Published online Dec 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i47.6743
Peer-review started: September 22, 2022
First decision: October 18, 2022
Revised: October 26, 2022
Accepted: November 27, 2022
Article in press: November 27, 2022
Published online: December 21, 2022
Processing time: 88 Days and 9.7 Hours
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a group of chronic diseases that includes ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease, and indeterminate colitis. Patients with IBD require prolonged treatment and high utilization of healthcare resources for proper management. The treatment of patients with IBD is focused on achieving therapeutic goals including clinical, biochemical, and endoscopic variables that result in improvement of the quality of life and prevention of disability. Ad
Core Tip: Patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) require prolonged treatment and high utilization of healthcare resources. About 40% of patients are refractory to different treatments with an increase need for hospitalization and surgery. Dual therapy, a strategy applicable to refractory IBD patients, includes the combination of two biologics or a biologic in combination with a small molecule drug. There are two distinct scenarios in IBD therapy in which this approach can be used: (1) Refractory active luminal disease without extraintestinal manifestations; and (2) patients with IBD in remission, but with active extraintestinal manifestations or immune-mediated inflammatory diseases.
- Citation: Balderramo D. Role of the combination of biologics and/or small molecules in the treatment of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(47): 6743-6751
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i47/6743.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i47.6743
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a group of chronic diseases that includes ulcerative colitis (UC), Crohn’s disease (CD), and indeterminate colitis. Patients with IBD require prolonged treatment and high utilization of healthcare resources for its proper management[1]. Medical treatment includes the use of so-called conventional drugs (mesalazine, immunosuppressants such as azathioprine or methotrexate and corticosteroids) and biologics [anti-tumor necrosis factor (anti-TNF), anti-integrins, and anti-interleukins (IL)], with small molecules (Janus kinase inhibitors and sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor modulators) having recently been added to the possible advanced treatments[2-5].
After the onset of therapy, the treatment of patients with IBD is focused on achieving therapeutic goals, which include improvement or normalization of clinical, biochemical, endoscopic variables, and also the quality of life and disability[6]. Despite the multiple treatments available, about 40% of patients are refractory to several treatments with different mechanisms of action, and these patients present with persistent symptoms that often have a great impact on their quality of life, due to the need for hospitalization and the requirement of surgery, which has to be carried out several times in some cases[7].
Extraintestinal manifestations (EIM) are present in about one-third of patients after diagnosis[8]. These mainly involve osteoarticular and dermatological manifestations. Some EIM are independent of IBD activity and require independent therapeutic management. In addition, some patients have multiple comorbidities throughout the course of the disease associated with prolonged corticosteroid treatment (diabetes, osteoporosis, adrenal insufficiency, and others), which is frequently used in these patients with a suboptimal response to advanced treatments[9].
Different studies have described a therapeutic window of opportunity, which implies the early use of advanced treatment in patients with IBD, especially in patients with early CD (< 2 years)[10]. These interventions are associated with a decrease in the progression of intestinal damage and complications such as stenosis and fistulas, and consequently reducing the need for hospitalization and surgery[10]. Finally, patients with long-standing IBD with persistent inflammatory activity represent a group at higher risk for the development of colorectal cancer, which develops by a different sequence to that of non-IBD colorectal cancer[11]. It has also been described that a better control of inflammatory activity may have an impact the development of this complication during long-term evolution[12,13].
The development of new molecules and the implementation of new strategies are necessary to achieve better control of IBD activity in patients who are refractory to currently available treatments[14]. However, there are multiple pathways of inflammatory activity activated in patients with IBD, and for this reason, treatment with monotherapies may not be sufficient for the management of all patients[15]. Related to this, there are many scenarios in medicine in which dual therapy is used in both the induction and maintenance of treatment. This strategy involves the combination of two or more treatments with the aim of achieving optimal control of pathologies with different therapeutic targets. Indeed, this modality has seen great development in oncological or hematological treatments[14]. Similarly, in patients with rheumatologic pathologies, this approach is used in some patient subgroups[16]. This approach is also applicable to patients with refractory IBD to advanced treatments (dual therapy) by using two biologics simultaneously or a biologic in combination with a small molecule[16,17]. In patients with IBD, there are two distinct scenarios in which it can be used: (1) Patients with refractory IBD without EIM; and (2) patients with IBD in remission, but with active EIM or immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMID)[18].
