Copyright
©The Author(s) 2003. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
酵母双杂交技术筛选鉴定乙型肝炎病毒核心蛋白结合蛋白新基因C-12的研究
陆荫英, 陈天艳, 成军, 邵清, 梁耀东, 王琳, 刘妍, 张健, 李克, 张玲霞
陆荫英, 陈天艳, 成军, 邵清, 梁耀东, 王琳, 刘妍, 张健, 李克, 张玲霞, 中国人民解放军第302医院传染病研究所基因治疗研究中心、全军病毒性肝炎防治研究重点实验室 北京市 100039
陆荫英, 女, 1973-08-27生, 贵州省贵阳市人, 汉族. 博士, 2003年军医进修学院毕业, 主治医师. 主要从事肝病的基础及临床工作.
ORCID number: $[AuthorORCIDs]
基金项目: 国家自然科学基金攻关项目, No. C03011402, No. C30070689, 军队"九、五"科技攻关项目, No. 98D063, 军队回国留学人员启动基金项目, No.98H038, 军队"十、五"科技攻关青年基金项目, No. 01Q138, 军队"十、五"科技攻关面上项目, No. 01MB135.
电话: 010-66933391 传真: 010-63801283
收稿日期: 2003-03-08
修回日期: 2003-03-20
接受日期: 2003-04-16
在线出版日期: 2003-08-15
目的
乙型肝炎病毒(HBV)核心蛋白(HBcAg)在HBV感染的肝细胞中可同时存在于细胞核和胞质中, 对于病毒前基因组RNA装配入核壳体是必须的, HBcAg还是HBV介导体液免疫反应和CD4+T细胞免疫反应的重要抗原, 寻找人肝细胞cDNA文库中与HBcAg相互作用蛋白的基因, 是研究HBcAg生物学功能的重要途径.
方法
用多聚酶链反应(PCR)法扩增HBcAg基因, 连接入酵母表达载体pGBKT7中构建诱饵质粒, 转化酵母细胞AH109并在其内表达, 然后与转化了人肝cDNA文库质粒pACT2的酵母细胞Y187进行配合, 在营养缺陷型培养基和X-α-半乳糖(X-α-gal)上进行双重筛选阳性菌落, PCR从中扩增出目的片段并测序, 进行生物信息学分析. 根据GenBank的信息设计新基因的引物, 从HepG2 细胞的mRNA中逆转录PCR扩增出C-12#新基因的完整序列, 连入另一酵母表达载体pGADT7, 并转化进酵母细胞Y187, 再次与转化了诱饵质粒的酵母细胞AH109配合(回交), 以进一步证实HBcAg与C-12新基因编码蛋白的结合作用.
结果
成功克隆出HBcAg基因并在酵母细胞中表达, 配合后选出既能在四缺(SD/-Trp-Leu-His-Ade)培养基又能在铺有X-α-gal的四缺培养基上均能生长, 并变成蓝色的真阳性菌落16个, 其中未知基因4个. 用自行设计的引物成功地从HepG2细胞的mRNA中扩增出C-12#新基因的完整序列, 回交实验再次证实二者之间的结合作用.
结论
成功克隆出HBcAg的肝细胞结合蛋白, 发现未知功能基因, 为进一步研究HBcAg在病毒装配、损害肝细胞、感染致病等方面的具体作用提供了新线索.
