Published online Mar 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i9.961
Peer-review started: February 11, 2021
First decision: March 28, 2021
Revised: April 25, 2021
Accepted: January 29, 2022
Article in press: January 29, 2022
Published online: March 7, 2022
Processing time: 384 Days and 10.5 Hours
Crohn’s disease (CD) is complicated by perianal fistulas in approximately 20% of patients. Achieving permanent fistula closure remains a challenge for physicians. An association between serum anti-tumor necrosis factor-α concentrations and clinical outcomes in patients with CD has been demonstrated; however, little information is available on serum adalimumab (ADA) concentrations and remission of perianal fistulas in such patients.
To study the relationship between serum ADA concentrations and clinical remission of CD-associated perianal fistulas.
This cross-sectional study of patients with CD-associated perianal fistulas treated with ADA was performed at four French hospitals between December 2013 and March 2018. At the time of each serum ADA concentration measurement, we collected information about the patients and their fistulas. The primary study endpoint was clinical remission of fistulas defined as the absence of drainage (in accordance with Present’s criteria), with a PDAI ≤ 4, absence of a seton and assessment of the overall evaluation as favorable by the proctologist at the relevant center. We also assessed fistula healing [defined as being in clinical and radiological (magnetic resonance imaging, MRI) remission] and adverse events.
The study cohort comprised 34 patients who underwent 56 evaluations (patients had between one and four evaluations). Fifteen patients had clinical remissions (44%), four of whom had healed fistulas on MRI. Serum ADA concentrations were significantly higher at evaluations in which clinical remission was identified than at evaluations in which it was not [14 (10-16) vs 10 (2-15) μg/mL, P = 0.01]. Serum ADA concentrations were comparable at the times of evaluation of patients with and without healed fistulas [11 (7-14) vs 10 (4-16) μg/mL, P = 0.69]. The adverse event rate did not differ between different serum ADA concentrations.
We found a significant association between high serum ADA concentrations and clinical remission of CD-associated perianal fistulas.
Core Tip: Perianal fistulas (PAFs) are a complication of Crohn’s disease (CD) in approximately 20% of patients. Adalimumab (ADA) was shown to treat CD-associated PAFs; however, little information is available on serum ADA concentrations and their remission. We performed a cross-sectional study at four hospitals in France to investigate this relationship, including 34 patients with 56 evaluations. Fifteen patients had clinical remission (44%). Serum ADA concentrations were significantly higher in evaluations showing clinical remission compared to those without. Thus, ADA serum concentrations that are required for PAF remission should be higher compared with the previously described concentrations associated with luminal remission.
- Citation: Sirmai L, Pelletier AL, Gault N, Zallot C, Bouguen G, Bouchard D, Roland Nicaise P, Peyneau M, Sironneau S, Bittencourt MDC, Petitcollin A, Fernandez P, Roblin X, Siproudhis L, Abramowitz L. Relationship between clinical remission of perianal fistulas in Crohn’s disease and serum adalimumab concentrations: A multi-center cross-sectional study. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(9): 961-972
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i9/961.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i9.961
Crohn’s disease (CD) is complicated by perianal fistulas (PAFs) in approximately 20% of patients and these PAFs can severely and negatively affect patients’ quality of life[1]. Treatment of CD-associated PAFs was revolutionized by the advent of anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α antibodies[2]. A meta-analysis of treatment with adalimumab (ADA), a TNF-α blocker, found that complete PAF closure occurred in 36% of patients with CD-associated fistulas (95%CI: 0.31-0.41) and partial responses in 31% (95%CI: 0.031-0.61)[3]. Its efficacy is better in anti-TNF-α-naive patients but it can also be effective after infliximab failure[4]. Adding surgical drainage with a seton has been shown to be superior to anti-TNF-α alone, with better responses and fewer recurrences[5,6]. Resolution of complex PAFs takes longer and timing of seton withdrawal depends on the effectiveness of the medical treatment and findings on clinico-radiological evaluation[5]. However, achieving permanent fistula closure remains a challenge for physicians.
Optimization of anti-TNF-α therapy (increasing the drug dosage and/or shortening the intervals between injections) is advised in patients with confirmed active disease, good compliance, and subtherapeutic drug serum concentrations in the absence of anti-drug antibodies[7]. Adding an immunosuppressive drug (in combination therapy) should also be considered[8]. Thus, optimization of treatment on the basis of anti-TNF-α (including ADA) and antibody serum concentrations has been evaluated[9-11]. Retrospective trials have suggested that higher target serum infliximab concentrations are required to reach remission in patients with CD-associated PAF than in those with luminal disease only[12-16]. Two recent retrospective trials also suggested that higher target serum ADA concentrations are associated with remission in patients with CD-associated PAF[15,16]. However, in those studies the evaluation criteria were mostly clinical, the studies were not confined to assessment of ADA, and they were small single-center studies. Our primary objective was, therefore, to study the relationship between serum ADA concentrations and clinical remission of CD-associated PAFs.
This cross-sectional study was conducted in four French centers between December 2013 and March 2018. Patients with at least one active CD-associated PAF at the time of ADA initiation, or who developed a PAF while being treated with ADA (thus requiring optimization of ADA), whose serum ADA concentrations were measured at least once during follow-up (induction or treatment maintenance) were considered eligible. The PAFs could be associated with upper, ileal, colonic, or rectal lesions. Patients who were eligible on the basis of the above criteria were included irrespective of the durations of their PAFs and ADA treatment, associated or previously received treatments, and surgical procedures performed, particularly the closure technique (glue, plug, or rectal advancement flap after removal of a seton). ADA treatment could have been optimized or not and an immunosuppressive drug may also be used in combination therapy. Pregnant or breastfeeding women and patients with a history of proctectomy or undrained abscesses were excluded.
Data were collected between October 2017 and March 2018 using a standardized paper collection file. The clinical data collected at each evaluation were as follows: remission of any fistula, perineal disease activity index (PDAI) score, presence of associated lesions in the rectum or anus, durations of PAFs and seton drainage, Harvey Bradshaw score, ADA dosage and duration of treatment, associated treatment, and adverse events. Patient characteristics collected and assessed were as follows: treatment center; age; sex; body mass index; co-morbidities; smoking status; Montreal classification; and medical and surgical history (abdominal surgery, number of fistula(e); simple, complex, or vaginal involvement; and surgical treatments for the PAF, including the type of closure performed). Pelvic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and colonoscopy findings obtained within 3 mo of clinical evaluation and in the absence of more recent changes in treatment were collected if performed, which was at the discretion of the physician. MRI images were reassessed by a single expert radiologist (Fernandez P). ADA and anti-ADA antibody serum concentrations were measured in the laboratories of each investigating center using a standardized drug-sensitive ELISA test (Lisa Tracker; Theradiag, France) or equivalent immunologic test[17]. If more than one serum ADA concentration was available, the trough concentration (Day 13 or 14 after ADA injection) was used, as recommended in a recent published study[18]. Serum ADA concentrations were measured systematically or at the times of clinical evaluations in accordance with the standard procedures at the participating centers. Some serum ADA concentrations were reported as greater than 16 μg/mL; therefore, all measures were recorded to a maximum of 16 μg/mL.
The primary study endpoint was clinical remission of PAF, defined as the absence of drainage (both spontaneous and after soft pressure on the orifice by the clinician, in accordance with Present’s criteria[2]), with a PDAI ≤ 4, absence of a seton and assessment of the overall evaluation as favorable by the proctologist at the relevant center. This outcome was defined after agreement by experts from the Proctology Research Group of the French National Society of Colo-Proctology, the investigators being members of these groups. If one of the above criteria were absent, the PAF was described as active. Favorable evaluation by the proctologist was defined as no inflammation of external(s) and internal(s) orifice(s) and absence of current or new associated anal lesions (stenosis, ulceration, or fistulous branching) that had developed after introduction of ADA or the most recent change in modality of medical or surgical treatment. In patients with multiple CD-associated PAFs, all lesions had to have resolved to conclude the evaluation was favorable. The clinical remission criteria were reviewed at all evaluations.
The secondary study endpoint was healing, which was defined as clinical remission (as described above) plus radiological healing on pelvic MRI, this definition having been reached by agreement of the Proctology Research Group’s experts and as reported by other research groups[19,20]. The full criteria were absence of hypersignal T2 or enhancement after gadolinium T1 injection, absence of any abscess, and absence of rectal inflammation.
ADA optimization was defined as shortening of the interval between injections to 7 d or increasing the dosage of injections to 80 mg (or both).
Combination therapy was defined as addition of an immunosuppressive drug (thiopurine or methotrexate) to ADA.
Endoscopic luminal remission was defined by a score of less than 6 on the CD Endoscopic Index of Severity.
Clinical luminal remission was defined by a Harvey Bradshaw score of less than 4.
ADA tolerance was assessed on the basis of occurrence of adverse events.
The following definitions apply to terms used in the remainder of this article. Immunization was defined as undetectable serum ADA concentrations and the presence of anti-ADA antibodies in concentrations above 20 ng/mL[21].
Complex PAFs were defined as PAF branched in two or more directions or presence of ramifications or diverticula[5,22].
PDAI scores are based on the presence of fistula drainage, pain, and its effects on activity, limitations on sexual activity, degree of induration, and type of fistula. A score greater than 4 indicates definite active disease.
First, patients’ characteristics are reported according to occurrence of clinical remission. Quantitative variables are presented as median and interquartile range and categorical variables as frequencies and percentages. The overall number and proportion of patients achieving clinical remission, achieving healing, and having at least one adverse event were determined.
The distribution of durations of PAFs and drainage, ongoing treatment, and serum albumin and C-reactive protein concentrations was further explored according to the clinical remission status at the time of evaluation.
The relationship between serum ADA concentrations and each of the following was assessed: clinical remission, healing, endoscopic luminal remission, clinical luminal remission, treatment optimization, and treatment with combination therapy. These relationships were studied using univariate generalized estimating equations models, considering an evaluation as the statistical unit (some patients having undergone several evaluations).
Association between serum ADA concentrations at each visit and clinical remission was also adjust on the duration of treatment.
All analyses were performed using R version 3.2.0. All tests were two-tailed, and the level of statistical significance was set at P = 0.05.
Of the 45 patients who were screened for inclusion, 34 were found to be eligible (9 from Paris, 8 from Rennes, 13 from Nancy, and 4 from Saint-Etienne), 16 of whom were women (47%). The remaining 11 patients were excluded for the following reasons: three for wrong diagnoses (two anal stenosis, one ulcerative colitis), three because they had undergone proctectomy, one was a minor, one had an undrained abscess, and three had PAFs that had resolved. Patients had between one and four evaluations (total of 56 evaluations), 50% of them having only one evaluation. Three of the 56 evaluations were performed during induction of ADA treatment.
Overall, 44% of the patients (n = 15) achieved clinical remission. Pelvic MRI was available for 23 of the 34 patients (56%) and showed that 17% (n = 4) had radiological evidence of healing. Of the patients in clinical remission, 44% had radiological evidence of healing.
Table 1 summarizes the characteristics of the participants that were collected at the first evaluation. Most of these characteristics were comparable between patients who achieved and did not achieve clinical remission (Table 1), particularly smoking status (43% vs 47%) and previous treatment with biotherapies including infliximab (47% vs 53%). More patients’ treatment was optimized at the first evaluation in patients who achieved clinical remission than in those who did not (60% vs 42%). Patients who achieved clinical remission tended to have fewer complex PAFs (73% vs 89%) and vaginal PAFs (7% vs 21%) and they had colonic lesions less frequently (33% vs 42%) Patients who achieved clinical remission tended to have undergone more fistula closure procedures than those who did not achieve remission (33% vs 16%).
| Clinical remission, n (%) unless otherwise specified | ||
| No, n = 19 | Yes, n = 15 | |
| Female sex | 10 (53%) | 6 (40%) |
| Age (yrs), Med [IQR] | 34 [27-38] | 35 [23-44] |
| BMI, Med [IQR] | 28 [19-32] | 22 [20-23] |
| Number of comorbidities1, Med [IQR] | 0 [0-1] | 0 [0-1] |
| Active smoking, 1 MD | 9 (47%) | 6 (43%) |
| Crohn’s disease phenotype (Montreal L) | ||
| Terminal ileum | 3 (16%) | 4 (27%) |
| Colon | 8 (42%) | 5 (33%) |
| Ileo-colon | 8 (42%) | 5 (33%) |
| Upper digestive tract | 0 (0%) | 1 (7%) |
| Crohn’s disease phenotype (Montreal B) | ||
| Non-stricturing, non-penetrating | 12 (63%) | 8 (53%) |
| Stricturing | 4 (21%) | 2 (13%) |
| Penetrating | 2 (11%) | 2 (13%) |
| Stricturing + penetrating | 1 (5%) | 3 (20%) |
| Number of fistulas, Med [IQR] | 2 [1-2] | 2 [1-2] |
| Complex fistula | 17 (89%) | 11 (73%) |
| Vaginal fistula | 4 (21%) | 1 (7%) |
| Previous treatment with infliximab | 10 (53%) | 7 (47%) |
| Previous treatment with another anti-TNF-α2 | 10 (53%) | 7 (47%) |
| Previous treatment with another form of biotherapy3 | 10 (53%) | 7 (47%) |
| Previous treatment with combination therapy | 12 (63%) | 5 (33%) |
| Previous abdominal surgery | ||
| No | 14 (74%) | 11 (73%) |
| Appendicectomy | 0 (0%) | 2 (13%) |
| Ileocecal resection | 4 (21%) | 2 (13%) |
| Colectomy | 1 (6%) | 0 (0%) |
| Previous fistulotomy | 4 (21%) | 6 (40%) |
| Previous seton | 18 (95%) | 13 (87%) |
| Previous flattening of abscesses | 8 (42%) | 10 (67%) |
| Previous closure techniques | 3 (16%) | 5 (33%) |
| Previous glue | 2 (11%) | 4 (27%) |
| Previous plug | 0 (0%) | 1 (7%) |
| Previous rectal advancement flap | 1 (5%) | 0 (0%) |
| Optimization at first visit | 8 (42%) | 9 (60%) |
| Combination therapy (with methotrexate or thiopurine) at first visit | 12 (63%) | 5 (33%) |
| Combination therapy and/or optimization at first evaluation | 15 (79%) | 9 (60%) |
None of the six patients who achieved remission and underwent more than one evaluation relapsed. These evaluations took place between 3 mo and 4 years after the first evaluation. All patients in clinical remission from PAF were in luminal remission (established by clinical and endoscopic evaluation), whereas half of the patients who did not achieve clinical remission from PAFs had luminal activity. Of the 19 patients with active disease, three had immunization status regarding ADA, five had undrained branches detected by MRI indicating insufficient surgical treatment, and six had low serum ADA concentrations (< 4 μg/mL) that could probably have benefited from optimization. The remaining five patients may have truly failed ADA treatment after 6 mo of well-conducted treatment.
Five patients (14.7%) had at least one adverse event leading to ADA discontinuation. Two of them were in the clinical remission group (pancytopenia and joint pain of no definite cause) and the remaining three in the activity group (axonal neuropathy attributed to ADA and digestive, pulmonary, and ganglionic tuberculosis; vertigo; and joint pain).
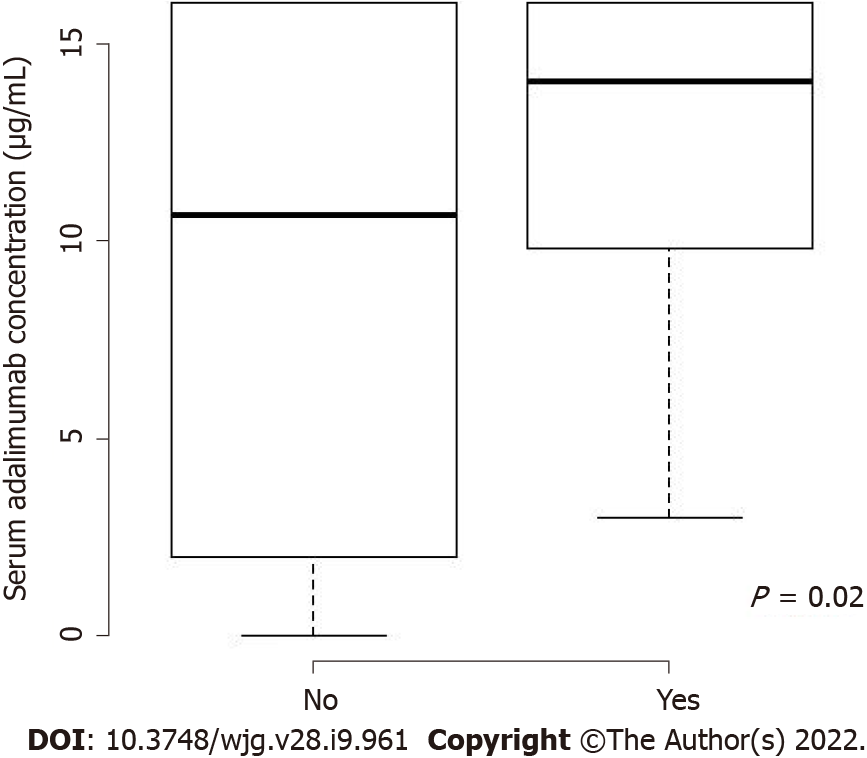
Median serum ADA concentrations were significantly higher in assessment visits of patients in clinical remission than in those not in clinical remission [14 (10-16) vs 10 (2-15) μg/mL, P = 0.02 after adjustment on the duration of treatment] (Figures 1 and 2), with an area under the ROC curve of 65.6%. Clinical remission was not identified in the three evaluations of patients with immunization status regarding ADA.
The duration of treatment with ADA tended to be longer in the clinical remission than in the non-clinical remission group (37 vs 12 mo). The median duration of drainage with a seton was 8 mo in the clinical remission group compared with 9 mo in the non-clinical remission group (Table 2). The median duration of PAFs tended to be longer in the clinical remission than no clinical remission group (53 mo vs 12 mo) (Table 2).
| Clinical remission, n (%) unless otherwise specified | ||
| No, n = 34 | Yes, n = 22 | |
| PAF duration (Time from fistula diagnosis to date of visit) in mo, Med [IQR] | 12 [8-23.5] | 53.5 [32.75-81.75] |
| Drainage duration (Time from seton setting down to date of visit) in mo, Med [IQR] | 9 [4.75-17] | 8 [4-19] |
| Combination therapy (with methotrexate or thiopurine) | 23 (68%) | 7 (32%) |
| Optimization | 19 (56%) | 14 (64%) |
| Serum concentrations of ADA (μg/mL), Med [IQR] | 10.7 [2.4-14.7] | 14.1 [9.8-16] |
| C reactive protein (mg/L), Med [IQR] | 2.7 [0.07-15.25] | 0.9 [0-1.8] |
| Serum albumin (g/L), Med [IQR] | 42 [38.25-47.3] | 43 [41.85-44.25] |
| Length of treatment by ADA in mo, Med [IQR] | 12 [6-34.75] | 37.5 [23.75-46.75] |
Median serum ADA concentrations did not differ significantly between evaluations in which healing (clinical and MRI remission) was identified and those in which it was not [11 (7-14) vs 10 (4-16) μg/mL, P = 0.69].
Serum ADA concentrations tended to be higher in patients whose treatment was optimized than in those whose treatment was not optimized [14 (5-16) μg/mL vs 10 (4-13) μg/mL, P = 0.20] and in patients receiving combination therapy than in those receiving ADA alone [12 (5-16) μg/mL vs 11 (5-14) μg/mL, P = 0.11]. Neither of these differences was statistically significant.
Median serum ADA concentrations tended to be higher in patients with endoscopic luminal remission and in those with clinical luminal remission than in those without it [12 (6-16) μg/mL vs 2 (1-4) μg/mL, and 14 (10-16) μg/mL vs 4.2 (1-11) μg/mL, respectively].
In this study, we found higher median serum ADA concentrations in patients who were in clinical remission of CD-associated PAFs than in those with active disease, the higher concentration not being associated with a higher incidence of adverse events. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first multicenter study dedicated to investigating the relationship between serum ADA concentrations and remission of CD-associated PAFs. Our definition of healing of PAFs included clinical and MRI criteria, as recently recommended[5,20,22,25].
Our findings suggest that remission of CD-associated PAFs requires higher serum concentrations of ADA than those previously reported for resolution of luminal disease (between 4.5 and 12 μg/mL based on results of clinical trials)[9,10]. The high serum concentrations that we found to be associated with clinical remission seem to be more frequently achieved through optimization of ADA dosage or combination therapy (or both).
Serum ADA concentrations have shown considerable variability and overlap between patients with and without clinical remission, as previously described[9]. It is likely that not all patients need to reach these high concentrations. For patients not achieving remission, we suggest measuring serum ADA concentrations and antibodies to exclude immunogenicity issue. Optimizing ADA dosage or adding combination therapy (or both) should be considered, even if we do not have yet a concentration to target.
In our study, patients with active lesions had more complex PAFs (89% vs 73%) and more vaginal fistulas, indicating the severity of the disease. No patients who achieved remission of PAFs had colorectal activity, highlighting the importance of achieving luminal remission when managing PAFs.
Four of the 23 patients (56% of the whole cohort) who had an MRI in our study achieved healing (17%).
Our low rate of healing of PAFs (clinical plus MRI remission) is likely attributable to our high rate of complex PAFs, the well-known delay between MRI remission compared with clinical remission (approximately 12 mo)[23], given that some follow up data were missing, and the fact that 44% of our patients did not undergo MRI evaluation.
We found no significant difference in serum ADA concentrations according to healing status [11 (7-14) μg/mL vs 10 (4-16) μg/mL, P = 0.69]. We think the lack of statistical significance is attributable to our small sample size, and our low rate of healing of PAFs, likely due to the accuracy of this robust criteria.
We found that the PAF duration was longer in patients with PAF activity than in those in remission (53.5 vs 12 mo), which likely reflects failure of medical or surgical (or both) treatment.
The three patients with anti-ADA antibodies and undetectable serum ADA had clinically active disease, which is consistent with the findings of a previous study that showed that the presence of anti-TNF-α antibodies is a risk factor for disease activity and recurrence[24].
Recently, two retrospective trials[15,16] were performed to assess the relationships between concentrations of anti-TNF medications, including ADA, and outcomes of CD-associated PAFs. Their results are consistent with ours: Strik et al[15] (19 patients treated with ADA) found significantly higher median serum ADA concentrations in patients with closed PAFs than in those with active PAFs [7 (6-11) μg/mL vs 5 (2-6) μg/mL, P = 0.003]. Additionally, Plevris et al[16] (35 patients treated with ADA) found significantly higher median ADA concentrations in individuals with healed fistulas than in those with unhealed fistulas (12.6 μg/mL vs. 2.7 μg/mL; P < 0.01).
Of note, our patients’ serum ADA concentrations were much higher than in these two studies. Possible explanations for this discrepancy are that more of our patients were receiving combination therapy or optimization of ADA treatment (or both) and we had a high rate of complex PAFs (82%), including 15% with vaginal involvement. One strength of our study is the very precise description of our study cohort and their PAFs (PAF complexity, the presence or absence of setons, and endoscopic data). We chose a stricter clinical definition of remission, incorporating PDAI scores, and a greater proportion of our patients underwent radiological evaluation (no MRIs in Plevris et al study and 15% in the Strik et al study vs 56% in our study), which has been shown to be very important in assessing healing of PAFs[25].
In our study, high serum ADA concentrations was not associated with an increased incidence of adverse events, knowing that we only took into account the serious adverse events leading to a stop of ADA. In the literature, Drobne et al[26] and Greener et al[27] studies found that higher infliximab serum concentrations are not associated with a higher frequency of infections. Interestingly, Landemaine et al[28] study found that infection risk was individually correlated with cumulative increase in drug exposure, but not infliximab trough level.
Our study had several important limitations. Being a cross-sectional, non-interventional, non-randomized study, management of patients was heterogeneous both in terms of surgical and medical treatment. Additionally, most data were collected retrospectively. However, it was an evaluation of management of CD-associated PAFs in real life in tertiary centers. We had a small sample size, as did the other two available studies, because of the competition of other biotherapies. Trough serum ADA concentrations were not always measured; thus, it is possible that ADA concentrations fluctuated between injections[18]. Timing of measurement of serum ADA concentrations was either systematic or clinically oriented, depending on the center, favoring non-responders or partial responders. With an area under the ROC curve that was close to 50%, we could not identify target serum ADA concentrations associated with clinical remission using the Youden index. Additionally, half of the patients had only one evaluation, limiting the availability of follow-up data.
In conclusion, there is an association between clinical remission of CD-associated PAFs and high serum ADA concentrations that is not associated with an increased incidence of adverse events. Our data suggest that higher ADA concentrations are associated with remission of CD-associated PAFs than in mucosal healing. Target serum ADA concentrations to guide physicians should be determined by a prospective trial.
Perianal fistulas (PAFs) are a complication of Crohn’s disease (CD) in approximately 20% of patients. Adalimumab (ADA) was shown to treat CD-associated PAFs. An association between serum anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α concentrations and clinical outcomes in patients with CD has been demonstrated; however, little information is available on serum ADA concentrations and PAFs remission.
Achieving permanent PAFs closure remains a challenge for physicians, especially for complex PAFs. Retrospective trials have suggested that higher target serum infliximab concentrations are required to reach remission in patients with CD-associated PAFs than in those with luminal disease only. Two recent retrospective trials also suggested that higher target serum ADA concentrations are associated with remission in patients with CD-associated PAFs. We lacked a study dedicated to the investigation of this relationship.
To study the relationship between serum ADA concentrations and clinical remission of CD-associated PAFs.
We performed a multicenter cross-sectional study in France to assessed the relationship between serum ADA concentrations and clinical remission of CD-associated PAFs. We used a strict criteria to define clinical remission: absence of drainage (in accordance with Present’s criteria), with a PDAI ≤ 4, absence of a seton and assessment of the overall evaluation as favorable by the proctologist at the relevant center. We also assessed healing defined by clinical and radiological (MRI) remission as a secondary endpoint.
We found higher median serum ADA concentrations in patients who were in clinical remission of CD-associated PAFs than in those with active disease, the higher concentration not being associated with a higher incidence of adverse events. We found no significant difference in serum ADA concentrations according to healing status, likely due to the accuracy of this robust criteria.
Our findings suggest that remission of CD-associated PAFs requires higher serum concentrations of ADA than those previously reported for resolution of luminal disease.
Target serum ADA concentrations to guide physicians should be determined by a prospective trial.
We thank Jodi Smith, PhD, and Dr Trish Reynolds, MBBS, FRACP for editing a draft of this manuscript. We thank Toni Alfaiate for statistical advices.
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Gastroenterology and Hepatology
Country/Territory of origin: France
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Drobne D, Liakina V S-Editor: Chang KL L-Editor: A P-Editor: Chang KL
| 1. | Schwartz DA, Loftus EV Jr, Tremaine WJ, Panaccione R, Harmsen WS, Zinsmeister AR, Sandborn WJ. The natural history of fistulizing Crohn's disease in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Gastroenterology. 2002;122:875-880. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 739] [Cited by in RCA: 712] [Article Influence: 31.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Present DH, Rutgeerts P, Targan S, Hanauer SB, Mayer L, van Hogezand RA, Podolsky DK, Sands BE, Braakman T, DeWoody KL, Schaible TF, van Deventer SJ. Infliximab for the treatment of fistulas in patients with Crohn's disease. N Engl J Med. 1999;340:1398-1405. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1969] [Cited by in RCA: 1839] [Article Influence: 70.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Fu YM, Chen M, Liao AJ. A Meta-Analysis of Adalimumab for Fistula in Crohn's Disease. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2017;2017:1745692. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Lichtiger S, Binion DG, Wolf DC, Present DH, Bensimon AG, Wu E, Yu AP, Cardoso AT, Chao J, Mulani PM, Lomax KG, Kent JD. The CHOICE trial: adalimumab demonstrates safety, fistula healing, improved quality of life and increased work productivity in patients with Crohn's disease who failed prior infliximab therapy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2010;32:1228-1239. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 115] [Cited by in RCA: 139] [Article Influence: 9.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 5. | Bouchard D, Abramowitz L, Bouguen G, Brochard C, Dabadie A, de Parades V, Eléouet-Kaplan M, Fathallah N, Faucheron JL, Maggiori L, Panis Y, Pigot F, Rouméguère P, Sénéjoux A, Siproudhis L, Staumont G, Suduca JM, Vinson-Bonnet B, Zeitoun JD. Anoperineal lesions in Crohn's disease: French recommendations for clinical practice. Tech Coloproctol. 2017;21:683-691. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 26] [Cited by in RCA: 24] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Hyder SA, Travis SP, Jewell DP, McC Mortensen NJ, George BD. Fistulating anal Crohn's disease: results of combined surgical and infliximab treatment. Dis Colon Rectum. 2006;49:1837-1841. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 131] [Cited by in RCA: 114] [Article Influence: 6.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Yanai H, Lichtenstein L, Assa A, Mazor Y, Weiss B, Levine A, Ron Y, Kopylov U, Bujanover Y, Rosenbach Y, Ungar B, Eliakim R, Chowers Y, Shamir R, Fraser G, Dotan I, Ben-Horin S. Levels of drug and antidrug antibodies are associated with outcome of interventions after loss of response to infliximab or adalimumab. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;13:522-530.e2. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 220] [Cited by in RCA: 250] [Article Influence: 25.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Colombel JF, Sandborn WJ, Reinisch W, Mantzaris GJ, Kornbluth A, Rachmilewitz D, Lichtiger S, D'Haens G, Diamond RH, Broussard DL, Tang KL, van der Woude CJ, Rutgeerts P; SONIC Study Group. Infliximab, azathioprine, or combination therapy for Crohn's disease. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:1383-1395. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2539] [Cited by in RCA: 2377] [Article Influence: 158.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 9. | Roblin X, Marotte H, Rinaudo M, Del Tedesco E, Moreau A, Phelip JM, Genin C, Peyrin-Biroulet L, Paul S. Association between pharmacokinetics of adalimumab and mucosal healing in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;12:80-84.e2. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 203] [Cited by in RCA: 219] [Article Influence: 19.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Yarur AJ, Jain A, Hauenstein SI, Quintero MA, Barkin JS, Deshpande AR, Sussman DA, Singh S, Abreu MT. Higher Adalimumab Levels Are Associated with Histologic and Endoscopic Remission in Patients with Crohn's Disease and Ulcerative Colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2016;22:409-415. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 79] [Cited by in RCA: 97] [Article Influence: 10.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Kennedy NA, Heap GA, Green HD, Hamilton B, Bewshea C, Walker GJ, Thomas A, Nice R, Perry MH, Bouri S, Chanchlani N, Heerasing NM, Hendy P, Lin S, Gaya DR, Cummings JRF, Selinger CP, Lees CW, Hart AL, Parkes M, Sebastian S, Mansfield JC, Irving PM, Lindsay J, Russell RK, McDonald TJ, McGovern D, Goodhand JR, Ahmad T; UK Inflammatory Bowel Disease Pharmacogenetics Study Group. Predictors of anti-TNF treatment failure in anti-TNF-naive patients with active luminal Crohn's disease: a prospective, multicentre, cohort study. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;4:341-353. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 497] [Cited by in RCA: 459] [Article Influence: 76.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | El-Matary W, Walters TD, Huynh HQ, deBruyn J, Mack DR, Jacobson K, Sherlock ME, Church P, Wine E, Carroll MW, Benchimol EI, Lawrence S, Griffiths AM. Higher Postinduction Infliximab Serum Trough Levels Are Associated With Healing of Fistulizing Perianal Crohn's Disease in Children. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2019;25:150-155. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 41] [Cited by in RCA: 72] [Article Influence: 12.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (2)] |
| 13. | Yarur AJ, Kanagala V, Stein DJ, Czul F, Quintero MA, Agrawal D, Patel A, Best K, Fox C, Idstein K, Abreu MT. Higher infliximab trough levels are associated with perianal fistula healing in patients with Crohn's disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2017;45:933-940. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 184] [Cited by in RCA: 232] [Article Influence: 29.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 14. | Davidov Y, Ungar B, Bar-Yoseph H, Carter D, Haj-Natour O, Yavzori M, Chowers Y, Eliakim R, Ben-Horin S, Kopylov U. Association of Induction Infliximab Levels With Clinical Response in Perianal Crohn's Disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2017;11:549-555. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 28] [Cited by in RCA: 40] [Article Influence: 5.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Strik AS, Löwenberg M, Buskens CJ, B Gecse K, I Ponsioen C, Bemelman WA, D'Haens GR. Higher anti-TNF serum levels are associated with perianal fistula closure in Crohn's disease patients. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2019;54:453-458. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 35] [Cited by in RCA: 59] [Article Influence: 9.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 16. | Plevris N, Jenkinson PW, Arnott ID, Jones GR, Lees CW. Higher anti-tumor necrosis factor levels are associated with perianal fistula healing and fistula closure in Crohn's disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;32:32-37. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 29] [Cited by in RCA: 52] [Article Influence: 10.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Desvignes C, Edupuganti SR, Darrouzain F, Duveau AC, Loercher A, Paintaud G, Mulleman D. Development and validation of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to measure adalimumab concentration. Bioanalysis. 2015;7:1253-1260. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Ward MG, Thwaites PA, Beswick L, Hogg J, Rosella G, Van Langenberg D, Reynolds J, Gibson PR, Sparrow MP. Intra-patient variability in adalimumab drug levels within and between cycles in Crohn's disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2017;45:1135-1145. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 37] [Cited by in RCA: 40] [Article Influence: 5.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Van Assche G, Vanbeckevoort D, Bielen D, Coremans G, Aerden I, Noman M, D'Hoore A, Penninckx F, Marchal G, Cornillie F, Rutgeerts P. Magnetic resonance imaging of the effects of infliximab on perianal fistulizing Crohn's disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003;98:332-339. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 74] [Cited by in RCA: 86] [Article Influence: 3.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Thomassin L, Armengol-Debeir L, Charpentier C, Bridoux V, Koning E, Savoye G, Savoye-Collet C. Magnetic resonance imaging may predict deep remission in patients with perianal fistulizing Crohn's disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2017;23:4285-4292. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 26] [Cited by in RCA: 26] [Article Influence: 3.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Paul S, Dronne W, Roblin X. Kinetics of Antibodies Against Adalimumab Are Not Associated With Poor Outcomes in IBD. Am J Gastroenterol. 2015;110:777-778. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Gecse KB, Bemelman W, Kamm MA, Stoker J, Khanna R, Ng SC, Panés J, van Assche G, Liu Z, Hart A, Levesque BG, D'Haens G; World Gastroenterology Organization, International Organisation for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases IOIBD, European Society of Coloproctology and Robarts Clinical Trials; World Gastroenterology Organization International Organisation for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases IOIBD European Society of Coloproctology and Robarts Clinical Trials. A global consensus on the classification, diagnosis and multidisciplinary treatment of perianal fistulising Crohn's disease. Gut. 2014;63:1381-1392. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 266] [Cited by in RCA: 277] [Article Influence: 25.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Ng SC, Plamondon S, Gupta A, Burling D, Swatton A, Vaizey CJ, Kamm MA. Prospective evaluation of anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy guided by magnetic resonance imaging for Crohn's perineal fistulas. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104:2973-2986. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 128] [Cited by in RCA: 122] [Article Influence: 7.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Baert F, Kondragunta V, Lockton S, Vande Casteele N, Hauenstein S, Singh S, Karmiris K, Ferrante M, Gils A, Vermeire S. Antibodies to adalimumab are associated with future inflammation in Crohn's patients receiving maintenance adalimumab therapy: a post hoc analysis of the Karmiris trial. Gut. 2016;65:1126-1131. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 65] [Cited by in RCA: 74] [Article Influence: 8.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 25. | Hindryckx P, Jairath V, Zou G, Feagan BG, Sandborn WJ, Stoker J, Khanna R, Stitt L, van Viegen T, Shackelton LM, Taylor SA, Santillan C, Mearadji B, D'Haens G, Richard MP, Panes J, Rimola J. Development and Validation of a Magnetic Resonance Index for Assessing Fistulas in Patients With Crohn's Disease. Gastroenterology. 2019;157:1233-1244.e5. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 40] [Cited by in RCA: 78] [Article Influence: 13.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Drobne D, Kurent T, Golob S, Svegl P, Rajar P, Terzic S, Kozelj M, Novak G, Smrekar N, Plut S, Sever N, Strnisa L, Hanzel J, Brecelj J, Urlep D, Osredkar J, Homan M, Orel R, Stabuc B, Ferkolj I, Smid A. Success and safety of high infliximab trough levels in inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2018;53:940-946. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 42] [Cited by in RCA: 39] [Article Influence: 5.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Greener T, Kabakchiev B, Steinhart AH, Silverberg MS. Higher Infliximab Levels Are Not Associated With an Increase in Adverse Events in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2018;24:1808-1814. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 31] [Cited by in RCA: 40] [Article Influence: 5.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Landemaine A, Petitcollin A, Brochard C, Miard C, Dewitte M, Le Balc'h E, Grainville T, Bellissant E, Siproudhis L, Bouguen G. Cumulative Exposure to Infliximab, But Not Trough Concentrations, Correlates With Rate of Infection. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;19:288-295.e4. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 26] [Article Influence: 6.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |