修回日期: 2002-11-15
接受日期: 2002-12-01
在线出版日期: 2003-04-15
比较分析肿瘤热休克蛋白70(HSP70)与IL-2对小鼠肝癌移植模型的治疗作用, 评价HSP70的疗效, 为应用HSP70治疗人类恶性肿瘤提供有重要参考价值的实验依据.
细胞培养、蛋白质纯化技术、电泳技术、Western-blot法、动物实验等.
IL-2及HSP70对小鼠肝癌移植模型均有治疗作用, 其中IL-2 10万U、HSP70 10 μg效果最佳, IL-2 5万U及HSP70 5 μg有部分治疗作用, 10万U的IL-2与5 μg HSP70治疗效果相当, HSP70 10 μg 治疗后有40%小鼠移植肿瘤全部消退, 长期生存790 d, 与对照组及其他各组相比, 差异具有显著性(P<0.01, P<0.05).
HSP70具有良好的抗肿瘤免疫活性, 其疗效明显优于IL-2, 本研究对于应用HSP70治疗人类的恶性肿瘤有十分重要的借鉴意义.
引文著录: 傅庆国, 沈晓东, 孟凡东, 郭仁宣. 热休克蛋白70与IL-2对小鼠肝癌移植模型的治疗比较. 世界华人消化杂志 2003; 11(4): 415-418
Revised: November 15, 2002
Accepted: December 1, 2002
Published online: April 15, 2003
To compare and analyze the therapeutic effect of tumor-derived heat shock protein 70 and globally accepted interleukin-2, to evaluate the anti-tumor capacity of HSP70, and to provide significant information for HSP70 administration to treat human cancers.
Cell Culture, techniques for protein extraction and purification, SDS-PAGE, Western-blot and animal experiment were used in this study.
Both IL-2 and HSP70 showed therapeutic effect in tumor-bearing mice. The best effect was observed in 100 000 U IL-2 and 10 μg HSP70 administrations, and partial efficacy was found in 50000 U IL-2 and 5 μg HSP70 administrations. The effect of 100000 U IL-2 was nearly as good as that of 5 μg HSP70. About 40 % mice receiving HSP70 10 μg administration survived over 90 days, the average survival period of this group was over 56.8 days, whereas the control group was 17.3 days, IL-2 50 000 group, 26.3 days, IL-2 100 000 group, 36.6 days, and 5 μg HSP70 group, 27.7 days. Significant difference was found (P<0.05) when compared with the HSP70 10 μg group and control group.
HSP70 has a specific anti-tumor effect and obviously exceeded IL-2 .Those data provide significant information for the treatment of human cancers.
- Citation: Fu QG, Shen XD, Meng FD, Guo RX. Comparison of therapeutic efficacy between tumor-derived heat shock protein 70 and interleukine-2. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi 2003; 11(4): 415-418
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1009-3079/full/v11/i4/415.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.11569/wcjd.v11.i4.415
恶性肿瘤的免疫疗法已经成为继手术、放化疗之后的又一重要的肿瘤综合治疗手段[1-8], 随着特异性肿瘤抗原的发现和研究的发展, 研究应用肿瘤特异性抗原, 进行人类恶性肿瘤的治疗已成为一个重要的方向[9-18]. 国内外对肿瘤热休克蛋白70(Heat Shock Protein 70, HSP70)进行了深入的研究, 发现HSP70确有明显的特异性的抗肿瘤作用[19-22], 不但能够使健康小鼠获得100%的保护性作用, 而且能使荷瘤小鼠的肿瘤生长受到明显的抑制, 部分动物长期生存、肿瘤全部消退, 而IL-2经过多年的实验与临床研究证实[23-25], 其中治疗有效率在20 %左右, 为评价HSP70的治疗作用, 作者以近交系615系小鼠对HSP70及IL-2的治疗作用进行动物实验对照, 以此为HSP70的应用提供有实用意义的参考依据.
