Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2023; 29(16): 2359-2368
Published online Apr 28, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i16.2359
Published online Apr 28, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i16.2359
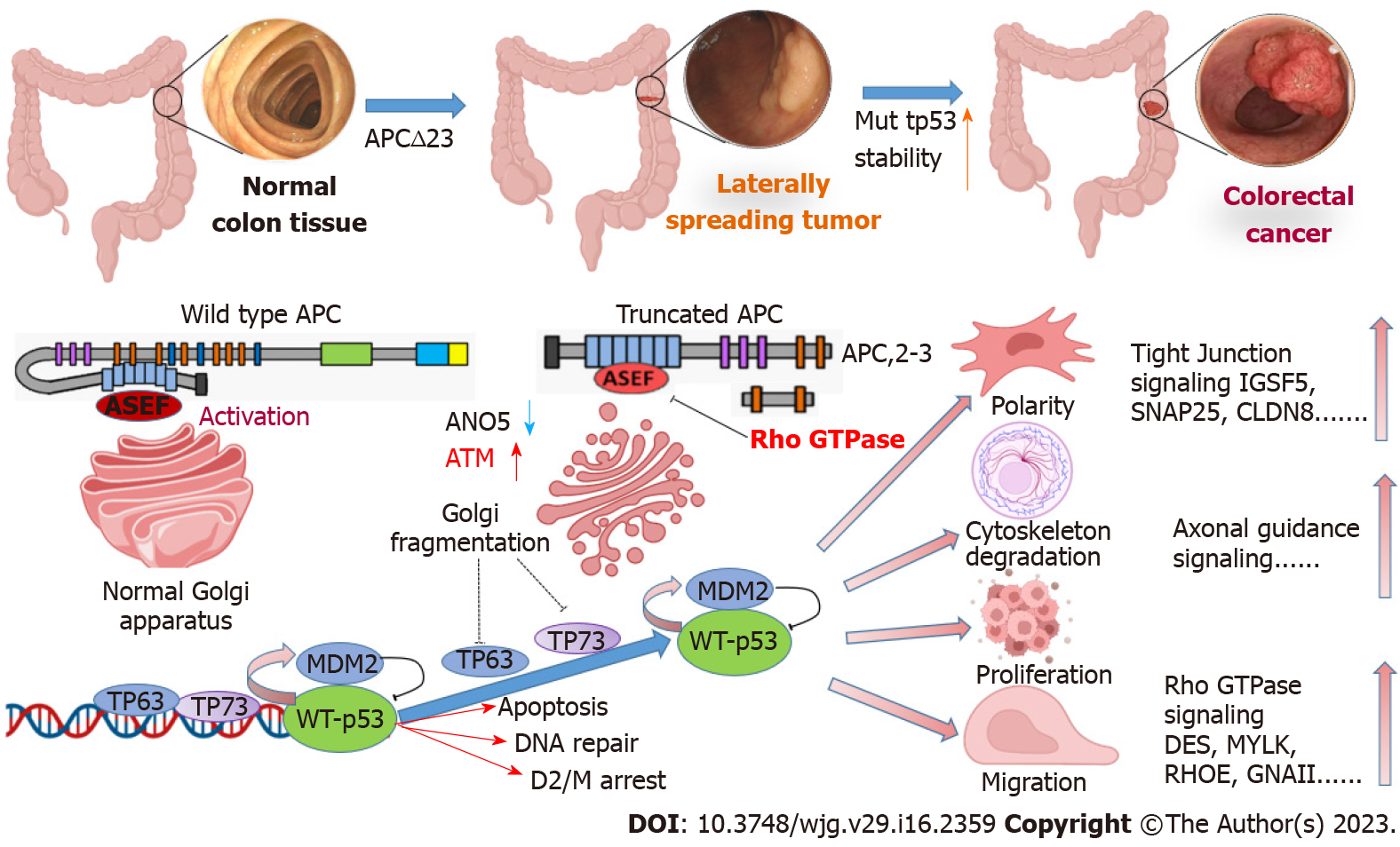
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of mechanism by which adenomatous polyposis coli-truncating mutations regulate P53 to promote laterally spreading tumor transition to colorectal cancer.
APC: Adenomatous polyposis coli; ASEF: Adenomatous polyposis coli-stimulated guanine nucleotide exchange factor; ANO5: Anoctamin 5; ATM: Ataxia-telangiectasia mutation; TP: Tumor protein; IGSF5: Immunoglobulin superfamily member 5; SNAP25: Synaptosome associated protein 25; DES: Desmin; MYLK: Myosin light chain kinase; RHOE: Ras homolog gene family, member E; GNALL: G protein subunit alpha i1.
- Citation: Lu S, Jia CY, Yang JS. Future therapeutic implications of new molecular mechanism of colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(16): 2359-2368
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i16/2359.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i16.2359