Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2023; 29(38): 5361-5373
Published online Oct 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i38.5361
Published online Oct 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i38.5361
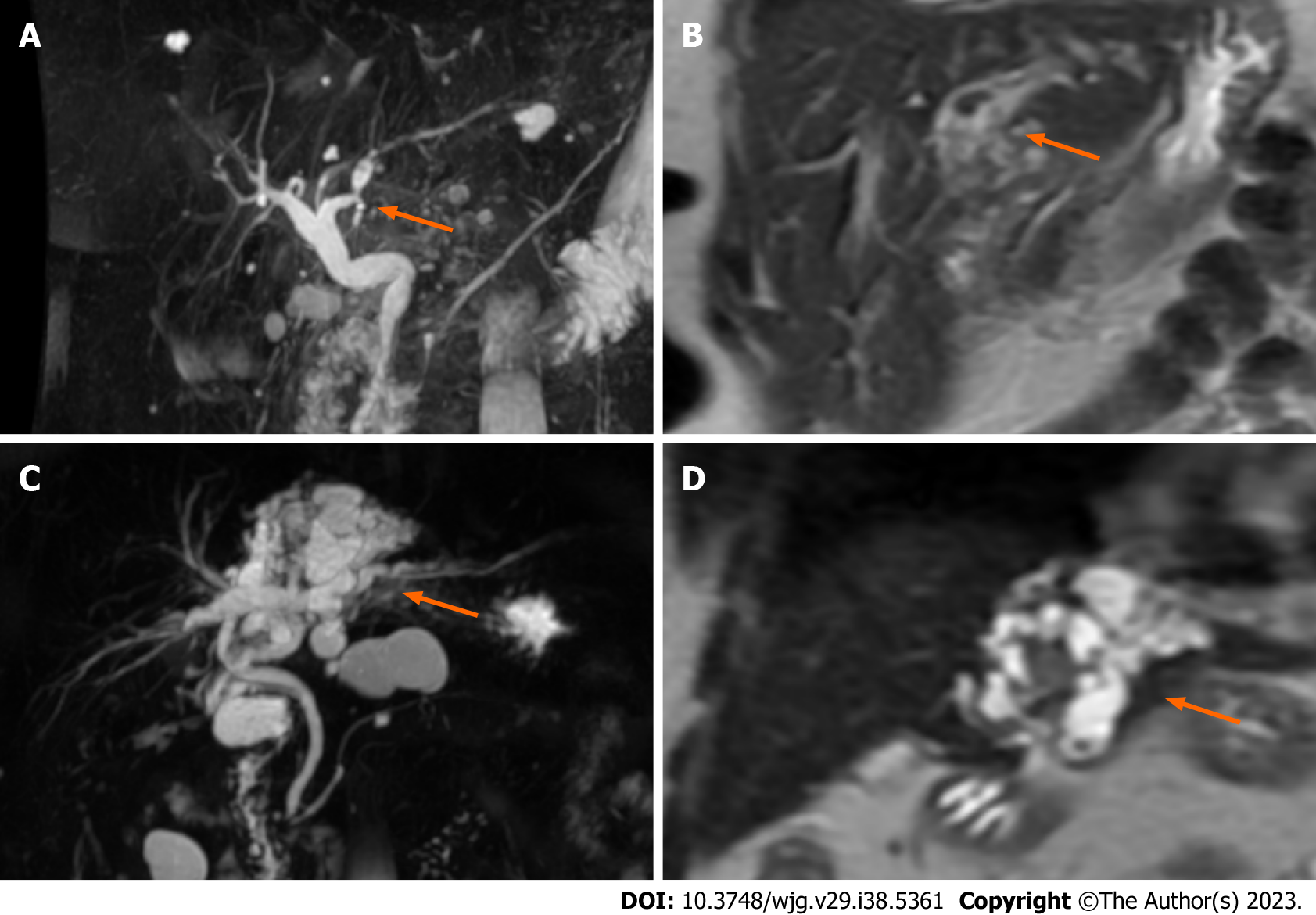
Figure 4 Magnetic resonance imaging of intraductal papillary neoplasms of the bile duct.
A: Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography showed an intraductal lesion of the left hepatic duct with upstream bile duct dilatation; B: Diffuse dilatation of the intrahepatic left lobe bile ducts with low intensity tumors (T2 weighted image, coronal section); C: Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography showed a cystic type intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct; D: Cystic type intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct (T2 weighted image, coronal section).
- Citation: Mocchegiani F, Vincenzi P, Conte G, Nicolini D, Rossi R, Cacciaguerra AB, Vivarelli M. Intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct: The new frontier of biliary pathology. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(38): 5361-5373
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i38/5361.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i38.5361