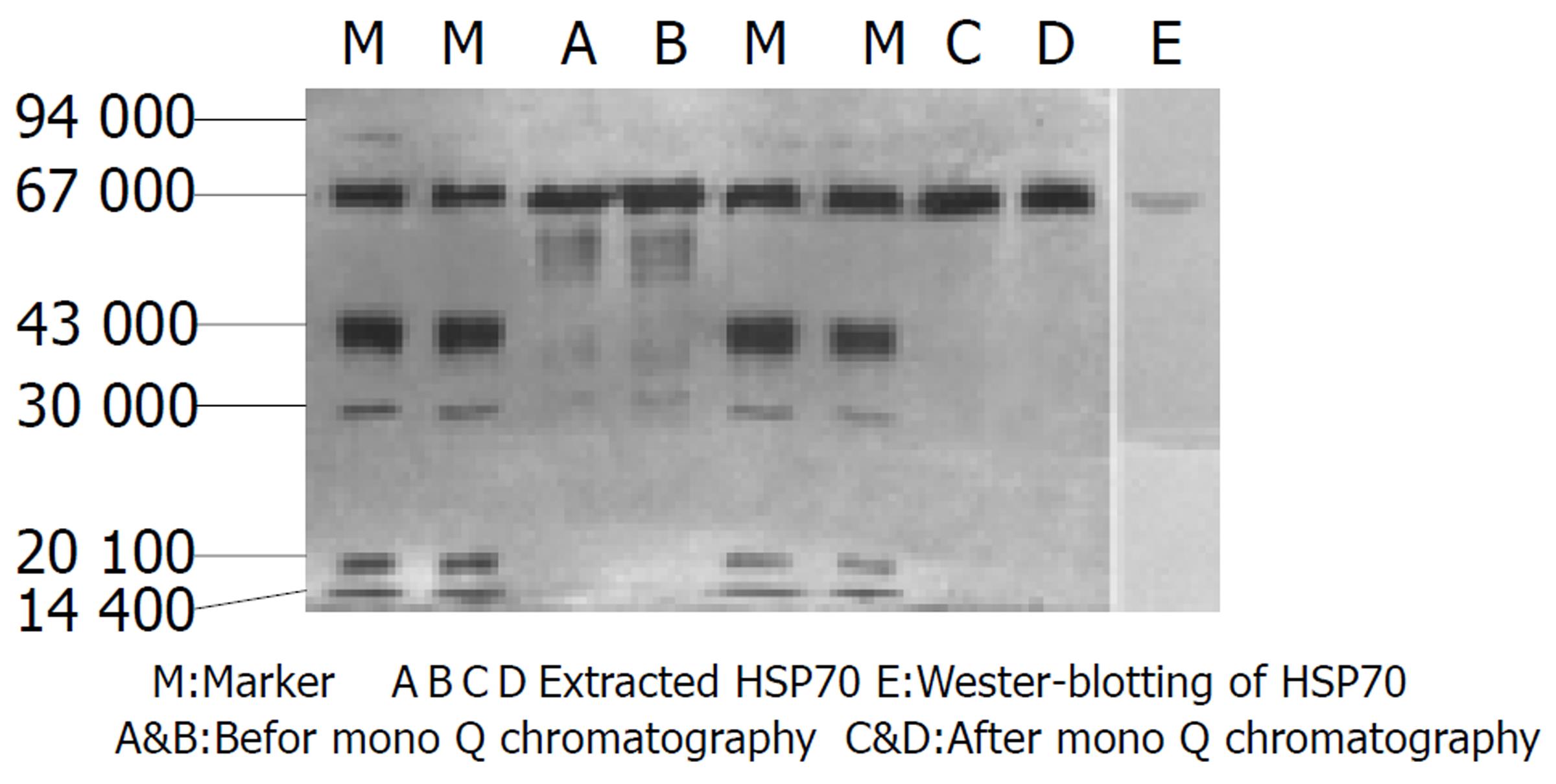
将5×109个HcaF细胞置于40 ml低渗缓冲液(30 mmol/L NaHCO3, 0.5 mmol/L苯甲基酰磺酰氟, pH7.2)中, 以超声粉碎机破碎, 4 ℃ 100000 g超速离心2 h, 取上清过 ConA-Sepharose柱, 收集未结合组分, 4 ℃缓冲液A (20 mmol/L Tris-HC1, 20 mmol/L NaC1, 15 mmol/L β-疏基乙醇, 3 mmol/L MgCl2, pH7.5)中透析过夜, 然后将样品加到 ADP-agarose柱上, 结合部分用含3 mmol/L ADP的缓冲液A进行洗脱, 将洗脱液加于 Mono Q柱, 用 FPLC系统进行分离, 200-500 mmol/L梯度NaC1洗脱, 分别收集各洗脱峰蛋白, 4 ℃缓冲液B(10 mmol/L Tris-HC1, pH7.5)中透析过夜. 将各色谱柱分离的样品及Mono Q柱的各洗脱峰样品在100 g/L SDS-PAGE上进行分子量及纯度测定, 银染色, 再转印至硝酸纤维素膜上, 以抗HSP70单抗为一抗, 碱性磷酸酶标记的羊抗小鼠IgG为二抗, 进行免疫印迹分析. 提取的HSP70以(动物实验)来鉴定其抗肿瘤活性.
动物分为对照组、 HSP70 5 μg组2个、HSP70 10 mg组2个, IL-2 5万U组2个、IL-2 10万U组2个, "IL-2化"组分别用于观察治疗作用. 治疗方法: 接种HcaF细胞1×106个/只, 7 d成瘤后, HSP70 : 第1个月1次/wk连4次; 第2个月10 d/次连3次; 以后15 d/次至实验结束. IL-2: 5万U、10万U1次/d, 连5 d皮下注射; 2 000U 1次/d, 连10 d皮下注射; 2 000U 2次/wk皮下注射, 至实验结束."IL-2化"组, 在对照组全部死亡后, 取5只健康小鼠先于1 wk连用IL-2 10万U/d, 连5 d, 作者称其为"IL-2化"(Interleukine-2 Preparation). 于第8天接种HcaF细胞1×106个/只, (同时)再取一组IL-2 10万U和HSP70 10 μg治疗组小鼠于不同于上次接种部位与IL-2化组同时再次接种HcaF细胞1×106个/只(活细胞率>96%), 同时停止治疗, 观察各组小鼠的肿瘤生长情况.
经过二次亲合层析和Mono Q柱的分离后, 得到纯度较高的分子质量约为70 kD的蛋白质, 经免疫印记分析证实该蛋白质即为HSP70(图1). 经毛细管电泳分析纯度达100 %.
IL-2与HSP70对小鼠肿瘤均有较明显的抑制作用, 应用免疫治疗后, 小鼠的生存期均有延长, 与对照组相比差异显著(P<0.01或0.05). 但HSP70较IL-2具有更显著的治疗作用, IL-2治疗组无一长期生存, 而HSP70 10 μg 组有40%的小鼠经治疗后获长期生存790 d, 其肿瘤最终全部消退(表1)(图2).
| 分组 | 肿瘤大小(cm) | 肿瘤质量(g) | 腹水量(g) | 腹水出现率(%) | 生存天数(d) | 长期生存率(%) |
| 对照组 | 1.92±0.43 | 3.89±1.57 | 10.8±2.3 | 100 | 17.3±5.6 | - |
| I5组1 | 1.86±1.78 | 3.74±0.93 | 6.4±4.8 | 60 | 26.3±3.1 | - |
| I10组1 | 1.93±2.18 | 3.69±0.47 | 1.0±2.0 | 20 | 36.6±4.8 | - |
| H5组1 | 1.63±0.34 | 3.54±0.64 | 3.0±0.8 | 40 | 27.7±5.6 | - |
| H10组1 | 0.36±0.11 | 0.56±0.15 | - | - | >56.8±32.4 | 40 |
为明确HSP70与IL-2治疗作用的不同, 我们设一IL-2化组, 对比观察再接种后肿瘤的再发率及对生存期、生存率的影响(表2). IL-2 10万U治疗后及预先应用IL-2均不能抑制肿瘤的发展, 而应用HSP70 10 mg后无一小鼠出现肿瘤, "IL-2化"组的生存期与对照组无差异显著性(P>0.25), 肿瘤大小及肿瘤重量之间亦无显著性差异(P>0.25), 但应用IL-2治疗后未出现腹水(图3).
