Published online Mar 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i11.1735
Peer-review started: December 3, 2022
First decision: December 19, 2022
Revised: January 2, 2023
Accepted: March 3, 2023
Article in press: March 3, 2023
Published online: March 21, 2023
Processing time: 103 Days and 21.4 Hours
Colorectal cancer is a frequent cause of cancer-related mortality in patients with lymph node or distant metastases. Pericolonic tumor deposits (TDs) are considered prognostically distinct from lymph node metastases.
To investigate risk factors for extranodal TDs in stage III colon cancer.
This was a retrospective cohort study. We selected 155 individuals diagnosed with stage III colon cancer from the database of the Cancer Registry of the Tri-Service General Hospital. The patients were allocated into the groups with/without N1c. Multivariate Cox regression analysis and Kaplan-Meier method were done. The primary outcomes investigate the association between the covariates and extranodal TDs, and prognostic significance of the covariates regarding the survival.
There were 136 individuals in the non-N1c group and 19 individuals in the N1c group. Patients with lymphovascular invasion (LVI) had a higher risk of TDs. Overall survival rates of patients with and without LVI were 6.64 years and 8.61 years, respectively (P = 0.027). The N1c patients without LVI had higher overall survival than those who with LVI (7.73 years vs 4.42 years, P = 0.010).
Patients having stage III colon cancer with LVI have a higher probability of having TDs than those with stage III colon cancer without LVI. Stage III colon cancer patients with TDs and LVI could have poor prognosis and outcome.
Core Tip: Tumor deposits has been associated with poor outcome in patient with colorectal cancer. In our study, we investigated the risk factors predicting extranodal tumor deposits in stage III colorectal cancer patients according to the new American Joint Committee on Cancer TNM staging and helped pathologist not to miss the subgroup of N1c patients. Sincerely, we look forward to more robust therapeutic approach and closer survivorship planning for this subgroup of high-risk stage III colon cancer patients in the future.
- Citation: Jhuang YH, Chou YC, Lin YC, Hu JM, Pu TW, Chen CY. Risk factors predict microscopic extranodal tumor deposits in advanced stage III colon cancer patients. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(11): 1735-1744
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i11/1735.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i11.1735
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the fourth most common cancer and the fifth most frequent cause of cancer-related mortalities worldwide[1]. The International Union Against Cancer/American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) TNM classification has been utilized for cancer staging[2] and its function has aimed to determine patient care and treatment, as well as to predict cancer prognosis. The TNM staging system is revised every few years as knowledge of cancer continually expands[3].
A pericolonic tumor deposit (TD) is a perineural, peri- or intra-vascular tumor extending beyond the muscularis mucosae. It is different from lymph node metastases and should not be contemplated its prognostic value[4-7]. The disease-free survival influence of even small pericolonic TDs is significant[8], recommending that pericolonic TDs of all volumes should be contemplated clinically important[7,9,10].
The TNM classification of pericolonic TDs as lymph node metastases or sporadic tumor extensions is perhaps inaccurate. The quantity and greatest dimension of pericolonic TDs should be stated separately from lymph node metastases. In the seventh edition of the AJCC TNM staging system, TD was classified as pN1c in stage III colon cancer patients without lymph node metastasis[11].
Extranodal deposits are a different form of metastatic disease in patients with CRC. The relationship with vascular invasion and earlier development of metastases probably implies that a significant information of extranodal deposits may represent blood-borne spread. Some researchers have indicated worse prognosis of patients with TDs and have claimed that TDs should be categorized as M classification[6,9].
In this single-institution retrospective study, we investigate the risk factors predicting extranodal TDs in stage III CRC patients according to the new (eighth edition) AJCC TNM staging. In regard to possible poor prognosis of stage III CRC patient with factors predicting extranodal TDs, adjust the adjuvant chemotherapy regimens with target therapy or immunotherapy might be considered.
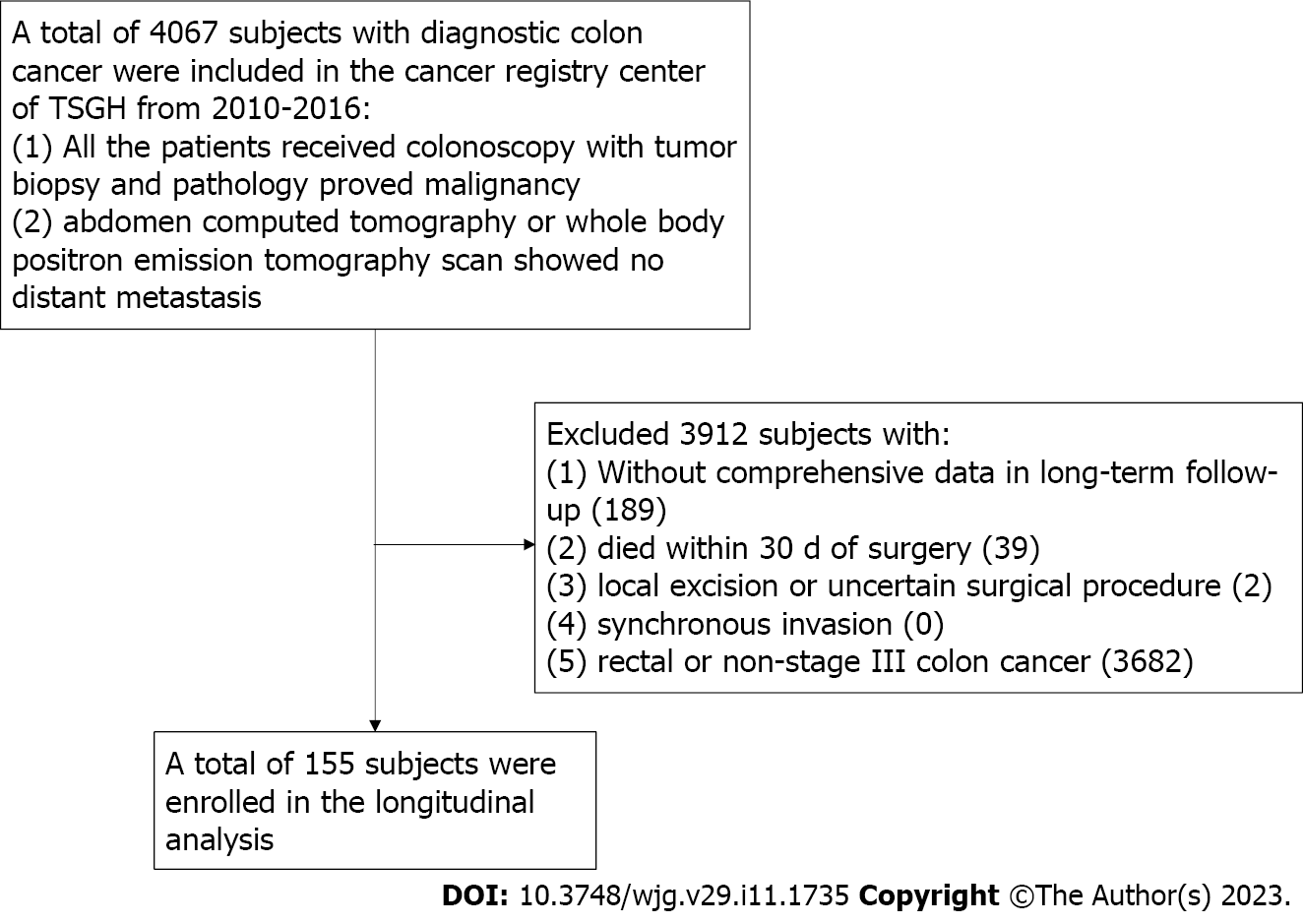
All data were obtained retrospectively from the Cancer Registry database of the Tri-Service General Hospital (TSGH), Taipei, Taiwan. The cancer registry of the TSGH included 4067 patients with CRC from 2010 to 2016. The inclusion criteria were described as follows: (1) All the patients received colonoscopy with tumor biopsy and pathology proved malignancy; and (2) abdomen computed tomography or whole body positron emission tomography scan showed no distant metastasis. All patients received regular postoperative follow-up at our colorectal outpatient department. The exclusion criteria were described as follows: (1) Lack of comprehensive data in long-term follow-up; (2) death within 30 d of surgery; (3) local excision or uncertain procedure; (4) synchronous tumors; and (5) rectal cancer or non-stage III colon cancer patients (Figure 1). A total of 155 individuals diagnosed with stage III colon cancer from a single institution of a medical center were enrolled. All patients signed informed consents, and the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of TSGH permitted our study (TSGHIRB No. C202005173). Our study was conducted only for medical research and was in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
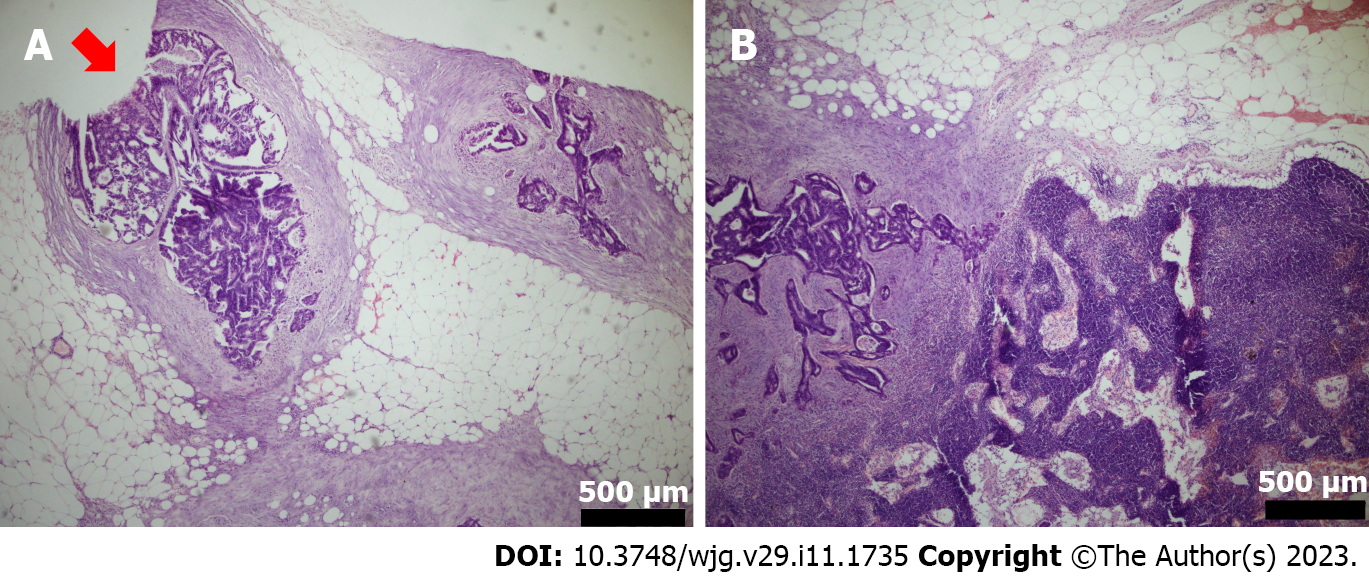
TDs, also called extranodal TDs, were defined as tumor cells in the pericolic or perirectal fat tissue without proof of residual lymph node tissue in the relevant lymphatic system of the primary tumor site[6]. According to the latest TNM 8th staging system announced in 2016, aiming to eliminate any lesion with identifiable structures pointing towards LN metastasis, extramural venous invasion or perineural invasion[12]. The hematoxylin eosin (HE) staining of extra-nodal TDs (N1c group) showed that there are nodules made up of tumor cells found in the structures near the colon that do not seem to be lymph nodes (Figure 2A). The HE staining of non-TDs (non-N1c group) showed that tumor cells revealed in regional lymph nodes (Figure 2B). A list of potential microscopic features that may be valuable to aid in the difference between tumor deposit and a positive lymph node was compiled and sent out for ranking with the virtual slides. The virtual slides were sent to three pathologists with a certain interest in gastrointestinal pathology for review. Each pathologist was asked to render an opinion of either tumor deposit or lymph node metastasis for each slide.
The covariates comprised age, gender, body mass index (BMI), cigarettes smoking and alcohol consumption habits, hypertension (HTN), diabetes mellitus (DM), neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR)[13], carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), CA 19-9, and tumor characteristics. The tumor characteristics included tumor location (right and left), T stage, mean tumor size, tumor type (ulcerative and polypoid), tumor grade (well, moderate, and poorly differentiated), epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) expression, and lymphovascular invasion (LVI). LVI was defined as tumor cells invading the lymphatic or blood vessels microscopically[14]. In our study, all specimens had been fixed immediately in formalin solution. For definite diagnosis, two pathologists resected our specimens for routine pathological examination independently by hematoxylin and eosin staining (H&E staining) and immunohistochemistry based on the eighth edition of the AJCC TNM system and the World Health Organization (WHO) criteria.
All data were analyzed using SPSS Statistics software (IBM Corp., Released 2016. IBM SPSS Statistics for MAC version 24.0. Armonk, NY, United States). Student’s t-test was used to analyze quantitative variables in terms of the mean with SD. The chi-square test was used to analyze the qualitative variables in terms of frequency and percentage. Multivariate Cox regression analysis was performed to investigate the association between the covariates and extranodal TDs. The Kaplan-Meier method was used to calculate the overall survival and disease-free survival rates. Statistical significance was set at P < 0.05.
We included 155 individuals with stage III colon cancer in our study; their clinicopathological characteristics are shown in Table 1. There were 136 (88%) individuals in the non-N1c group and 19 (12%) individuals in the N1c group. The mean age of the N1c and non-N1c groups was 66.8 years and 65.2 years, respectively. N1c was observed mainly in male patients. The other characteristics showed no significant difference between the N1c and non-N1c groups, except for LVI (P = 0.049).
| Item | N1c | Non-N1c | P value |
| Sample size (n) | 19 | 136 | |
| Gender | 0.08 | ||
| Male | 13 (68.4) | 64 (47.1) | |
| Female | 6 (31.6) | 72 (52.9) | |
| Mean age (yr) | 66.79 | 65.17 | 0.09 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.77 | 23.41 | 0.15 |
| Habit of smoking | 8 (42.1) | 46 (33.8) | 0.48 |
| Habit of alcoholic drinking | 4 (21.1) | 13 (9.6) | 0.13 |
| Hypertension | 6 (31.6) | 46 (33.8) | 0.85 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 4 (21.1) | 29 (21.3) | 0.98 |
| Neutrophil to Lymphocyte ratio | 4.33 | 4.62 | 0.42 |
| CEA (mg/dL) | 12.83 | 18.23 | 0.62 |
| CA 19-9 (mg/dL) | 23.61 | 29.14 | 0.20 |
| Tumor characteristics | |||
| Location | 0.27 | ||
| Right colon | 6 (9) | 61 (91) | |
| Left colon | 13 (14.8) | 75 (85.2) | |
| T stage | 0.90 | ||
| T1 | 1 (5.3) | 5 (3.7) | |
| T2 | 1 (5.3) | 12 (8.8) | |
| T3 | 16 (84.2) | 110 (80.9) | |
| T4a | 0 (0) | 4 (2.9) | |
| T4b | 1 (5.3) | 5 (3.7) | |
| Mean tumor size (cm) | 4.24 | 4.8 | 0.98 |
| Tumor type | 0.26 | ||
| Polypoid | 8 (42.1) | 76 (55.9) | |
| Ulcerative | 11 (57.9) | 60 (44.1) | |
| Tumor grade | 0.62 | ||
| Well | 0 | 5 (100) | |
| Moderate | 16 (13.3) | 104 (86.7) | |
| Poor | 3 (10.0) | 27 (90.0) | |
| EGFR | 17 (89.5) | 117 (86.0) | 0.68 |
| Lymphovascular invasion | 3 (15.8) | 53 (39.0) | 0.049 |
We investigated the association between the covariates and extranodal TDs using multivariate analysis (Table 2). There was no significant relationship between N1c and other confounding factors, such as age (HR = 1.03, 95%CI = 0.99-1.08), BMI (HR = 1.03, 95%CI = 0.68-1.04), HTN (HR = 0.87, 95%CI = 0.21-3.85), type II DM (HR = 0.69, 95%CI = 0.19-2.52), NLR (HR = 1.03, 95%CI = 0.92-1.15), CEA (HR = 1.00, 95%CI = 1.00-1.01), CA 19-9 (HR = 1.02, 95%CI = 0.99-1.04), and tumor characteristics. Notably, in stage III colon cancer, male patients (HR = 6.16, 95%CI = 1.24-30.10) with LVI (HR = 4.62, 95%CI = 1.17-18.33) had a higher risk of extranodal TDs.
| Item | Multivariable logistic regression | ||
| Exp (B) | 95%CI | P value | |
| Gender | |||
| Female | Reference | ||
| Male | 4.62 | (1.17-18.33) | 0.030 |
| Age | 1.03 | (0.99-1.08) | 0.190 |
| BMI | 0.84 | (0.68-1.04) | 0.110 |
| Habit of smoking | 0.92 | (0.27-3.07) | 0.890 |
| Habit of alcoholic drinking | 1.41 | (0.29-6.81) | 0.670 |
| Hypertension | 0.87 | (0.21-3.85) | 0.850 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 0.69 | (0.19-2.52) | 0.570 |
| Neutrophil to Lymphocyte ratio | 1.03 | (0.92-1.15) | 0.660 |
| CEA | 1.00 | (1.00-1.01) | 0.770 |
| CA 19-9 | 1.02 | (0.99-1.04) | 0.200 |
| Tumor characteristics | |||
| Location | |||
| Right colon | Reference | ||
| Left colon | 1.67 | (0.45-6.21) | 0.440 |
| T stage | |||