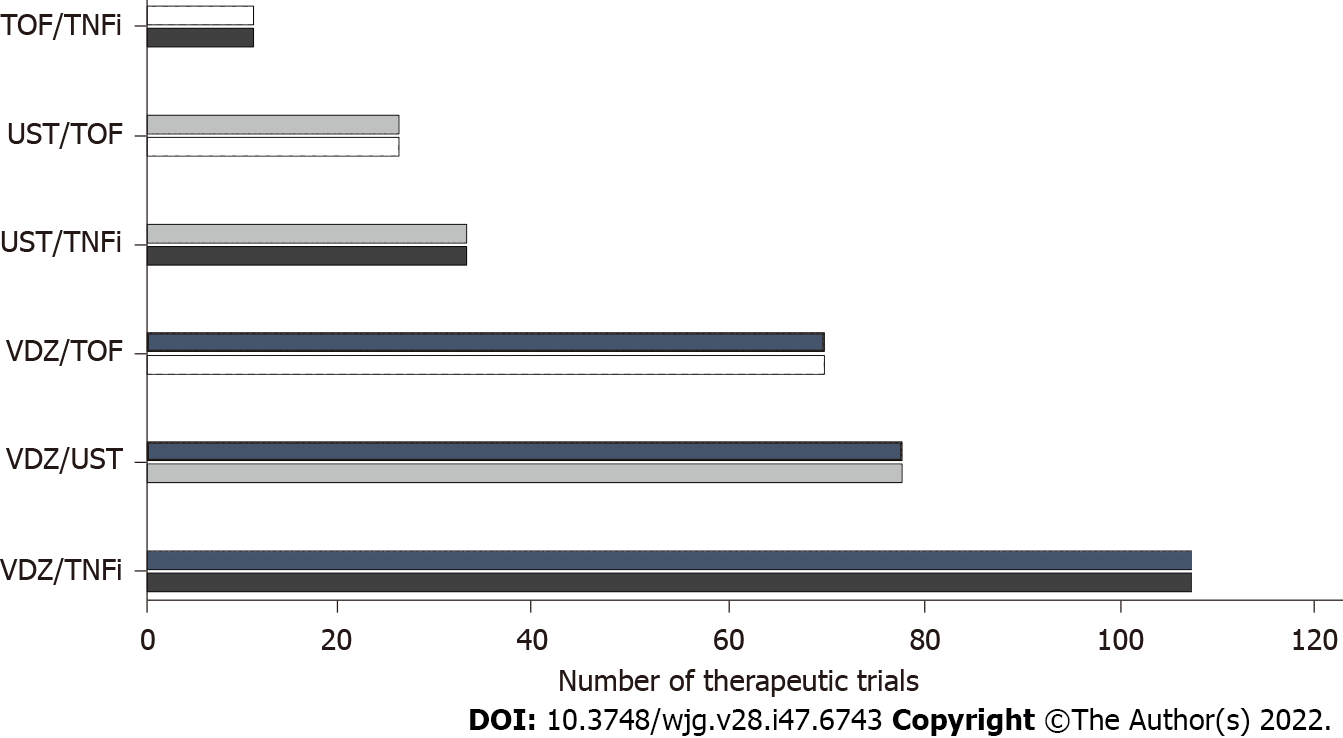
The first clinical trial that assessed a combination of biologics was developed in 2007[19,20]. Later, in 2010, the SONIC trial demonstrated that the association of infliximab and azathioprine is more effective compared with either infliximab or azathioprine monotherapy in CD patients, since which time multiple publications have described the results of different combinations of advanced drugs in patients with UC and CD, both in adults and in the pediatric population[21-35] (Figure 1). These combinations have varied according to the availability and practical experience of the drugs that were approved after the anti-TNFs. Table 1 shows the data from publications related to drug combination in patients with IBD. A major limitation of the dual therapy data is that they are mostly retrospective[19]. For this reason, the definitions of response evaluation (clinical, endoscopic and biochemical) are abbreviated and with the exception of few series are only described for short periods[33]. In addition, the definition of complications and the requirement for hospitalization and surgery can be subject to biases related to the follow-up time and the clinical condition prior to the start of the combined treatment[16]. Also, the differential evaluation of this strategy in patients with UC vs CD is not reported in many publications, which makes assessment difficult in some cases. Finally, some series include data on patients who received more than one combination, and it is possible that the effectiveness and adverse events could be different depending on the sequencing order of these combinations.
| Ref. | Study type (type of patients) | Disease (number of patients) | Combinations | Efficacy | Adverse events |
| Sands et al[20], 2007 | Randomized controlled trial (adults) | CD (52) | NAT + IFX | Remission 37% | Headache, CD exacerbation, nausea, nasopharyngitis |
| Buer et al[22], 2018 | Prospective cohort (adults) | CD (4), UC (6) | 9 IFX + VDZ, 1 ADA + UST | Remission 100 % | 3 upper airway infections |
| Mao et al[23], 2018 | Case series (adults) | CD (4) | 1 TNFi + UST/VDZ, 1 VDZ + UST, 2 VDZ + GOL | Remission 3/4 | 1 hand, foot and mouth disease, 1 influenza, 1 Clostridiodes difficile |
| Kwapisz et al[24], 2020 | Retrospective cohort (adults) | CD (14), UC (1) | 8 VDZ + TNFi, 5 VDZ + UST, 2 UST + TNFi | Improvement 11/15 | Salmonella, Clostridiodes difficile, 4 infections, arthralgia |
| Olbjørn et al[25], 2020 | Retrospective cohort (pediatrics) | CD (9), UC (4) | 8 IFX + VDZ, 5 IFX + UST | Remission 9/13 | Elevated transaminases, eczema, skin infection |
| Fumery et al[26], 2020 | Case series (adults) | CD (5), UC (2) | 5 TNFi + UST, 2 TNF + VDZ | Remission 6/7 | No |
| Glassner et al[27], 2020 | Retrospective cohort (adults) | CD (30), UC (18), IBD-U (1) | 7 VDZ + TNFi, 25 VDZ + UST, 9 TOF + TNFi, 8 TOF + VDZ, 3 TOF + UST | Remission 50% | 3 bacterial enteric infections (E. coli), 3 Clostridiodes difficile, 1 peristomal cellulitis, 2 abdominal wall abscesses |
| Privitera et al[28], 2020 | Retrospective cohort (adults) | CD (11), UC (5) | 3 VDZ + UST, 9 VDZ + TNFi/other, 3 VDZ + UST | Clinical response 43% | 1 cutaneous reaction, 1 drug-induced liver injury, 1 perianal abscess |
| Yang et al[29], 2020 | Retrospective cohort (adults) | CD (22) | 8 VDZ + UST, 13 VDZ + TNFi, 3 UST + TNFi | Remission 41% | 1 drug induced lupus, 1 pneumonia, 1 Clostridiodes difficile, 1 acinetobacter bacteremia |
| Alayo et al[30], 2021 | Retrospective cohort (adults) | CD (10), UC (25) | 24 VDZ + TOF, 5 TOF + UST | Remission 70% at 26 wk | 1 Clostridiodes difficile, 1 candida esophagitis, 1 abnormal lipid profile |
| Dolinger et al[31], 2021 | Retrospective cohort (pediatrics) | CD (7), UC (8), IBD-U (1) | 9 VDZ + TOF, 4 VDZ + UST, 3 UST + TOF | Remission 12/16 | 1 septic arthritis, 1 deep vein thrombosis |
| Llano et al[32], 2021 | Retrospective cohort (adults) | CD (3), UC (10), IBD-U (1) | 3 UST + VDZ, 2 VDZ + TNFi, 9 VDZ + TOF | Clinical or biochemical remission 50% | 2 Clostridiodes difficile, 2 pneumonia, 3 abnormal lipid profile |
| Goessens et al[33], 2021 | Retrospective cohort (adults) | CD (58), UC (40) | 41 VDZ + TNFi, 21 VDZ + UST, 11 UST + TNFi, 1 TOF + TNFi, 13 TOF + VDZ, 17 other | Clinical response 44% | 10 serious or opportunistic infections |
| Howard et al[34], 2022 | Case series (pediatrics) | CD (3) | 3 VDZ + UST | Clinical remission 100% | Not reported |
| Lee et al[35], 2022 | Retrospective cohort (adults) | CD (19) | 7 TOF + VDZ, 11 TOF + UST, 1 TOF + TNFi | Remission 60% | 1 basal cell carcinoma |
The partial or complete response in patients with indication for dual therapy for refractory IBD has been evaluated using different meta-analyses[16,19,36]. In these studies, the patients included were mainly those with CD (70%), and in the great majority, the indication for dual therapy was for refractory endoluminal activity[16]. Overall, the observed clinical response varied between 60% and 84% in most of the publications[16,19]. However, clinical remission, which is a difficult clinical situation to achieve considering that these are multi-refractory patients, ranged between 47% and 80% of the patients who received combined therapy[16,18]. The therapeutic response of the different combinations has not been reported to reveal significant variation with respect to the main indication (refractory luminal activity vs active EIM or IMID)[16]. Persistence in the treatment of dual therapy varies according to the follow-up period. It has been published that globally 45% of patients may discontinue the dual scheme during its evolution, with loss of response being the main cause (64%) and intolerance together with adverse effects representing a smaller percentage (12%)[33]. It is noteworthy that in a recent study, 21% of patients were able to discontinue one of the drugs in the combination without impacting the subsequent evolution[33]. It is important to mention that many series have included a recycling strategy. This involves the use in the combination of a drug, which the patient did not respond to[14]. Several publications have mentioned such a situation, and have observed that the response in these patients was similar to that observed in those who had not been previously exposed to that drug[18]. This strategy requires further evolution, especially in areas with limited resources for access to new advanced treatments.
The combination of two biologics or a biologic plus a small molecule has been associated with a higher rate of complications in other indications[17,18]. This has been observed in studies of patients with rheumatologic diseases who received combination therapy[14]. However, in these series, a significant percentage of patients received different treatments with medications that present a higher rate of adverse events, such as the use of rituximab, abatacept, and tocilizumab[18]. On the other hand, in patients with IBD, most of the proposed combinations include drugs with a high relevant safety profile such as vedolizumab or ustekinumab, which are used in both the pediatric and adult populations[25,29]. In a recent meta-analysis, the presence of adverse events varied from 6%-24% according to the combinations[16]. However, the presence of severe adverse events with indication for hospitalization or surgery was only present in 0%-12% of patients[16]. Within these severe adverse events, 75% were due to both intestinal and soft tissue infections[16]. In a recently published European series, a higher number of infections requiring hospitalization was observed in patients who received anti-TNF, corticosteroids, and immunomodulators, and who had a concomitant diagnosis of IMID/EIM (most frequently ankylosing spondylitis)[33]. Nevertheless, in this series, these complications developed only in patients with CD. Importantly, no case of reactivation of herpes zoster has been reported in any publication. Although one case of herpetic meningoencephalitis was diagnosed in a 43-year-old patient with CD who had received a combination including certolizumab, vedolizumab, and methotrexate, this was resolved after treatment[33]. Finally, one incident case of benign skin neoplasia (clear cell acanthoma) and one case of recurrence of basal cell skin cancer were reported[33,35]. No other cancers or treatment-related deaths have been reported.
Different case series in pediatric patients have reported results with various combinations in both CD and UC[37]. In one study, 75% of patients with luminal activity achieved a clinical remission free of corticosteroids at 6 mo, with the median time to achieve this goal being 88 d[31]. Interestingly, another potential indication that has been described in pediatric patients is the use of dual therapy (vedolizumab and tofacitinib) in patients with acute severe UC[31]. Nevertheless, more data are needed to explore this indication in an urgent and severe situation in patients with IBD. Different adverse events have been described in pediatric patients, but in general there are less frequent than in adult patients[25]. In a series of 16 pediatric patients, 1 (6%) patient presented septic arthritis and subsequent deep vein thrombosis[31].
It is necessary to establish new strategies for the use of advanced treatments in patients with refractory IBD, which must take into account health costs in order to be sustainable[14]. The sequencing of biologics or small molecules in patients in remission is a strategy that probably results in a better cost balance. Related to this, some series described patients who achieved remission with two biologics, with the subsequent suspension of one of these (usually anti-TNF) not leading to the presence of disease reactivation during follow-up[22]. In addition, other studies have shown that patients in remission on infliximab were able to maintain their clinical status after initiation of vedolizumab and discontinuation of anti-TNF[38]. The implementation of these strategies requires further research, and in particular, clinical trials are needed to establish their effectiveness during long-term follow-up.
The use of artificial intelligence and the implementation of new biomarkers in the future will possibly be able to differentiate the patients who will benefit from certain combination schemes. Artificial intelligence may also enable remote monitoring to provide new data as well as algorithms to ensure better decision making in refractory patients[39]. In addition, biomarkers might improve patient stratification. Recent data have shown that HLA-DQA1*05 is non-uniformly distributed in patients with or without anti-TNF failure[40]. Likewise, IL-23 receptor expansion is a mechanism of anti-TNF resistance and is reflected as a secondary loss of response[41]. According to this, the use of ustekinumab may allow to regained response in patients with prior anti-TNF.
It is possible that in the near future new combinations with different effectiveness and safety profile will be described, with the use of ozanimod, upadacitinib, risankizumab, guselkumab, and miriki
Another point to consider is that some good results have been reported after the change of formulation (from intravenous to subcutaneous) of the same drug such is the case of as infliximab or vedolizumab[46,47]. This could be important in future combinations, since it would facilitate logistics and reduce associated costs. In addition to the combination of biological drugs or small molecules, the future role of other approaches should be determined, such as the use of probiotics and gut flora regulators as well as the role of microbiota transplantation[48,49].
Finally, the development of more real-life evidence will be of great importance. Currently most of the data comes from Europe and North America[16]. In this sense, it would be very useful to develop international registries involving several countries currently experiencing a clear increase in the incidence of IBD, such as Latin America and Asia, and which have greater difficulty in accessing advanced treatments[50-52]. In this regard, the costs associated with dual therapy are the main limitation to access, which restrict the provision of a personalized treatment in patients with indication for this strategy[53]. Moreover, it is of great relevance to inform the health insurance of these patients about the objectives and advantages of the dual therapy strategy to obtain the appropriate approval in a timely manner for the indication.
The combination of biologics and/or small molecules is a strategy applicable to refractory IBD patients in two distinct scenarios: (1) Refractory active luminal disease without extraintestinal manifestations; and (2) patients with IBD in remission, but with active extraintestinal manifestations or immune-mediated inflammatory diseases. The observed clinical response using this strategy varied between 60% and 84% in most of the publications, and severe adverse events were observed in a few patients. However, most of the data on dual therapy are retrospective and with short-term follow-up. New clinical trials are needed to establish dual therapy effectiveness and safety during long-term follow-up. Finally, it is expected that new combinations using new drugs with different efficacy and safety profiles will be described in the coming years, expanding the current options.
The author thanks Dr. Paul Hobson, a native speaker, for the English edition of the manuscript.
Provenance and peer review: Invited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Gastroenterology and hepatology
Country/Territory of origin: Argentina
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B, B
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Gravina AG, Italy; M'Koma AE, United States; Parra RS, Brazil S-Editor: Zhang H L-Editor: Filipodia P-Editor: Zhang H
| 1. | van der Have M, Mangen MJ, van der Valk ME, Smeets HM, van Bodegraven A, Dijkstra G, Fidder HH, de Jong DJ, Pierik M, Ponsioen CY, van der Meulen-de Jong AE, van der Woude CJ, van de Meeberg PC, Romberg-Camps MJ, Clemens CH, Jansen JM, Mahmmod N, Bolwerk CJ, Vermeijden JR, Siersema PD, Leenders M, Oldenburg B; COIN Study Group; Dutch Initiative on Crohn and Colitis. Effect of aging on healthcare costs of inflammatory bowel disease: a glimpse into the future. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2014;20:637-645. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Feuerstein JD, Isaacs KL, Schneider Y, Siddique SM, Falck-Ytter Y, Singh S; AGA Institute Clinical Guidelines Committee. AGA Clinical Practice Guidelines on the Management of Moderate to Severe Ulcerative Colitis. Gastroenterology. 2020;158:1450-1461. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 296] [Cited by in RCA: 471] [Article Influence: 94.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (3)] |
| 3. | Raine T, Bonovas S, Burisch J, Kucharzik T, Adamina M, Annese V, Bachmann O, Bettenworth D, Chaparro M, Czuber-Dochan W, Eder P, Ellul P, Fidalgo C, Fiorino G, Gionchetti P, Gisbert JP, Gordon H, Hedin C, Holubar S, Iacucci M, Karmiris K, Katsanos K, Kopylov U, Lakatos PL, Lytras T, Lyutakov I, Noor N, Pellino G, Piovani D, Savarino E, Selvaggi F, Verstockt B, Spinelli A, Panis Y, Doherty G. ECCO Guidelines on Therapeutics in Ulcerative Colitis: Medical Treatment. J Crohns Colitis. 2022;16:2-17. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 584] [Cited by in RCA: 551] [Article Influence: 183.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Torres J, Bonovas S, Doherty G, Kucharzik T, Gisbert JP, Raine T, Adamina M, Armuzzi A, Bachmann O, Bager P, Biancone L, Bokemeyer B, Bossuyt P, Burisch J, Collins P, El-Hussuna A, Ellul P, Frei-Lanter C, Furfaro F, Gingert C, Gionchetti P, Gomollon F, González-Lorenzo M, Gordon H, Hlavaty T, Juillerat P, Katsanos K, Kopylov U, Krustins E, Lytras T, Maaser C, Magro F, Marshall JK, Myrelid P, Pellino G, Rosa I, Sabino J, Savarino E, Spinelli A, Stassen L, Uzzan M, Vavricka S, Verstockt B, Warusavitarne J, Zmora O, Fiorino G. ECCO Guidelines on Therapeutics in Crohn's Disease: Medical Treatment. J Crohns Colitis. 2020;14:4-22. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 991] [Cited by in RCA: 902] [Article Influence: 180.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (2)] |
| 5. | Feuerstein JD, Ho EY, Shmidt E, Singh H, Falck-Ytter Y, Sultan S, Terdiman JP; American Gastroenterological Association Institute Clinical Guidelines Committee. AGA Clinical Practice Guidelines on the Medical Management of Moderate to Severe Luminal and Perianal Fistulizing Crohn's Disease. Gastroenterology. 2021;160:2496-2508. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 69] [Cited by in RCA: 232] [Article Influence: 58.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Turner D, Ricciuto A, Lewis A, D'Amico F, Dhaliwal J, Griffiths AM, Bettenworth D, Sandborn WJ, Sands BE, Reinisch W, Schölmerich J, Bemelman W, Danese S, Mary JY, Rubin D, Colombel JF, Peyrin-Biroulet L, Dotan I, Abreu MT, Dignass A; International Organization for the Study of IBD. STRIDE-II: An Update on the Selecting Therapeutic Targets in Inflammatory Bowel Disease (STRIDE) Initiative of the International Organization for the Study of IBD (IOIBD): Determining Therapeutic Goals for Treat-to-Target strategies in IBD. Gastroenterology. 2021;160:1570-1583. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 473] [Cited by in RCA: 1625] [Article Influence: 406.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 7. | Peyrin-Biroulet L, Lémann M. Review article: remission rates achievable by current therapies for inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2011;33:870-879. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 120] [Cited by in RCA: 146] [Article Influence: 10.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Balderramo D, Trakal J, Herrera Najum P, Vivas M, Gonzalez R, Benavidez A, López Villa D, Daino D, Raiden K, Germán A, Corzo MA, Ponce de León J, Ferrer L, Germán C, Bálzola S, Idoeta A, Zárate F, Defagó MR; Grupo Córdoba de Cooperación para el Manejo y Estudio de la Enfermedad Inflamatoria Intestinal (CEMEI Group). High ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease ratio in a population-based registry from Córdoba, Argentina. Dig Liver Dis. 2021;53:852-857. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 3.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | McDonnell M, Harris RJ, Borca F, Mills T, Downey L, Dharmasiri S, Patel M, Zare B, Stammers M, Smith TR, Felwick R, Cummings JRF, Phan HTT, Gwiggner M. High incidence of glucocorticoid-induced hyperglycaemia in inflammatory bowel disease: metabolic and clinical predictors identified by machine learning. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2020;7:e000532. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Ungaro RC, Aggarwal S, Topaloglu O, Lee WJ, Clark R, Colombel JF. Systematic review and meta-analysis: efficacy and safety of early biologic treatment in adult and paediatric patients with Crohn's disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2020;51:831-842. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 56] [Cited by in RCA: 78] [Article Influence: 15.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Rajamäki K, Taira A, Katainen R, Välimäki N, Kuosmanen A, Plaketti RM, Seppälä TT, Ahtiainen M, Wirta EV, Vartiainen E, Sulo P, Ravantti J, Lehtipuro S, Granberg KJ, Nykter M, Tanskanen T, Ristimäki A, Koskensalo S, Renkonen-Sinisalo L, Lepistö A, Böhm J, Taipale J, Mecklin JP, Aavikko M, Palin K, Aaltonen LA. Genetic and Epigenetic Characteristics of Inflammatory Bowel Disease-Associated Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology. 2021;161:592-607. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 78] [Cited by in RCA: 124] [Article Influence: 31.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Bonovas S, Fiorino G, Lytras T, Nikolopoulos G, Peyrin-Biroulet L, Danese S. Systematic review with meta-analysis: use of 5-aminosalicylates and risk of colorectal neoplasia in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2017;45:1179-1192. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 62] [Cited by in RCA: 87] [Article Influence: 10.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 13. | Wijnands AM, de Jong ME, Lutgens MWMD, Hoentjen F, Elias SG, Oldenburg B; Dutch Initiative on Crohn and Colitis (ICC). Prognostic Factors for Advanced Colorectal Neoplasia in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Gastroenterology. 2021;160:1584-1598. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 54] [Cited by in RCA: 152] [Article Influence: 38.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Privitera G, Pugliese D, Lopetuso LR, Scaldaferri F, Neri M, Guidi L, Gasbarrini A, Armuzzi A. Novel trends with biologics in inflammatory bowel disease: sequential and combined approaches. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2021;14:17562848211006669. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 20] [Cited by in RCA: 48] [Article Influence: 12.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Graham DB, Xavier RJ. Pathway paradigms revealed from the genetics of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature. 2020;578:527-539. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 459] [Cited by in RCA: 466] [Article Influence: 93.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Alayo QA, Fenster M, Altayar O, Glassner KL, Llano E, Clark-Snustad K, Patel A, Kwapisz L, Yarur AJ, Cohen BL, Ciorba MA, Thomas D, Lee SD, Loftus EV Jr, Fudman DI, Abraham BP, Colombel JF, Deepak P. Systematic Review With Meta-analysis: Safety and Effectiveness of Combining Biologics and Small Molecules in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Crohns Colitis 360. 2022;4:otac002. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 48] [Cited by in RCA: 49] [Article Influence: 16.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Abreu MT. Combining Biologic Agents in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2019;15:549-551. [PubMed] |
| 18. | Gold SL, Steinlauf AF. Efficacy and Safety of Dual Biologic Therapy in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Review of the Literature. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2021;17:406-414. [PubMed] |
| 19. | Ahmed W, Galati J, Kumar A, Christos PJ, Longman R, Lukin DJ, Scherl E, Battat R. Dual Biologic or Small Molecule Therapy for Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20:e361-e379. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 28] [Cited by in RCA: 102] [Article Influence: 34.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 20. | Sands BE, Kozarek R, Spainhour J, Barish CF, Becker S, Goldberg L, Katz S, Goldblum R, Harrigan R, Hilton D, Hanauer SB. Safety and tolerability of concurrent natalizumab treatment for patients with Crohn's disease not in remission while receiving infliximab. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2007;13:2-11. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 152] [Cited by in RCA: 147] [Article Influence: 8.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 21. | Colombel JF, Sandborn WJ, Reinisch W, Mantzaris GJ, Kornbluth A, Rachmilewitz D, Lichtiger S, D'Haens G, Diamond RH, Broussard DL, Tang KL, van der Woude CJ, Rutgeerts P; SONIC Study Group. Infliximab, azathioprine, or combination therapy for Crohn's disease. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:1383-1395. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2539] [Cited by in RCA: 2373] [Article Influence: 158.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 22. | Buer LCT, Høivik ML, Warren DJ, Medhus AW, Moum BA. Combining Anti-TNF-α and Vedolizumab in the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Case Series. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2018;24:997-1004. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 31] [Cited by in RCA: 50] [Article Influence: 7.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Mao EJ, Lewin S, Terdiman JP, Beck K. Safety of dual biological therapy in Crohn's disease: a case series of vedolizumab in combination with other biologics. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2018;5:e000243. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 21] [Cited by in RCA: 38] [Article Influence: 5.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Kwapisz L, Raffals LE, Bruining DH, Pardi DS, Tremaine WJ, Kane SV, Papadakis KA, Coelho-Prabhu N, Kisiel JB, Heron V, Faubion WA, Loftus EV Jr. Combination Biologic Therapy in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Experience From a Tertiary Care Center. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;19:616-617. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 37] [Cited by in RCA: 60] [Article Influence: 15.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Olbjørn C, Rove JB, Jahnsen J. Combination of Biological Agents in Moderate to Severe Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Case Series and Review of the Literature. Paediatr Drugs. 2020;22:409-416. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 39] [Cited by in RCA: 45] [Article Influence: 9.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Fumery M, Yzet C, Brazier F. Letter: combination of biologics in inflammatory bowel diseases. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2020;52:566-567. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Article Influence: 3.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Glassner K, Oglat A, Duran A, Koduru P, Perry C, Wilhite A, Abraham BP. The use of combination biological or small molecule therapy in inflammatory bowel disease: A retrospective cohort study. J Dig Dis. 2020;21:264-271. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 23] [Cited by in RCA: 55] [Article Influence: 11.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 28. | Privitera G, Onali S, Pugliese D, Renna S, Savarino E, Viola A, Ribaldone DG, Buda A, Bezzio C, Fiorino G, Fantini MC, Scaldaferri F, Guidi L, Danese S, Gasbarrini A, Orlando A, Armuzzi A. Dual Targeted Therapy: a possible option for the management of refractory Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2020;. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 27] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 4.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Yang E, Panaccione N, Whitmire N, Dulai PS, Vande Casteele N, Singh S, Boland BS, Collins A, Sandborn WJ, Panaccione R, Battat R. Efficacy and safety of simultaneous treatment with two biologic medications in refractory Crohn's disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2020;51:1031-1038. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 50] [Cited by in RCA: 104] [Article Influence: 20.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Alayo QA, Khatiwada A, Patel A, Zulfiqar M, Gremida A, Gutierrez A, Rood RP, Ciorba MA, Christophi G, Deepak P. Effectiveness and Safety of Combining Tofacitinib With a Biologic in Patients With Refractory Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2021;27:1698-1702. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Article Influence: 4.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Dolinger MT, Spencer EA, Lai J, Dunkin D, Dubinsky MC. Dual Biologic and Small Molecule Therapy for the Treatment of Refractory Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2021;27:1210-1214. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 60] [Article Influence: 15.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Llano EM, Shrestha S, Burstein E, Boktor M, Fudman DI. Favorable outcomes combining vedolizumab with other biologics or tofacitinib for treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Crohns Colitis 360. 2021;3:otab030. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 33. | Goessens L, Colombel JF, Outtier A, Ferrante M, Sabino J, Judge C, Saeidi R, Rabbitt L, Armuzzi A, Domenech E, Michalopoulos G, Cremer A, García-Alonso FJ, Molnar T, Karmiris K, Gecse K, Van Oostrom J, Löwenberg M, Farkas K, Atreya R, Ribaldone DG, Selinger C, Hoentjen F, Bihin B, Sebastian S; European COMBIO study group, Rahier JF. Safety and efficacy of combining biologics or small molecules for inflammatory bowel disease or immune-mediated inflammatory diseases: A European retrospective observational study. United European Gastroenterol J. 2021;9:1136-1147. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 40] [Cited by in RCA: 25] [Article Influence: 6.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 34. | Howard G, Weiner D, Bar-Or I, Levine A. Dual biologic therapy with Vedolizumab and Ustekinumab for refractory Crohn's disease in children. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;34:372-374. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 35. | Lee SD, Singla A, Harper J, Barahimi M, Jacobs J, Kamp KJ, Clark-Snustad KD. Safety and Efficacy of Tofacitinib in Combination With Biologic Therapy for Refractory Crohn's Disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2022;28:309-313. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 3.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 36. | Ribaldone DG, Pellicano R, Vernero M, Caviglia GP, Saracco GM, Morino M, Astegiano M. Dual biological therapy with anti-TNF, vedolizumab or ustekinumab in inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review with pool analysis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2019;54:407-413. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 53] [Cited by in RCA: 50] [Article Influence: 8.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 37. | Wlazło M, Kierkuś J. Dual Biologic Therapy for the Treatment of Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Review of the Literature. J Clin Med. 2022;11. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 38. | Wang Y, Wang J, Pekow J, Dalal S, Cohen RD, Ollech J, Israel A, Shogan BD, Micic D, Cannon L, Umanskiy K, Hurst R, Hyman N, Rubin DT, Sakuraba A. Outcome of elective switching to vedolizumab in inflammatory bowel disease patients under tumor necrosis factor antagonist-maintained clinical remission. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;34:2090-2095. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 39. | Gubatan J, Levitte S, Patel A, Balabanis T, Wei MT, Sinha SR. Artificial intelligence applications in inflammatory bowel disease: Emerging technologies and future directions. World J Gastroenterol. 2021;27:1920-1935. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 49] [Cited by in RCA: 73] [Article Influence: 18.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 40. | Sazonovs A, Kennedy NA, Moutsianas L, Heap GA, Rice DL, Reppell M, Bewshea CM, Chanchlani N, Walker GJ, Perry MH, McDonald TJ, Lees CW, Cummings JRF, Parkes M, Mansfield JC, Irving PM, Barrett JC, McGovern D, Goodhand JR, Anderson CA, Ahmad T; PANTS Consortium. HLA-DQA1*05 Carriage Associated With Development of Anti-Drug Antibodies to Infliximab and Adalimumab in Patients With Crohn's Disease. Gastroenterology. 2020;158:189-199. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 300] [Cited by in RCA: 278] [Article Influence: 55.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 41. | Schmitt H, Billmeier U, Dieterich W, Rath T, Sonnewald S, Reid S, Hirschmann S, Hildner K, Waldner MJ, Mudter J, Hartmann A, Grützmann R, Neufert C, Münster T, Neurath MF, Atreya R. Expansion of IL-23 receptor bearing TNFR2+ T cells is associated with molecular resistance to anti-TNF therapy in Crohn's disease. Gut. 2019;68:814-828. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 186] [Cited by in RCA: 180] [Article Influence: 30.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 42. | Efficacy and Safety of Combination Induction Therapy With Guselkumab and Golimumab in Participants With Moderately to Severely Active Ulcerative Colitis: Results Through Week 12 of a Phase 2a Randomized, Double-Blind, Active-Controlled, Parallel-Group, Multicenter, Proof-of-Concept Study. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2022;18:9-10. [PubMed] |
| 43. | A Study of Combination Therapy with Guselkumab and Golimumab in Participants with Moderately to Severely Active Ulcerative Colitis. [accessed 2022 Sept 10]. In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): U.S. National Library of Medicine. Available from: http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT05242484 ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT05242484. |
| 44. | Triple Combination Therapy in High-Risk Crohn's Disease. [accessed 2022 Sept 10]. In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): U.S. National Library of Medicine. Available from: http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02764762 ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02764762. |
| 45. | Sandborn WJ, D'Haens GR, Reinisch W, Panés J, Chan D, Gonzalez S, Weisel K, Germinaro M, Frustaci ME, Yang Z, Adedokun OJ, Han C, Panaccione R, Hisamatsu T, Danese S, Rubin DT, Sands BE, Afzali A, Andrews JM, Feagan BG; GALAXI-1 Investigators. Guselkumab for the Treatment of Crohn's Disease: Induction Results From the Phase 2 GALAXI-1 Study. Gastroenterology. 2022;162:1650-1664.e8. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 56] [Cited by in RCA: 136] [Article Influence: 45.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 46. | Buisson A, Nachury M, Reymond M, Yzet C, Wils P, Payen K, Laugie M, Manlay L, Mathieu N, Pereira B, Fumery M. Effectiveness of Switching From Intravenous to Subcutaneous Infliximab in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: the REMSWITCH Study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 50] [Article Influence: 25.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 47. | Sandborn WJ, Baert F, Danese S, Krznarić Ž, Kobayashi T, Yao X, Chen J, Rosario M, Bhatia S, Kisfalvi K, D'Haens G, Vermeire S. Efficacy and Safety of Vedolizumab Subcutaneous Formulation in a Randomized Trial of Patients With Ulcerative Colitis. Gastroenterology. 2020;158:562-572.e12. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 105] [Cited by in RCA: 210] [Article Influence: 42.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 48. | Parada Venegas D, De la Fuente MK, Landskron G, González MJ, Quera R, Dijkstra G, Harmsen HJM, Faber KN, Hermoso MA. Short Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs)-Mediated Gut Epithelial and Immune Regulation and Its Relevance for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Front Immunol. 2019;10:277. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 970] [Cited by in RCA: 2173] [Article Influence: 362.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 49. | Pu D, Zhang Z, Feng B. Alterations and Potential Applications of Gut Microbiota in Biological Therapy for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:906419. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 50. | Windsor JW, Kaplan GG. Evolving Epidemiology of IBD. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2019;21:40. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 108] [Cited by in RCA: 226] [Article Influence: 37.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 51. | Kaplan GG. The global burden of IBD: from 2015 to 2025. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;12:720-727. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1157] [Cited by in RCA: 1865] [Article Influence: 186.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 52. | Kotze PG, Underwood FE, Damião AOMC, Ferraz JGP, Saad-Hossne R, Toro M, Iade B, Bosques-Padilla F, Teixeira FV, Juliao-Banos F, Simian D, Ghosh S, Panaccione R, Ng SC, Kaplan GG. Progression of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Throughout Latin America and the Caribbean: A Systematic Review. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;18:304-312. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 138] [Cited by in RCA: 125] [Article Influence: 25.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 53. | Santiago M, Dias CC, Alves C, Ministro P, Gonçalves R, Carvalho D, Portela F, Correia L, Lago P, Magro F. The Magnitude of Crohn's Disease Direct Costs in Health Care Systems (from Different Perspectives): A Systematic Review. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2022;28:1527-1536. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 3.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |