Published online Aug 15, 1999. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v5.i4.362
Revised: March 3, 1999
Accepted: April 19, 1999
Published online: August 15, 1999
- Citation: Huang ZS, Wang ZW, Huang ZY, Zhong SQ, Li QM, Xu Q. Hujin Pill′s antisteatosis of rat liver: evaluation of histopathology and ultrastructure. World J Gastroenterol 1999; 5(4): 362-364
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v5/i4/362.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v5.i4.362
Hujin Pill, is composed of rhizoma polygoni cuspidati, radix curcumae, rhizoma alismatis, radix notoginseng, fructus czataegi and ganoderma lucidum, and has the actions of soothing the liver, removing the blood stasis, promoting the blood circulation and lowering the blood fat[1]. Our clinical practice have revealed that it has a marked effect in treating fatty liver[1]. Our phamacodynamic study also indicated that Hujin Pill could evidently improve the experimental rat fatty liver and markedly decrease the concentration of cholesterol, triglyceride and malondialdehyde in serum and liver, it al so could reduce the plasma medium molecular level[2]. In order to further testify these effects and investigate its mechanism, the effects of Hujin Pill on the histomorphology of rat fatty liver were observed.
SD rats, female, 200 g ± 18.5 g, were supplied by the Experimental Animal Center of Guangzhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine. According to their body weight, the 50 experimental rats were divided randomly into control group A, pathology group B, tabellae jiaogulanosidi treatment group C, low dose Hujin Pill group D (5 g/kg body weight) and high dose Hujin Pill group E(4 g/kg body weight).
Chojkier′s method was slightly modified[3]. This high fat diet was composed of 79.5% standard diet, 20% lard, 0.4% cholesterol and 0.1% bile salt. The control group was fed with standard diet and others with high fat diet.
According to the ratio of the formula, the herbs were decocted and filtered for three times, then merged and condensed to a concentration of 1 g/mL. Before use, it was diluted to 0.5 g/mL or concentrated to 1.4 g/mL. Tabellae jiaogulanosidi (No. 960738), provided by Shaanxi Ankang Chinese Pharmaceutical Factory, was administered at a dose of 0.5 g/kg body weight (BW).
The animals were given 30% ethnol at a dose of 1.0 mL/100 g BW per day except the control group, 40% CCl4 vegetable oil solution was given to posteri or limb by subcutaneous injection of each rat on the 1st, 5th, 10th and 15th day. On the first day, the dose was 0.5 mL/100 g BW, and was 0.3 mL/100 g BW on the other three days. The rats were treated with different drugs at a dose of 1 mL/100 g BW each day 2 h before sethnol was given. At the same time, the control group was given (i.g, s.c) the same do se of physiological saline solution.
The rats were killed after 15 d of treatment and their livers were taken out and weighed. The left liver lobe was cut into 4-5 mm3 masse s and fixed in 200 mL/L formaldehyde solution, the paraffin masses were embedded routinely, HE stained, frozen and sectioned. The samples were stained with Sudan III and observed under light microscope. On the other hand, the central part of another liver lobe was cut into 1 mm3 masses and fixed in 25 mL/L glutaraldehyde and 10 mL/L OsO4. After they were rinse d and dehydrated step by step, osmosis and embedding were conducted. The Al tracut E microtome was used to cut these liver masses into sections, which were stained in uranium acetate and lead citrate and observed under JEM-1200EX electron microscope.
The livers of control group had no abnormal manifestation. However, the pathological model of livers changed evidently. It could be seen that both their volume and weight increased remarkably (Table 1), their capsules were tense, their edges were obtuse, their sections were greasy and milk-yellow. These were the typical features of hepatocyte steatosis. On the other hand, different doses of Hujin Pill and tabelae jiaogulanosidi could markedly improve the color, quality, volume and weight of rat livers.
No abnormal change was found in the livers of control rats, but diffuse steatosis was found in the pathological model of rat livers and some severe cases became involved with inflammatory infiltration, fat necrosis and fibrosis. These fatty hepatocytes were mainly located in the peripheral zone and middle zone of hepatic lobules. They extremely swelled and were round in shape. Their volume was 2 to 3 times larger than normal one. A large amount of little fat vacuoles, which are very like foam cells, were found in cytoplasm and some of them became bullous or locally necrosed. The degree of liver steatosis was significantly alleviated with the number of fat drops decreased and the volume of livers reduced. Other changes such as inflammatory infiltration and fat necrosis were also largely decreased with almost no proliferation of fibrous tissue.
According to the range and extent of pathological changes in liver and hepatic lobules, liver steatosis could be divided into five grades. Meanwhile, by using rank test, a statistical analysis was made for the number of rat liver steatosis in each group. The results showed that, compared with control group, significant difference was found in the degree of steatosis in the other four groups. The rate of steatosis was 100%, the serious steatosis rate was 80% in group B, while it was much lower in groups C, D and E. Administration of Hujin Pill at a dose of 5 g/kg had the best effect, and no significant difference was found between the two groups. These results suggested that there was no dose-effect relationship for Hujin Pill (Table 2).
| Group | The degree of liver steatosis | Number of liver steatosis | Rate of liver steatosis | ||||
| - | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ | |||
| A | 9 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 10 |
| B | 0 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 10 | 100 |
| C | 4 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 6 | 60 |
| D | 5 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 5 | 50 |
| D | 4 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 6 | 60 |
The volume of normal rat hepatocytes was relatively great. These hepatocytes were closely arranged with some desmosomes near the cholangiole. Most of these cells were circular or oval in shape and had monokayons with reticular or angular 1-3 nucleoli. There was abundant roughly surfaced endoplasmic reticulum in cytoplasm that was usually distributed near the mitochondrion. However, there was only a small number of smoothly surfaced endoplasmic reticula and ample mitchondri a in the cytoplasm, most of which had clear cristae. Meanwhile, a small part of them had high electron densities and indistinct cristae. Occasionally, in cytoplasm, there were a few round or elliptic fat drops which were irregular in tint and their diameter was less than 1 μm.
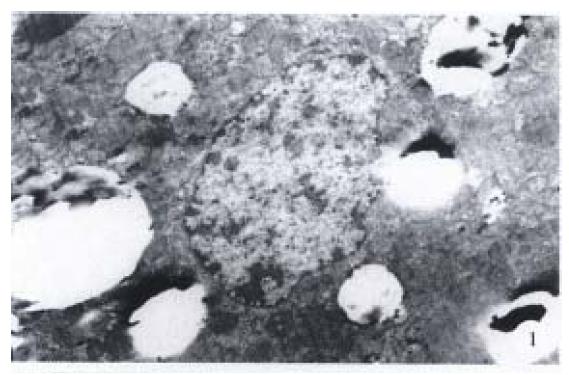
In pathological group, obvious ultrastructure change of hepatocytes was found (Figure 1). A lot of fat drops were densely accumulated in cytoplasm. Most of them were circular in shape and the diameter of some single fat drops could reach 4 μm. The roughly surfaced endoplasm was broken, degranulated and dilated into vesicular with distortion, concentration, desalination, swellin g and adventitia destruction around mitochodria. Mitochondrial crista was unclear and accompanied by more lysosomes. The nuclei were crushed by lots of fat drops and became distorted and shrunken. The diameter of nucleus was decreased obviously and perinuclea r space was large. The sinusoidal endothelial cells obviously swelled with the sinusoid and Diss space became wide, and microvilli were found in some of them. Fat-storing cell and Kupffer cell were obviously hyperplastic. The perinuclea r space of Kupffer cell near the sinusoid was obviously broadened. Masses could be found occasionally in the space.