关键词: N/A
引文著录: 陆荫英, 陈天艳, 成军, 邵清, 梁耀东, 王琳, 刘妍, 张健, 李克, 张玲霞. 酵母双杂交技术筛选鉴定乙型肝炎病毒核心蛋白结合蛋白新基因C-12的研究. 世界华人消化杂志 2003; 11(8): 1122-1125
Screening and identification of a novel gene coding for hepatitis B virus core antigen interacting protein C-12 in hepatocytes
Yin-Ying Lu, Tian-Yan Chen, Jun Cheng, Qing Shao, Yao-Dong Liang, Lin Wang, Yan Liu, Jian Zhang, Ke Li, Ling-Xia Zhang
Yin-Ying Lu, Tian-Yan Chen, Jun Cheng, Qing Shao, Yao-Dong Liang, Lin Wang, Yan Liu, Jian Zhang, Ke Li, Ling-Xia Zhang, Gene Therapy Research Center, Institute of Infectious Diseases, The 302 Hospital of PLA, 100 Xisihuan Zhonglu, Beijing 100039, China
Supported by: Grants from National Natural Science Foundation No. C03011402, No. C30070689, and Returned Scholarship of General Logistics Department of PLA.
Correspondence to: Dr. Jun Cheng, Gene Therapy Research Center, Institute of Infectious Diseases, 302 Hospital of PLA, 100 Xisihuanzhong Road, Beijing 100039, China. cj@genetherapy.com.cn
Received: March 8, 2003
Revised: March 20, 2003
Accepted: April 16, 2003
Published online: August 15, 2003
AIM
Hepatitis B virus(HBV) core protein (HBcAg) is present in the nucleus and cytoplasm of infected hepatocytes. Phosphorylation of HBcAg was a prerequisite for pregenomic RNA encapsidation into viral capsids. HBcAg capsids are extremely immunogenic and can activate naive B cells by cross-linking their surface receptors and HBcAg-specific CD4(+) T-cell responses are believed to play an important role in the control of human HBV infection. To investigate the complex biological functions of HBcAg, we employed yeast-two hybrid technique to screen proteins in hepatocytes interacting with HBcAg.
METHODS
HBcAg gene was amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The pGBKT7-HBcAg bait plasmid was constructed by using yeast-two hybrid system 3 and transformed into yeast cells AH109, then mated with yeast cells Y187 containing liver cDNA library plasmid in 2×YPDA medium. Diploid yeast was plated on synthetic dropout nutrient medium (SD/-Trp-Leu-His-Ade) and synthetic dropout nutrient medium (SD/-Trp-Leu-His-Ade) containing x-α-gal for selection two times. After extracting and sequencing of plasmid from blue colonies, we conducted bioinformatics analysis. Primers of new gene were designed according to the information in GenBank and used to amplify the complete sequence of new gene C-12. Gene of C-12 was ligated into another yeast expression vector pGADT7 and transformed into yeast cell Y187 and mated with yeast cell AH109 containing pGBKT7-HBcAg bait plasmid to further verify the interaction between HBcAg and the novel protein coded by the new gene C-12.
RESULTS
Sixteen colonies were sequenced. Among them, there were four new genes with unknown function. The complete sequence of new gene C-12 was successfully amplified from the mRNA of HepG2 cell by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction(RT-PCR). The interaction between HBcAg and the novel protein coded by the new gene C-12 was further confirmed by re-mating.
CONCLUSION
Genes of HBcAg interacting proteins in hepatocytes were successfully cloned. The findings of new genes coding for HBcAg associated proteins pave the way for studying the biological functions of HBcAg.
Key Words: N/A
0 引言
在HBV感染的肝细胞中, HBcAg同时存在于胞核和胞质内, 具有保护病毒mRNA, 防止其被RNA酶降解的作用; HBcAg与病毒mRNA和DNA聚合酶共同构成核心颗粒, 在核心颗粒中完成病毒DNA的合成[1,2], 其磷酸化作用对于乙肝病毒前基因组RNA的装配入核壳体、基因组DNA的合成必不可少[3-5]. 在介导免疫应答方面, HBcAg特异性CD4+T细胞免疫应答是清除HBV的重要反应[6-8]; 另外, B细胞刺突尖部有HBcAg的抗原决定簇, 可产生相应的体液免疫反应[9]. 利用酵母双杂交技术寻找HBcAg与肝细胞中相互作用的蛋白, 对于明确HBV致病机制, 有效防治乙型肝炎有着重要意义[10-16].
1 材料和方法
1.1 材料
AH109酵母菌株(MA Ta, trp1-901, leu2-3, 112, ura3-52, his3-200, gal4△, gal80△, LYS2: : GAL1UAS-GAL1TATA-HIS3, GAL2UAS-GAL2TATA-ADE2URA3: : MEL1TATA-lac Z MEL1)、预转化的cDNA肝文库(Y187)、pGBKT7-BD克隆载体及酵母YPD培养基、SD/-Trp、SD/-Leu, SD/-Trp-Leu-His, SD/-Trp-Leu-His-Ade等培养基、X-α-gal购于Clontech公司. 大肠杆菌DH5α及HBV ayw亚型基因全序列质粒载体pCP10为本室保存, c-myc单克隆抗体本室自制. 辣根过氧化物酶标记羊抗鼠IgG购于北京中山生物公司. Taq DNA 聚合酶、T4 DNA连接酶、EcoR I和Pst I购于Takara生物公司. 丙烯酰胺、N, N-'亚甲双丙烯酰胺、IPTG及X-β-Gal及pGEM-T载体、Trizol RNA提取及RT-PCR试剂盒购于Promega公司. TEMED购于宝林曼公司. 醋酸锂、半硫酸腺苷购于Sigma公司. HBcAg扩增引物(P1 5' GAATTCATGGACATCGACCCTTATAA 3' P2 5' CTGCAGAACATTGAGATTCCC GAGAT 3', 肝文库插入序列扩增引物(P3 5'-CTATTCGATGATGAAGATACCCC ACCAAACCC-3', P4 5'-GTGAACTTGCGGGGTTT TTCAGTATCTACGA-3'), 新基因扩增引物(P5 5'-GAATTCATGGACATCGACCCTTATAA-3', P6 5'-CT CAGAACATTGAGATTCCCGAGAT-3')合成及DNA测序由上海博亚公司承担.
1.2 方法
(1)诱饵质粒的构建及表达: PCR扩增HBcAg基因与pGBKT7载体连接, 酶切鉴定后转化入酵母菌株AH109, 提取酵母蛋白质用十二烷基磺酸钠-聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳(SDS-PAGE)和Western免疫印迹法验证HBcAg在酵母中的表达. (2)诱饵与肝文库的酵母配合: 挑取在SD/-Trp培养基上生长的pGBKT7-HBcAg质粒的酵母AH109菌落一到数个接种于SD/-Trp培养基中, 30 °C 250 r.min-1振摇过夜, 次日离心后用2×YPDA培养液5 mL重悬细胞, 计数细胞数大于1×1012.l-1时与1 μL的肝文库酵母细胞在50 μL 2×YPDA中30 °C 30-50 r.min-1配合18-24 h, 离心用1×YPDA 10 mL重悬细胞, 分别取250 μL铺于15 cm的SD/-Trp-Leu-His(3缺), SD/-Trp-Leu-His-Ade (4缺)培养基各25块上, 同时将配合产物按1:10、1:100、1:1000铺于SD/-Trp-Leu培养基上检验配合效率. 生长6-18 d后挑取大于直径3 mm的菌落再次画线于铺有X-α-gal的4缺培养基上检查X-α-gal酶活性, 在此培养基上能生长且变成蓝色的为真阳性菌落. PCR扩增出文库靶基因片段后测序并进行生物信息学分析. (3) C-12新基因的克隆: Trizol RNA提取试剂盒提取HepG2细胞的RNA, 逆转录成cDNA, 以cDNA为模板, 以P5、P6为引物行PCR扩增出C-12新基因的完整序列, 酶切后并连接入另一酵母表达载体pGADT7中. (4)回交实验: 将构建好的pGADT7-C12新基因质粒转化入α型酵母细胞Y187, 接种在1缺亮氨酸的SD平板上, 筛选出的阳性菌落再次与转化了诱饵质粒的α型酵母细胞AH109配合, 4缺/SD培养基上筛选鉴定, 进一步验证HBcAg与C-12新基因表达产物的结合作用.
2 结果
2.1 pGBKT7-HBcAg重组诱饵质粒的构建及表达
利用引物P1、P2成功扩增出HBcAg基因片段, 经10 g/L琼脂糖凝胶电泳分析显示片段为549 bp, 测序结果完全符合报告序列. 连接到用相同酶所切的pGBKT7载体中, 经酶切鉴定结果正确. 醋酸锂法将诱饵质粒转化入酵母AH109后在SD/-Trp培养基上筛选生长6-8 d, 挑取阳性菌落培养后提酵母蛋白质, 进行SDS-PAGE和Western免疫印迹分析结果显示, 对照无表达而转化了pGBKT7-HBcAg的酵母蛋白提取物Western印迹分析可见明显目的条带(图1), 说明HBcAg基因已成功地在酵母中表达.
图1 pGBKT7-HBcAg酵母细胞表达Western免疫印迹分析.
2.2 诱饵与肝文库酵母菌株配合结果
配合后筛选出既能在在四缺(SD/-Trp-Leu-Ade-His)培养基又能在铺有X-α-半乳糖(X-α-gal)的四缺培养基上均能生长并变成蓝色的真阳性菌落16个, 用文库扩增引物行PCR, 扩增出目的片段并测序, 结果在GenBank中进行分析, 找到未知基因4个.
2.3 新基因C-12全序列的克隆
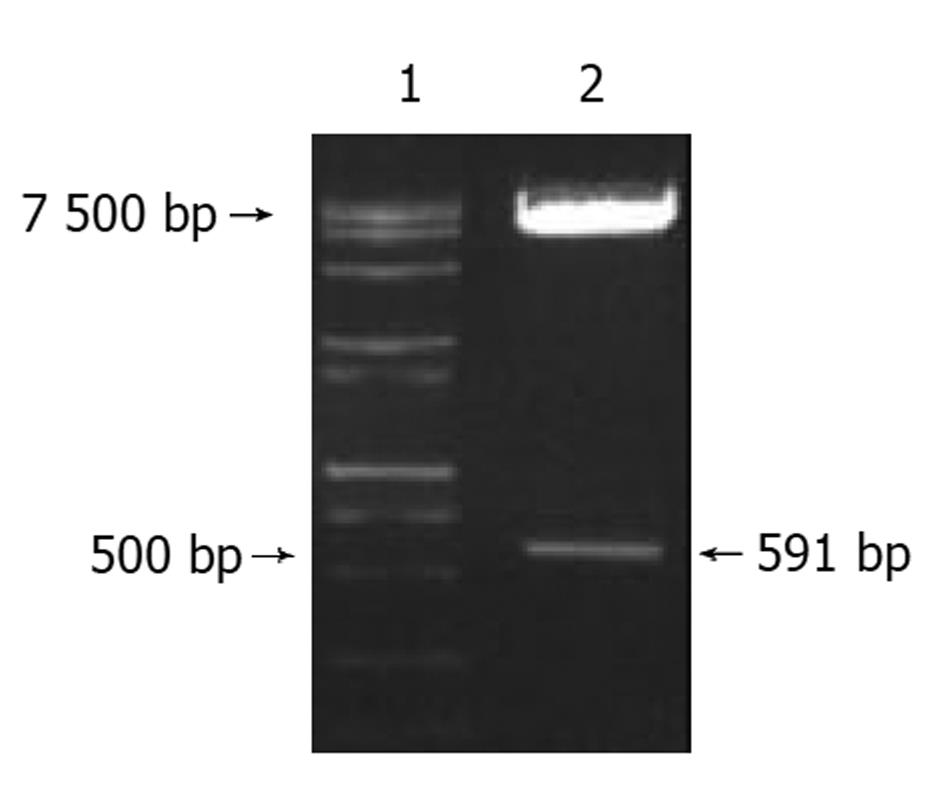
用引物P5, P6成功地从HepG2细胞cDNA中扩增出C-12新基因的全序列长591 bp(图2), 并连入载体pGADT7中(图3).
图2 c-12#新基因序列图 (HBcbp, Genbank number: AF 529371).
图3 pGADT7-C12质粒酶切图.
1: DNA Marker; 2: pGADT7-C12质粒.
2.4 回交实验
pGADT7-C12重组质粒转化入酵母Y187, 在缺亮氨酸的SD平板上长出阳性菌落, 再次与转化了诱饵质粒的酵母AH109配合, 配合后的二倍体酵母能在4缺/SD平板上长出阳性菌落, 说明HBcAg和C12编码的蛋白有结合作用.
3 讨论
近年来新发展起来的酵母双杂交系统是一种分析真核细胞中蛋白-蛋白、蛋白-DNA、蛋白-RNA相互作用的一种分子生物学技术, 他的产生为研究蛋白在体内生理情况下相互作用提供了有效的遗传学方法. 分别融合到一酵母转录激活因子GAL4的BD和AD上的两种蛋白X和Y之间的相互作用重构了激活因子, 导致下游报告基因的转录, 产生容易探测到的表型, 间接证明X和Y两蛋白间有相互作用[17,18].
HBcAg在感染肝细胞中可同时存在于胞核和胞质, 在病毒成熟过程中, 核壳和外膜相互作用, 形成病毒颗粒分泌的信号, 他在肝内的分布与病毒的复制状态、炎症活动程度密切相关[19]. HBcAg有高免疫原性, 几乎所有HBV感染者均产生抗-HBc, HBcAg通过B细胞表面受体轻重链的FR1-CDR1连接区域结合而激活B细胞产生抗体[20], 同时还是CTL免疫应答的靶抗原, 针对HBcAg的细胞免疫应答在病毒清除中起重要作用[21].HBcAg受细胞激酶或病毒编码的激酶作用部分磷酸化, 磷酸化是前基因组RNA包被入病毒核壳体过程中必不可少的环节; HBcAg有鱼精蛋白样亲胞核性的羧基末端, 磷酸化后该末端的核定位序列暴露, HBcAg与核孔复合体结合通过直接转运介导病毒基因组向核内转运, 而其他嗜肝DNA病毒的核壳体蛋白都不转运核内, 但到目前为止还没有发现宿主肝细胞中有与之有关的任何激酶[22,23]. HBcAg与肝细胞蛋白的相互作用是病毒装配、释放、清除过程中关键的环节, 找出其间的联系对于探明HBV致病机制, 寻找有效的防治方法有着深远意义[24-28].
本研究中所用的Clontech公司的酵母双杂交系统3, 下游采用了3种报告基因, 由于增加了报告基因的种类, 使单个报告基因自激活出现假阳性的几率大大降低, 筛选结果的真阳性率可达95% [29-32]. 我们在真核表达载体pGBKT7中构建pGBKT7-HBcAg诱饵质粒并在酵母菌株AH109中表达了HBcAg基因, 与转化了人肝cDNA文库的酵母菌株Y187进行配合, 筛选出与之相互作用的蛋白基因16种, 其中4种为未知基因, 在GenBank中未发现同源序列. 根据GenBank的信息, 我们设计了新基因C-12的上下游引物, 并成功地从HepG2细胞的mRNA中逆转录出该基因的完整序列, 说明该基因也能在HepG2细胞中表达.由于C-12新基因序列的大小与HBcAg相差仅几十个碱基, 体外免疫共沉淀后电泳很难将二者分开, 因此我们只有将其连入另一酵母表达载体pGADT7, 转化入酵母菌株Y187, 并再次与表达了HBcAg的AH109配合, 通过回交实验进一步证实HBcAg与C-12新基因表达产物结合. 新基因的发现为我们研究HBcAg的功能提出了新线索, 对新基因功能的深入研究将对感染机制的了解及阻断提出新的思路, 对HBV感染的防治工作有着重要意义.