Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2023; 29(20): 3084-3102
Published online May 28, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i20.3084
Published online May 28, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i20.3084
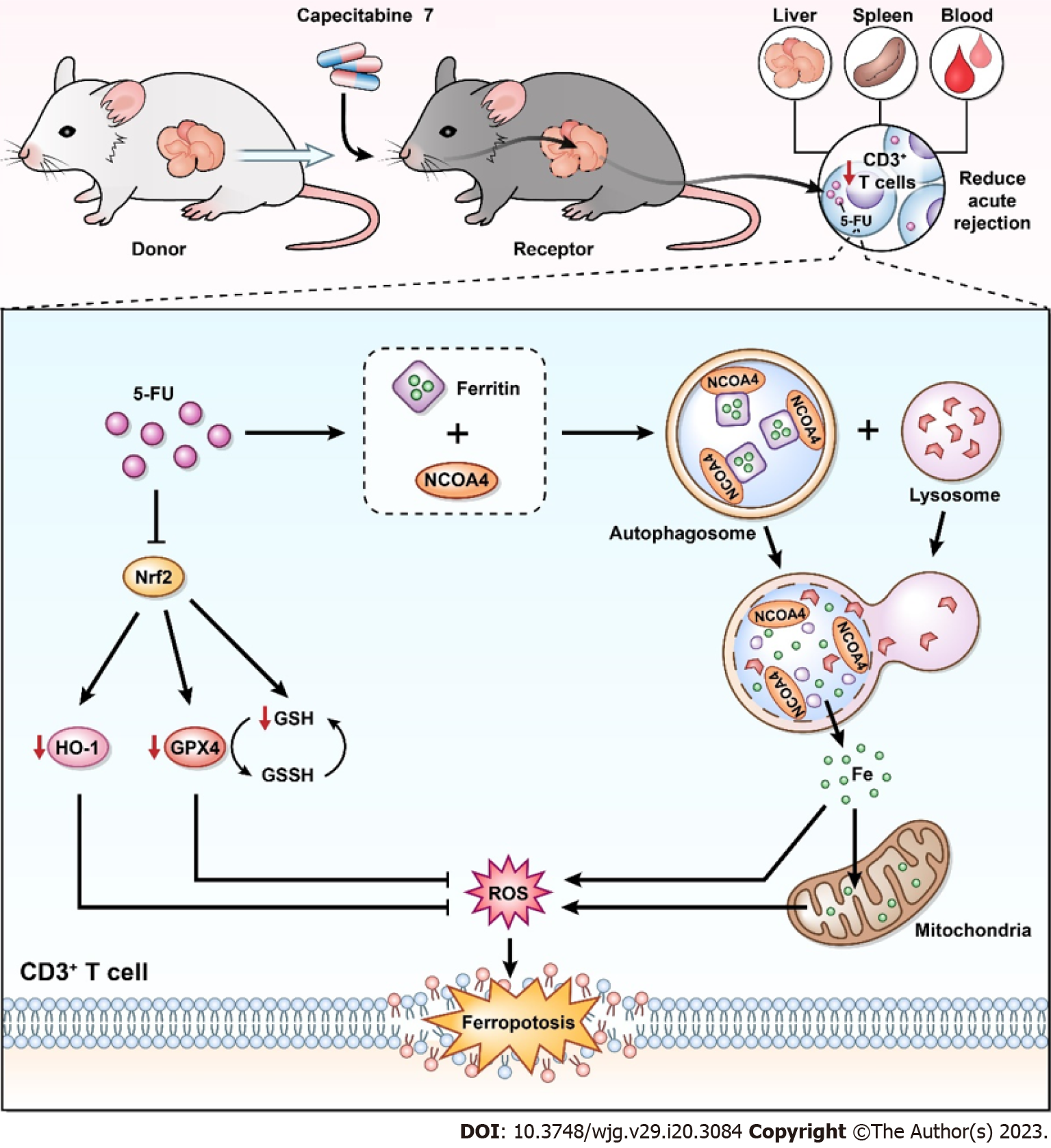
Figure 8 Possible immunosuppressive mechanisms of metronomic capecitabine on T cells by ferroptosis induction.
In the rat model of acute rejection after liver transplantation, metronomic capecitabine (CAP) exerts an immunosuppressive effect by decreasing T cell numbers in peripheral blood, liver graft, and spleen. Metronomic CAP increases the concentration of free ferrous ions by inducing ferritin degradation while inhibiting the expression of antioxidant proteins. Eventually, these effects lead to peroxidation damage and iron toxicity, which induce T cell death. 5-FU: 5-fluorouracil; Nrf2: Nuclear erythroid 2 p45-related factor 2; NCOA4: Nuclear receptor coactivator 4; HO-1: Heme oxygenase-1; GPX4: Glutathione peroxidase 4; GSH: Glutathione; GSSH: Oxidized glutathione; ROS: Reactive oxygen species.
- Citation: Wang H, Wang ZL, Zhang S, Kong DJ, Yang RN, Cao L, Wang JX, Yoshida S, Song ZL, Liu T, Fan SL, Ren JS, Li JH, Shen ZY, Zheng H. Metronomic capecitabine inhibits liver transplant rejection in rats by triggering recipients’ T cell ferroptosis. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(20): 3084-3102
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i20/3084.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i20.3084