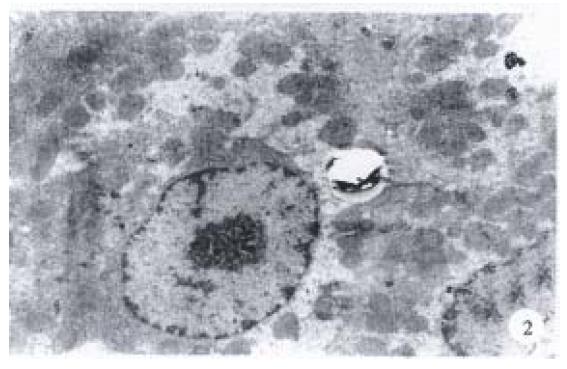
The structure of hepatocytes of rats administered with 5 g/kg BW (Figure 2), 14 g/kg BW Hujin Pill or tabelle jiaogulanosidi, was markedly improve d. The best effect was achieved in those that administered Hujin Pill at the dos e of 5 g/kg BW and the cell ultrastructure almost returned to normal. It also could be observed that the fat drops in cytoplasm were largely lessened with insignificantly dilated endoplasm and enlarged mitochodria. The deletion o f mitochodria crista was mild and most of the nuclei were regular in shape. The perinuclear space became normal and some of them were slightly shrunken and the chromatin was evenly distributed. Now and then, some fat-storing cells could b e found.
Generally, it was considered that CCl4 in hepatocytes could be activated by liver microsome cytochrome P450 and turned into CCl3 which could induce microsome lipid peroxide and cause liver steatosis. In this research, we duplicated rat models of fatty liver with comprehensive pathologic factors. The results confirmed that this method not only is reliable and consistent with that reported in literature[4], but also need shorter time than other methods. On the other hand, the effect of Hujin Pill on steatosis hepatocytes also suggested that this drug could be used in treating fatty liver. Our conclusion was coincided with that of pharmacodynamic study. It provides a further basis for the treatment of fatty liver with Hujin Pill.
The pathogenesis of fatty liver is so far unclear. Some researchers hold that the phospholipid of hepatocyte membrane is involved in its formation. Lu et al[5] showed that the relative percentage of phosphatidyl choline and sphingomyelin in total phospholipid would change when liver was damaged by CCl4. From this point of view, we believe that improvement of steatos hepatocytes by Hujin Pill can be achieved by means of protecting membrane structure and cell organ stabilizing the content of phospholipid. Its exact mechanism needs to be further studied.
Professor Zhao-Sheng Huang, male, born on 1953-09-02 in Jieyang City, Guangdong Province, and graduated from Guangzhou University of TCM as a postgraduate in 1984, master of Chinese Herbal Drugs, now head of the College of Chinese Herbal Drugs, Guangzhou University of TCM, having more than 30 papers and 10 books published.
Edited by WANG Xian-Lin
| 1. | Huang ZS, Xu ZH, Zhong SQ, Xiao XH. Clinic observation of Hujin Pill in treating fatty liver. Shiyong Zhongxiyi Jiehe Zazhi. 1997;10:21-28. |
| 2. | Huang ZS, Wang ZW, Liu MP, Zhou L. Pharmacodynamic study on Hujin Pill in treating fatty liver. Zhongcheng Yao. 1998;20:27-28. |
| 3. | Chojkier M, Lyche KD, Filip M. Increased production of collagen in vivo by hepatocytes and nonparenchymal cells in rats with carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic fibrosis. Hepatology. 1988;8:808-814. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 53] [Cited by in RCA: 53] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Huang ZP, Liang KH, Wang HJ, Ruan YB. Influence of radix angelica sinesis on liver ultrastructure in the rat with chronic CCl4-induced liver injury. Zhongxiyi Jiehe Ganbing Zazhi. 1996;6:16-17. |
| 5. | Lu LG, Wang ZM, Zhang YX, Zhu QS, You YZ. A study on mechanism of liver lesion induced by carbon tetrachloride in rats. Zhongxiyi Jiehe Ganbing Zazhi. 1996;6:24-25. |