Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2023; 29(9): 1475-1491
Published online Mar 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i9.1475
Published online Mar 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i9.1475
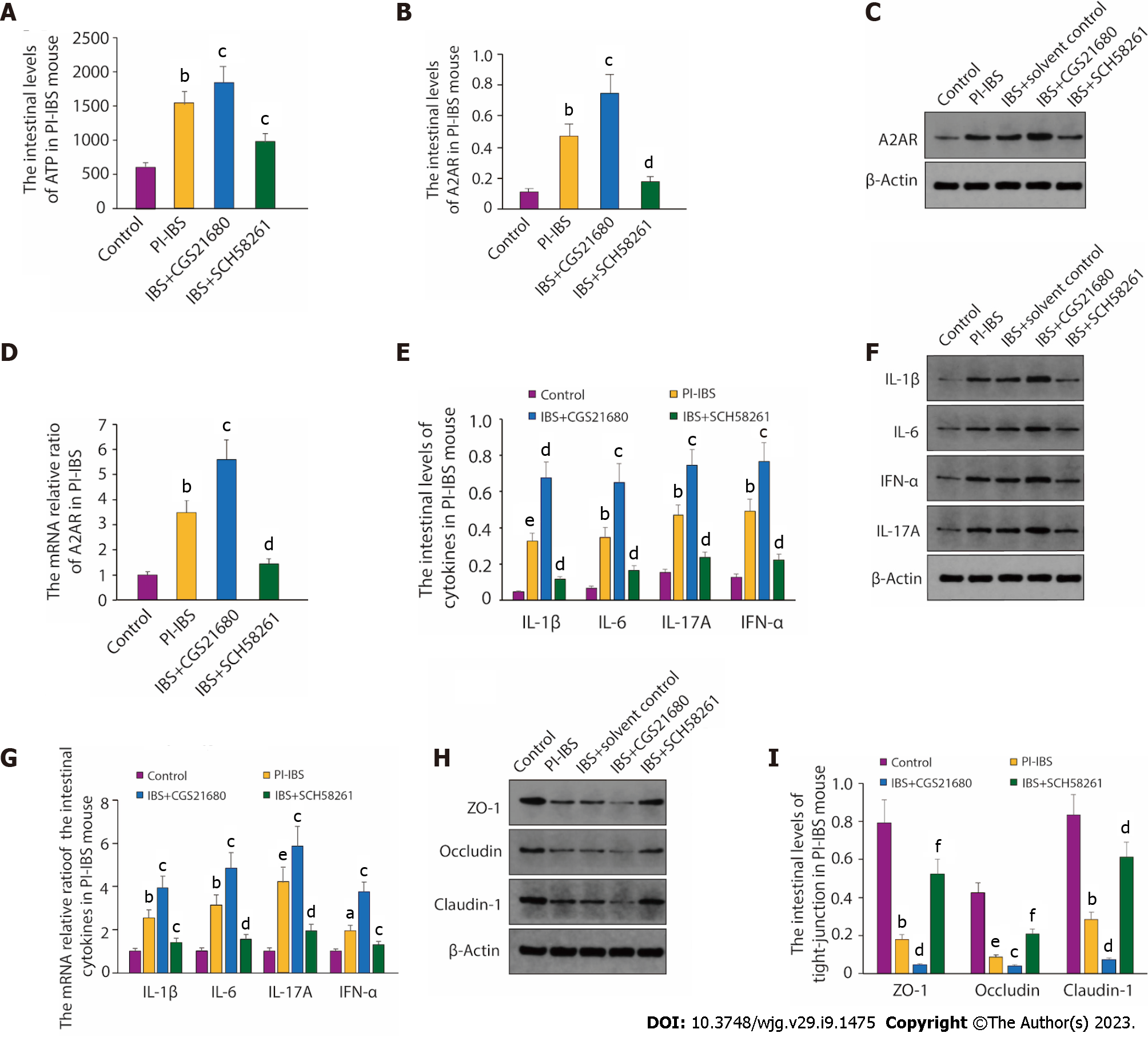
Figure 2 The intestinal ATP and adenosine 2A receptor expression in post-infectious irritable bowel syndrome mouse.
A: The level of ATP in post-infectious irritable bowel syndrome (PI-IBS) mouse. The results were independently repeated three times; B and C: The intestinal levels of adenosine 2A receptor (A2AR) in PI-IBS mouse; D: The mRNA relative ratio of A2AR in PI-IBS mouse. The results were independently repeated three times; E and F: The intestinal levels of the inflammatory cytokines in PI-IBS mice were measured by ELISA and western blot, respectively. The ELISA results were obtained from six mice; G: The mRNA relative ratio of the intestinal cytokines in PI-IBS mouse. The samples were from mice mentioned in E and F. The results were independently repeated three times; H and I: The intestinal levels of tight junction proteins in PI-IBS mice were tested through western blot and quantified by image J software. β-Actin is used as the loading control for both western blot and reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, eP < 0.001 vs the Control group; cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01, fP < 0.001 vs the PI-IBS group.
- Citation: Dong LW, Chen YY, Chen CC, Ma ZC, Fu J, Huang BL, Liu FJ, Liang DC, Sun DM, Lan C. Adenosine 2A receptor contributes to the facilitation of post-infectious irritable bowel syndrome by γδ T cells via the PKA/CREB/NF-κB signaling pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(9): 1475-1491
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i9/1475.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i9.1475