Published online Nov 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i43.6157
Peer-review started: August 24, 2022
First decision: September 8, 2022
Revised: September 22, 2022
Accepted: November 7, 2022
Article in press: November 7, 2022
Published online: November 21, 2022
Processing time: 83 Days and 19.2 Hours
Gastroduodenal endoscopy and biopsy following positive specific serology is considered the gold standard to diagnose celiac disease (CeD) in adults. Whether upper endoscopy helps detect comorbid conditions is unknown.
To investigate the prevalence of non-celiac endoscopic findings in patients in whom endoscopy was performed to confirm CeD diagnosis.
This is an observational, descriptive, multicenter, retrospective study that reports endoscopic findings obtained in adult patients enrolled in local registries from four tertiary centers. We collected data reported on first endoscopy, indicated for investigation of CeD. Diagnosis of CeD was performed by histology (≥ Marsh 2 type mucosal damage) and specific serology. Two European and one North American center included biopsy-confirmed CeD following positive serology. A fourth center (South America) included symptomatic patients undergoing endoscopy, irrespective of CeD serology. The latter cohort included a non-CeD control group.
A total of 1328 patients (80% female; 35 years median age) were enrolled, of whom 95.6% had positive specific serology. In 135 patients, endoscopy revealed 163 abnormalities unrelated to CeD (prevalence: 10.1%). Erosive reflux esophagitis (6.4%), gastric erosions (2.0%), and suspicion of esophageal metaplasia (1.2%) were the most common findings. Biopsy-confirmed Barrett’s esophagus was infrequent (0.2%). No endoscopic cancer was detected. Older patients (≥ 51 years of age) had a higher prevalence of endoscopic findings than those ≤ 50 (P < 0.01). Within the South American cohort, CeD was associated with a lower rate (8.2%) of comorbid endoscopic findings compared with controls (29.1%; P < 0.001). In the adjusted multivariate analysis of this cohort, having CeD was associated with a 72% reduction in the risk of any endoscopic abnormality (P < 0.0001), and having alarm symptoms was associated with a 37% reduction in the risk of finding at least one endoscopic lesion (P < 0.02).
In this large multicenter study, young adults with positive CeD serology had few comorbid endoscopic findings. Although patients over 51 years had a high prevalence of non-CeD gastroduodenal mucosal damage, no malignancy or premalignant lesions were found.
Core Tip: We offer novel data on the prevalence of non-celiac endoscopic findings at the time of endoscopy performed to confirm celiac disease (CeD) diagnosis. Based on the very high performance of specific serology tests, the diagnosis of CeD without duodenal biopsy has been proposed in recent years. However, some guidelines do not recommend avoiding endoscopy because relevant comorbid diagnosis can be missed. Our results found that comorbid upper gastrointestinal endoscopic pathology is uncommon in patients with positive CeD serology at the time of diagnostic endoscopy suggesting that a non-biopsy strategy is unlikely to clinically miss significant concomitant endoscopic findings unrelated to CeD.
- Citation: Stefanolo JP, Zingone F, Gizzi C, Marsilio I, Espinet ML, Smecuol EG, Khaouli M, Moreno ML, Pinto-Sánchez MI, Niveloni SI, Verdú EF, Ciacci C, Bai JC. Upper gastrointestinal endoscopic findings in celiac disease at diagnosis: A multicenter international retrospective study. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(43): 6157-6167
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i43/6157.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i43.6157
Celiac disease (CeD) is one of the most common life-long chronic diseases affecting people with a genetic predisposition conferred by HLA-DQ2 or DQ8[1]. Current recommendations for diagnosing CeD in adult patients involve a combination of specific serology and a duodenal biopsy demonstrating some degree of intestinal atrophy[2,3]. When CeD is clinically suspected, upper gastroduodenal endoscopy with duodenal biopsy confirms diagnosis[4]. Based on the very high specificity and predictive values of specific serology tests[5], the diagnosis of CeD without duodenal biopsy has been proposed in recent years[6-8]. Indeed, European pediatric societies recommend a non-biopsy approach under specific and strict criteria[9,10]. However, other pediatric societies (e.g., the North American Pediatric Gastroenterology Society) do not recommend this, in part because relevant comorbid diagnosis could be missed[11]. This is of particular concern in patients with alarm symptoms such as weight loss, anemia, or abdominal pain[2,12,13]. However, relatively few studies have explored this in-depth, particularly in adult patients undergoing endoscopy to confirm CeD diagnosis[14-16].
Thus, we conducted a multicenter study involving four cohorts of patients diagnosed in three countries to investigate the prevalence of coincidental upper gastrointestinal endoscopic findings in CeD patients at the time of diagnosis. We also compared upper gastrointestinal mucosal injury diagnoses across centers and age groups. Finally, we studied the pathological findings in patients with a confirmed diagnosis of CeD vs those in whom the disease was ruled out.
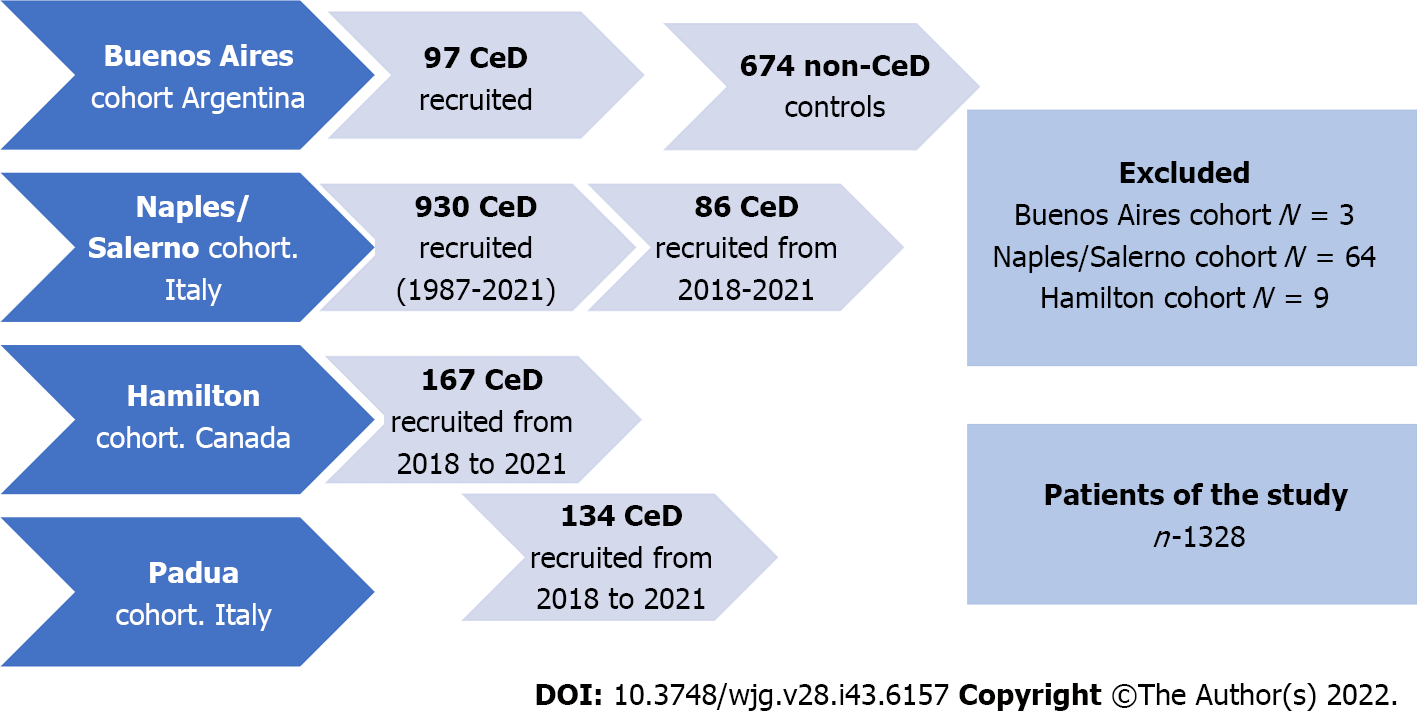
We conducted a descriptive multicenter retrospective study on endoscopic findings from adult patients who met standard clinical, serological, and histological criteria for CeD. Patients from four different CeD-specialized centers were included. Two European cohorts (Universities of Naples/Salerno and Padua; Italy) and a North American cohort (McMaster University, Hamilton; Canada) recruited consecutive patients enrolled in local registers. CeD was diagnosed by positive serology and confirmed by biopsy. The Naples/Salerno cohort included consecutive patients seen between 1987 and 2021, the Padua cohort between 2017 and 2021, and the Hamilton cohort between 2018 and 2020. A fourth (Small Bowel Section, Dr. C. Bonorino Udaondo Gastroenterology Hospital, Buenos Aires; Argentina) included patients referred for endoscopy and duodenal biopsy due to the presence of symptoms and/or signs compatible with CeD but, irrespective of serology, all of them part of prior research and study[7,15]. Thus, the fourth cohort included CeD and non-CeD participants (controls). Figure 1 and Table 1 summarize the demographic characteristics of the cohorts. The Ethics and Research Board of the Dr. C. Bonorino Udaondo Gastroenterology Hospital approved the study because of the prospective design and intervention in the Buenos Aires cohort. Ethics approval was obtained from Hamilton Integrated Research Ethics Board (HiREB# 14460/5415). In Italy, Ethical Committee review was not required for retrospective studies while patient data remained anonymously coded.
| Demographic data and upper GI endoscopic findings | Naples/Salerno cohort | Buenos Aires cohort | Hamilton cohort | Padua cohort | Overall CeD population |
| Total population | 930 (70.0) | 97 (7.3) | 167 (12.6) | 134 (10.1) | 1328 |
| Age in yr | 34 (26-42) | 35 (27-44) | 39 (27-54) | 35 (23-46) | 35 (26-43) |
| Female sex | 754 (81.1) | 88 (90.7) | 122 (73.0) | 100 (74.6) | 1064 (80.1) |
| Patients with positive serology | 899 (96.7) | 97 (100) | 147 (88.0) | 130 (97.0) | 1269 (95.6) |
| Patients with at least one significant endoscopic abnormality | 89 (9.6) | 8 (8.2) | 34 (20.4) | 4 (3.0) | 135 (10.2) |
| Reflux esophagitis with erosions | 78 (8.4) | 1 (1.0) | 6 (3.6) | 0 | 85 (6.4) |
| Esophageal peptic ulcers | 0 | 0 | 1 (0.6) | 0 | 1 (0.2) |
| Esophageal malignancy | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Suspicion of esophageal metaplasia | 3 (0.3) | 0 | 13 (7.8) | 0 | 16 (1.2) |
| Biopsy confirmed Barrett’s esophagus | 2 (0.2) | 0 | 1(0.6) | 0 | 3 (0.2) |
| Gastric erosions | 0 | 7 (7.2) | 16 (9.6) | 4 (3.0) | 27 (2.0) |
| Gastric ulcers | 1 (0.1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (0.1) |
| Gastric cancer | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Duodenal erosions | 0 | 0 | 15 (9.0) | 0 | 15 (1.1) |
| Duodenal ulcers | 8 (0.9) | 1 (1.0) | 6 (3.6) | 0 | 15 (1.1) |
| Duodenal cancer | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
In all CeD centers, experienced gastroenterologists performed upper gastrointestinal endoscopies and obtained duodenal biopsies per shared standard of care protocols. Endoscopic reports were generated using a standard format, and the data were entered into a common database. Duodenal biopsies were sent to each institution’s experienced pathologist. A standard number of biopsies were taken when any endoscopic abnormality was detected (e.g., endoscopic evidence of esophageal metaplasia). Endoscopic abnormalities were defined as follows[17]: (1) Erosive esophagitis: Esophageal mucosal damage characterized by one or more mucosal breaks that do not extend across the top of mucosal folds and confluent lesions or ulcers of any size; (2) Suspected esophageal metaplasia: Endoscopically suspected columnar mucosa without histological confirmation of specialized intestinal metaplasia; (3) Barrett’s esophagus confirmed by biopsy: Metaplastic columnar epithelium replacing the stratified squamous epithelium in biopsies from suspected metaplasia or presence of intestinal metaplasia; (4) Gastric and duodenal erosions: Presence of erythema and erosions in stomach or duodenum; (5) Esophageal, gastric, or duodenal ulcers extending into the muscularispropria; and (6) Esophageal, gastric, or duodenal cancer: Suspected endoscopic lesions were confirmed by specialized pathology.
CeD was diagnosed based on duodenal histology (Marsh’s classification)[1,18]. Inclusion criteria were Marsh 2 enteropathy or higher and positive CeD-specific serology [presence of either anti-TTG immunoglobulin (Ig)A, Anti-EmA IgA, anti-DGP IgA/IgG]. When serology was negative, CeD was diagnosed based on histology and clinical response to the gluten free diet (GFD)[18]. If patients had known exposure to gluten before the endoscopy, intestinal biopsies were taken. As previously stated, the Buenos Aires cohort was part of a research study in which the diagnosis was made first on histological grounds and then confirmed by serology. The standard specific CeD test for all centers was IgA transglutaminase 2[5]. Patients with normal biopsy or minimal inflammation (Marsh 0 or 1) were excluded from the study, regardless of serology or GFD response. In the Hamilton cohort, diagnosis of seronegative CeD patients was based on histology and a clinical and histological response to the GFD.
Statistical analysis was carried out using STATA (STATA version 14.0 Corp, College Station, TX, United States). Categorical variables were reported as frequencies and percentages, while continuous variables were reported as mean ± SD and/or median and 25%-75% interquartile ranges, according to their distribution. Comparisons of categorical variables between groups were made using the χ2 test or Fisher’s exact test. P values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant. For comparisons of continuous variables the analysis of variance test was used. Logistic regression was used to assess the risk of endoscopic lesions. The model included the report of significant lesions in endoscopy and/or histology reports as a dependent variable and factors such as age, sex, personal history, and signs/symptoms as independent variables.
Given the different recruitment times between centers, a subgroup analysis was performed to compare results in the Naples/Salerno cohort, focusing on cases diagnosed between 2018 and 2021 vs previous endoscopies, estimating that such analysis could detect differences by using more actualized endoscopic protocols that were temporally concordant with those reported from patients collected in the Padua and Ontario cohorts.
Overall, 1404 patients were diagnosed with CeD and 1328 of them were included in the study (Figure 1). Patients with slightly positive serology but Marsh 0 or 1 (n = 76) were not diagnosed as CeD.
The number of participants recruited varied between centers (Tables 1 and 2). The Naples/Salerno cohort contained most (70.0%) of the patients, while the Buenos Aires cohort had the fewest patients (7.3%). The European and North American centers differed in the length of time the celiac centers had been operational. The South American center included patients and controls over a specific time previously enrolled in a different study. There was a female predominance in all groups. There was no difference in the age at which diagnostic endoscopy was performed. There were no differences in baseline demographics across centers. The percentage of patients testing positive for celiac specific antibodies ranged from 88% (Hamilton) to 100% (Buenos Aires).
| Demographic data and upper GI endoscopic findings | Overall CeD population | ≤ 50 yr | 51-60 yr | ≥ 61 yr |
| Patients | 1328 | 1140 (85.8) | 114 (8.6) | 74 (5.6) |
| Age in yr | 35 (26-43) | 33 (25-39) | 55 (53-56) | 67 (63-71) |
| Female sex | 1064 (80.1) | 931 (81.7) | 82 (71.9) | 51 (41.0) |
| Patients with positive serology | 1269 (95.6) | 1092 (95.8) | 109 (95.6) | 68 (91.9) |
| Patients with at least one significant endoscopic abnormalities | 135 (10.1) | 102 (8.9)1 | 20 (17.5) | 13 (17.6) |
| Reflux esophagitis with erosions | 85 (6.4) | 69 (6.0) | 12 (10.5) | 4 (5.4) |
| Esophageal ulcers | 1 (0.2) | 1 (0.1) | 0 | 0 |
| Esophageal cancer | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Suspicion of metaplasia | 16 (1.2) | 10 (0.9) | 3 (2.6) | 2 (2.7) |
| Biopsy confirmed Barrett’s esophagus | 3 (0.2) | 2 (0.2) | 0 | 1 (1.3) |
| Gastric erosions | 27 (2.0) | 20 (1.7) | 3 (2.6) | 4 (5.4) |
| Gastric ulcers | 1 (0.1) | 1 (0.1) | 0 | 0 |
| Gastric cancer | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Duodenal erosions | 15 (1.1) | 8 (0.7) | 3 (2.6) | 4 (5.4) |
| Duodenal ulcers | 15 (1.1) | 10 (0.9) | 4 (3.5) | 1 (1.3) |
| Duodenal cancer | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Endoscopy revealed 163 distinct abnormalities in 135 patients with CeD (10.1%) (Table 1). The most common finding was erosive reflux esophagitis (6.4%), with the highest prevalence in the Naples/Salerno cohort (8.4%) and the lowest in the Buenos Aires (1%) and Padua (0%) cohorts. Peptic esophageal ulcers were only found in 1 patient within the total cohort. Although Barrett’s esophagus was suspected in 1.2% of the patients, it was biopsy confirmed in 0.2% of cases (18.7% of those suspected and subsequently biopsied). The Hamilton cohort had a higher suspicion of metaplasia (n = 13), but Barrett’s esophagus was confirmed in 1 patient (Table 1). Gastric ulcers were found in 1 patient (0.1%) within the Naples/Salerno cohort, while gastric erosions were found in 2.0% of the total population, with a higher prevalence in the Buenos Aires (7.2%) and the Hamilton (9.6%) cohorts. In the latter, 9.1% of patients with duodenal erosion were documented. Overall, 1.1% of duodenal ulcers were discovered, with a higher frequency encountered in the Hamilton cohort (3.6%). No cancers were reported at any level of the upper gastrointestinal (GI) tract of CeD patients.
Patients under the age of 50 had a lower risk of having at least one abnormality compared with patients over the age of 51 (P < 0.01). This indicated a 96.6% increase in lesions found in older patients (8.9% vs 17.5%), which was primarily driven by erosive esophagitis and gastric erosions (Table 2). We performed a subgroup analysis of the Naples/Salerno cohort, including patients diagnosed between 2018 and 2021. Compared with the overall Naples/Salerno cohort, patients diagnosed recently (n = 86) had a higher percentage of at least one significant endoscopic abnormality (29.2% vs 9.6%, respectively), owing to a higher proportion of cases with erosive reflux esophagitis (20.0% vs 8.4%) and duodenal ulcers (8.2% vs 0.9%, respectively). These endoscopic features were more common in the Naples/ Salerno cohort (after 2018) than in the other cohorts (Padua and Hamilton) (P < 0.01). Compared with the Padua cohort, the Salerno cohort had a higher proportion of patients with at least one endoscopic abnormality (29.1% vs 3.0%; P < 0.01) (Supplementary Table 1).
We compared CeD patients (n = 97) vs non-CeD controls (n = 674) (Table 3) using the Buenos Aires cohort. The median age at endoscopy in non-CeD controls was 11 years higher than in patients with CeD, and the percent of females was lower (P < 0.01 for both). Compared with patients with CeD, a higher proportion of controls were under the age of 50 (P < 0.001) (Table 3). CeD specific serology was positive in 1.3% of non-CeD controls. IgA transglutaminase positive levels in controls were less than three times the upper limit of normal. Endoscopic findings were more frequent in controls than in CeD patients (P < 0.001). In all age groups, gastric erosions were most common. Two control subjects, both older than 51, had a stomach adenocarcinoma and another a duodenal cancer at diagnostic endoscopy. In contrast, no cancers were discovered in CeD patients. Metaplasia was found in 1.0% of controls, with Barrett’s esophagus being confirmed after biopsy in two of these cases. Controls over the age of 51 had 12.9% more frequent mucosal damage compared with younger subjects (overall prevalence 31.4% vs 27.8%, respectively).
| Demographic data and upper GI endoscopic findings | CeD population | Non-CeD population | ≤ 50 yr non-CeD | 51-60 yr non-CeD | ≥ 61 yr non-CeD |
| Patients | 97 (12.6) | 674 (87.4) | 435 (64.5) | 135 (20.0) | 104 (15.4) |
| Age in yr | 35 (27-44) | 45 (33-55)a | 37 (29-44) | 55 (53-58) | 68 (63-72) |
| Female sex | 88 (90.7) | 472 (70.0)a | 312 (71.7) | 92 (68.1) | 68 (65.4) |
| Patients with positive serology | 97 (100) | 9 (1.3)a | 6 (1.3) | 3 (2.2) | 0 |
| Patients with at least one significant endoscopic abnormalities | 8 (8.2) | 196 (29.1)b | 121 (27.8) | 48 (35.6) | 27 (26.0) |
| Reflux esophagitis with erosions | 1 (1.0) | 21 (3.1) | 11 (2.5) | 2 (1.5) | 5 (4.8) |
| Esophageal ulcers | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Esophageal cancer | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Suspicion of metaplasia | 0 | 7 (1.0) | 5 (1.1) | 2 (1.5) | 0 |
| Biopsy confirmed Barrett's esophagus | 0 | 2 (0.3) | 2 (0.5) | 0 | 0 |
| Gastric erosions | 7 (7.22) | 165 (24.5)a | 103 (23.7) | 43 (31.8) | 19 (18.3) |
| Gastric ulcers | 0 (0) | 11 (1.6) | 4(0.9) | 2 (1.5) | 5 (4.8) |
| Gastric cancer | 0 | 2 (0.3) | 0 | 1 (0.7) | 1 (1.0) |
| Duodenal erosions | 0 | 10 (1.5) | 6 (1.4) | 2 (1.5) | 2 (1.9) |
| Duodenal ulcers | 1 (1.0) | 5 (0.7) | 2 (0.5) | 2 (1.5) | 1 (1.0) |
| Duodenal cancer | 0 | 1 (0.1) | 1 (0.2) | 0 | 0 |
The crude multivariate analysis based on CeD patients and non-CeD controls found that a CeD diagnosis and presence of alarm symptoms(weight loss, anemia, bleeding, dysphagia, epigastric pain, or history of malignancy) reduced the risk of having at least one lesion by 78.0% and 49.0% (P < 0.0001 for both), respectively. According to the adjusted multivariate analysis, having CeD was associated with a 72% reduction in the risk of any endoscopic lesion (P < 0.0001), and having alarm symptoms was associated with a 37% reduction in the risk of having at least one endoscopic lesion (P < 0.02; Table 4).
| Independent variable | At least one endoscopic lesion1 (Buenos Aires cohort) | |||
| OR (95%CI) | P value | Adjusted2 OR (95%CI) | P value | |
| Male sex | 1.19 (0.83-1.69) | 0.34 | 1.03 (0.72-1.48) | 0.860 |
| Age | 1.01 (1.00-1.02) | 0.14 | 1.00 (0.99-1.01) | 0.550 |
| Celiac disease | 0.22 (0.10-0.46) | < 0.0001 | 0.28 (0.13-0.60) | 0.001 |
| Alarm symptoms3 | 0.51 (0.35-0.74) | < 0.0001 | 0.63 (0.43-0.93) | 0.020 |
The study’s main finding was that upper endoscopy performed concurrently with duodenal biopsies for CeD diagnosis revealed no concomitant damage in 92.0% of cases. Only 1.6% of CeD patients had relevant findings with the potential to progress to severe disease, comprised by esophageal and gastric ulcers and Barrett’s esophagus. While 8.9% of patients demonstrated upper GI injury, only 1.3% potentially had dangerous lesions. The low yield of relevant concomitant findings in this study does not support the usefulness of upper endoscopy beyond the need of obtaining biopsies for the diagnosis of CeD.
The possibility of detecting important or relevant esophageal, gastric, or duodenal pathology during diagnostic endoscopy has been put forward as an added benefit to the confirmation of CeD. Previous findings in CeD patients include reflux esophagitis, esophageal eosinophilia or eosinophilic esophagitis (mostly in children), Barrett’s esophagus, Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection and autoimmune gastritis[14-16]. These were, however, reported in small populations and single center studies. Our study, which included cohorts from the European Union, North America, and South America, gathered the largest sample of patients reported to date. The sample size collectively obtained allowed for subgroup and age category comparisons. The majority of CeD patients were young and female, as expected. The Buenos Aires cohort was prospectively designed to diagnose symptomatic patients suspected of having CeD, which allowed for comparisons between CeD patients and controls biopsy (Marsh’s 0 or 1 histology categorization).
Our findings in a large multicenter population confirm recent reports that adult patients with alarm symptoms have a very low prevalence of major endoscopic and histological findings in the upper GI tract other than CeD features at presentation and was comparable to that of patients without alarm symptoms[14,16]. The definition of what constitutes an alarming symptom for CeD at the time of diagnosis appears to be central to this analysis. Weight loss, iron deficiency anemia, pain, or mal
Erosive reflux esophagitis was the most common endoscopic finding at the time of diagnosis (6.4%). Notably, undiagnosed patients with classical or subclinical CeD frequently seek treatment for gastroesophageal reflux symptoms prior to diagnosis, which has been shown to be more common in subjects in whom CeD is ruled out or in those treated with the GFD[20]. We previously reported that up to 30% of newly diagnosed CeD patients perceive moderate to severe reflux symptoms, which does not respond to anti-reflux therapy prior to CeD diagnosis[21,22]. Most of these “non-responsive” patients to anti-reflux therapy will rapidly improve after starting the GFD. Surprisingly, between 2018 and 2021, the Naples/Salerno cohort revealed higher prevalence of overall endoscopic lesions, and specifically of erosive reflux esophagitis, compared with diagnoses made before that time. This could be attributed to the characteristics of the CeD population over time or to differences in the reporting of endoscopic and histology findings.
The possibility of missing severe lesions or potentially dangerous diseases in CeD patients if a diagnostic endoscopy is not performed has been a source of concern in CeD guidelines[2,4]. With respect to Barrett’s esophagus or esophageal metaplasia, an Italian study published in 2005 showed metaplasia in 26.6% of CeD patients compared with 10.9% of the control population[23]. This was not confirmed in studies from the United States[24] and South America[15,21] nor by the present study. Reasons for this discrepancy could be related to differences in populations and in the definition of Barrett’s esophagus, which required confirmation by biopsy in our study.
In the present study, we did not find mucosal eosinophilic infiltration. A pediatric prospective longitudinal study based on systematic esophageal biopsies found that diagnoses of eosinophilic esophagitis and/or eosinophilia were not clinically relevant, suggesting esophageal biopsy is not necessary in the absence of clinical suspicion[25]. A 2015 cross-sectional population study in the United States based on a national pathology database involving over 88000 CeD patients with both esophageal and duodenal biopsies, reported a slight increase in comorbid eosinophilic esophagitis and CeD[24]. However, no link between reflux esophagitis or Barrett’s esophagus and CeD has been reported. Finally, autoimmune atrophic gastritis was previously modestly associated with CeD[26]. Our study, as well as other population-based studies and systematic reviews, did not confirm the association[27,28].
An earlier prospective study[15] collected consecutive patients and non-CeD controls in a high-risk population for having CeD, and gastric and duodenal biopsies were performed systematically at the time of the diagnostic endoscopy CeD and biopsy. Gastric biopsies from untreated CeD patients also revealed a significantly higher intraepithelial lymphocyte count in the antrum and corpus when compared with controls[15,29,30]. According to an Irish study, 10% of CeD patients have lymphocytic gastritis, which is twice the rate of non-CeD controls[12,14]. These findings are attributed to H. pylori infection, autoimmune atrophic gastritis[15,26], or a pan-mucosal gluten-related inflammation[14,15,29,30].
Our study showed only 1 CeD patient had a gastric peptic ulcer. Previous studies found 18.1% of CeD children with gastric ulcers, with a higher prevalence in H. pylori negative patients and those with no history of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use[31,32]. The rate of H. pylori infection across centers was not consistently reported here, and this could explain the difference in results. Previous research, however, has shown that high rates of biopsy-confirmed H. pylori infection are not associated with an increased risk of malignancy in the long term[27,33]. However, several studies have also shown that when endoscopic appearance is normal, histological evaluation (both in the stomach and the esophagus) is not cost-effective, especially when performed in experienced academic centers[34-36].
There was no diagnosis of gastric adenocarcinoma in CeD. Despite the small number of cases studied, this is consistent with previous findings that the prevalence of other cancers (breast, colon, pulmonary, and gynecological cancers) in CeD appears to be lower than in the general population[27,28]. Small bowel carcinoma is extremely rare in the general population, and CeD patients are three times more likely to develop it[1,28]. However, malignancies in the duodenum are still uncommon at the time of CeD diagnosis, which implies diagnostic CeD endoscopy should not be recommended as surveillance for upper GI cancer[28]. Overall, the current findings, as well as those from previous studies, suggest that a biopsy-avoiding approach in adult patients who meet recommended and strict serological criteria for CeD is possible[12,37-40].
Study strengths included the multicenter design, the large number of patients diagnosed at specialized centers for CeD in whom confirmatory biopsy diagnosis was obtained, as well as the use of standard endoscopic protocols. Despite the small numbers in sub-analyses, the study also provided novel data related to the association of endoscopic findings according to age and time. Study limitations included the observational design, the retrospective collection of endoscopic reports (with potential missing data), the differences in time of enrollment across the four centers, the lack of systematic collection of biopsies from the esophagus and stomach, and the limited number of non-CeD controls. Although the current study suggests that missing potentially serious events is unlikely, this should be confirmed in a larger population.
In conclusion, this multicenter, retrospective study found that comorbid upper GI endoscopic pathology is uncommon in patients with positive CeD serology at the time of diagnostic endoscopy. The risk of severe or premalignant lesions is extremely low, and no malignancies were found in patients who displayed potential warning signs. Our findings suggest that a non-biopsy strategy for diagnosing CeD in adults is unlikely to miss clinically significant concomitant endoscopic findings unrelated to CeD. The results of this study should encourage future population-based or prospective studies in this area.
Celiac disease (CeD) is currently diagnosed in adult patients using a combination of specific serology tests and a duodenal biopsy obtained through an upper endoscopy. Upper endoscopy is also considered necessary for CeD diagnosis because non-CeD comorbidities can be missed.
The prevalence of upper gastrointestinal comorbidities at the time of CeD diagnosis has received little attention.
To investigate the prevalence of coincidental upper gastrointestinal endoscopic findings at the time of diagnostic endoscopy in four cohorts of patients diagnosed in three different countries.
We conducted a descriptive multicenter retrospective study reporting endoscopic findings from adult patients who met standard criteria for diagnosing CeD.
Of 1328 adult patients enrolled, 95.6% had positive specific serology. In 135 patients, endoscopy revealed 163 abnormalities unrelated to CeD (10.1%). Erosive reflux esophagitis (6.4%), gastric erosions (2.0%), and suspicion of esophageal metaplasia (1.2%) were the most common findings. Biopsy-confirmed Barrett’s esophagus was infrequent (0.2%). No other neoplastic or malignancies lesions were detected. Patients with alarm symptoms or signs had a lower rate of concomitant findings.
Adults with positive CeD serology had few comorbid endoscopic findings when CeD was diagnosed.
These findings raise the possibility that adult patients who meet recommended and strict serological criteria for CeD could be diagnosed without undergoing endoscopy and biopsy.
Provenance and peer review: Invited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Gastroenterology and hepatology
Country/Territory of origin: Argentina
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): A
Grade B (Very good): B
Grade C (Good): 0
Grade D (Fair): D
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Taavela J, Finland; Zhang X, United States; Zhang JW, China S-Editor: Fan JR L-Editor: Filipodia P-Editor: Fan JR
| 1. | Catassi C, Verdu EF, Bai JC, Lionetti E. Coeliac disease. Lancet. 2022;399:2413-2426. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 274] [Cited by in RCA: 232] [Article Influence: 77.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 2. | Al-Toma A, Volta U, Auricchio R, Castillejo G, Sanders DS, Cellier C, Mulder CJ, Lundin KEA. European Society for the Study of Coeliac Disease (ESsCD) guideline for coeliac disease and other gluten-related disorders. United European Gastroenterol J. 2019;7:583-613. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 293] [Cited by in RCA: 599] [Article Influence: 99.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 3. | Lebwohl B, Sanders DS, Green PHR. Coeliac disease. Lancet. 2018;391:70-81. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 539] [Cited by in RCA: 668] [Article Influence: 95.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Lebwohl B, Rubio-Tapia A, Assiri A, Newland C, Guandalini S. Diagnosis of celiac disease. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2012;22:661-677. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 46] [Cited by in RCA: 43] [Article Influence: 3.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Husby S, Murray JA. Diagnosing coeliac disease and the potential for serological markers. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;11:655-663. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 23] [Cited by in RCA: 26] [Article Influence: 2.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Valdimarsson T, Franzen L, Grodzinsky E, Skogh T, Ström M. Is small bowel biopsy necessary in adults with suspected celiac disease and IgA anti-endomysium antibodies? Dig Dis Sci. 1996;41:83-87. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 85] [Cited by in RCA: 82] [Article Influence: 2.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Kurppa K, Taavela J, Saavalainen P, Kaukinen K, Lindfors K. Novel diagnostic techniques for celiac disease. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;10:795-805. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 1.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Fuchs V, Kurppa K, Huhtala H, Laurila K, Mäki M, Collin P, Salmi T, Luostarinen L, Saavalainen P, Kaukinen K. Serology-based criteria for adult coeliac disease have excellent accuracy across the range of pre-test probabilities. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2019;49:277-284. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 46] [Cited by in RCA: 69] [Article Influence: 11.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Husby S, Koletzko S, Korponay-Szabó IR, Mearin ML, Phillips A, Shamir R, Troncone R, Giersiepen K, Branski D, Catassi C, Lelgeman M, Mäki M, Ribes-Koninckx C, Ventura A, Zimmer KP; ESPGHAN Working Group on Coeliac Disease Diagnosis; ESPGHAN Gastroenterology Committee; European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition. European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition guidelines for the diagnosis of coeliac disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2012;54:136-160. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1708] [Cited by in RCA: 1837] [Article Influence: 141.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (5)] |
| 10. | Husby S, Koletzko S, Korponay-Szabó I, Kurppa K, Mearin ML, Ribes-Koninckx C, Shamir R, Troncone R, Auricchio R, Castillejo G, Christensen R, Dolinsek J, Gillett P, Hróbjartsson A, Koltai T, Maki M, Nielsen SM, Popp A, Størdal K, Werkstetter K, Wessels M. European Society Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Guidelines for Diagnosing Coeliac Disease 2020. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2020;70:141-156. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 363] [Cited by in RCA: 694] [Article Influence: 138.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Hill ID, Fasano A, Guandalini S, Hoffenberg E, Levy J, Reilly N, Verma R. NASPGHAN Clinical Report on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Gluten-related Disorders. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2016;63:156-165. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 125] [Cited by in RCA: 164] [Article Influence: 18.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Efthymakis K, Serio M, Milano A, Laterza F, Bonitatibus A, Di Nicola M, Neri M. Application of the Biopsy-Sparing ESPGHAN Guidelines for Celiac Disease Diagnosis in Adults: A Real-Life Study. Dig Dis Sci. 2017;62:2433-2439. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 23] [Cited by in RCA: 30] [Article Influence: 3.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Husby S, Murray JA, Katzka DA. AGA Clinical Practice Update on Diagnosis and Monitoring of Celiac Disease-Changing Utility of Serology and Histologic Measures: Expert Review. Gastroenterology. 2019;156:885-889. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 123] [Cited by in RCA: 158] [Article Influence: 26.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Feeley KM, Heneghan MA, Stevens FM, McCarthy CF. Lymphocytic gastritis and coeliac disease: evidence of a positive association. J Clin Pathol. 1998;51:207-210. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 64] [Cited by in RCA: 48] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Diamanti A, Maino C, Niveloni S, Pedreira S, Vazquez H, Smecuol E, Fiorini A, Cabanne A, Bartellini MA, Kogan Z, Valero J, Mauriño E, Bai JC. Characterization of gastric mucosal lesions in patients with celiac disease: a prospective controlled study. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999;94:1313-1319. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 42] [Cited by in RCA: 40] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Maimaris S, Schiepatti A, Gabrielli GM, Costetti M, Costa S, Sanders DS, Zingone F, Carroccio A, Ciacci C, Di Sabatino A, Biagi F. Low prevalence of upper endoscopic gastrointestinal findings despite high frequency of alarm symptoms at the time of diagnosis in adult coeliac disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;32:1447-1451. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 2.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Aabakken L, Barkun AN, Cotton PB, Fedorov E, Fujino MA, Ivanova E, Kudo SE, Kuznetzov K, de Lange T, Matsuda K, Moine O, Rembacken B, Rey JF, Romagnuolo J, Rösch T, Sawhney M, Yao K, Waye JD. Standardized endoscopic reporting. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;29:234-240. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 40] [Cited by in RCA: 32] [Article Influence: 2.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Kelly CP, Bai JC, Liu E, Leffler DA. Advances in diagnosis and management of celiac disease. Gastroenterology. 2015;148:1175-1186. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 215] [Cited by in RCA: 184] [Article Influence: 18.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Tack GJ, Verbeek WH, Schreurs MW, Mulder CJ. The spectrum of celiac disease: epidemiology, clinical aspects and treatment. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;7:204-213. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 189] [Cited by in RCA: 176] [Article Influence: 11.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Ludvigsson JF, Aro P, Walker MM, Vieth M, Agréus L, Talley NJ, Murray JA, Ronkainen J. Celiac disease, eosinophilic esophagitis and gastroesophageal reflux disease, an adult population-based study. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2013;48:808-814. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 39] [Cited by in RCA: 42] [Article Influence: 3.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Leffler DA, Kelly CP. Celiac disease and gastroesophageal reflux disease: yet another presentation for a clinical chameleon. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;9:192-193. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Reilly NR, Husby S, Sanders DS, Green PHR. Coeliac disease: to biopsy or not? Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;15:60-66. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 24] [Cited by in RCA: 24] [Article Influence: 3.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Maieron R, Elli L, Marino M, Floriani I, Minerva F, Avellini C, Falconieri G, Pizzolitto S, Zilli M. Celiac disease and intestinal metaplasia of the esophagus (Barrett's esophagus). Dig Dis Sci. 2005;50:126-129. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Jensen ET, Eluri S, Lebwohl B, Genta RM, Dellon ES. Increased Risk of Esophageal Eosinophilia and Eosinophilic Esophagitis in Patients With Active Celiac Disease on Biopsy. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;13:1426-1431. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 38] [Cited by in RCA: 47] [Article Influence: 4.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Cristofori F, D'Abramo FS, Rutigliano V, Dargenio VN, Castellaneta S, Piscitelli D, De Benedittis D, Indrio F, Raguseo LC, Barone M, Francavilla R. Esophageal Eosinophilia and Eosinophilic Esophagitis in Celiac Children: A Ten Year Prospective Observational Study. Nutrients. 2021;13. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Zingone F, Marsilio I, Fassan M, Pilotto V, Maddalo G, Lorenzon G, Savarino EV, Farinati F. Duodenal Histological Findings and Risk of Coeliac Disease in Subjects with Autoimmune Atrophic Gastritis: A Retrospective Evaluation. Digestion. 2021;102:615-621. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Lebwohl B, Green PHR, Söderling J, Roelstraete B, Ludvigsson JF. Association Between Celiac Disease and Mortality Risk in a Swedish Population. JAMA. 2020;323:1277-1285. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 125] [Cited by in RCA: 113] [Article Influence: 22.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Pelizzaro F, Marsilio I, Fassan M, Piazza F, Barberio B, D'Odorico A, Savarino EV, Farinati F, Zingone F. The Risk of Malignancies in Celiac Disease-A Literature Review. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 28] [Cited by in RCA: 22] [Article Influence: 5.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Lynch DA, Sobala GM, Dixon MF, Gledhill A, Jackson P, Crabtree JE, Axon AT. Lymphocytic gastritis and associated small bowel disease: a diffuse lymphocytic gastroenteropathy? J Clin Pathol. 1995;48:939-945. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 37] [Cited by in RCA: 63] [Article Influence: 2.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Cuoco L, Cammarota G, Tursi A, Papa A, Certo M, Cianci R, Fedeli G, Gasbarrini G. Disappearance of gastric mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue in coeliac patients after gluten withdrawal. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1998;33:401-405. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Levine A, Domanov S, Sukhotnik I, Zangen T, Shaoul R. Celiac-associated peptic disease at upper endoscopy: how common is it? Scand J Gastroenterol. 2009;44:1424-1428. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Tumgor G, Agin M, Doran F, Cetiner S. Frequency of Celiac Disease in Children with Peptic Ulcers. Dig Dis Sci. 2018;63:2681-2686. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 33. | Ciacci C, Squillante A, Rendina D, Limauro S, Bencivenga C, Labanca F, Romano R, Mazzacca G. Helicobacter pylori infection and peptic disease in coeliac disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2000;12:1283-1287. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 30] [Cited by in RCA: 31] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 34. | Levy N, Stermer E, Boss JM. Accuracy of endoscopy in the diagnosis of inflamed gastric and duodenal mucosa. Isr J Med Sci. 1985;21:564-568. [PubMed] |
| 35. | Dahshan A, Rabah R. Correlation of endoscopy and histology in the gastroesophageal mucosa in children: are routine biopsies justified? J Clin Gastroenterol. 2000;31:213-216. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 24] [Cited by in RCA: 25] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 36. | Sheiko MA, Feinstein JA, Capocelli KE, Kramer RE. The concordance of endoscopic and histologic findings of 1000 pediatric EGDs. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015;81:1385-1391. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 24] [Cited by in RCA: 27] [Article Influence: 2.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 37. | Wolf J, Petroff D, Richter T, Auth MKH, Uhlig HH, Laass MW, Lauenstein P, Krahl A, Händel N, de Laffolie J, Hauer AC, Kehler T, Flemming G, Schmidt F, Rodrigues A, Hasenclever D, Mothes T. Validation of Antibody-Based Strategies for Diagnosis of Pediatric Celiac Disease Without Biopsy. Gastroenterology. 2017;153:410-419.e17. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 68] [Cited by in RCA: 92] [Article Influence: 11.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 38. | Oyaert M, Vermeersch P, De Hertogh G, Hiele M, Vandeputte N, Hoffman I, Bossuyt X. Combining antibody tests and taking into account antibody levels improves serologic diagnosis of celiac disease. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2015;53:1537-1546. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 23] [Cited by in RCA: 29] [Article Influence: 3.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 39. | Penny HA, Raju SA, Lau MS, Marks LJ, Baggus EM, Bai JC, Bassotti G, Bontkes HJ, Carroccio A, Danciu M, Derakhshan MH, Ensari A, Ganji A, Green PHR, Johnson MW, Ishaq S, Lebwohl B, Levene A, Maxim R, Mohaghegh Shalmani H, Rostami-Nejad M, Rowlands D, Spiridon IA, Srivastava A, Volta U, Villanacci V, Wild G, Cross SS, Rostami K, Sanders DS. Accuracy of a no-biopsy approach for the diagnosis of coeliac disease across different adult cohorts. Gut. 2021;70:876-883. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 93] [Cited by in RCA: 96] [Article Influence: 24.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 40. | Holmes G, Ciacci C. The serological diagnosis of coeliac disease - a step forward. Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2018;11:209-215. [PubMed] |