| 分组 | 肿瘤大小(cm) | 肿瘤质量(g) | 腹水量(g) | 生存天数(d) | 腹水出现率(%) | 长期生存率(%) |
| 对照组 | 192±0.43 | 3.89±1.57 | 10.8±2.3 | 17.3±5.6 | 100 | - |
| IL-2治 | 1.96±0.38 | 3.62±0.88 | - | 29.1±8.7 | - | - |
| 疗组2(n =4) | ||||||
| "IL-2化"组 | 1.95±0.64 | 3.31±0.86 | 1.0±2.0 | 18.2±3.7 | 20 | - |
| H10治疗组2 | - | - | - | >58.7±28.9 | - | 40 |
HSP70在很多恶性肿瘤组织中均有较高的表达, 实验研究证明肿瘤组织来源的HSP70是一种肿瘤特异性抗原, 诱导体内CD8+T淋巴细胞成为肿瘤特异性的CTL并使Th1型细胞因子升高[28], 具有特异的抗肿瘤作用[29-34], HSP70具有良好的应用前景, 研究其治疗作用, 评价其疗效有重要的实用意义. IL-2是由活化的T淋巴细胞产生的具有调节免疫功能和抗肿瘤作用的重要的细胞因子, 已证明其对肿瘤的有效率为20 %左右, IL-2通过增强LAK、NK、TIL等促进其他细胞因子的表达等作用, 调节机体的免疫功能, 发挥抗肿瘤免疫效应[35-40].
本研究证实, IL-2及HSP70均具有抑制肿瘤的作用, 通过比较分析, 表明应用10万UIL-2与HSP70 5 mg的治疗作用相当, 而应用10 mg HSP70显示了显著的治疗及抑瘤作用, 该组小鼠不但肿瘤显著缩小, 而且40%获长期生存, 肿瘤完全消退, 充分证明HSP70的抗肿瘤作用明显优于IL-2.
为进一步研究HSP70与IL-2在治疗作用上的差异, 作者进行了再接种实验, 结果表明, 应用IL-2治疗后或预先应用IL-2都不能有效地抑制肿瘤的进展, 提示IL-2的应用要足量、连续, 而停用IL-2后抗肿瘤免疫功能亦减弱, IL-2不能使机体维持长期的、主动的抗肿瘤免疫效应, 这正是由于IL-2不具特异性抗肿瘤作用的表现. 但应用HSP70治疗后再接种HcaF细胞, 无一小鼠再发生肿瘤, 且生存率及生存期限未受到影响, 证明HSP70能够诱导机体产生特异性的抗肿瘤免疫效应, 这种效应在治疗停止后可在相对较长时间内维持, 有助于延缓肿瘤的复发, 更加证明HSP70具有IL-2不可比拟的优越性.我们以IL-2作为已为大多学者所认可的治疗作用为参照, 研究了HSP70的治疗作用, 结果显示, HSP70较IL-2具有显著的抑瘤和治疗作用, 更主要的是HSP70诱导的抗肿瘤免疫在停止治疗后仍可在较长时间内维持, 这对防止肿瘤复发、延缓肿瘤进展, 有重要意义, 本研究对于研究以HSP70治疗人类的恶性肿瘤有重要的参考价值.
| 1. | Fu QG, Meng FD, Shen XD, Guo RX. Efficacy of intraperitoneal thermochemotherapy and immunotherapy in intraperitoneal recurrence after gastrointestinal cancer resection. World J Gastroenterol. 2002;8:1019-1022. [DOI] |
| 2. | Huang J, Cai MY, Wei DP. HLA class I expression in primary hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2002;8:654-657. [DOI] |
| 3. | Jin J, Yang JY, Liu J, Kong YY, Wang Y, Li GD. DNA immunization with fusion genes encoding different regions of hepatitis C virus E2 fused to the gene for hepatitis B surface antigen elicits immune responses to both HCV and HBV. World J Gastroenterol. 2002;8:505-510. [DOI] |
| 4. | Wang FS, Liu MX, Zhang B, Shi M, Lei ZY, Sun WB, Du QY, Chen JM. Antitumor activities of human autologous cytokine induced killer (CIK) cells against hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo. World J Gastroenterol. 2002;8:464-468. [DOI] |
| 5. | Zhang J, Zhang JK, Zhuo SH, Chen HB. Effect of a cancer vaccine prepared by fusions of hepatocarcinoma cells with dendritic cells. World J Gastroenterol. 2001;7:690-694. [DOI] |
| 6. | Lu RR, Shou NH, Jiang XH. Study on the colorectal lymphatic metastasis related tumor cell proliferation activity and cytokone levels. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi. 2001;9:455-456. |
| 7. | Luo ZB, Luo YH, Lu R, Jin HY, Zhang PB, Xu CP. Immunohistochemical study on in gastric dendritic mucosa of patients with gastric and cancer precancerous lesions. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi. 2000;8:400-402. |
| 8. | Qian SB, Chen SS. Transduction of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells with human alpha-interferon gene via retroviral vector. World J Gastroenterol. 1998;4:210-213. [DOI] |
| 9. | Ren JM, Zou QM, Wang FK, He Q, Chen W, Zen WK. PELA microspheres loaded H. pylori lysates and their mucosal immune response. World J Gastroenterol. 2002;8:1098-1102. [DOI] |
| 10. | Guo DL, Dong M, Wang L, Sun LP, Yuan Y. Expression of gastric cancer-associated MG7 antigen in gastric cancer, precancerous lesions and H. pylori -associated gastric diseases. World J Gastroenterol. 2002;8:1009-1013. [DOI] |
| 11. | Zhong YW, Cheng J, Wang G, Shi SS, Li L, Zhang LX, Chen JM. Preparation of human single chain Fv antibody against hepatitis C virus E2 protein and its identification in immunohistochemistry. World J Gastroenterol. 2002;8:863-867. [DOI] |
| 12. | Liu LX, Jiang HC, Liu ZH, Zhou J, Zhang WH, Zhu AL, Wang XQ, Wu M. Integrin gene expression profiles of human hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2002;8:631-637. [DOI] |
| 13. | Liu LX, Liu ZH, Jiang HC, Qu X, Zhang WH, Wu LF, Zhu AL, Wang XQ, Wu M. Profiling of differentially expressed genes in human gastric carcinoma by cDNA expression array. World J Gastroenterol. 2002;8:580-585. [DOI] |
| 14. | Woitas RP, Petersen U, Moshage D, Brackmann HH, Matz B, Sauerbruch T, Spengler U. HCV-specific cytokine induction in monocytes of patients with different outcomes of hepatitis C. World J Gastroenterol. 2002;8:562-566. [DOI] |
| 15. | Guan XJ, Guan XJ, Wu YZ, Jia ZC, Shi TD, Tang Y. Construction and characterization of an experimental ISCOMS-based hepatitis B polypeptide vaccine. World J Gastroenterol. 2002;8:294-297. [DOI] |
| 16. | Shen LZ, Wu WX, Xu DH, Zheng ZC, Liu XY, Ding Q, Hua YB, Yao K. Specific CEA-producing colorectal carcinoma cell killing with recombinant adenoviral vector containing cytosine deaminase gene. World J Gastroenterol. 2002;8:270-275. [DOI] |
| 17. | Ji WS, Hu JL, Qiu JW, Pan BR, Peng DR, Shi BL, Zhou SJ, Wu KC, Fan DM. Relationship between genotype and phenotype of flagellin C in Salmonella. World J Gastroenterol. 2001;7:864-867. [DOI] |
| 18. | Schrayer DP, Kouttab N, Hearing VJ, Wanebo HJ. Synergistic effect of interleukin-2 and a vaccine of irradiated melanoma cells transfected to secrete staphylococcal enterotoxin A. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2002;19:43-53. |
| 19. | Li MS, Yuan AL, Zhang WD, Liu SD, Lu AM, Zhou DY. Dendritic cells in vitro induce efficient and specific anti-tumor immune response. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi. 1999;7:161-163. |
| 20. | Chen HB, Zhang JK, Huang ZL, Sun JL, Zhou YQ. Effect of cytokines on dendritic cells against human hepatoma cell line. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi. 1999;7:191-193. |
| 21. | Wei CY, Li T, Zhang CM, Yang NW, Tan YC. Treating primary liver cancer with S-TIL combining Chinese traditional medicine. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi. 2000;8:478. |
| 22. | Du QY, Wang FS, Xu DP, Liu H, Lei ZY, Liu MX, Wang YD, Chen JM, Wu ZZ. Cytotoxic effects of CIK against hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi. 2000;8:863-866. |
| 23. | Zheng N, Ye SL, Sun RX, Zhao Y, Tang ZY. Effects of cryopreserva-tion and phenylacetate on biological characters of adherent LAK cells from patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2002;8:233-236. [DOI] |
| 24. | Indaram AV, Nandi S, Weissman S, Lam S, Bailey B, Blumstein M, Greenberg R, Bank S. Elevated basal intestinal mucosal cytokine levels in asymptomatic first-degree relatives of patients with Crohn's disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2000;6:49-52. [DOI] |
| 25. | Zeis M, Zunkel T, Steinmann J, Schmitz N, Uharek L. Enhanced antitumoral effectiveness of idiotype vaccination induced by the administration of Flt3 ligand combined with interleukin 2 against a murine myeloma. Br J Haematol. 2002;117:93-102. [DOI] |
| 27. | Rosenberg SA, Mule JJ, Spiess PJ. Regression of established pulmonary metastases and subcutaneous tumor mediated by the systemic administration of high-dose recombinant interleukin 2. J Exp Med. 1985;5:1165-1188. [DOI] |
| 28. | 傅 庆国, 孟 凡东, 郭 仁宣. 热休克蛋白70诱导抗肿瘤免疫的机制研究. 细胞与分子免疫学杂志. 2002;4:393-394. |
| 29. | Robert J, Gantress J, Rau L, Bell A, Cohen N. Minor histocompatibility antigen-specific MHC-restricted CD8 T cell responses elicited by heat shock proteins. J Immunol. 2002;168:1697-1703. [DOI] |
| 30. | Manjili MH, Wang XY, Park J, Facciponte JG, Repasky EA, Subjeck JR. Immunotherapy of cancer using heat shock proteins. J Front Biosci. 2002;7:43-52. [DOI] |
| 31. | Schueller G, Paolini P, Friedl J, Stift A, Dubsky P, Bachleitner-Hofmann T, Jakesz R, Gnant M. Heat treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma cells: increased levels of heat shock proteins 70 and 90 correlate with cellular necrosis. Anticancer Res. 2001;21:295-300. |
| 32. | Multhoff G, Pfister K, Botzler C, Jordan A, Scholz R, Schmetzer H, Burgstahler R, Hiddemann W. Adoptive transfer of human natural killer cells in mice with severe combined immunodeficiency inhibits growth of Hsp70-expressing tumors. Int J Cancer. 2000;88:791-797. [DOI] |
| 33. | Vanaja DK, Grossmann ME, Celis E, Young CY. Tumor prevention and antitumor immunity with heat shock protein 70 induced by 15-deoxy-delta12, 14-prostaglandin J2 in transgenic adenocarcinoma of mouse prostate cells. Cancer Res. 2000;60:4714-4718. |
| 34. | Oamoto M, Tazawa K, Kawagoshi T, Maeda M, Honda T, Sakamoto T, Tsukada K. The combined effect against colon-26 cells of heat treatment and immunization with heat treated colon-26 tumour cell extract. Int J Hyperthermia. 2000;16:263-273. [DOI] |
| 35. | Liu XJ, Wang BM. Biotherapy to esophageal cancer. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi. 2000;8:1027-1029. |
| 36. | Liu JD, Chai YH. Randomized contrasted trial of the therapeutic effect of 5-FU+LV combining IFN/IL-2 to developed pancreatic cancer. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi. 2000;8:828. |
| 37. | Dietz AB, Litzow MR, Bulur PA, Vuk-Pavlovic S. Transgenic interleukin 2 secreted by CML dendritic cells stimulates autologous TH1 T cells. S Cytotherapy. 2001;3:97-105. [DOI] |
| 38. | Budagian V, Nanni P, Lollini PL, Musiani P, Di Carlo E, Bulanova E, Paus R, Bulfone-Paus S. Enhanced inhibition of tumour growth and metastasis, and induction of antitumour immunity by IL-2-IgG2b fusion protein. Scand J Immunol. 2002;55:484-492. [DOI] |
| 39. | Ewan PW. New insight into immunological mechanisms of venom immunotherapy. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001;1:367-374. [DOI] |
| 40. | Liu Z, Smyth FE, Renner C, Lee FT, Oosterwijk E, Scott AM. Anti-renal cell carcinoma chimeric antibody G250: cytokine enhancement of in vitro antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2002;51:171-177. [DOI] |