Published online Jun 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i22.2923
Revised: April 30, 2024
Accepted: May 20, 2024
Published online: June 14, 2024
Processing time: 84 Days and 22 Hours
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, showed a wide spectrum of intestinal and extra-intestinal manifestations, which rendered the patients physically inactive and impaired their quality of life. It has been found that physical activity is a non-pharmacological intervention that improves the quality of life for those patients. Irisin is one member of the myo
Core Tip: Irisin is a sports hormone secreted with muscle contraction and serves as an anti-inflammatory biomarker as well as attenuating the intestinal microbiota diversity. Low serum levels of irisin were observed in patients with ulcerative colitis, which can be increased with physical activity. Physical activity is useful in patients presented with extra-intestinal manifestations of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Exogenous irisin may overcome the barriers of physical activity in IBD, producing beneficial anti-inflammatory effects and attenuating the microbiota diversity.
- Citation: Al-Nimer MS. Interaction between inflammatory bowel disease, physical activity, and myokines: Assessment of serum irisin levels. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(22): 2923-2926
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i22/2923.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i22.2923
I read with great interest an elegant editorial by Stafie et al[1] who commented on the article published in an issue of the World Journal of Gastroenterology[2]. Stafie et al[1], made a good comment, and they highlighted certain aspects of the barriers to physical activity (PA) in the relapse of inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD). Recent studies showed that PA can be assessed in laboratories by measuring specific markers named myokines. Therefore, it will be useful to fill the gap on the role of PA in IBD by supplementing the commentary with changes in the myokine levels in IBD patients who were doing any PA.
IBD are emerging as a significant global health concern as their incidence continues to rise on a global scale, with detrimental impacts on quality of life[2]. One of the extra-intestinal manifestations of the IBD is musculoskeletal manifestations that occurred as peripheral arthritis, axial spondyloarthritis (ax-SpA), and enthesitis[3]. It has been found that PA significantly and positively impacts the ax-SpA, improving the quality of life[4]. Therefore, PA is a useful non-pharmacological intervention that combats the SpA in IBD, and it is worth trying to look for a biological marker that indicates the benefit of PA in IBD presented with SpA as a comorbidity of extra-intestinal manifestations (EIMs)[3]. It is possible to use the levels of myokines, notably the serum levels of irisin, as a marker for the training or limitation of PA in patients with IBD. Irisin is a member of the myokines derived from the FNDC5 protein, which is produced by myocytes and secreted into the circulation in response to muscle contraction[5]. It is important to know that the irisin levels increased following the exercise, but they did not maintain their higher levels for the long period that followed the exercise[6].
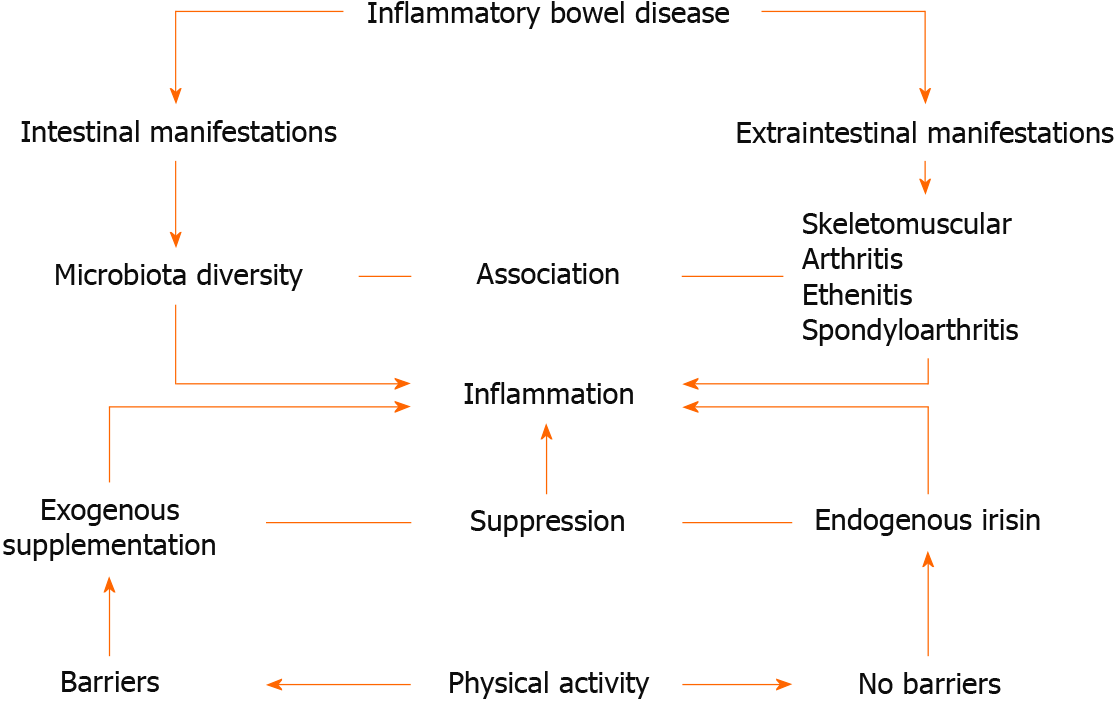
Figure 1 shows the beneficial interactions between the IBD and their EIMs with the production of irisin by PA or using exogenous irisin. Lower serum levels of irisin were significantly observed in patients with ax-SpA presented with sacroilitis and negative HLA-B27 status and who were treated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs[7]. Exercises trigger the production of irisin, which is sometimes called sport hormone, and play a role in decreasing the inflammation associated with the risk factors of systematic diseases, e.g., non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[8], obesity[9], heart diseases[10,11], etc.
In an experimental animal model of 2,4,6-trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid colitits fed a high-fat diet, exercised mice showed significantly higher levels of irisin, which is associated with decreased histological changes of the intestinal mucosa, increased colonic blood flow, and attenuation of the plasma levels of inflammatory markers compared with sedentary mice[12]. In an experimental animal model of ulcerative colitis, it has been found that exogenous irisin modulates the intestinal microbiota (by altering the diversity of microorganisms in the stool) and suppresses inflammation in the intestinal mucosa, indicating that irisin has anti-inflammatory properties[13]. It has been suggested that the anti-inflammatory effects of irisin are related to the inhibition of cytotoxicity and apoptosis via inhibiting the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway[14]. The sports activity is a barrier for patients with active Crohn’s disease (intestinal manifestations) because it flares up the symptoms[15]. Some authors believe that the barriers to sports medicine are related to psychosocial factors and alterations in the physiological responses to exercise, characterized by a lower sympathetic tone and body temperature[16]. In the scoping review, which included 28 articles, the authors recommended that moderately intense PA is a useful non-pharmacological intervention to improve the quality of life and attenuate the activity of Crohn’s disease[17]. Another scoping review highlighted an important issue about the accuracy of the assessment of the health-related physical fitness status of patients with Crohn’s disease due to some limitations in the intensity and type of PA[18]. There is no evidence for using exogenous irisin as an anti-inflammatory medicine in patients with Crohn’s disease; therefore, exogenous irisin could be used as a nutriceutical and pharmacological anti-inflammatory medicine[19], as well as a biomarker for certain diseases and PA. In conclusion, PA is a non-pharmacological therapeutic tool in the management of the IBD as it suppressed the inflammation; attenuating the diversity of intestinal microbiota; reliving the symptoms of skeletomuscular complaint. The effects of exogenous irisin, which is still under experimental studies, are similar to the effects of PA and it may substitute the PA in IBD patients with limitations to do exercises.
The author thanks Stafie R, Singeap AM, Rotaru A, Stanciu C, Trifan A, for their letter on the barriers of the PA to the patients presented with inflammatory bowel disease.
| 1. | Stafie R, Singeap AM, Rotaru A, Stanciu C, Trifan A. Bridging the gap: Unveiling the crisis of physical inactivity in inflammatory bowel diseases. World J Gastroenterol. 2024;30:1261-1265. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 12.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 2. | Gravina AG, Pellegrino R, Durante T, Palladino G, D'Onofrio R, Mammone S, Arboretto G, Auletta S, Imperio G, Ventura A, Romeo M, Federico A. Inflammatory bowel diseases patients suffer from significant low levels and barriers to physical activity: The "BE-FIT-IBD" study. World J Gastroenterol. 2023;29:5668-5682. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 36] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 3. | Rogler G, Singh A, Kavanaugh A, Rubin DT. Extraintestinal Manifestations of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Current Concepts, Treatment, and Implications for Disease Management. Gastroenterology. 2021;161:1118-1132. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 86] [Cited by in RCA: 461] [Article Influence: 115.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Ingram T, Sengupta R, Standage M, Barnett R, Rouse P. Correlates of physical activity in adults with spondyloarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review. Rheumatol Int. 2022;42:1693-1713. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Waseem R, Shamsi A, Mohammad T, Hassan MI, Kazim SN, Chaudhary AA, Rudayni HA, Al-Zharani M, Ahmad F, Islam A. FNDC5/Irisin: Physiology and Pathophysiology. Molecules. 2022;27. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 22] [Cited by in RCA: 98] [Article Influence: 32.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Fox J, Rioux BV, Goulet EDB, Johanssen NM, Swift DL, Bouchard DR, Loewen H, Sénéchal M. Effect of an acute exercise bout on immediate post-exercise irisin concentration in adults: A meta-analysis. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2018;28:16-28. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 73] [Cited by in RCA: 116] [Article Influence: 14.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Remuzgo-Martínez S, Rueda-Gotor J, Pulito-Cueto V, López-Mejías R, Corrales A, Lera-Gómez L, Pérez-Fernández R, Portilla V, González-Mazón Í, Blanco R, Expósito R, Mata C, Llorca J, Hernández-Hernández V, Rodríguez-Lozano C, Barbarroja N, Ortega-Castro R, Vicente E, Fernández-Carballido C, Martínez-Vidal MP, Castro-Corredor D, Anino-Fernández J, Peiteado D, Plasencia-Rodríguez C, Galíndez-Agirregoikoa E, García-Vivar ML, Vegas-Revenga N, Urionaguena I, Gualillo O, Quevedo-Abeledo JC, Castañeda S, Ferraz-Amaro I, González-Gay MÁ, Genre F. Irisin as a Novel Biomarker of Subclinical Atherosclerosis, Cardiovascular Risk and Severe Disease in Axial Spondyloarthritis. Front Immunol. 2022;13:894171. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 3.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Zhu W, Sahar NE, Javaid HMA, Pak ES, Liang G, Wang Y, Ha H, Huh JY. Exercise-Induced Irisin Decreases Inflammation and Improves NAFLD by Competitive Binding with MD2. Cells. 2021;10. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 35] [Cited by in RCA: 70] [Article Influence: 17.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Gonzalez-Gil AM, Elizondo-Montemayor L. The Role of Exercise in the Interplay between Myokines, Hepatokines, Osteokines, Adipokines, and Modulation of Inflammation for Energy Substrate Redistribution and Fat Mass Loss: A Review. Nutrients. 2020;12. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 126] [Cited by in RCA: 171] [Article Influence: 34.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Restuccia R, Perani F, Ficarra G, Trimarchi F, Bitto A, di Mauro D. Irisin and Vascular Inflammation: Beneficial Effects of a Healthy Lifestyle Beyond Physical Activity. Curr Pharm Des. 2021;27:2151-2155. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Ho MY, Wang CY. Role of Irisin in Myocardial Infarction, Heart Failure, and Cardiac Hypertrophy. Cells. 2021;10. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 65] [Article Influence: 16.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Mazur-Bialy AI, Bilski J, Wojcik D, Brzozowski B, Surmiak M, Hubalewska-Mazgaj M, Chmura A, Magierowski M, Magierowska K, Mach T, Brzozowski T. Beneficial Effect of Voluntary Exercise on Experimental Colitis in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet: The Role of Irisin, Adiponectin and Proinflammatory Biomarkers. Nutrients. 2017;9. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 42] [Cited by in RCA: 43] [Article Influence: 5.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Huangfu LX, Cai XT, Yang JN, Wang HC, Li YX, Dai ZF, Yang RL, Lin XH. Irisin attenuates inflammation in a mouse model of ulcerative colitis by altering the intestinal microbiota. Exp Ther Med. 2021;22:1433. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 30] [Article Influence: 7.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Ma Y, Du Y, Yang J, He Q, Wang H, Lin X. Anti-inflammatory effect of Irisin on LPS-stimulated macrophages through inhibition of MAPK pathway. Physiol Res. 2023;72:235-249. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 4.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Papadimitriou K. The Influence of Aerobic Type Exercise on Active Crohn's Disease Patients: The Incidence of an Elite Athlete. Healthcare (Basel). 2022;10. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 3.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 16. | Tornero-Aguilera JF, Sánchez-Molina J, Parraca JA, Morais A, Clemente-Suárez VJ. Are Crohn's Disease Patients Limited in Sport Practise? An UltraEndurance Case-Control Study Response. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Neal WN, Jones CD, Pekmezi D, Motl RW. Physical Activity in Adults With Crohn's Disease: A Scoping Review. Crohns Colitis 360. 2022;4:otac022. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 1.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Demers K, Bak MTJ, Bongers BC, de Vries AC, Jonkers DMAE, Pierik MJ, Stassen LPS. Scoping review on health-related physical fitness in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: Assessment, interventions, and future directions. World J Gastroenterol. 2023;29:5406-5427. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Flori L, Testai L, Calderone V. The "irisin system": From biological roles to pharmacological and nutraceutical perspectives. Life Sci. 2021;267:118954. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 47] [Article Influence: 9.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |