修回日期: 2002-09-20
接受日期: 2002-10-03
在线出版日期: 2003-06-15
研究蛋白激酶C(PKC)在肝细胞缺氧预处理中的作用.
建立体外肝细胞缺氧预处理模型, 应用PKC抑制剂白屈菜季铵碱(chelerythrine chloride, CHE)和激动剂豆蔻酸佛波酰乙酯(phorobol12-myristate13-acetate, PMA), 通过检测PKC磷酸化活性, 细胞存活率, 同时在透射电镜下观察肝细胞超微结构改变, 研究PKC的作用. 对相关数据进行统计学处理.
和缺氧复氧组的PKC磷酸化活性(710.5±78.8) fkat/g比较, 缺氧预处理组的PKC磷酸化活性(1823.7±268.2) fkat/g和PKC激动剂组的PKC磷酸化活性(2541.2±326.5) fkat/g显著增高(P<0.01), 肝细胞结构损伤改变较小; 和缺氧预处理组比较, PKC抑制剂组相应指标呈相反的变化, PKC磷酸化活性(1 088.0±89.3) fkat/g(P<0.01).
肝细胞缺氧预处理细胞保护作用中, PKC通路起到至关重要的作用.
引文著录: 单毓强, 高毅, 王瑜, 潘明新. 蛋白激酶C在肝细胞缺氧预处理中的作用. 世界华人消化杂志 2003; 11(6): 723-725
Revised: September 20, 2002
Accepted: October 3, 2002
Published online: June 15, 2003
To investigate the effects of protein kinase C (PKC) on hypoxic preconditioning (HP) for hepatocyte.
Through a normal liver cell HP model, PKC inhibitor and activator were utilized to analyze the phosphorylation of PKC. The cellular structure and viability were also observed. All the data were statistically analyzed.
Compared with the phosphorylation of PKC in the control without HP [(710.5±78.8) fkat/g], the phosphorylation of PKC was obviously increased in HP treated model [(1823.7±268.2) fkat/g] and PMA treated model [(2 541.2±326.5) fkat/g] (P<0.01). Cellular changes were less. In addition, opposite changes were found in PKC inhibited groups, and the phosphorylation of PKC was [(1 088.0±89.3) fkat/g] (P<0.01).
The activation of PKC is the important chain of HP in the preservation of liver cell, and its mechanism may be involved in protein phosphorylation.
- Citation: Shang YQ, Gao Y, Wang Y, Pan MX. Effect of protein kinase C during hepatocyte hypoxic precondition. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi 2003; 11(6): 723-725
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1009-3079/full/v11/i6/723.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.11569/wcjd.v11.i6.723
缺血预处理能够提高器官组织对缺血再灌注损伤的耐受能力[1-4], 缺血预处理对肝脏也有保护作用[5,6], 但保护机制的研究较少, 为研究PKC在缺氧预处理肝细胞保护效应中的作用, 以缺氧复氧损伤模型为研究对象, 应用PKC激动剂、抑制剂和等信号转导工具药, 观察其在缺氧预处理中的作用, 以期进一步探讨PKC在缺氧预处理在体内的作用机制.
正常人肝细胞株L02购自中国医学科学院上海细胞所. 厌氧培养箱(上海医疗器械厂), 50 ml/L CO2电热恒温培养箱(Harris公司); 白屈菜季铵碱(Calbiochem公司), 硝酸纤维素滤膜(PVDF膜): 宝灵曼公司, PKC活性测定试剂盒: Promega Corp, γ-32p: Amersham公司, PMA.
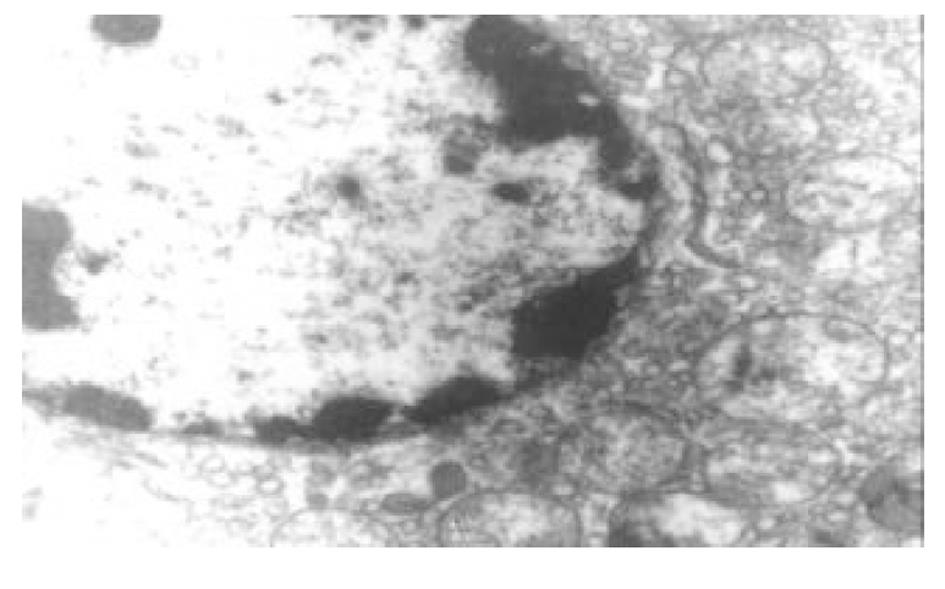
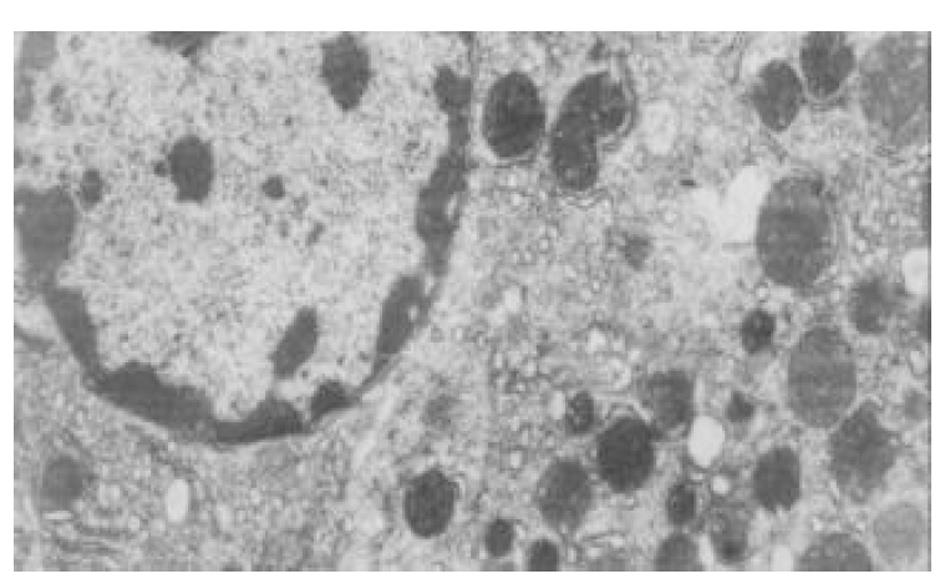
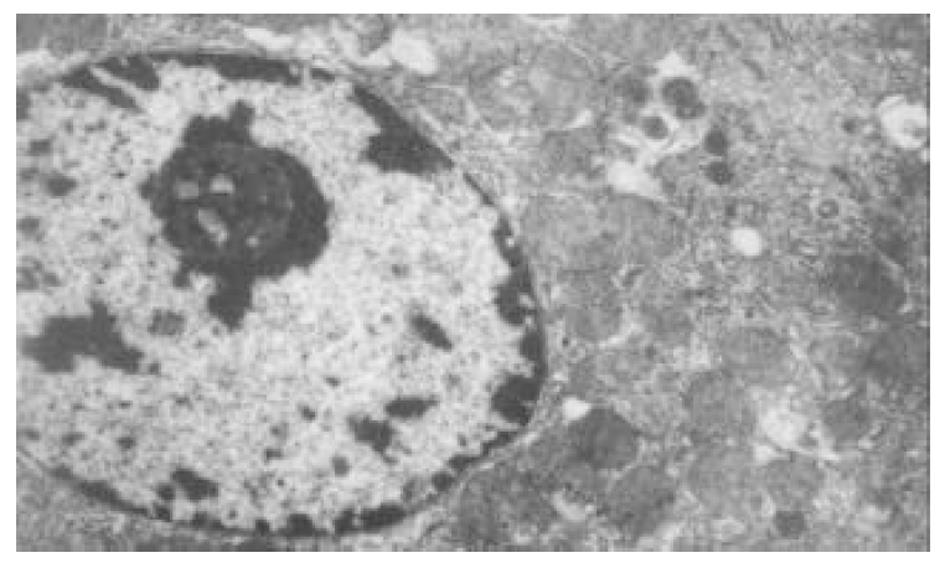
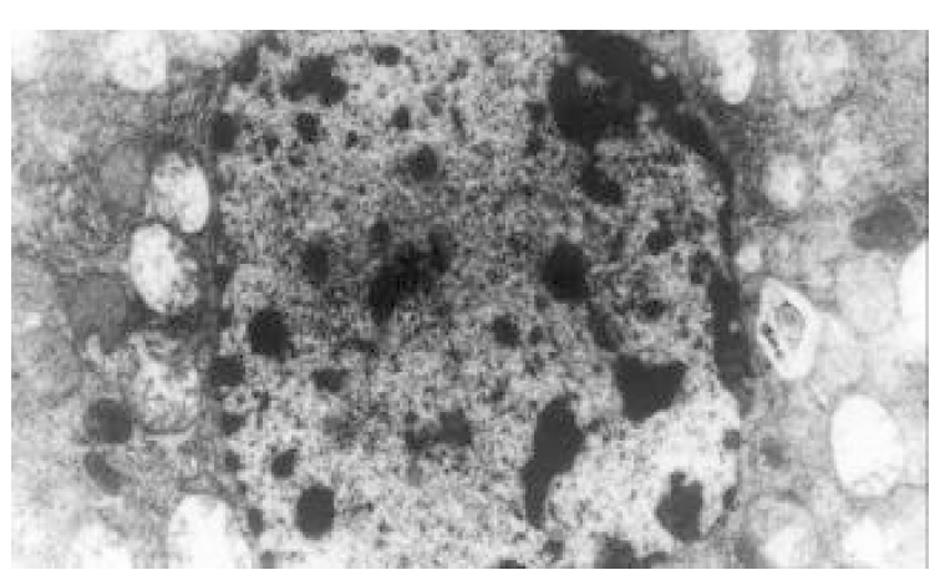
正常人肝L02细胞株接种贴壁于含100 ml/L灭活胎牛血清的RPMI1640培养液中, 培养箱内常规培养, 维持细胞处于对数生长期. 缺氧培养采用去氧和去血清培养: 混合气(0.90 N2+0.08 CO2+0.02 H2)平衡KHH[7]平衡盐溶液1 h, 测血气PO2≤4 kPa, 细胞培养液换成平衡KHH平衡盐溶液, 在厌氧培养箱(0.90 N2+0.08 CO2+0.02 H2)中培养, 最大限度模拟体内肝脏缺血状态; 复氧培养, 采用含血清培养基进行常规培养. 随机分组进行处理, 每组6个样本: (1)正常对照组(control, C), 常规孵育培养; (2)缺氧复氧组(hypoxia reoxygenation HR), 缺氧培养6 h, 复氧培养9 h; (3)缺氧预处理组(hypoxic precondition, HP), 缺氧培养5 min, 复氧培养5 min, 进行3个循环的缺氧复氧预处理, 随后处理同HR组; (4)HR+PMA组, PMA终浓度为150 nmol/L[8]加于培养液, 10 min后, 处理同HR组; (5)HP+白屈菜季铵碱(CHE)组; 加终浓度为50 nmol/L[9]的白屈菜季铵碱于培养液, 10 min以后, 处理同HP组. 使用四唑盐比色法(MTT)常规检测细胞存活率. 按以上各组描叙方法分组处理后, 含2 g/L DMOS 2.50 g/L胰酶消化成的单细胞悬液, 按PKC活性测定试剂盒(promega corp)检测操作步骤进行测定每组PKC活性. 按以上各组描叙方法分组处理后, 含2 g/L DMOS 2.50 g/L胰酶消化成的单细胞悬液, 收集细胞在透射电镜下观察组织超微结构.
统计学处理 各组数据用均数±标准差(n = 6, mean±SD), 应用S.A.S 6.12统计软件包对检测数据进行方差分析处理. P<0.05表示统计学上有显著性差异, P>0.05则为无差异.
在各组中, HR组细胞存活率(35.6±4.0%)最低, 和C组(95.0±10.8%)比较差异显著(P<0.01); 和HR组比较, HP组(81.5±12.1%)的显著升高(P<0.01); 和HP组比较, CHE(47.2±5.4%)组下降明显, 存在显著性差异(P<0.01); 和HR组比较, PMA组(75.3±11.9%)显著增高(P<0.01).
HR组PKC活性(710.5±78.8) fkat/g和C组(544.5±85.2) fkat/g比较无显著性差异(P<0.01). 和HR组比较, HP组PKC活性(1823.7±268.2) fkat/g显著升高(P<0.01); 和HP组比较, HP+CHE组PKC活性(1 088.0±89.3) fkat/g下降明显, 存在显著性差异(P<0.01); 和HR组比较, HR+PMA组PKC活性(2 541.2±326.5) fkat/g显著增高(P<0.01).
目前研究普遍认为缺血预处理的细胞保护机制为多种因素综合作用的结果. 缺血预处理信号转导方面的机制研究主要来自于心脏和脑的资料, 其研究结果推测保护效应细胞内信号转导途径是: 缺血预处理引起内源性触发物质释放, 如腺苷、去甲肾上腺素、活性氧、缓激肽、血管紧张素II、NO等[10-13], 作用于细胞膜上相应的受体[14-16], 使受体偶联的G蛋白[17]发生空间构象的改变, 细胞内信号转导开始启动, 激活磷脂酶, 水解膜磷脂产生二酰基甘油(diacylglyccerol, DAG)[18], 并和Ca2+协同作用于PKC, 使膜转位PKC激活[19], 从而导致一系列的信号通路开放[20-23], 大量研究证实, PKC的激活在缺血预处理信号转导中是非常重要的环节[24-26], 其中PKC-ε亚型发挥关键的传递者作用[27], 而在肝细胞预处理中, PKC的作用未见结论性报道, 肝细胞内信号转导是否和心脏相似尚不清楚[28-30]. 本实验通过建立体外人正常肝细胞缺氧预处理模型, 检测PKC磷酸化活性, 细胞存活率, 同时在透射电镜下观察肝细胞超微结构改变, 以及使用PKC抑制剂和激动剂来判定PKC在信号转导中的作用[5]. 实验表明缺氧预处理引起PKC磷酸化活性增强, 细胞存活率明显升高, 细胞电镜超微结构损伤改变减轻, 细胞器基本维持正常, 出现保护效应. 同时, 通过抑制PKC活性, 细胞器损伤明显, 增加细胞死亡, 预处理保护效应消失.然而, 不经预处理的作用, 直接用激动剂活化PKC, 同样能模拟出预处理类似的保护, 验证了PKC通路在其中的作用, 由此我们推测, 在预处理对人肝细胞的保护作用中, PKC通路激活和预处理导致细胞保护作用是密切相关的, PKC磷酸化激活是信号通路中不可缺少的重要环节.
然而, PKC的众多亚型对细胞的作用各不相同, PKC-ε是预处理中激活发挥作用的主要PKC亚型之一, 应用转基因方法特异激活PKC-ε就能诱导出预处理的保护作用, 本实验通过检测总的PKC活性, 得出PKC激活参与了细胞保护, 可能和某个亚型激活有关, 但是, 各亚型在信号转导过程中作用机制大相径庭, 那些具体亚型在其中的主导作用, 有待于进一步探讨.
| 1. | Murry CE, Jennings RB, Reimer KA. Preconditioning with ischemia: a delay of lethal cell injury in ischemic myocardium. Circulation. 1986;74:1124-1136. [DOI] |
| 2. | Tanhehco EJ, Yasojima K, McGeer PL, McGeer EG, Lucchesi BR. Preconditioning reduces myocardial complement gene expression in vivo. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2000;279:H1157-1165. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 3. | Baxter GF, Goma FM, Yellon DM. Involvement of protein kinase C in the delayed cytoprotection following sublethal ischaemia in rabbit myocardium. Br J Pharmacol. 1995;115:222-224. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 4. | Lei DX, Peng CH, Peng SY, Jiang XC, Wu YL, Shen HW. Safe upper limit of intermittent hepatic inflow occlusion for liver resection in cirrhotic rats. World J Gastroenterol. 2001;7:713-717. [DOI] |
| 5. | Ricciardi R, Meyers WC, Schaffer BK, Kim RD, Shah SA, Wheeler SM, Donohue SE, Sheth KR, Callery MP, Chari RS. Protein kinase C inhibition abrogates hepat ischemic preconditioning responses. J Surg Res. 2001;97:144-149. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 6. | Chen XH, Li ZZ, Bao MS. Ischemic preconditioning protects liver from ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Xin Xiaohuabingxue Zazhi. 1997;5:763-764. |
| 7. | Carini R, De Cesaris MG, Splendore R, Bagnati M, Albano E. Ischemic preconditioning reduces Na+ accumulation and cell killing in isolated rat hepatocytes exposed to hypoxia. Hepatology. 2000;31:166-172. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 8. | Zhao J, Renner O, Wightman L, Sugden PH, Stewart L, Miller AD, Latchman DS, Marber MS. The expression of constitutively active isotypes of protein kinase C to investigate preconditioning. The J Bio Chem. 1998;36:23072-23079. [DOI] |
| 9. | Marra F, Arrighi MC, Fazi M, Caligiuri A, Pinzani M, Romanelli RG, Efsen E, Laffi G, Gentilini P. Extracellual signal-regulated kinase activation differentially regulates platelet-derived growth factor actions in hepatic stellate cells, and is induced by in vivo liver injury in the rat. Hepatology. 1999;30:951-958. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 10. | Sun JZ, Tang XL, Knowlton AA, Park SW, Qiu Y, Bolli R. Late preconditioning against myocardial stunning: an endogenous protective mechanism that confers resistance to postischemic dysfunction 24 hours after brief ischemia in conscious pigs. J Clin Invest. 1995;95:388-403. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 11. | Dana A, Baxter GF, Walker JM, Yellon DM. Prolonging the delayed phase of myocardial protection: repetitive adenosine A1 receptor activation maintains rabbit myocardium in a preconditioned state. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1998;31:1142-1149. [DOI] |
| 12. | Tang XL, Takano H, Rizvi A, Turrens JF, Qiu Y, Wu WJ, Zhang Q, Bolli R. Oxidant species trigger late preconditioning against my ocardial stunning in conscious rabbits. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2002;282:H281-291. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 13. | Yamashita N, Hoshida S, Taniguchi N, Kuzuya T, Hori M. Whole-body hyperthermia provides biphasic cardioprotection against ischemia/reperfusion injury in the rat. Circulation. 1998;98:1414-1421. [DOI] |
| 14. | Matoba S, Tatsumi T, Keira N, Kawahara A, Akashi K, Kobara M, Asayama J, Nakagawa M. Cardioprotective effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition against hypoxia/ reoxygenation injury in cultured rat cardiac myocytes. Circulation. 1999;99:817-822. [DOI] |
| 15. | Parsons M, Young L, Lee JE, Jacobson KA, Liang BT. Distinct cardioprotective effects of adenosine mediated by differential coupling of receptor subtypes to phospholipases C and D. FASEB J. 2000;14:1423-1431. [DOI] |
| 16. | Liu GS, Thornton J, Van Winkle DM, Stanley AW, Olsson RA, Downey JM. Protection against infarction afforded by preconditioning is mediated by A1 adenosine receptors in rabbit heart. Circulation. 1991;84:350-356. [DOI] |
| 17. | Farfel Z, Bourne H, Iiri T. The expanding spectrum of G protein diseases. New Egl J Med. 1999;340:1012-1020. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 18. | Cohen MV, Liu Y, Liu GS, Wang P, Weinbrenner C, Cordis GA, Das DK, Downey JM. Phospholipase D plays a role in ischemic preconditioning in rabbit heart. Circulation. 1996;94:1713-1718. [DOI] |
| 19. | Lee HT, Emala CW. Protein kinase C and G(i/o) proteins are involved in adenosine and ischemic preconditioning-mediated renal protection. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2001;12:233-240. [PubMed] |
| 20. | Finkel T. Oxygen radicals and signaling. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1998;10:248-253. [DOI] |
| 21. | Iwai T, Tanonaka K, Koshimizu M, Takeo S. Preservation of mitochondrial function by diazoxide during sustained ischaemia in the rat heart. Br J Pharmacol. 2000;129:1219-1227. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 22. | Carroll R, Yellon DM. Myocardial adaptation to ischaemia-the preconditioning phenomenon. Int J Cardiol. 1999;68:S93-101. [DOI] |
| 23. | Yao Z, Tong J, Tan X, Li C, Shao Z, Kim WC, vanden Hoek TL, Becker LB, Head CA, Schumacker PT. Role of reactive oxygen species in acetylcholine-induced preconditioning in cardiomyocytes. Am J Physiol. 1999;277:H2504-H2509. [PubMed] |
| 24. | Carini R, De Cesaris MG, Splendore R, Vay D, Domenicotti C, Nitti MP, Paola D, Pronzato MA, Albano E. Signal pathway involved in the development of hypoxic preconditioning in rat hepatocytes. Hepatology. 2001;33:131-139. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 25. | Wu S, Li HY, Wong TM. Cardioprotection of preconditioning by metabolic inhibition in the rat ventricular myocyte involvement of kappa-opioid receptor. Circ Res. 1999;84:1388-1395. [DOI] |
| 26. | Inagaki K, Kihara Y, Hayashida W, Izumi T, Iwanaga Y, Yoneda T, Takeuchi Y, Suyama K, Muso E, Sasayama S. Anti-ischemic effect of a novel cardioprotective agent, JTV519, is mediated through specific activation of delta-isoform of protein kinase C in rat ventricular myocardium. Circulation. 2000;101:797-804. [DOI] |
| 27. | Ping P, Zhang J, Cao X, Li RC, Kong D, Tang XL, Qiu Y, Manchikalapudi S, Auchampach JA, Black RG. PKC-dependent activation of p44/p42 MAPKs during myocardial ischemica-reperfusion in conscious rabbits. Am J Physiol. 1999;276:1468-1481. |
| 28. | Peralta C, Hotter G, Closa D, Prats N, Xaus C, Gelpi E, Rosello-Catafau J. The protective role of adenosine in inducing nitric oxide synthesis in rat liver ischemia preconditioning is The mediated by activation of adenosine A2 receptors. Hepatology. 1999;29:126-132. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 29. | Peralta C, Closa D, Xaus C, Gelpi E, Rosello-Catafau J, Hotter G. Hepatic preconditioning in rats is defined by a balance of adenosine and xanthine. Hepatology. 1998;28:768-773. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 30. | Peralta C, Closa D, Hotter G, Gelpi E, Prats N, Rosello-Catafau J. Liver ischemic preconditioning is mediated by the inhibitory action of nitric oxide on endothelin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996;229:264-270. [DOI] |