS法作黏液组织化学染色以确认属于不完全性结肠化生者; 然后再结合临床的中医辨证, 符合诊断者纳入. 心、肝、肾功能明显异常, 病理诊断已属癌变者不列入本研究. 中医辨证诊断按照《中药新药临床研究指导原则第一辑. 1993: 88, 108》拟定, 具体如下. 气阴两虚主症: 胃脘痞满; 堵闷不舒, 食后加重; 舌质胖嫩, 或有齿印; 色淡红; 苔薄白或少苔; 脉沉细或濡缓. 次证: 神疲乏力; 少气懒言; 自汗; 口干少饮; 形体消瘦. 凡具备上述主症2项(其中舌象或脉象必备一项), 加次症2项即可诊断. 兼气滞症: 胃脘胀满不适; 胀痛连胁; 嗳气频作; 反酸或嘈杂; 脉弦. 兼血瘀症: 久痛不已; 痛有定处; 刺痛; 舌质暗或有瘀斑或瘀点. 兼胃热症: 口干口苦; 大便干结; 舌苔黄. 具备以上兼症中任何两项即为兼有该兼症. 随机双盲法收集GPL病例共40例, 包括中度异型增生24例, 重度9例, 不完全性结肠化生7例; 男32例, 女8例; 中医辨证兼气滞症10例, 兼胃热症12例, 兼血瘀症18例. 平均年龄52. ±11岁; 病程小于5年者24例, 5-10年者13例, 大于10年者3例.
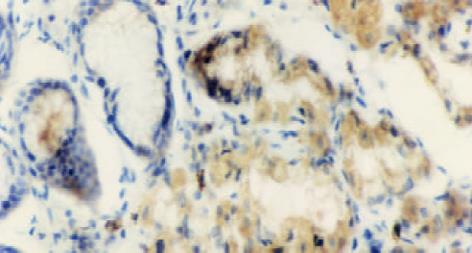
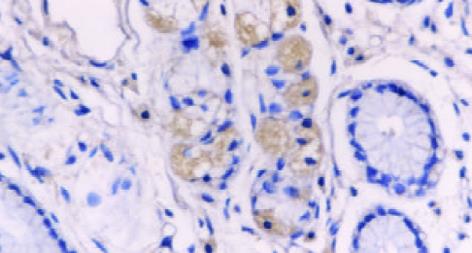
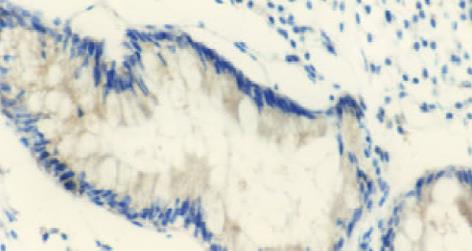
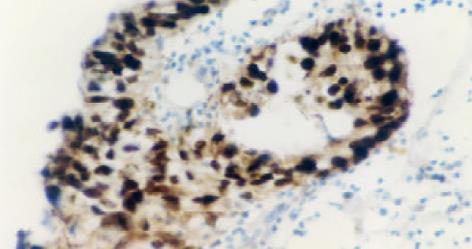
采用抗生蛋白链菌素-生物素免疫组织化学标记的方法(labeled streptavidin biotin method, LSAB). 鼠抗人p21ras单克隆抗体、兔抗人c-erbB-2癌基因蛋白、鼠抗人p53蛋白(DO-7)及LSAB试剂盒均为丹麦DAKO产品; DAB 为福建迈新公司产品. 用PBS替代一抗作阴性对照, 已知的阳性片作阳性对照, 阳性示棕黄色均细颗粒, p21ras及c-erbB-2位于胞质, p53位于胞核.
统计学处理 采用SPSS10. 0统计分析软件包进行χ2检验及χ2分割检验
p21ras, c-erbB-2表达主要定位于胞质(图1, 2), 部分以腺腔缘明显(图3); p53表达主要位于胞核(图4), 但少量也表达在胞质. p21ras, c-erbB-2及p53表达均随着病变的进展而逐渐增加, 但中重度异型增生及不完全性结肠化生之间未见显著性差异, P>0.05, 见表1.
| 病变 | n | p21ras | c-erbB-2 | p53 |
| 中度异型增生 | 24 | 45.8 | 50.0 | 37.5 |
| 重度异型增生 | 9 | 66.7 | 77.8 | 44.4 |
| 不完全性结肠上皮化生 | 7 | 28.6 | 42.8 | 14.3 |
p21ras是c-Ha-ras癌基因的蛋白产物, 为增生和分化受体介导信号传导途径中的重要组成部分. 研究表明p21ras在翻译和转录水平的过表达并不局限于胃黏膜的恶性病变, 而是在异型增生阶段即出现, 且随着病变的加重而表达逐渐增加, 其在一定水平持续过度表达与肿瘤的启动有关[28-29]. c-erbB-2癌基因定位于染色体17q21, 具有酪氨酸蛋白激酶活性. 研究发现, 胃黏膜异型增生中c-erbB-2癌基因蛋白的表达随着病变的进展呈上升趋势, 至重度异型增生达顶峰[30-31]. p53抑癌基因位于染色体17p13.1, 编码393个氨基酸残基的胞核磷蛋白, 是维持正常细胞生长和分裂的负调节因子, 可因不同位点的突变或等位基因的缺失而失活. p53基因的点突变和过表达不仅存在于胃癌各临床分期, 而且可发生于癌变前的不同阶段, 在肠化生, 特别是不完全性结肠化生和异型增生阶段也有较高的检出率[32-36]. 上述研究为p21ras, c-erbB-2, p53癌基因过表达均可发生在GPL阶段提供了强有力的证据. 尽管如此, 现代医学在针对GPL的治疗却未见明显的突破, 追踪随访仍为预防的主要措施, 一旦伴有胃黏膜重度异型增生有癌变倾向时则考虑行外科手术治疗.
GPL属于中医"痞满"、"胃脘痛"之范畴, 临床以胃脘痞满、痛或不痛、纳呆食少、大便不正常为主要表现. 通过国家"八五"攻关对GPL进行临床和实验的系统研究以来, 已较一致地认为GPL是以脾胃气阴两虚为本, 兼有气滞、或胃热、或血瘀的本虚标实之证; 因虚挟邪, 因实致虚是其主要的病机转化规律[37]. 大量的研究也表明, 中药治疗不仅能使GPL患者的临床症状缓解, 而且也在一定程度上使GPL组织中相关癌基因蛋白的异常表达得到改善[15-27]. 但不论是各相关基因蛋白在GPL组织中不同病理改变的异常表达, 还是中药对之的调控作用均存在着一定的差异. GPL中这种基因表达的差异是否与不同兼症有关?各兼症之间的转化, 又是如何形成的?基于此, 我们进行了初浅的探讨. 结果表明, 本组研究病例中, p21ras, c-erbB-2及p53有过表达, 并随着病变的进展而表达逐渐增加, 与文献[1-14,28-37]报道相符. 不同中医兼症中, 上述各癌基因蛋白的表达均以兼血瘀者最高, 兼胃热者次之, 兼气滞者最低, 提示p21ras、c-erbB2及p53的表达与GPL的不同兼症呈平行关系. 从中医的角度看, GPL的三种兼症中, 以兼气滞症者病情最轻, 兼胃热者较重, 兼血瘀者最重, 即所谓的病久入络. 上述研究结果提示, GPL组织中p21ras, c-erbB-2及p53表达与中医对GPL的认识是相吻合的, GPL不同中医兼症与胃黏膜组织中上述相关癌基因的表达有一定的相关性; 推测GPL兼症间的转化, 其病理基础与p21ras, c-erbB-2及p53表达也可能有一定的联系. 通过对GPL中医分型与基因表达相关性的研究, 一方面可为揭示GPL证型的客观化开辟了一条新的途径; 同时, 确立GPL的中医分型对GPL辨证论治的客观化, 为深入研究其病理实质及相关药物的作用机制又提供了必要的前提条件.
编辑: N/A
| 4. | Kasper HU, Schneider-Stock R, Mellin W, Roessner A. P21 protein expression and ras-oncogene mutations in gastric carcinoma: correlation with clinical data. Int J Oncol. 1998;12:69-74. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 5. | Sowa M, Nakata B. [Genome analyses for precancerous lesions in the gastrointestinal tract]. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2000;27:335-340. [PubMed] |
| 6. | Lu W, Chen L, Gong H. [Helicobacter pylori infection and expression of PCNA, p53, c-erbB-2 in carcinoma and precancerours lesions of the stomach]. Zhonghua Zhongliu Zazhi. 1999;21:125-127. [PubMed] |
| 7. | Morgan C, Jenkins GJ, Ashton T, Griffiths AP, Baxter JN, Parry EM, Parry JM. Detection of p53 mutations in precancerous gastric tissue. Br J Cancer. 2003;89:1314-1319. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 8. | Yang GB, Hu FL, Lü YY. [The relation between Helicobacter pylori infection and p53 mutation, MG-7 antigen and AgNORs expression in the development of gastric mucosa lesions]. Zhonghua Yixue Zazhi. 2003;83:1331-1335. [PubMed] |
| 9. | Unger Z, Molnár B, Prónai L, Szaleczky E, Zágoni T, Tulassay Z. Mutant p53 expression and apoptotic activity of Helicobacter pylori positive and negative gastritis in correlation with the presence of intestinal metaplasia. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2003;15:389-393. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 10. | Tian SF, Xiong YY, Yu SP, Lan J. [Relationship between Helicobacter pylori infection and expressions of tumor suppressor genes in gastric carcinoma and related lesions]. Ai Zheng. 2002;21:970-973. [PubMed] |
| 11. | Xu A, Li S, Liu J. [Correlation between apoptosis and proliferation in gastric pre-carcinoam]. Zhonghua Yixue Zazhi. 1999;79:185-186. [PubMed] |
| 16. | 张 旭晨, 高 瑞丰, 李 炳庆, 马 连生, 梅 立新, 吴 玉珍, 刘 凤芹, 廖 振林. 胃细胞逆转丸治疗胃癌前期病变的临床与实验研究. 新消化病学杂志. 1997;5:216-218. |
| 23. | 胡 玲, 劳 绍贤. 胃癌癌前病变相关基因表达及胃炎消治疗机制的初步探讨. 中国中西医结合脾胃杂志. 1999;7:91-92. |
| 27. | 唐 纯志, 劳 绍贤, 胡 玲, 匡 忠生. 胃炎消治疗胃癌前病变对细胞凋亡及相关基因表达的影响. 中国中西医结合脾胃杂志. 2000;8:263-264. |
| 28. | Hao Y, Zhang J, Lu Y, Yi C, Qian W, Cui J. The role of ras gene mutation in gastric cancer and precancerous lesions. J Tongji Med Univ. 1998;18:141-144. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 29. | 惠 延平, 黄 高升, 王 文亮, 王 映梅, 朱 晓慧, 马 福成. 胃癌及其癌前病变中ras, C-erbB-2, p53癌基因产物的表达. 第四军医大学学报. 2001;22:220-223. |
| 31. | 李 晓清, 郝 丽萍, 张 小丽, 龚 飞跃, 郭 惠学, 伍 尤泉. 胃黏膜异型增生C-erbB-2基因表达及其癌变率的研究. 胃肠病学和肝病学杂志. 2002;11:269-271. |
| 32. | Testino G, Gada D, De Iaco F, Cornaggia M. p53 and Ki-67 expression in epithelial gastric dysplasia and in gastric cancer. Panminerva Med. 2002;44:369-371. [PubMed] |
| 33. | Feng CW, Wang LD, Jiao LH, Liu B, Zheng S, Xie XJ. Expression of p53, inducible nitric oxide synthase and vascular endothelial growth factor in gastric precancerous and cancerous lesions: correlation with clinical features. BMC Cancer. 2002;2:8. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 34. | Ming SC. Cellular and molecular pathology of gastric carcinoma and precursor lesions: A critical review. Gastric Cancer. 1998;1:31-50. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 35. | Wang J, Chi DS, Kalin GB, Sosinski C, Miller LE, Burja I, Thomas E. Helicobacter pylori infection and oncogene expressions in gastric carcinoma and its precursor lesions. Dig Dis Sci. 2002;47:107-113. [PubMed] [DOI] |