| Tumor size | 0.99 | (0.96-1.02) | 0.550 |
| Tumor type | |||
| Polypoid | Reference | ||
| Ulcerative | 1.75 | (0.62-4.92) | 0.290 |
| Tumor grade | 0.51 | (0.12-2.21) | 0.370 |
| EGFR | 1.05 | (0.20-5.48) | 0.950 |
| Lymphovascular invasion | 6.16 | (1.24-30.10) | 0.027 |
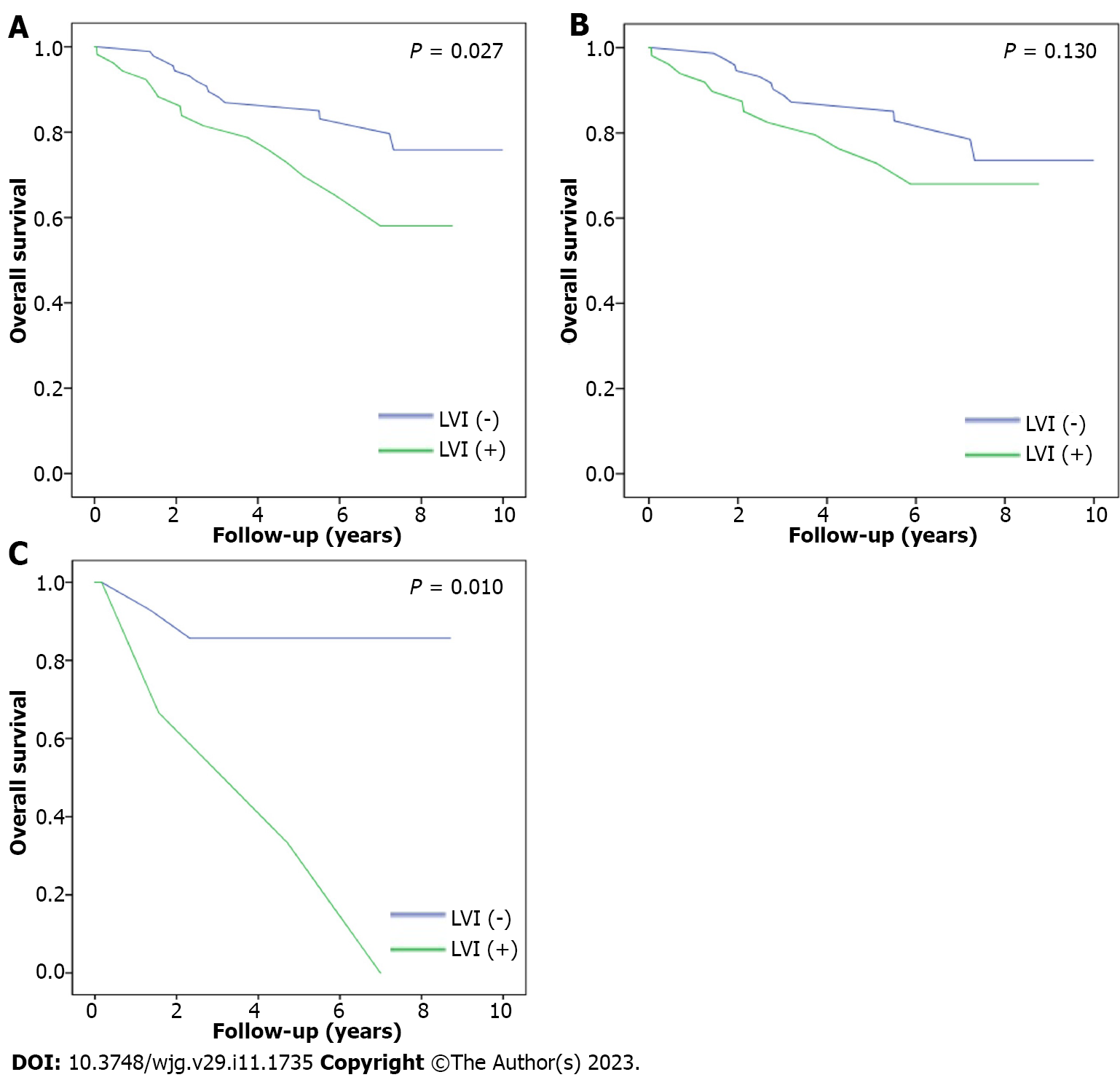
The overall survival rates of patients with and without LVI were 6.64 years and 8.61 years, respectively (P = 0.027, Figure 3A), indicating that patients without LVI had higher overall survival than those with LVI. Furthermore, we divided the patients into N1c and non-N1c groups for subgroup analysis in regards to the impact of LVI on overall survival. In the non-N1c group, the overall survival rates of the patients with and without LVI were 6.91 years and 8.56 years, respectively (P = 0.13, Figure 3B), whereas the overall survival rates of the individuals with and without LVI in the N1c group were 4.42 years and 7.73 years, respectively (P = 0.01, Figure 3C).
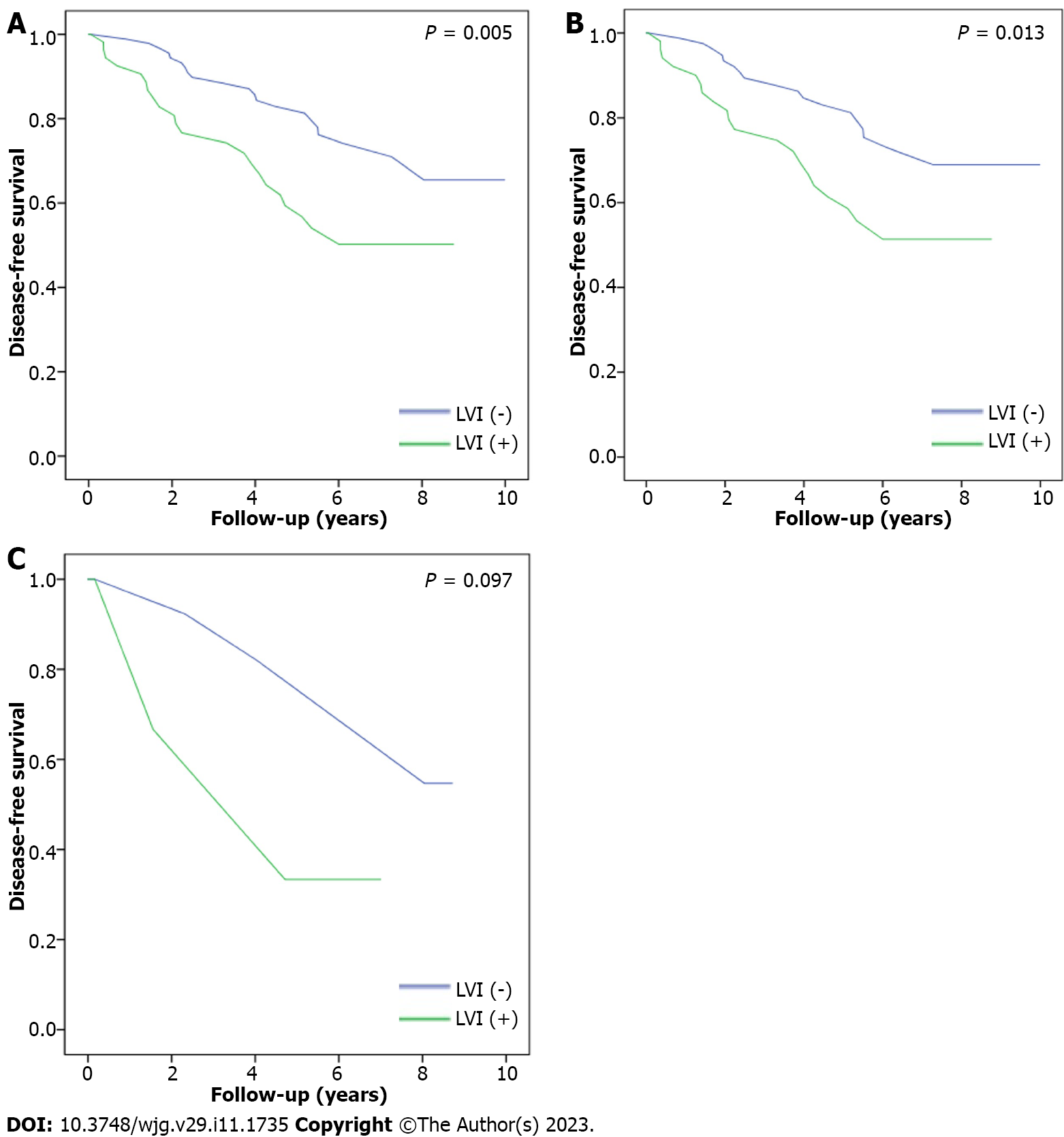
The disease-free survival rates of patients with and without LVI were 5.92 years and 8.16 years, respectively (P = 0.005, Figure 4A), indicating that patients without LVI had higher disease-free survival than those with LVI. As before, subgroup analysis of LVI was performed by patient grouping into N1c and non-N1c groups. The disease-free survival rates of the patients in the non-N1c group with and without LVI were 5.98 years and 8.18 years, respectively (P = 0.013, Figure 4B). However, in the N1c group, the disease-free survival rates were 4.42 years and 7.56 years, respectively, for patients with and without LVI (P = 0.097, Figure 4C).
Patients with stage III colon cancer are contemplated to have a clinically significant hazard of distant metastasis after surgical resection. However, individuals with stage III colon cancer have a spectrum of risk of progressive disease. Beside tumor stage, the NCCN identifies LVI, TDs, and perineural invasion as histopathological characters related with patient survival[15]. In addition, TDs have been comprehensively studied in colon cancer, with most studies representing that they are an essential prognostic variable[15]. Some studies have even stated that TDs and tumor budding are the only histological variables that individually predict tumor recurrence in stage III colon cancer and should be comprised as part of a regular comprehensive pathological risk appraisal. TDs are defined as a discrete focus of tumor within the lymph node drainage area of the primary carcinoma with no distinguishable lymph node[15].
TDs are defeined as extramural focal aggregates of cancer cells located in the peritumoral fatty tissue (either mesocolon or mesorectum), which have no continuity with the main tumor mass and are not associated with a lymph node[16]. However, there is still a debate about what TDs really are, as they usually share different morphologies that make their origin unclear[16]. Some studies believe that TDs simply represent a stage of the LVI and/or perineural invasion process during which malignant cells begin to proliferate, giving rise to distinct nodules of cancer[16] that have to be distinguished from the involved lymph nodes. Other studies believe that TDs either represent a sporadic tumor spread, a totally replaced lymph node (LN), venous invasion with extravascular extension, and/or less commonly, a small vessel or perineural invasion[17]. TDs are generally present in about 4.5%-45.0% of CRC patients[16], while their incidence looks to be greater in advanced and/or metastatic tumors[16]. Jin et al[17] demonstrated that about 10% of CRCs have TDs, and 2.5% of colon cancers and 3.3% of rectal cancers have TDs without positive LNs.
Interobserver variability exists among pathologists in interpreting TDs[17]. It is clear that the determination of TD remains subjective, and no single criterion or group of criteria are comprehensively used or agreed upon. However, knowledge of the potential challenges and possible solutions may help reduce interobserver variability. In our study, we used the multivariable Cox regression model to analyze characteristics, including age, sex, comorbidities, tumor location, tumor staging, and tumor markers, of the CRC patients. We showed that LVI could predict CRC patients with N1c component, and this could allow pathologists to pay more attention to this subgroup of patients.
LVI positivity, characterized by the extension of tumor cells into lymphatic and/or blood vessels, has long been recognized as a probable indicator of lymph node metastasis, prognostic indicator, and predictor of patient outcomes. Many studies have investigated the presence of LVI in CRC and have determined it to be a strong stage-independent prognostic marker[18]. Patients with LVI usually have a higher chance of disease progression and poorer prognosis[18]. On the other hand, in recent years, TDs have become a hotspot in colon cancer study. In the seventh and eighth editions of the AJCC staging system, TDs were included in the nodal staging[19]. TD patients without regional lymph node metastasis were correlated with other high-risk characters, because there was more LV and perineural invasion in this group. This finding correlates with histopathologic results in other studies because TDs were revealed to be of perineural origin in 77% of cases, intravascular origin in 83% of cases, and a combined perineural, perivascular, and intravascular origin in 40%[20].
In a recent systematic review and meta-analysis of stage I-IV CRC, TDs were always related with worse overall survival and disease-free survival[20]. One study stated that the survival curves of all patients in stages I-III with TDs were more similar to the survival curves of the stage IV than stage III patients, and patients with TDs in stages I-III showed similar mortality rates as stage IV patients[21]. Another up-to-date study has indicated that the presence of TD in individuals with stage III colon cancer is related with a 2.2-fold increased risk of developing disease recurrence[22]. In our study, the results reported that LVI could predict TDs in patients with stage III colon cancer. The subgroup of N1c stage III colon cancer patients with LVI showed poor prognosis regarding overall survival, while the non-N1c subgroup patients showed no significant difference.
Despite showing that the predicted risk factor of LVI makes the prognostic significance of TDs in stage III colon cancer patients more promising, there are still some limitations to the study. This is a retrospective study of observational data using a small sample of patients, the prevalence of N1c in colon cancer could as low as 1.59% in the previous study[23], which might result in statistical bias with inconsistent results between overall and disease-free survival. Further prospective studies with more patients involved might address our result more promising. There might also be systematic differences in the pathological evaluation of the surgical specimens, which may have biased the outcomes.
Patients with stage III colon cancer with LVI might be more likely to have TDs. Interobserver variability among pathologists and the multidisciplinary committee might at times influence consistent interpretation and reporting, and the frequent association between co-occurrence of TDs and LVI may postulate extra insight into the nature and derivation of TDs. Pathologist should not miss these subgroups of N1c patients, because TDs in combination with LVI could predict poor patient outcomes. Greater attention must be paid to the subject of TD positivity and prompt suitable risk stratification by considering a more robust therapeutic approach and closer survivorship planning for this subgroup of high-risk stage III colon cancer patients, who might be undertreated and require adjustment of adjuvant chemotherapy regimens. Amendment in the delivery of proper care to these patients may increase survival and should be an object of future quality ambition.
In the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) TNM staging system, tumor deposit (TD) was classified as pN1c in stage III colon cancer patients without lymph node metastasis, but extranodal deposits are a distinct form of metastatic disease in patients with colon cancer in some studies.
To conduct a retrospective study to investigate risk factors for extranodal TDs in stage III colon cancer.
We used SPSS Statistics software. Student’s t-test and the chi-square test were utilized to investigate quantitative variables and qualitative variables. Multivariate Cox regression analysis was performed to investigate the association between the covariates and extranodal TDs. The Kaplan-Meier method was utilized to analyze the overall survival and disease-free survival rates.
We selected 155 patients diagnosed with stage III colon cancer from the database of the Cancer Registry of the Tri-Service General Hospital retrospectively. The patients were categorized into the groups with/without N1c. Multivariate Cox regression analysis and Kaplan-Meier method were done. The primary outcomes investigate the association between the covariates and extranodal TDs, and prognostic significance of the covariates regarding the survival.
Patients with lymphovascular invasion (LVI) had a higher risk of TDs. Overall survival rates of patients with and without LVI were 6.64 years and 8.61 years, respectively. The N1c patients without LVI had higher overall survival than those who with LVI.
Stage III colon cancer patients with TDs and LVI could have poor prognosis and outcome.
Greater attention must be paid to the issue of TD. Amendment in the delivery of proper care to these patients may increase survival and should be a target of future quality ambition.
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Gastroenterology and hepatology
Country/Territory of origin: Taiwan
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B, B
Grade C (Good): C, C, C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Khefacha F, Tunisia; Wang P, China; Zhang Z, China S-Editor: Chen YL L-Editor: A P-Editor: Chen YL
| 1. | Weitz J, Koch M, Debus J, Höhler T, Galle PR, Büchler MW. Colorectal cancer. Lancet. 2005;365:153-165. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 862] [Cited by in RCA: 945] [Article Influence: 47.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Greene FL. Current TNM staging of colorectal cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2007;8:572-573. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 47] [Cited by in RCA: 57] [Article Influence: 3.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Quirke P, Williams GT, Ectors N, Ensari A, Piard F, Nagtegaal I. The future of the TNM staging system in colorectal cancer: time for a debate? Lancet Oncol. 2007;8:651-657. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 105] [Cited by in RCA: 119] [Article Influence: 6.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Belt EJ, van Stijn MF, Bril H, de Lange-de Klerk ES, Meijer GA, Meijer S, Stockmann HB. Lymph node negative colorectal cancers with isolated tumor deposits should be classified and treated as stage III. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17:3203-3211. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 60] [Cited by in RCA: 78] [Article Influence: 5.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Goldstein NS, Turner JR. Pericolonic tumor deposits in patients with T3N+MO colon adenocarcinomas: markers of reduced disease free survival and intra-abdominal metastases and their implications for TNM classification. Cancer. 2000;88:2228-2238. [PubMed] |
| 6. | Puppa G, Maisonneuve P, Sonzogni A, Masullo M, Capelli P, Chilosi M, Menestrina F, Viale G, Pelosi G. Pathological assessment of pericolonic tumor deposits in advanced colonic carcinoma: relevance to prognosis and tumor staging. Mod Pathol. 2007;20:843-855. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 87] [Cited by in RCA: 105] [Article Influence: 5.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Ueno H, Mochizuki H, Shirouzu K, Kusumi T, Yamada K, Ikegami M, Kawachi H, Kameoka S, Ohkura Y, Masaki T, Kushima R, Takahashi K, Ajioka Y, Hase K, Ochiai A, Wada R, Iwaya K, Nakamura T, Sugihara K. Actual status of distribution and prognostic impact of extramural discontinuous cancer spread in colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:2550-2556. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 40] [Cited by in RCA: 45] [Article Influence: 3.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Nagayoshi K, Ueki T, Nishioka Y, Manabe T, Mizuuchi Y, Hirahashi M, Oda Y, Tanaka M. Tumor deposit is a poor prognostic indicator for patients who have stage II and III colorectal cancer with fewer than 4 lymph node metastases but not for those with 4 or more. Dis Colon Rectum. 2014;57:467-474. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 38] [Cited by in RCA: 52] [Article Influence: 4.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Al Sahaf O, Myers E, Jawad M, Browne TJ, Winter DC, Redmond HP. The prognostic significance of extramural deposits and extracapsular lymph node invasion in colon cancer. Dis Colon Rectum. 2011;54:982-988. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 31] [Cited by in RCA: 35] [Article Influence: 2.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Tateishi S, Arima S, Futami K, Kawahara K, Tachikawa D, Naritomi K, Iwashita A. A clinicopathological investigation of "tumor nodules" in colorectal cancer. Surg Today. 2005;35:377-384. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 40] [Cited by in RCA: 45] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Edge SB, Compton CC. The American Joint Committee on Cancer: the 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17:1471-1474. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5537] [Cited by in RCA: 6447] [Article Influence: 429.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Amin MB, Greene FL, Edge SB, Compton CC, Gershenwald JE, Brookland RK, Meyer L, Gress DM, Byrd DR, Winchester DP. The Eighth Edition AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: Continuing to build a bridge from a population-based to a more "personalized" approach to cancer staging. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67:93-99. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2341] [Cited by in RCA: 4372] [Article Influence: 546.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (4)] |
| 13. | Haram A, Boland MR, Kelly ME, Bolger JC, Waldron RM, Kerin MJ. The prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in colorectal cancer: A systematic review. J Surg Oncol. 2017;115:470-479. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 104] [Cited by in RCA: 144] [Article Influence: 18.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Hogan J, Chang KH, Duff G, Samaha G, Kelly N, Burton M, Burton E, Coffey JC. Lymphovascular invasion: a comprehensive appraisal in colon and rectal adenocarcinoma. Dis Colon Rectum. 2015;58:547-555. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 37] [Cited by in RCA: 38] [Article Influence: 3.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Landau MA, Zhu B, Akwuole FN, Pai RK. Histopathological Predictors of Recurrence in Stage III Colon Cancer: Reappraisal of Tumor Deposits and Tumor Budding Using AJCC8 Criteria. Int J Surg Pathol. 2019;27:147-158. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 18] [Article Influence: 2.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Athanasakis E, Xenaki S, Venianaki M, Chalkiadakis G, Chrysos E. Newly recognized extratumoral features of colorectal cancer challenge the current tumor-node-metastasis staging system. Ann Gastroenterol. 2018;31:525-534. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Jin M, Frankel WL. Lymph Node Metastasis in Colorectal Cancer. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2018;27:401-412. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 54] [Cited by in RCA: 100] [Article Influence: 12.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Aktekin A, Özkara S, Gürleyik G, Odabaşi M, Müftüoğlu T, Sağlam A. The Factors Effecting Lymphovascular Invasion in Adenocarcinoma of the Colon and Rectum. Indian J Surg. 2015;77:314-318. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Zheng P, Chen Q, Li J, Jin C, Kang L, Chen D. Prognostic Significance of Tumor Deposits in Patients With Stage III Colon Cancer: A Nomogram Study. J Surg Res. 2020;245:475-482. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 3.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 20. | Wong-Chong N, Motl J, Hwang G, Nassif GJ Jr, Albert MR, Monson JRT, Lee L. Impact of Tumor Deposits on Oncologic Outcomes in Stage III Colon Cancer. Dis Colon Rectum. 2018;61:1043-1052. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 35] [Article Influence: 5.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Lino-Silva LS, Anchondo-Núñez P, Chit-Huerta A, Aguilar-Romero E, Morales-Soto J, Salazar-García JA, Guzmán-López CJ, Maldonado-Martínez HA, Meneses-García A, Salcedo-Hernández RA. Stage I-III colon cancer patients with tumor deposits behave similarly to stage IV patients. Cross-section analysis of 392 patients. J Surg Oncol. 2019;120:300-307. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 16] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 2.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Pricolo VE, Steingrimsson J, McDuffie TJ, McHale JM, McMillen B, Shparber M. Tumor Deposits in Stage III Colon Cancer: Correlation With Other Histopathologic Variables, Prognostic Value, and Risk Stratification-Time to Consider "N2c". Am J Clin Oncol. 2020;43:133-138. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 43] [Article Influence: 8.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Simon HL, Reif de Paula T, Spigel ZA, Keller DS. N1c colon cancer and the use of adjuvant chemotherapy: a current audit of the National Cancer Database. Colorectal Dis. 2021;23:653-663. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |