Published online Oct 28, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i40.5557
Peer-review started: July 24, 2023
First decision: September 18, 2023
Revised: October 1, 2023
Accepted: October 23, 2023
Article in press: October 23, 2023
Published online: October 28, 2023
Processing time: 95 Days and 4.7 Hours
Percutaneous drainage (PCD) and endoscopic approaches have largely replaced surgical drainage as the initial approach for (peri) pancreatic fluid collections (PFC)s, while complications associated with endoscopic stent implantation are common.
To introduce a novel endoscopic therapy named endoscopic transgastric fenestration (ETGF), which involves resection of tissue by endoscopic accessory between gastric and PFCs without stent implantation, and to evaluate its efficacy and safety compared with PCD for the management of PFCs adjacent to the gastric wall.
Patients diagnosed with PFCs adjacent to the gastric wall and who subsequently received ETGF or PCD were restrospectively enrolled. Indications for intervention were consistent with related guidelines. We analyzed patients baseline characteristics, technical and clinical success rate, recurrence and reintervention rate, procedure-related complications and adverse events.
Seventy-two eligible patients were retrospectively identified (ETGF = 34, PCD = 38) from October 2017 to May 2021. Patients in the ETGF group had a significantly higher clinical success rate than those in the PCD group (97.1 vs 76.3%, P = 0.01). There were no statistically significant differences regarding recurrence, reintervention and incidence of complication between the two groups. While long-term catheter drainage was very common in the PCD group.
Compared with PCD, ETGF has a higher clinical success rate in the management of PFCs adjacent to the gastric wall. ETGF is an alternative effective strategy for the treatment of PFCs adjacent to the gastric wall.
Core Tip: Inspired by endoscopic full-thickness resection, we proposed the concept of endoscopic transgastric fenestration (ETGF), which involves resection of connect tissue between the gastric wall and (peri) pancreatic fluid collections (PFCs) with the assistance of endoscopic accessory to treat PFCs secondary to pancreatitis adjacent to the gastric wall, avoiding the stent implantation. In the current study, we evaluate the efficacy and safety of ETGF by comparing with percutaneous drainage for the management of PFCs adjacent to the gastric wall.
- Citation: Zhang HM, Ke HT, Ahmed MR, Li YJ, Nabi G, Li MH, Zhang JY, Liu D, Zhao LX, Liu BR. Endoscopic transgastric fenestration versus percutaneous drainage for management of (peri)pancreatic fluid collections adjacent to gastric wall (with video). World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(40): 5557-5565
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i40/5557.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i40.5557
Pancreatic and peripancreatic fluid collections (PFCs) are causes of fluid leakage or liquefaction of pancreatic necrosis following acute pancreatitis, chronic pancreatitis, surgery or abdominal trauma[1]. Collections usually forms 4 wk after the onset of acute pancreatitis and the majority resolve spontaneously[1]. Indications to intervene PFCs include infection and symptomatic sterile necrosis, while persistent collections that are asymptomatic may be observed[1-3]. Percutaneous drainage (PCD) and an endoscopic approach with stent implantation have replaced surgical drainage as the initial treatment for PFCs which reduce the complications and costs of hospitalization[3-7]. The European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy recommends endoscopy or PCD as the first interventional method for PFCs[8]. PCD is an attractive and conventional approach that appears to be safe and the least invasive. However, inability to remove necrotic debris in the cavity has restricted its use[5,6,9]. Commonly, transluminal endoscopic drainage with stent implantation is an effective method[4,7]. However, embedding, displacement, and bleeding related to stent implantation are common complications, which leads to multi-interventions, and hence resulting in additional cost[10-12]. In addition, application of stent has been limited due to its high cost and is not commercial in some tertiary hospitals in China. Inspired by endoscopic full-thickness resection (EFTR), Liu et al[13] first conducted endoscopic transgastric fenestration (ETGF), an innovative endoscopic treatment avoiding the implantation of a stent to manage PFCs. ETGF involves endoscopic resection of connected tissues between gastric and pancreatic lesions with the assistance of endoscopic accessory, which can drain the collection of fluid in the cavity and debride the necrotic debris inside. In this retrospective study, the primary objective was to assess the availability of ETGF by comparing the rate of technical and clinical success, recurrence and reintervention with patients who received PCD. The secondary objective was to assess its safety by evaluating complications related to the procedure.
Patients diagnosed with PFCs at the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University between October 2017 and May 2021 were enrolled in this study. Inclusion criteria included patients diagnosed with PFCs that was adjacent to the gastric wall and who subsequently received ETGF or PCD. Indications to intervene PFCs were consistent with related guidelines[1,8]. Patients with incomplete clinical data and who were lost to follow-up were excluded. All patients underwent ultrasonography (USG), computed tomography (CT) scan or magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography to evaluate the lesion prior to the procedure. Patients in the ETGF group underwent endoscopy at least twice to observe the absorption of the cavity and the natural healing of the artificial fistula between the gastric wall and the cavity, the majority of which almost healed within 1 mo. CT or USG was reviewed within 6 mo after treatment. The study was approved by the institutional ethics committee and all patients were provided written informed consent to undergo the procedures (KY-2021-00642).
PFCs were defined according to the revised Atlanta consensus related to acute pancreatitis[1]. Technical success was defined as the ability to access the lesion. Clinical success was defined as symptom relief with PFCs reduced to < 2 cm within 6 mo without another alternative drainage procedure.
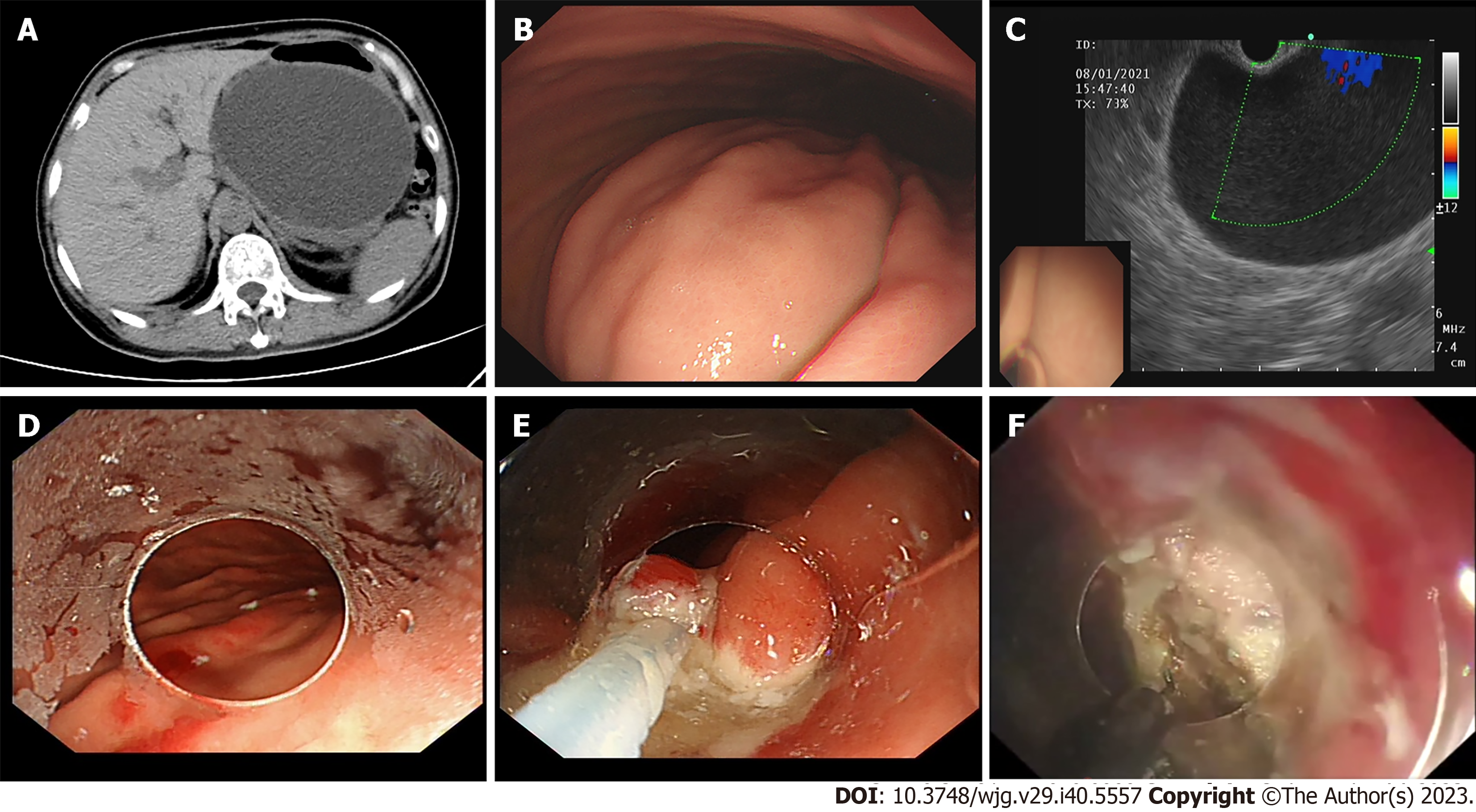
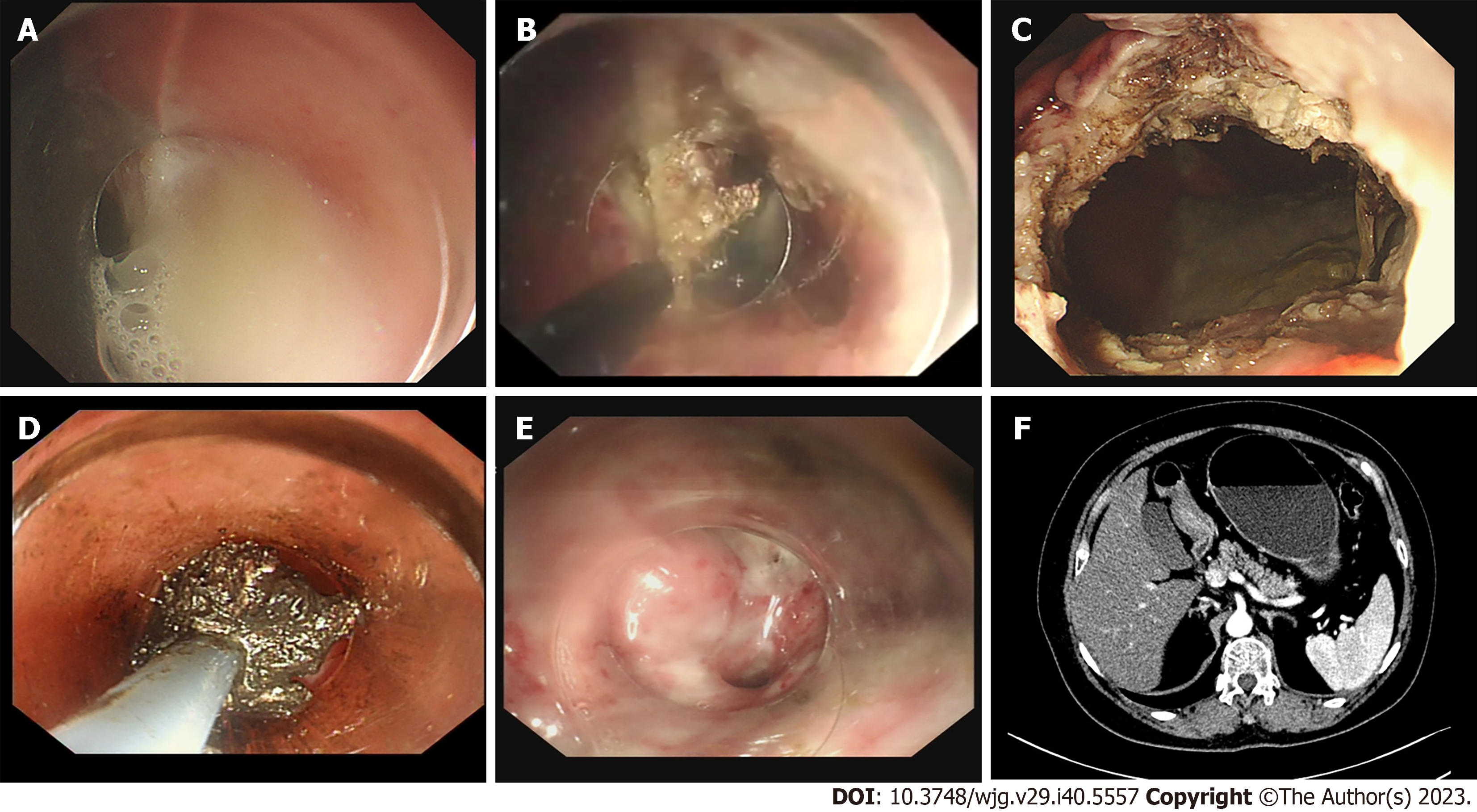
Endoscopic drainages were performed under general anesthesia with endotracheal intubation as follows: (1) Endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) was used to determine the lesion location, whether a large vessel was hidden in the operative region and marked the site of fenestration using a Hook knife (KD-620LR, Olympus); (2) then the mucosal layer of the fenestration site was then removed with an endoscopic snare and full-thickness incision was subsequently made with the Hook knife, fluid in the collection was seen to pour out spontaneously; (3) re-evaluation of the fistula between the stomach and cavity; (4) the gastric-collections incision was enlarged to a diameter of approximately 2 cm to the facilitate the operation and drainage by EFTR; (5) coagulating styptic forcep was used for hemostasis (Coagrasper, FD-410LR; Olympus); (6) the endoscope was advanced into the collection, and the content of the PFCs was further cleaned with saline rinse and vacuum suction, debris was removed by snare assistance, and (7) nasocystic tube (18 Fr) was indwelled if necessary (large or complicated with infection) and endoscopy was undertaken twice to observe the healing of the artificial fistula, most of which closed within one month (Figures 1 and 2, Video).
Under local anesthesia using lignocaine, an 18-gauge needle was placed into the PFCs percutaneously with the guidance of USG or CT scan and the fluid was aspirated. A guidewire was then advanced into the collection. The tract was dilated and then a pigtail catheter of 8 or 10 Fr was inserted into the lesion. The catheter was replaced when the drainage tube failed due to obstruction and eventually removed when the collections was < 2 cm in length.
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS Statistics v26.0. For continuous variables, the mean ± SD was used to describe data that fitted a normal distribution and quartiles were used for data that did not conform to normal distribution. Statistical significance was analyzed by the t-test and nonparametric test respectively. Counting card information was described by percentage and performed by the chi-square test. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
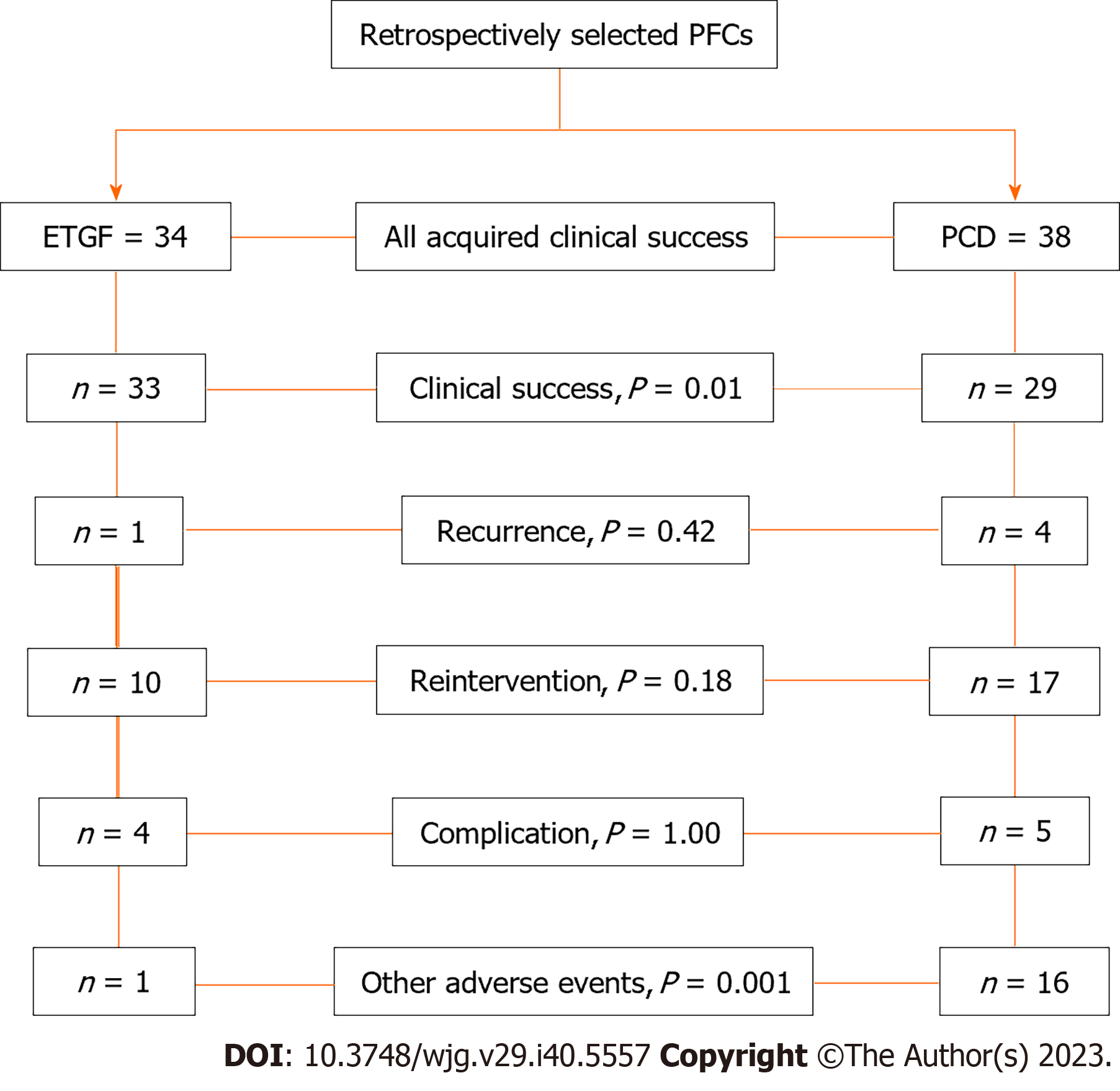
Between October 2017 and May 2021, a total of 72 patients were enrolled in this study (ETGF = 34, PCD = 38, Figure 3). There were no statistically differences regarding sex and size of the lesion between the two groups. Patients in the ETGF group were younger than in PCD group (36.8 ± 12.9 years vs 46.0 ± 16.8years, P = 0.01). The clinical success rate in the ETGF group was significantly higher than that in the PCD group (97.1 vs 76.3%, P = 0.01). There were no statistically significant differences regarding recurrence and reintervention between the two groups. Although the complication rate was similar in the two groups, catheter related adverse events were common in the PCD group (2.9 vs 34.3 %, P = 0.001). Patients were followed up by the electronic medical record system combined with telephone consultation for a median follow-up of 35 wk (9-85 wk). There was no procedure related mortality in either groups. The largest lesion was encountered in the endoscopic group with a length of 220 mm. Baseline characteristics and patient demographics are shown in Table 1. Primary and secondary outcomes are shown in Table 2.
| ETGF (%) | PCD (%) | P value | |
| Total | 34 | 38 | |
| Male | 24 (70.6) | 26 (68.4) | 0.84 |
| Mean age | 36.8 ± 12.9 | 46.0 ± 16.8 | 0.01 |
| Mean length of lesions (mm) | 109.4 ± 7.8 | 94.8 (80.8-133.2) | 0.89 |
| Cause of pancreastitis | |||
| Hyperlipidemia | 10 (29.4) | 8 (21.1) | |
| Gallstone | 8 (23.5) | 8 (21.1) | |
| Alcohol | 9 (26.5) | 6 (15.8) | |
| Trauma | 1 (2.9) | 4 (10.5) | |
| Autoimmunity | 1 (2.9) | 3 (7.9) | |
| Pancreatic duct stones | 3 (8.8) | ||
| Choledochocyst | 1 (2.6) | ||
| Idiopathic | 1 (2.9) | 8 (21.1) | |
| Clinical symptoms1 | |||
| Abdominal pain (%) | 24 (70.6) | 27 (71.1) | |
| Abdominal distention (%) | 6 (17.65) | 5 (13.2) | |
| Nausea or vomiting | 5 | 3 | |
| Fever | 6 | 1 | |
| Asymptomatic | 1 | 2 | |
| Preintervention | 6 | 4 | |
| PCD | 4 | 3 | |
| ETGF | 1 | ||
| Surgery | 1 | 1 | |
| Opportunity of intervention2 | 0.381 | ||
| < 4 wk | 7 | 13 | |
| > 4 wk | 21 | 24 | |
| Total interventions | 1.03 ± 0.03 | 1.32 ± 0.09 | 0.003 |
| Total hospital visits | 1.0 (0) | 1.0 (1.0) | 0.278 |
| Total hospital stays(days) | 14.5 (10.25) | 19.0 (20.5) | 0.177 |
| Total cost ($) | 4852 (3877) | 5206 (8377) | 0.955 |
| ETGF | PCD | P value | |
| Technical success | 34 (100) | 38 (100) | |
| Clinical success | 33/34 (97.1) | 29/38 (76.3) | 0.01 |
| Recurrence | 1/34 (2.94) | 4/38 (10.5) | 0.42 |
| Reintervention | 10/34 (29.4) | 171/38 (44.7) | 0.18 |
| Complication | 1.00 | ||
| Bleeding 4 (11.76) | Bleeding 2 (5.26) | ||
| Local infection 2 (5.26) | |||
| Adhesion to surrounding tissue 1 (2.63) | |||
| Catheter related adverse events | 0.001 | ||
| Tube dislodgment 1 (2.9) | Intubation time > 8 wk 11 (28.9) | ||
| Drainage obstruction 5 (13.2) |
Six of 34 patients had previous therapeutic history in another hospital: one received ETGF, one received surgical treatment, and the other four received PCD. The average age of the participants was 36.8 ± 12.9 years old. The mean length of PFCs was 109.4 ± 7.8 mm. The average total interventions were 1.03 sessions. The total duration of hospital stays and total cost was 14.5 d and 4852 $ respectively. Clinical success was achieved in 33 patients (97.1%). One recurrence was observed in this group. With regard to reintervention, 9 cases received a second therapeutic endoscopy for infection in the cavity, and another patient transferred to PCD as a result of inadequate drainage due to small caliber of the fenestration. Procedure related bleeding occurred in 4 patients (11.76%) and was resolved by endoscopy. An nasocystic tube was inserted in seven patients for pus or necrosis collection, and the mean duration of the indwelling nasocystic tube was 8.6 d.
Four of 38 patients received preintervention but failed, which included one open surgery and 3 cases of PCD. The average age of the participants was 46.0 ± 16.8 years old with more male patients than female patients (26 vs 12). Approximately three quarters of patients suffered from abdominal pain (27/38). The average length of PFCs was 94.8 mm (80.8-133.2 mm). Hyperlipidemia, gallstones, and alcohol-related pancreatitis were the etiologies in 57.9% of patients (22/38). The average total interventions was 1.32 sessions. The total duration of hospital stays and total cost was 19 days and 5206 $ respectively. Clinical success was achieved in 29 patients (76.3%). Four patients showed recurrence (10.5%) and reintervention occurred in 17 of 38 patients (44.7%). With regard to adverse events, two patients developed bleeding which stopped spontaneously, two had local infection, and one had drainage adhesion to surrounding tissue. In 11 patients, the duration of catheterization was more than 8 wk. Drainage obstruction was encountered in 5 cases.
Surgical treatment has been traditionally used for PFCs[3]. Recently, PCD and endoscopic management have replaced surgery as the main treatment for PFCs due to their minimal invasiveness[6,8]. However, PCD cannot debride necrosis and an external drainage tube affects quality of life, which has limited its clinical use[5,14-16]. Endoscopic treatment can not only drainage the pus inside but also remove debris in the cavity and is beneficial to patient’s health[5,6,14,17]. While previously endoscopic therapy involved stent implantation, embedding, displacement, and bleeding were inevitable[10-12]. Different to conventional endoscopic management, ETGF was conducted by means of ETFR to drain and debride PFCs adherent to the gastric wall, avoiding stent implantation.
Our findings are basically consistent with previous studies on conventional endoscopic drainage which actually involves plastic or metal stent implantation and the PCD approach[16,18-20]. A respective study from the United States reported that the technical and clinical success rate of EUS-guided drainage of PFCs was 100% and 97% respectively[18]. Similarly, ETGF had a relatively favorable effect with 100% technical success and 97.1% clinical success. Jianhua et al performed a comparative study on drainage of PFCs and initial clinical success was considerably higher in patients who received transluminal endoscopic drainage than those in the PCD group (94.9% vs 65.0%)[20]. In our study, the clinical success rate in the PCD group was 65.8% which was also lower than that in the ETGF group.
PCD was associated with a high rate of reintervention and the endoscopic stent implantation approach was shown to significantly reduce the rate of retreatment, which resulted in short hospital stay, low cost and a reduced number of follow-up abdominal imaging studies[9,15]. In the present study, the total cost and reintervention rate following ETGF was lower than that in PCD, but was not statistically significantly different.
Keane et al[15] agreed that there was no difference between PCD and transluminal endoscopic drainage of PFCs in terms of recurrence. In another study, endoscopic drainage with stent implantation was an effective and appropriate method with the advantage of fewer recurrences compared to PCD[19]. In the present study, we found that there was no difference in the recurrence rate between two groups. In a long-term follow up study about PFCs, the recurrence of transluminal endoscopic drainage reported by Nabi et al was 6.7%[11]. In this study, one recurrence was encountered in ETGF group (2.94%).
The procedural adverse events rate was high in the PCD group compared with the transluminal endoscopic drainage with stent implantation group[20]. In the current study, the rate of complications in the ETGF group was similar with that in the PCD. Bleeding was encountered in ETGF patients and was managed by conservative treatment totally , which was consistent with previous studies[21].
Research by Storm et al[18] on endoscopic drainage of PFCs discovered that size of collections > 100 mm was correlated with an increased risk of adverse events. The size of PFCs was an independent risk factor for infection related to the cavity, and large PFCs with a diameter > 150 mm were more likely to become infected[22]. In the present study, seven patients had nasocystic tube implanted due to pus and necrosis in the cavity, of which 3 lesions were more than 150 mm and another 3 lesions were > 100 mm. A study on ETGF found that there were 3 of 5 patients received a nasocystic tube and the mean catheterization time was 10 d, which was longer than that in our study (8.6 d)[23]. We also recommended an indwelling nasocystic tube for large lesion or lesions combined with infection.
A previous study reported that the average length of time the drainage catheter in place was as long as 44.5 d in PCD[14]. Similarly, in our study, there were 28.9% of patients (11/38) whose underwent drainage for more than 8 wk. In addition, drainage obstruction occurred in 5 patients due to pus or necrosis, all of which led to further discomfort. Furthermore, an external catheter requires long-term care, as well as reminding the patient of their underlying disease state, and results in significant patient discomfort and compromised the quality of life[14]. During ETGF we used a natural orifice as the access route, avoiding an external catheter and scarring, which was beneficial to mental health and improved quality of life.
The limitations of this study were as follows. Firstly, we didn’t examine how different types of PFCs affected the therapeutic efficacy. Secondly, prognostic factors associated with postoperative infection (size of PFCs, the area of fenestration) were not been identified in ETGF. A quality of life scale was not used in this study, thus, how the two different methods affected the quality of life is not known. A large, prospective, multicenter study is necessary to confirm our results.
Both PCD and ETGF can be used effectively for the treatment of PFCs, although ETGF is superior to PCD as it has a higher rate of clinical success and a lower rate of adverse events. ETGF is an innovative, effective, safe and scarless strategy for the management of PFCs adherent to the gastric wall. However, further studies especially clinical trials are needed before final recommendations are made.
Percutaneous drainage (PCD) and endoscopic approaches with stent implantation have largely replaced surgical drainage as the initial approach for (peri) pancreatic fluid collections (PFCs). While stent implantation guided by endoscopic ultrasound has been mature and preferred treatment, but stent displacement, bleeding and embedding should not be neglected.
Inspired by endoscopic full-thickness resection, we conducted endoscopic transgastric fenestration (ETGF), which involves resection of connected tissues between gastric wall and PFCs, so as to drain the collection of fluid in the cavity and debride the necrosis inside.
The study aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of ETGF by accessing its success and complication rate compared with PCD.
This retrospective analysis enrolled patients diagnosed with PFCs adjacent to the gastric wall and subsequently received ETGF or PCD during 4 years, analyzed patients baseline characteristics, technical and clinical success rate, recurrence and reintervention rate, procedure related complication and adverse events.
Seventy-two eligible patients were retrospectively identified (ETGF = 34, PCD = 38). Patients in the ETGF group acquired significantly higher clinical success rate than that in PCD (97.1 vs 76.3%, P = 0.01). There was no statistical difference about recurrence, reintervention and incidence of complication between the two groups.
ETGF would be an alternative effective and safe strategy for the treatment of PFCs adjacent to the gastric wall.
ETGF can drainage fluid inside and debride necrosis, which improves its clinical success. Therefore, in our opinion ETGF may be an alternative treatment for PFCs adjacent to gastric, especially for large lesions or leions that associated with infection or necrosis.
We express our gratitude to Professor Shi Niu, Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Inner Mongolia People’s Hospital, China, for his encouragement and assistance in preparing the audio and revising the manuscript.
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Gastroenterology and hepatology
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): A
Grade B (Very good): B, B
Grade C (Good): 0
Grade D (Fair): D
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Kitamura K, Japan; Shelat VG, Singapore; Thandassery RB, United States; Sharma S, India S-Editor: Qu XL L-Editor: A P-Editor: Chen YX
| 1. | Banks PA, Bollen TL, Dervenis C, Gooszen HG, Johnson CD, Sarr MG, Tsiotos GG, Vege SS; Acute Pancreatitis Classification Working Group. Classification of acute pancreatitis--2012: revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut. 2013;62:102-111. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4932] [Cited by in RCA: 4343] [Article Influence: 361.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (45)] |
| 2. | Hines OJ, Pandol SJ. Management of severe acute pancreatitis. BMJ. 2019;367:l6227. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 56] [Cited by in RCA: 98] [Article Influence: 16.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Saftoiu A, Vilmann A, Vilmann P. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts. Endosc Ultrasound. 2015;4:319-323. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 16] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Singhal S, Rotman SR, Gaidhane M, Kahaleh M. Pancreatic fluid collection drainage by endoscopic ultrasound: an update. Clin Endosc. 2013;46:506-514. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 59] [Cited by in RCA: 70] [Article Influence: 5.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Kawakami H, Itoi T, Sakamoto N. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided transluminal drainage for peripancreatic fluid collections: where are we now? Gut Liver. 2014;8:341-355. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 30] [Cited by in RCA: 41] [Article Influence: 3.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Baron TH, DiMaio CJ, Wang AY, Morgan KA. American Gastroenterological Association Clinical Practice Update: Management of Pancreatic Necrosis. Gastroenterology. 2020;158:67-75.e1. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 240] [Cited by in RCA: 418] [Article Influence: 83.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (2)] |
| 7. | Bang JY, Arnoletti JP, Holt BA, Sutton B, Hasan MK, Navaneethan U, Feranec N, Wilcox CM, Tharian B, Hawes RH, Varadarajulu S. An Endoscopic Transluminal Approach, Compared With Minimally Invasive Surgery, Reduces Complications and Costs for Patients With Necrotizing Pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 2019;156:1027-1040.e3. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 255] [Cited by in RCA: 216] [Article Influence: 36.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Arvanitakis M, Dumonceau JM, Albert J, Badaoui A, Bali MA, Barthet M, Besselink M, Deviere J, Oliveira Ferreira A, Gyökeres T, Hritz I, Hucl T, Milashka M, Papanikolaou IS, Poley JW, Seewald S, Vanbiervliet G, van Lienden K, van Santvoort H, Voermans R, Delhaye M, van Hooft J. Endoscopic management of acute necrotizing pancreatitis: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) evidence-based multidisciplinary guidelines. Endoscopy. 2018;50:524-546. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 221] [Cited by in RCA: 292] [Article Influence: 41.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Akshintala VS, Saxena P, Zaheer A, Rana U, Hutfless SM, Lennon AM, Canto MI, Kalloo AN, Khashab MA, Singh VK. A comparative evaluation of outcomes of endoscopic versus percutaneous drainage for symptomatic pancreatic pseudocysts. Gastrointest Endosc. 2014;79:921-8. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 81] [Cited by in RCA: 87] [Article Influence: 7.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Bang JY, Navaneethan U, Hasan MK, Sutton B, Hawes R, Varadarajulu S. Non-superiority of lumen-apposing metal stents over plastic stents for drainage of walled-off necrosis in a randomised trial. Gut. 2019;68:1200-1209. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 171] [Cited by in RCA: 246] [Article Influence: 41.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Nabi Z, Lakhtakia S, Basha J, Chavan R, Gupta R, Ramchandani M, Kalapala R, Pal P, Darisetty S, Rao GV, Nageshwar Reddy D. Endoscopic drainage of pancreatic fluid collections: Long-term outcomes in children. Dig Endosc. 2017;29:790-797. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 24] [Cited by in RCA: 23] [Article Influence: 2.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Yang J, Chen YI, Friedland S, Holmes I, Paiji C, Law R, Hosmer A, Stevens T, Matheus F, Pawa R, Mathur N, Sejpal D, Inamdar S, Berzin TM, DiMaio CJ, Gupta S, Yachimski PS, Anderloni A, Repici A, James T, Jamil LH, Ona M, Lo SK, Gaddam S, Dollhopf M, Alammar N, Shieh E, Bukhari M, Kumbhari V, Singh V, Brewer O, Sanaei O, Fayad L, Ngamruengphong S, Shin EJ, Baron TH, Khashab MA. Lumen-apposing stents versus plastic stents in the management of pancreatic pseudocysts: a large, comparative, international, multicenter study. Endoscopy. 2019;51:1035-1043. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 27] [Cited by in RCA: 37] [Article Influence: 6.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Liu BR, Song JT, Zhang XY. Video of the Month: Emergency Endoscopic Fenestration for Treatment of a Recurrence Pancreatic Pseudocyst. Am J Gastroenterol. 2015;110:644. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Kwon YM, Gerdes H, Schattner MA, Brown KT, Covey AM, Getrajdman GI, Solomon SB, D'Angelica MI, Jarnagin WR, Allen PJ, Dimaio CJ. Management of peripancreatic fluid collections following partial pancreatectomy: a comparison of percutaneous versus EUS-guided drainage. Surg Endosc. 2013;27:2422-2427. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 45] [Cited by in RCA: 58] [Article Influence: 4.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Keane MG, Sze SF, Cieplik N, Murray S, Johnson GJ, Webster GJ, Thorburn D, Pereira SP. Endoscopic versus percutaneous drainage of symptomatic pancreatic fluid collections: a 14-year experience from a tertiary hepatobiliary centre. Surg Endosc. 2016;30:3730-3740. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 47] [Cited by in RCA: 75] [Article Influence: 7.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 16. | Fabbri C, Luigiano C, Lisotti A, Cennamo V, Virgilio C, Caletti G, Fusaroli P. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided treatments: are we getting evidence based--a systematic review. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:8424-8448. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 105] [Cited by in RCA: 98] [Article Influence: 8.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Varadarajulu S, Bang JY, Sutton BS, Trevino JM, Christein JD, Wilcox CM. Equal efficacy of endoscopic and surgical cystogastrostomy for pancreatic pseudocyst drainage in a randomized trial. Gastroenterology. 2013;145:583-90.e1. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 370] [Cited by in RCA: 325] [Article Influence: 27.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 18. | Storm AC, Levy MJ, Kaura K, Abu Dayyeh BK, Cleary SP, Kendrick ML, Truty MJ, Vargas EJ, Topazian M, Chandrasekhara V. Acute and early EUS-guided transmural drainage of symptomatic postoperative fluid collections. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020;91:1085-1091.e1. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 22] [Article Influence: 4.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Xie LT, Zhao QY, Gu JH, Ying HJ, Tian G, Jiang TA. Endoscopic Ultrasonography-Guided Versus Percutaneous Drainage for the Recurrent Pancreatic Fluid Collections. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:5785-5794. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Wan J, Wu D, He W, Zhu Y, Zeng H, Liu P, Xia L, Lu N. Comparison of percutaneous vs endoscopic drainage in the management of pancreatic fluid collections: A prospective cohort study. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;35:2170-2175. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 2.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Künzli HT, Timmer R, Schwartz MP, Witteman BJ, Weusten BL, van Oijen MG, Siersema PD, Vleggaar FP. Endoscopic ultrasonography-guided drainage is an effective and relatively safe treatment for peripancreatic fluid collections in a cohort of 108 symptomatic patients. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;25:958-963. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Guo J, Feng L, Sun S, Ge N, Liu X, Wang S, Wang G, Sun B. Risk factors for infection after endoscopic ultrasonography-guided drainage of specific types of pancreatic and peripancreatic fluid collections (with video). Surg Endosc. 2016;30:3114-3120. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Liu F, Wu L, Wang XD, Xiao JG, Li W. Endoscopic gastric fenestration of debriding pancreatic walled-off necrosis: A pilot study. World J Gastroenterol. 2020;26:6431-6441. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |