Published online Aug 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i32.4681
Peer-review started: April 16, 2022
First decision: May 12, 2022
Revised: May 25, 2022
Accepted: July 31, 2022
Article in press: July 31, 2022
Published online: August 28, 2022
Processing time: 132 Days and 2.5 Hours
For patients with portal hypertension (PH), portal vein thrombosis (PVT) is a fatal complication after splenectomy. Postoperative platelet elevation is considered the foremost reason for PVT. However, the value of postoperative platelet elevation rate (PPER) in predicting PVT has never been studied.
To investigate the predictive value of PPER for PVT and establish PPER-based prediction models to early identify individuals at high risk of PVT after splenectomy.
We retrospectively reviewed 483 patients with PH related to hepatitis B virus who underwent splenectomy between July 2011 and September 2018, and they were randomized into either a training (n = 338) or a validation (n = 145) cohort. The generalized linear (GL) method, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO), and random forest (RF) were used to construct models. The receiver operating characteristic curves (ROC), calibration curve, decision curve analysis (DCA), and clinical impact curve (CIC) were used to evaluate the robustness and clinical practicability of the GL model (GLM), LASSO model (LSM), and RF model (RFM).
Multivariate analysis exhibited that the first and third days for PPER (PPER1, PPER3) were strongly associated with PVT [odds ratio (OR): 1.78, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.24-2.62, P = 0.002; OR: 1.43, 95%CI: 1.16-1.77, P < 0.001, respectively]. The areas under the ROC curves of the GLM, LSM, and RFM in the training cohort were 0.83 (95%CI: 0.79-0.88), 0.84 (95%CI: 0.79-0.88), and 0.84 (95%CI: 0.79-0.88), respectively; and were 0.77 (95%CI: 0.69-0.85), 0.83 (95%CI: 0.76-0.90), and 0.78 (95%CI: 0.70-0.85) in the validation cohort, respectively. The calibration curves showed satisfactory agreement between prediction by models and actual observation. DCA and CIC indicated that all models conferred high clinical net benefits.
PPER1 and PPER3 are effective indicators for postoperative prediction of PVT. We have successfully developed PPER-based practical models to accurately predict PVT, which would conveniently help clinicians rapidly differentiate individuals at high risk of PVT, and thus guide the adoption of timely interventions.
Core Tip: For patients with portal hypertension related to hepatitis B virus, postoperative platelet elevation rate (PPER) is an important predictor of the formation of portal vein thrombosis (PVT) after splenectomy. This study was the first to construct PPER-based practical models for predicting PVT, which would be helpful for clinicians to recognize individuals at high risk of PVT as soon as possible.
- Citation: Li J, Wu QQ, Zhu RH, Lv X, Wang WQ, Wang JL, Liang BY, Huang ZY, Zhang EL. Machine learning predicts portal vein thrombosis after splenectomy in patients with portal hypertension: Comparative analysis of three practical models. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(32): 4681-4697
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i32/4681.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i32.4681
Liver cirrhosis is recognized as an extremely important and rapidly increasing disease burden in the world[1]. In the progressive stage of liver cirrhosis, the complications caused by portal hypertension (PH), including esophagogastric variceal bleeding and hypersplenism, pose a great threat to the patients’ life and health[2,3]. Liver transplantation is currently recommended as a curative treatment for liver cirrhosis combined with PH; however, due to the shortage of liver sources and high trans-plantation cost, its clinical practicability is limited[4,5]. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt seems to be a gospel for PH, but unfortunately, restenosis or/and hepatic encephalopathy will occur in more than 60% of patients[6,7]. In Asia, splenectomy (or combined with devascularization) has been widely adopted as an effective treatment for hypersplenism or esophageal and gastric variceal bleeding caused by PH[8,9].
Portal vein thrombosis (PVT) is often defined as thrombosis within the portal vein trunk or intrahepatic portal branches, with or without the splenic vein or superior mesenteric vein involvement[10,11]. PVT is considered a dreaded complication after splenectomy for patients with PH[12], and the probability of PVT has been reported to be 4.8%-51.5%[13-15]. For patients with acute PVT and PVT resulting in superior mesenteric vein thrombosis, it has been reported that PVT may be closely associated with acute liver failure and could influence mortality[16]. Hence, strategies are needed to prevent PVT in patients who underwent splenectomy. In clinical practice, anticoagulation is a critical method for the prevention and treatment of PVT in patients after splenectomy. However, when the anticoagulation therapy should be started remains controversial. Early anticoagulation may result in life-threatening bleeding events for patients with liver cirrhosis. Whether anticoagulant therapy should be prescribed to all patients after splenectomy deserves careful consideration. In addition, the majority of patients with PVT are asymptomatic and only a few experience abdominal discomfort[12]. Therefore, there is an urgent requirement to find effective diagnostic methods to early and rapidly identify individuals with high risk of PVT after splenectomy, and then further guide clinicians to take intervention measures. Color Doppler ultrasonography and/or contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) is commonly applied for the final diagnosis of PVT[17]; however, they seem to be useless for screening out the high-risk individuals who are vulnerable to PVT. Given this, many scholars attempted to investigate the risk factors closely related to the occurrence of PVT after splenectomy[8,18-21]. Several investigators paid attention to the fact that preoperative low platelet count (PLT) and postoperative high PLT may be crucial predictors of the risk of PVT postoperatively[19,22].
Generally speaking, patients with PH will experience rebounding rises in PLT after splenectomy[23], combined with hemodynamic changes in the portal venous system, and thus these patients are highly prone to developing PVT[24]. However, the effect of the amplitude of sharp postoperative rises in PLT on PVT has received little attention. We speculated that the postoperative platelet elevation rate (PPER) should be an important predictor of PVT. To the best of our knowledge, there are no reports on the relationship between PPER and PVT.
In recent years, to meet the urgent demand of finding effective methods to predict PVT after splenectomy, several studies have attempted to construct predictive models for PVT after splenectomy in patients with cirrhosis using multivariate regression analysis[25,26]. However, there are few clinical variables included in the analysis and the accuracy of these prediction models is still unsatisfactory. Therefore, there is an urgent need for an efficient and accurate visualization model.
Nowadays, novel machine learning algorithms based on more clinical features have shown great potential in various aspects of medical research, especially in the construction of predictive models, and the features screened for model construction are clinically interpretable[27-29]. Gao et al[28] constructed four machine learning models based on 53 raw clinical features of coronavirus disease 2019 patients to distinguish individuals at high risk for mortality, with an area under the receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curve (AUC) of 0.976. Kawakami et al[29] developed seven supervised machine learning classifiers based on 32 clinical parameters, among which the random forest (RF) model showed the best performance in distinguishing epithelial ovarian cancer from benign ovarian tumors with an AUC of 0.968. The wide range of applications of machine learning methods has surpassed conventional statistical analysis due to their higher accuracy, which might enable machine learning to be increasingly applied in the field of medical research[30-32]. Although compared with traditional multivariate analysis methods, machine learning algorithms have overwhelming advantages in constructing clinical prediction models, so far, only Wang et al[33] have tried to construct a prediction model of PVT after splenectomy in cirrhotic patients with PH using machine learning algorithms. The model that they constructed has greatly improved the prediction efficiency compared with the traditional models. However, the clinical parameters involved in the construction of the model are extremely complex, which limits its clinical use.
Therefore, the purpose of this study was to evaluate the predictive value of PPER for the risk of PVT after splenectomy for patients with PH. In addition, we sought to build simple, efficient, and accurate practical models for predicting PVT with machine learning algorithms to facilitate assisting clinicians in the early identification of individuals at high risk of PVT after splenectomy and taking intervention measures in time. We present the following article in accordance with the TRIPOD reporting checklist.
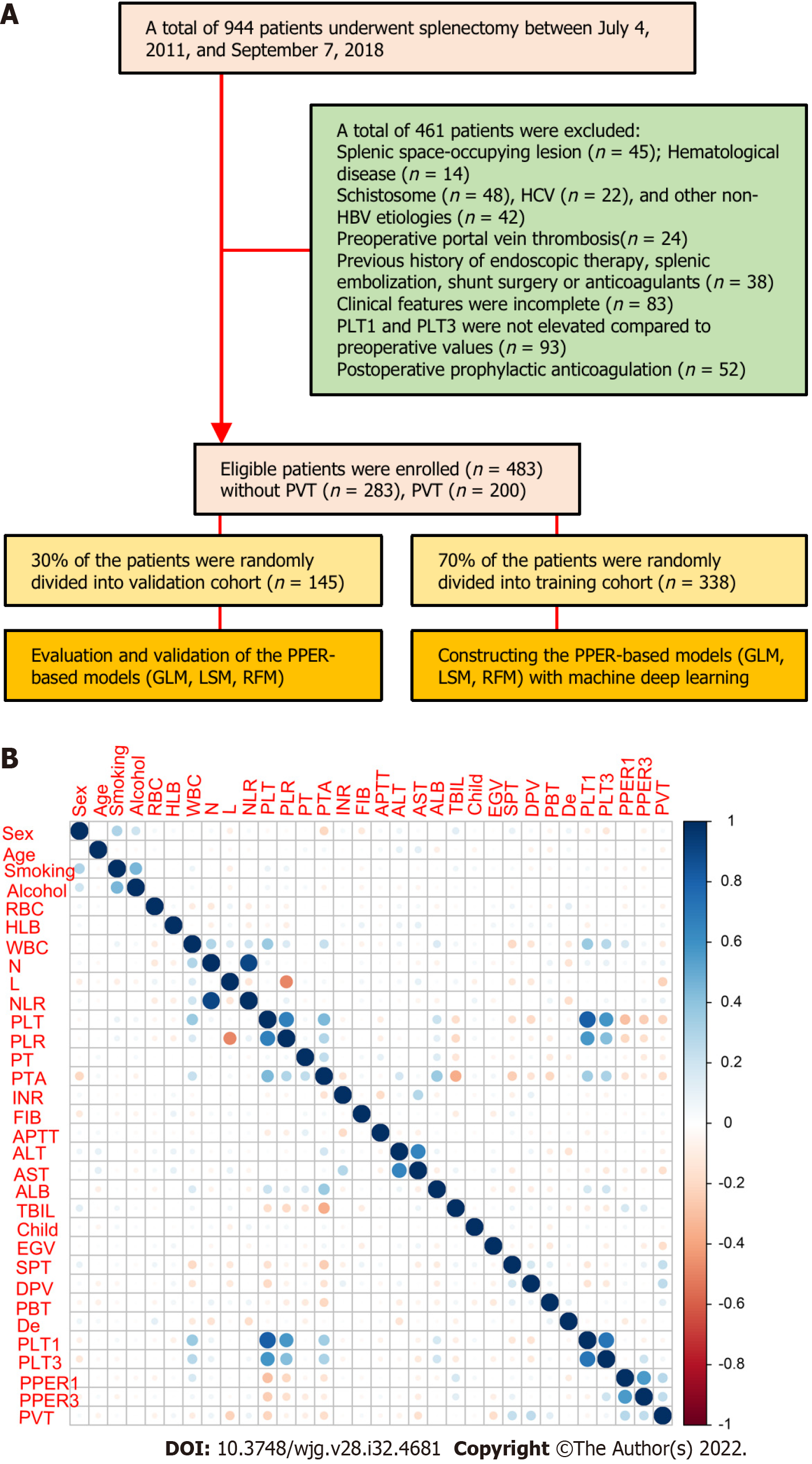
We retrospectively recruited 944 consecutive patients aged no less than 18 years who underwent splenectomy at our institution between July 4, 2011 and September 7, 2018. The patients with the following conditions were excluded: (1) Splenic space-occupying lesion; (2) Hematological disease; (3) PH caused by non-hepatitis B virus (HBV) related etiologies, such as schistosome, hepatitis C virus, or other unknown causes; (4) Presence of PVT confirmed by preoperative imaging; (5) Previous history of endoscopic therapy, splenic embolization, shunt surgery, or anticoagulants; (6) Incomplete clinical features; (7) Unelevated PLT on the first (PLT1) and third day (PLT3) after the operation compared to the preoperative values; and (8) Receiving prophylactic anti-coagulant therapy after splenectomy. Finally, a total of 483 patients with PH interrelated to HBV were included in this study. The flow diagram of patient selection and study design is shown in Figure 1A. The study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology. Owing to the retrospective nature of this study, written informed consent was waived.
All the patients’ clinical features were acquired from the electronic medical record system in our institution, which mainly included sex, age, smoking and drinking history, previous treatment history, etiologies, blood biochemical parameters, and imaging information. The blood biochemical parameters included routine blood tests [red blood cells (RBC), reference interval: 4.30-5.80 × 1012/L; hemoglobin, reference interval: 130.0-175.0 g/L; white blood cells (WBC), reference interval: 3.50-9.50 × 109/L; neutrophil count (N), reference interval: 1.80-6.30 × 109/L; lymphocyte count (L), reference interval: 1.10-3.20 × 109/L; neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR); PLT, reference interval: 125.0-350.0 × 109/L; platelet to lymphocyte ratio], coagulation function [prothrombin time, reference interval: 11.5-14.5 s; prothrombin activity (PTA), reference interval: 75.0%-125.0%; international normalized ratio, reference interval: 0.80-1.20; fibrinogen, reference interval: 2.00-4.00 g/L; activated partial thromboplastin time, reference interval: 29.0-42.0 s], and liver function [alanine aminotransaminase (ALT), reference interval: ≤ 41 U/L; aspartate aminotransaminase (AST), reference interval: ≤ 40 U/L; serum albumin, reference interval: 35.0-52.0 g/L; serum total bilirubin, reference interval: ≤ 26 μmol/L] within 7 d before surgery, as well as PLT1 and PLT3. The preoperative Child-Pugh grade was divided into three levels of A, B, and C[34], with grade C excluded. Information on the esophageal and gastric varices (EGV), spleen thickness (SPT), diameter of the portal vein (DPV), and preoperative blood transfusion (PBT) within 7 d before the operation was also collected.
We diagnosed PVT by color Doppler ultrasound examination[35] and contrast-enhanced CT would be applied as an auxiliary examination when its diagnosis was questioned[36]. In this study, abdominal ultrasound and contrast-enhanced CT examinations were routinely performed within 7 d before the operation. Routine ultrasonography was performed on the 7th day after the operation[19,20], or at any time when there were suspected clinical symptoms of PVT such as fever, severe abdominal pain, vomiting, abnormal liver function, and leukocytosis[12].
According to the definition of varices[8], EGV was divided into EGV without varices and EGV with varices in this study. SPT was defined as the vertical distance between the splenic hilum and the cut point of the lateral margin, and DPV was measured as the largest anteroposterior diameter at the point of intersection with the hepatic artery, during the patient’s breath holding[37].
The PPER was calculated from the preoperative PLT and postoperative PLT. For example, PPER1 (at the first day) was calculated as (PLT1 - PLT)/ PLT × 100%, and PPER3 (at the third day) was calculated as (PLT3 - PLT)/ PLT × 100%.
All candidates were randomly divided into two parts by using the “caret” package, of which 70% were assigned to a training cohort and 30% were assigned to a validation cohort. All model building was performed in the training cohort. Multivariate forward stepwise logistic regression analysis was used to select valuable variables to construct the generalized linear model (GLM). The least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) was a well-established shrinkage method that can effectively screen meaningful variables from a large set of variables with potential multicollinearity to develop the LASSO model (LSM)[38], which was implemented by using the “glmnet” package. RF was composed of a great number of individual decision trees running as a whole[39]. These multifarious decision tree models were applied for the construction of the RF model (RFM)[40]. The importance of candidate variables was reflected by the mean decreased Gini (MDG) score.
The robustness and clinical practicability of models were assessed using the ROC curve, calibration curve, decision curve analysis (DCA), and clinical impact curve (CIC). The AUC were used to estimate the discernment of each model by using “rms” packages. The calibration curves were applied to examine the calibration ability of each model and calibrated with 1000 bootstrap samples to reduce overfitting bias. The clinical applicability of each model was informed by DCA and CIC using “rms” and “rmda” packages.
Statistical analyses were performed with R Statistical Software (version 4.1.2, https://www.r-project.org/). Continuous variables were tested for normality. Those with normality are described as the mean ± SD, while those without normality are described as the median and interquartile range. Continuous variables were compared using the student’s t-test or non-parametric rank-sum test (Kruskal-Wallis test) as appropriate. Categorical variables are described as numbers (percentage) and were compared using the Chi-square test or Fisher exact test as appropriate. Correlations between candidate variables were determined by Spearman’s correlation coefficient. All statistical tests were two-tailed, and P < 0.05 was considered significant.
The detailed clinical characteristics of 483 patients with PH are summarized in Table 1. All participants were randomly and automatically divided into a training cohort (n = 338, 70%) and a validation cohort (n = 145, 30%). The presence of PVT was diagnosed in 200 (41.4%) cases, 135 (39.9%) cases, and 65 (44.8%) cases in the overall cohort, training cohort, and verification cohort, respectively. Consistent with the results of the intergroup comparison, among the 31 candidate variables included, 14 were associated with PVT, including RBC, WBC, L, NLR, PLT, PTA, ALT, AST, EGV, SPT, DPV, PBT, PPER1, and PPER3 (Figure 1B and Supplementary Table 1), which indicated that PPER1 and PPER3 were highly likely to be potential predictors of PVT.
| Variable | Training cohort | Validation cohort | ||||
| Without PVT (n = 203) | PVT (n =135) | P value | Without PVT (n = 80) | PVT (n = 65) | P value | |
| Sex, n (%) | 0.312 | 0.86 | ||||
| Female | 69 (34.0) | 38 (28.1) | 20 (25.0) | 18 (27.7) | ||
| Male | 134 (66.0) | 97 (71.9) | 60 (75.0) | 47 (72.3) | ||
| Age, n (%) | 0.179 | 0.999 | ||||
| < 60 yr | 165 (81.3) | 118 (87.4%) | 71 (88.8) | 58 (89.2) | ||
| ≥ 60 yr | 38 (18.7) | 17 (12.6%) | 9 (11.2) | 7 (10.8) | ||
| Smoking, n (%) | 0.703 | 0.983 | ||||
| No | 167 (82.3) | 108 (80.0) | 64 (80.0) | 51 (78.5) | ||
| Yes | 36 (17.7) | 27 (20.0) | 16 (20.0) | 14 (21.5) | ||
| Alcohol, n (%) | 0.577 | 0.587 | ||||
| No | 167 (82.3) | 115 (85.2) | 69 (86.2) | 53 (81.5) | ||
| Yes | 36 (17.7) | 20 (14.8) | 11 (13.8) | 12 (18.5) | ||
| RBC1 (× 1012/L) | 3.59 (3.20-3.93) | 3.57 (3.21-3.90) | 0.69 | 3.74 (3.49-4.02) | 3.55 (3.22-3.93) | 0.044 |
| HLB1 (g/L) | 89.3 (78.1-103) | 93.2 (82.1-104) | 0.093 | 89.5 (79.5-107) | 91.1 (82.8-101) | 0.965 |
| WBC1 (× 109/L) | 2.51 (1.83-3.40) | 2.18 (1.48-2.87) | 0.007 | 2.46 (1.95-3.21) | 2.09 (1.58-2.92) | 0.06 |
| N1 (× 109/L) | 1.35 (0.98-2.09) | 1.27 (0.85-2.00) | 0.177 | 1.38 (1.06-1.98) | 1.15 (0.87-1.77) | 0.147 |
| L1 (× 109/L) | 0.79 (0.56-1.14) | 0.50 (0.38-0.79) | < 0.001 | 0.78 (0.51-1.11) | 0.63 (0.45-0.91) | 0.045 |
| NLR1 | 1.78 (1.18-2.99) | 2.43 (1.42-4.18) | 0.003 | 1.90 (1.23-3.08) | 2.16 (1.39-3.16) | 0.559 |
| PLT1 (× 109/L) | 48.0 (36.0-64.5) | 33.8 (26.0-47.9) | < 0.001 | 46.0 (32.1-57.0) | 35.0 (27.0-48.0) | 0.012 |
| PLR1 | 60.6 (43.4-97.0) | 72.5 (35.0-99.7) | 0.779 | 55.6 (37.9-91.3) | 58.8 (31.8-86.8) | 0.692 |
| PT1 (s) | 15.5 (14.1-16.6) | 15.3 (12.9-16.4) | 0.221 | 15.7 (14.4-16.3) | 15.3 (13.9-16.2) | 0.294 |
| PTA1 (%) | 64.0 (57.0-73.5) | 60.0 (50.0-69.0) | < 0.001 | 67.0 (57.0-73.0) | 63.0 (54.0-72.0) | 0.269 |
| INR1 | 1.34 (1.23-1.47) | 1.42 (1.29-1.62) | < 0.001 | 1.32 (1.23-1.50) | 1.36 (1.23-1.50) | 0.519 |
| FIB1 (g/L) | 2.35 (1.62-3.86) | 2.52 (1.82-3.78) | 0.269 | 2.29 (1.74-4.14) | 2.57 (1.83-3.62) | 0.764 |
| APTT1 (s) | 40.7 (37.5-44.8) | 40.6 (36.9-44.9) | 0.787 | 41.3 (37.9-44.3) | 41.0 (38.5-44.1) | 0.822 |
| ALT1 (U/L) | 22.0 (16.0-30.5) | 21.0 (15.0-28.0) | 0.578 | 25.5 (17.8-40.0) | 18.0 (15.0-27.0) | 0.007 |
| AST1 (U/L) | 29.0 (22.0-40.0) | 25.0 (22.0-35.0) | 0.021 | 30.5 (24.8-43.5) | 25.0 (21.0-34.0) | 0.009 |
| ALB1 (g/L) | 35.9 (32.7-39.5) | 35.8 (32.6-39.5) | 0.881 | 35.7 (33.1-38.3) | 36.4 (33.7-39.6) | 0.551 |
| TBIL1 (μmol/L) | 18.1 (12.4-24.6) | 18.8 (12.4-27.0) | 0.671 | 18.8 (13.6-24.6) | 18.0 (14.4-26.1) | 0.796 |
| Child-Pugh grade, n (%) | 0.644 | 0.999 | ||||
| A | 146 (71.9) | 101 (74.8) | 58 (72.5) | 48 (73.8) | ||
| B | 57 (28.1) | 34 (25.2) | 22 (27.5) | 17 (26.2) | ||
| EGV, n (%) | 0.023 | 0.001 | ||||
| No | 67 (33.0) | 62 (45.9) | 17 (21.2) | 32 (49.2) | ||
| Yes | 136 (67.0) | 73 (54.1) | 63 (78.8) | 33 (50.8) | ||
| SPT1 (cm) | 5.50 (4.60-6.40) | 6.40 (5.40-7.55) | < 0.001 | 5.70 (4.45-6.70) | 6.30 (5.30-7.30) | 0.034 |
| DPV1 (cm) | 1.30 (1.10-1.40) | 1.50 (1.25-1.70) | < 0.001 | 1.30 (1.10-1.50) | 1.40 (1.20-1.60) | 0.088 |
| PBT, n (%) | 0.126 | 0.023 | ||||
| No | 159 (78.3) | 95 (70.4) | 67 (83.8) | 43 (66.2) | ||
| Yes | 44 (21.7) | 40 (29.6) | 13 (16.2) | 22 (33.8) | ||
| De, n (%) | 0.457 | 0.344 | ||||
| No | 16 (7.88) | 7 (5.19) | 4 (5.00) | 6 (9.23) | ||
| Yes | 187 (92.1) | 128 (94.8) | 76 (95.0) | 59 (90.8) | ||
| PLT11 (× 109/L) | 79.0 (61.0-106) | 79.0 (64.0-102) | 0.866 | 74.0 (57.7-93.8) | 77.0 (61.0-102) | 0.418 |
| PLT31 (× 109/L) | 103 (78.5-158) | 117 (85.0-164) | 0.131 | 98.5 (75.5-140) | 112 (81.0-156) | 0.122 |
| PPER11 (%) | 0.59 (0.34-0.88) | 1.18 (0.57-2.31) | < 0.001 | 0.70 (0.36-1.11) | 0.87 (0.64-2.03) | 0.002 |
| PPER31 (%) | 1.15 (0.62-2.02) | 2.38 (1.52-3.87) | < 0.001 | 1.32 (0.79-2.04) | 2.29 (1.36-3.54) | < 0.001 |
Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses for risk factors associated with PVT in the overall cohort are presented in Table 2. In the univariate analysis, a total of 11 variables with P < 0.05 were included in the further multivariate analysis. Finally, the following six variables were revealed to be closely associated with the occurrence of PVT: L [odds ratio (OR): 0.28, 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.14-0.54, P < 0.001], EGV (OR: 0.51, 95%CI: 0.32-0.79, P = 0.003), SPT (OR: 1.22, 95%CI: 1.06-1.40, P = 0.005), DPV (OR: 3.57, 95%CI: 1.86-7.03, P < 0.001), PPER1 (OR: 1.78, 95%CI: 1.24-2.62, P = 0.002), and PPER3 (OR: 1.43, 95%CI: 1.16-1.77, P < 0.001). This result demonstrated that PPER1 and PPER3 were independent risk factors for the occurrence of PVT.
| Variable | Univariate | Multivariate1 | ||
| OR (95%CI) | P value | OR (95%CI) | P value | |
| Sex (female vs male) | 1.18 (0.79-1.76) | 0.42 | ||
| Age (< vs ≥ 60 yr) | 0.68 (0.40-1.16) | 0.16 | ||
| Smoking (no vs yes) | 1.15 (0.73-1.81) | 0.56 | ||
| Alcohol (no vs yes) | 0.96 (0.59-1.56) | 0.86 | ||
| RBC2 (× 1012/L) | 0.71 (0.44-1.14) | 0.16 | ||
| HLB2 (g/L) | 1.01 (0.99-1.02) | 0.22 | ||
| WBC2 (× 109/L) | 0.87 (0.76-1.00) | 0.05 | ||
| N2 (× 109/L) | 1.05 (0.98-1.12) | 0.20 | ||
| L2 (× 109/L) | 0.27 (0.16-0.45) | < 0.001 | 0.28 (0.14-0.54) | < 0.001 |
| NLR2 | 1.07 (1.01-1.14) | 0.03 | 1.03 (0.98-1.11) | 0.42 |
| PLT2 (× 109/L) | 0.98 (0.97-0.99) | < 0.001 | 0.99 (0.98-1.01) | 0.98 |
| PLR2 | 1.00 (1.00-1.00) | 0.18 | ||
| PT2 (s) | 0.94 (0.89-1.00) | 0.07 | ||
| PTA2 (%) | 0.97 (0.96-0.99) | < 0.001 | 0.99 (0.98-1.02) | 0.73 |
| INR2 | 0.98 (0.88-1.09) | 0.74 | ||
| FIB2 (g/L) | 1.06 (0.93-1.21) | 0.42 | ||
| APTT2 (s) | 0.99 (0.96-1.01) | 0.38 | ||
| ALT2 (U/L) | 0.99 (0.98-1.00) | 0.16 | ||
| AST2 (U/L) | 0.98 (0.97-0.99) | < 0.001 | 0.99 (0.98-1.00) | 0.14 |
| ALB2 (g/L) | 1.00 (0.97-1.04) | 0.97 | ||
| TBIL2 (μmol/L) | 1.00 (0.99-1.02) | 0.78 | ||
| Child-Pugh (A vs B) | 0.88 (0.59-1.33) | 0.56 | ||
| EGV (no vs yes) | 0.48 (0.33-0.69) | < 0.001 | 0.51 (0.32-0.79) | 0.003 |
| SPT2 (cm) | 1.34 (1.19-1.50) | < 0.001 | 1.22 (1.06-1.40) | 0.005 |
| DPV2 (cm) | 4.72 (2.69-8.29) | < 0.001 | 3.57 (1.86-7.03) | < 0.001 |
| PBT (no vs yes) | 1.78 (1.17-2.70) | 0.01 | 1.33 (0.79-2.26) | 0.28 |
| De (no vs yes) | 1.09 (0.53-2.25) | 0.81 | ||
| PLT12 (× 109/L) | 1.00 (0.99-1.00) | 0.32 | ||
| PLT32 (× 109/L) | 1.00 (1.00-1.00) | 0.25 | ||
| PPER2 (%) | 2.77 (2.1-3.66) | < 0.001 | 1.78 (1.24-2.62) | 0.002 |
| PPER32 (%) | 1.86 (1.58-2.19) | < 0.001 | 1.43 (1.16-1.77) | < 0.001 |
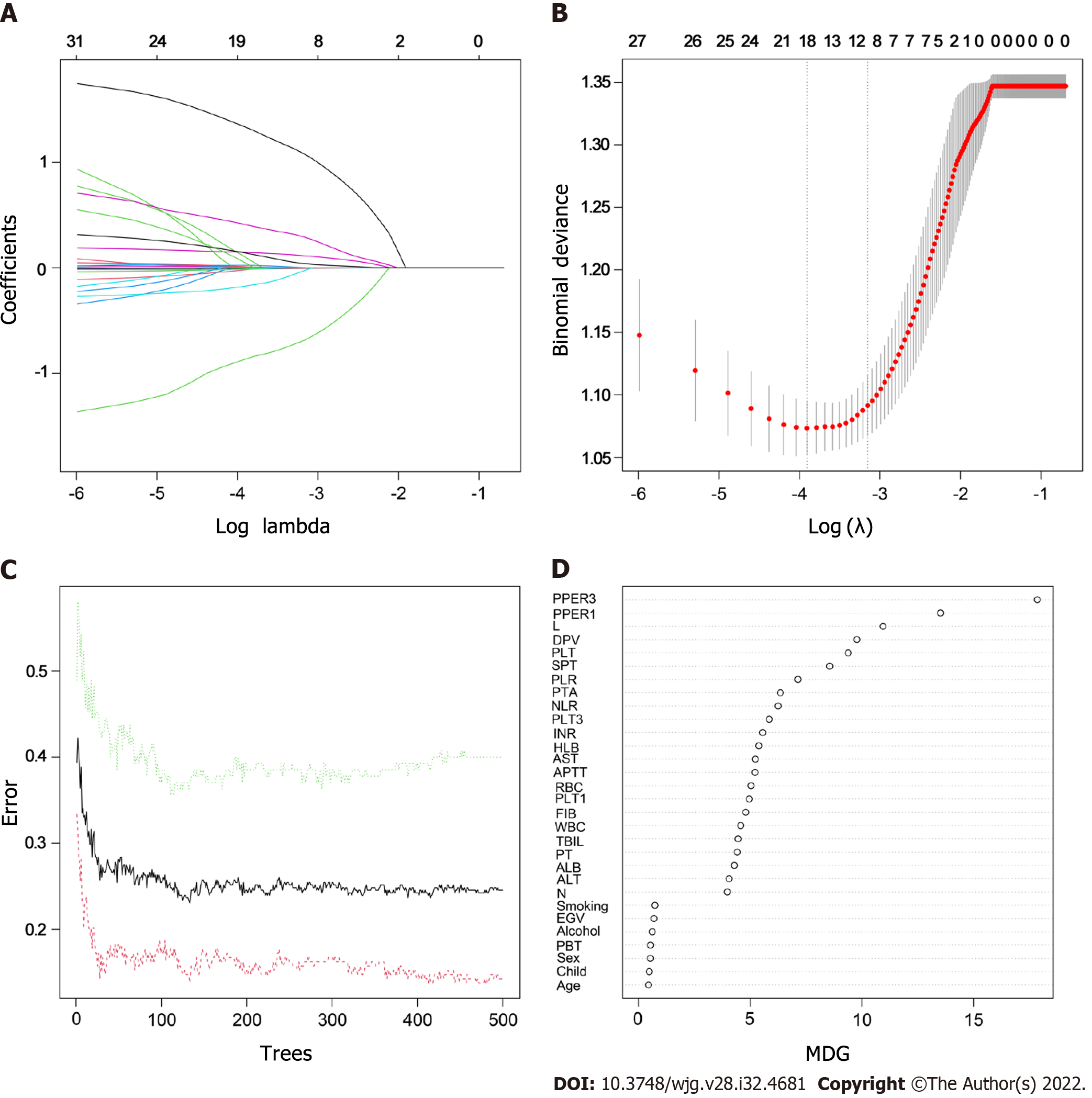
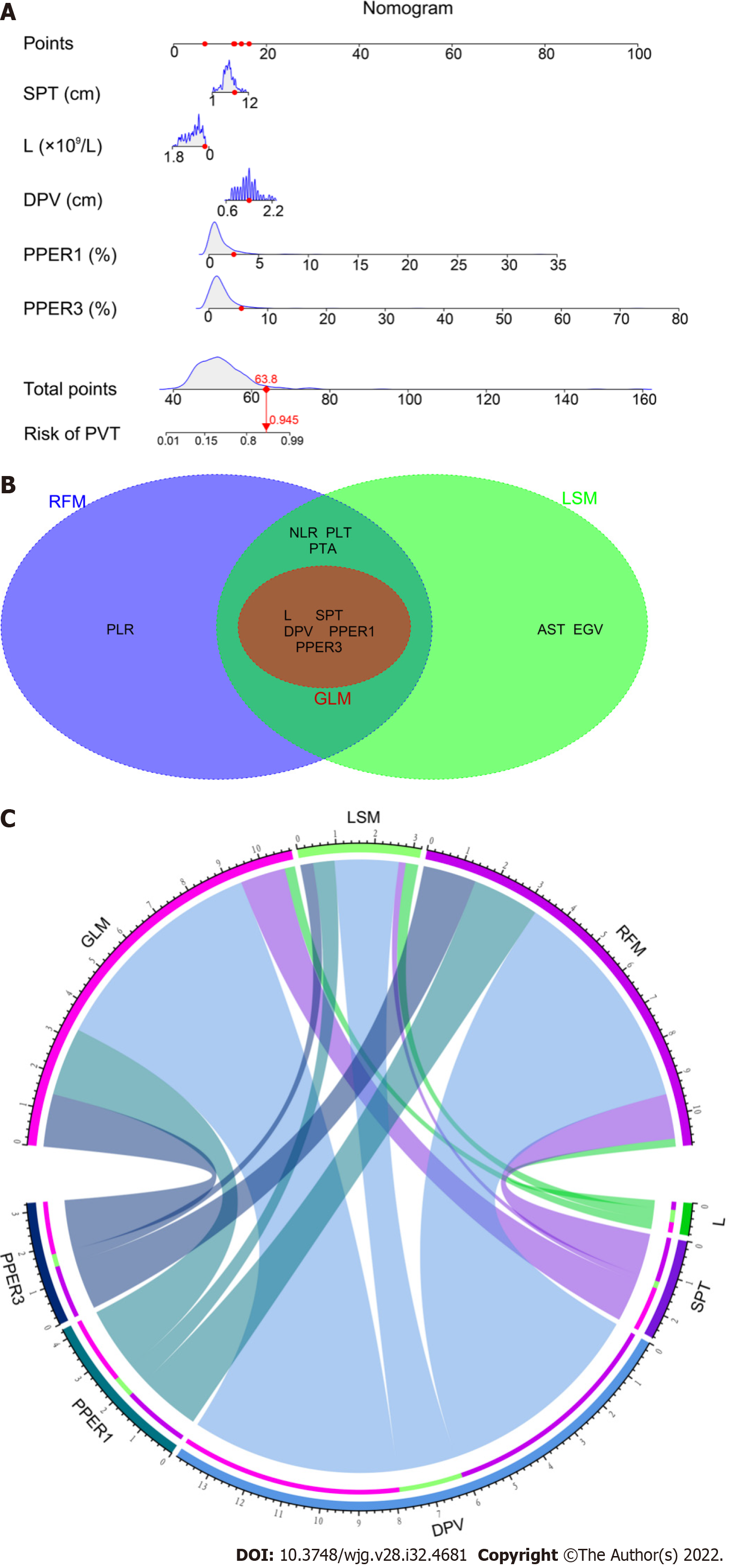
As shown in Supplementary Table 2, the following five variables strongly associated with PVT were chosen to construct the GLM: L (OR: 0.34, 95%CI: 0.14-0.77, P = 0.01), SPT (OR: 1.21, 95%CI: 1.02-1.44, P = 0.02), DPV (OR: 5.85, 95%CI: 2.57-14.05, P < 0.001), PPER1 (OR: 1.77, 95%CI: 1.13-2.82, P = 0.01), and PPER3 (OR: 1.42, 95%CI: 1.12-1.84, P = 0.005). The optimal LSM was obtained when all 31 candidate variables were shrunk to 10 through the LASSO (Figure 2A and B), which included L, NLR, PLT, PTA, AST, EGV, SPT, DPV, PPER1, and PPER3. In the RF, the total sample group had the smallest error of 24.56%, when the number of random trees was 133 (Figure 2C). A total of 133 random trees were set and passed through five iterations, and the importance scores of the candidate variables are presented in Figure 2D. Ultimately, nine variables with higher MDG scores were selected to construct the RFM.
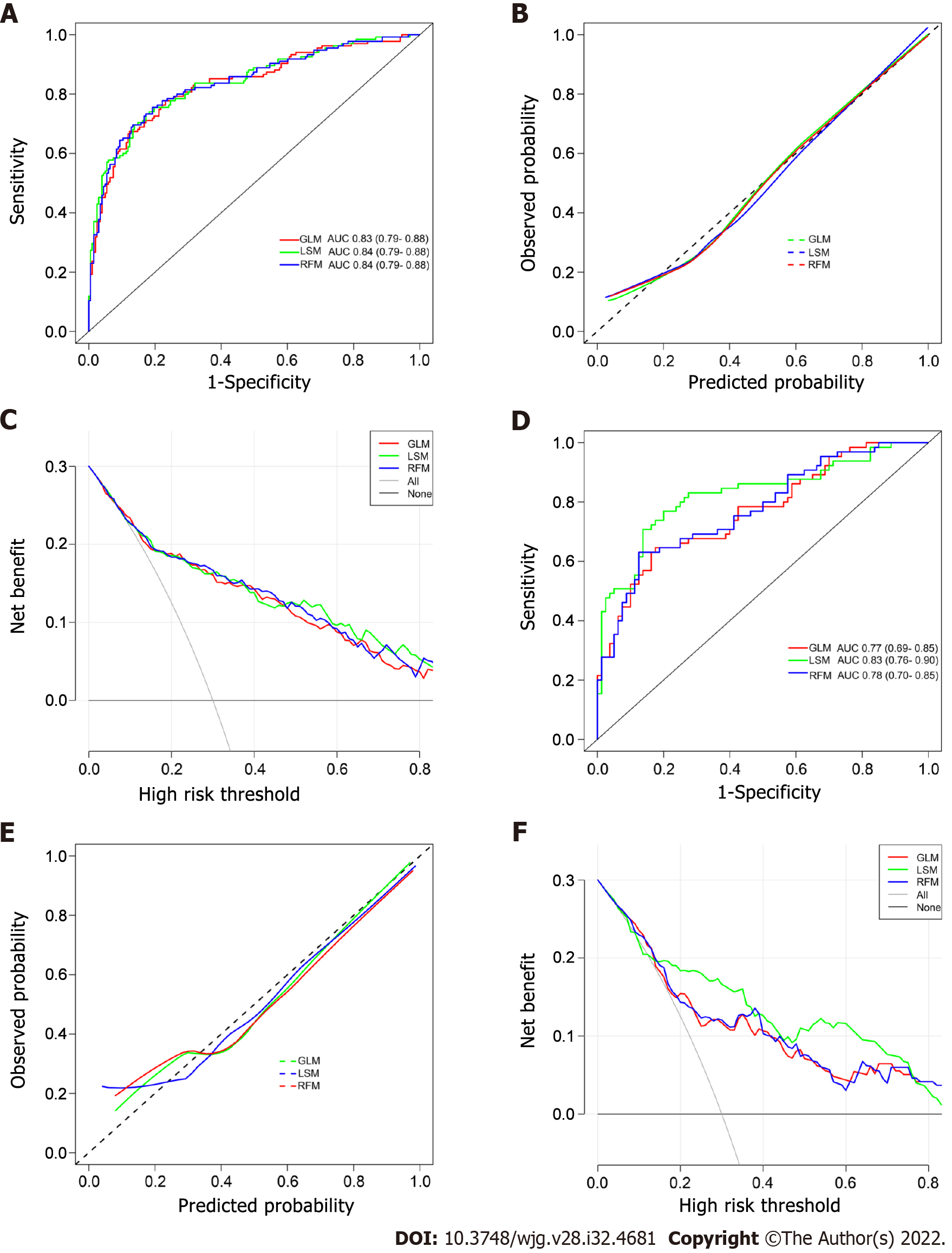
The ROC curves of the GLM, LSM, and RFM in the training cohort are shown in Figure 3A, and their AUCs were 0.83 (95%CI: 0.79-0.88), 0.84 (95%CI: 0.79-0.88), and 0.84 (95%CI: 0.79-0.88), respectively. All models had excellent calibration ability in the training cohort (Figure 3B). DCA and CIC revealed that they both conferred high clinical net benefits (Figures 3C and 4A-C).
In the validation cohort, the ROC curves of all models are presented in Figure 3D, and their AUC were 0.77 (95%CI: 0.69-0.85), 0.83 (95%CI: 0.76-0.90), and 0.78 (95%CI: 0.70-0.85), respectively. All models demonstrated highly satisfactory calibration capability and clinical functionality (Figures 3E and F and 4D-F).
As shown in Figure 5A, the nomogram for GLM recruited a total of five variables, including L, SPT, DPV, PPER1, and PPER3, which happened to be the intersection variables of the GLM, LSM, and RFM (Figure 5B). From this, it appeared that the aforementioned variables were significant predictors of the occurrence of PVT and they produced remarkable effects on the construction of the models. Moreover, the present study revealed that among these variables shared by the GLM, LSM, and RFM, the order of weight from high to low was DPV, PPER1, PPER3, SPT, and L (Figure 5C), which fully promulgated the predictive value of the PPER (PPER1 and PPER3) for PVT in all models.
The performance of three PPER-based models in predicting PVT in different cohorts is shown in Table 3. In the overall cohort, the accuracy of the GLM, LSM, and RFM was 76.2%, 77.4%, and 77.4% respectively. In the training cohort, the accuracy of the GLM, LSM, and RFM was 79.6%, 79.0%, and 78.7% respectively. In the validation cohort, the accuracy of the GLM, LSM, and RFM was 74.5%, 79.3%, and 76.6% respectively. When other metrics of the models, such as AUC, sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value, kappa values, and Brier scores, were comprehensively considered, the LSM and RFM appeared to be slightly superior to the GLM.
| AUC (95%CI) | Sensitivity (95%CI) | Specificity (95%CI) | PPV (95%CI) | NPV (95%CI) | Accuracy (%) | F1 | Kappa | Brier | |
| Overall cohort | |||||||||
| GLM | 0.812 (0.773-0.851) | 0.710 (0.642-0.772) | 0.799 (0.747-0.844) | 0.714 (0.650-0.775) | 0.796 (0.740-0.841) | 76.2 | 0.712 | 0.509 | 0.169 |
| LSM | 0.822 (0.784-0.861) | 0.640 (0.569-0.706) | 0.869 (0.824-0.906) | 0.776 (0.709-0.824) | 0.774 (0.718-0.832) | 77.4 | 0.701 | 0.522 | 0.163 |
| RFM | 0.814 (0.775-0.854) | 0.665 (0.595-0.730) | 0.852 (0.805-0.891) | 0.760 (0.695-0.812) | 0.782 (0.727-0.837) | 77.4 | 0.709 | 0.526 | 0.168 |
| Training cohort | |||||||||
| GLM | 0.833 (0.787-0.879) | 0.674 (0.588-0.752) | 0.877 (0.824-0.919) | 0.784 (0.705-0.842) | 0.802 (0.736-0.865) | 79.6 | 0.725 | 0.564 | 0.157 |
| LSM | 0.839 (0.794-0.884) | 0.733 (0.650-0.806) | 0.828 (0.768-0.877) | 0.739 (0.662-0.810) | 0.824 (0.759-0.874) | 79.0 | 0.736 | 0.562 | 0.153 |
| RFM | 0.838 (0.793-0.883) | 0.756 (0.674-0.825) | 0.808 (0.747-0.860) | 0.723 (0.647-0.800) | 0.832 (0.769-0.879) | 78.7 | 0.739 | 0.559 | 0.154 |
| Validation cohort | |||||||||
| GLM | 0.769 (0.691-0.846) | 0.646 (0.518-0.761) | 0.825 (0.724-0.901) | 0.750 (0.625-0.839) | 0.742 (0.628-0.847) | 74.5 | 0.694 | 0.477 | 0.190 |
| LSM | 0.826 (0.755-0.897) | 0.708 (0.582-0.814) | 0.863 (0.767-0.929) | 0.807 (0.687-0.883) | 0.784 (0.676-0.884) | 79.3 | 0.754 | 0.577 | 0.163 |
| RFM | 0.777 (0.700-0.853) | 0.631 (0.502-0.747) | 0.875 (0.782-0.938) | 0.804 (0.678-0.876) | 0.745 (0.632-0.864) | 76.6 | 0.707 | 0.516 | 0.187 |
Undoubtedly, PVT is a lethal complication after splenectomy in cirrhotic patients with PH[12]. Once PVT exists, there will be elevated portal venous pressure, ischemic bowel necrosis, progressive impairment of liver function, and even liver failure, which can eventually be life-threatening[41,42]. Therefore, research on the optimization of early detection of individuals at high risk of PVT after splenectomy is urgently needed. In this study, we successfully constructed the PPER-based models for predicting PVT by machine/deep learning, which would be conducive to early identifying the population at high risk of PVT.
In the present study, conventional generalized linear (CGL) method and machine/deep learning (including the LASSO and RF) were applied separately to screen out the variables that greatly affected the PVT prediction. The CGL method is characterized by strong interpretability, especially when the multifactorial forward stepwise regression method is used, and therefore, it has been widely applied as the traditional method to construct a predictive model[43]. However, with the rapid progress of artificial intelligence technology, a novel prediction model based on machine/deep learning has emerged with a higher probability of accuracy, which has led some clinicians to question the value of the CGL model in the clinical application of individualized patients[44]. Coincidentally, our research results proclaimed that the performance of the LSM and RFM seemed to be slightly better than the GLM.
Interestingly, the PPER-based models contained the following five intersecting factors, namely, SPT, DPV, L, PPER1, and PPER3, which sufficiently illustrated that these were the main contributors to the higher incidence of PVT. Previous studies found that preoperative SPT and DPV were important predictors of the formation of PVT after splenectomy in patients with PH[8,45], which was highly consistent with our findings. A very reasonable explanation is that a wide preoperative DPV and SPT will lead to slow portal vein blood flow, which is closely related to postoperative thrombosis[45,46].
In most cases, platelet, erythrocyte, and leukocyte counts rose dramatically over a short time after splenectomy in patients with PH, and the blood was hypercoagulable[8]. Therefore, previous studies suggested that preoperative low platelet and leukocyte counts were founders of the formation of PVT postoperatively[47]. This study revealed that preoperative L was an influential factor in PVT postoperatively, which coincided with the above view. Of note, the present study employed the PPER to reflect the magnitude of dynamic changes in preoperative and postoperative PLT. Subsequently, it was found that the PPER had high predictive value for the risk of PVT postoperatively, which was not addressed previously.
Stamou et al[48] reported that the median time to the formation of PVT after splenectomy in patients with PH was the 6th day (range, 3-11). Lu et al[8] concluded that 49.19% of patients developed PVT within 7 d after splenectomy. Therefore, scholars routinely applied ultrasonography examination to diagnose the PVT on the 7th day after splenectomy[8,19,20]. In this study, combined with the preoperative predictors and PPER, the PPER-based models that we constructed can effectively discriminate individuals with high risk of PVT as early as the first 3 d after the operation, which was extremely critical for guiding clinicians’ treatment strategies.
Currently, there is no standard preventive regimen for PVT after splenectomy in cirrhotic patients with PH[49]. Most scholars have recently advocated that the prophylactic anticoagulant therapy is administered earlier postoperatively, which will be more helpful in reducing the incidence of PVT[50,51]. However, it should be cautiously chosen because in patients with liver cirrhosis, it cannot avoid the risk of bleeding[51]. In addition, if the preventive regimens are routinely adopted for all individuals with PH after splenectomy, it is bound to raise the suspicion of overtreatment. Excitingly, in the present study, the accuracy of the PPER-based models in predicting PVT was up to 80%, which can distinguish individuals at high risk of PVT with high efficiency, and thus guide clinicians to take targeted individualized preventive measures in time.
The present study has some limitations. First, due to the retrospective nature of the study, selection bias cannot be eliminated. Second, the uncommon preoperative factors that may influence the formation of PVT, such as splenic vein diameter, spleen volume, and portal vein flow velocity[8,19], were not routinely measured in our institution and thus failed to be included in the present study. However, the SPT and DPV in this study can indirectly reflect these indicators to a certain extent[45,46]. Third, this was a monocentric study design. Although the PPER-based models demonstrated excellent performance for predicting PVT, they still lacked the verification of external cohorts. Therefore, large-scale prospective multicenter studies are warranted, which are beneficial to the popularity and application of the PPER-based models.
PPER1 and PPER3 are effective indicators for postoperative prediction of PVT. We have successfully developed the PPER-based practical models for predicting PVT, which could help clinicians identify individuals at high risk for PVT early and efficiently, and thus guide the timely intervention measures.
Patients with portal hypertension (PH) often experience rebounding rises in platelets following splenectomy. However, the value of postoperative platelet elevation rate (PPER) in predicting portal vein thrombosis (PVT) is unknown.
PVT is a potentially fatal complication after splenectomy for patients with PH, and the probability of PVT has been reported to be nearly 50%. Therefore, there is an imperious demand for effective diagnostic methods to early and rapidly identify individuals at high risk of PVT after splenectomy to further help clinicians take intervention measures as soon as possible.
We aimed to investigate the predictive value of PPER for PVT and establish PPER-based practical prediction models to early identify individuals at high risk of PVT after splenectomy.
We retrospectively reviewed 483 patients with PH related to hepatitis B virus who underwent splenectomy between July 2011 and September 2018, and they were randomized into either a training (n = 338) or a validation (n = 145) cohort. The generalized linear (GL) method, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO), and random forest (RF) were used to construct models. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves, calibration curve, decision curve analysis (DCA), and clinical impact curve (CIC) were used to evaluate the robustness and clinical practicability of the GL model (GLM), LASSO model (LSM), and RF model (RFM).
PPER at the first (PPER1) and third (PPER3) days were strongly associated with PVT [odds ratio (OR): 1.78, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.24-2.62, P = 0.002; OR: 1.43, 95%CI: 1.16-1.77, P < 0.001, respectively] in the multivariate logistic regression analysis. The areas under ROC curves of the GLM, LSM, and RFM in the training cohort were 0.83 (95%CI: 0.79-0.88), 0.84 (95%CI: 0.79-0.88), and 0.84 (95%CI: 0.79-0.88), respectively; and were 0.77 (95%CI: 0.69-0.85), 0.83 (95%CI: 0.76-0.90), and 0.78 (95%CI: 0.70-0.85) in the validation cohort, respectively. The calibration curves showed satisfactory agreement between prediction by models and actual observation. DCA and CIC indicated that all models conferred high clinical net benefit.
PPER1 and PPER3 are effective indicators for predicting PVT. We have successfully developed the PPER-based practical models to accurately predict PVT, which could conveniently help clinicians rapidly differentiate individuals at high risk of PVT, and further guide the adoption of timely interventions.
According to our experience, patients with a more remarkable increase in platelet count in the first 3 d after operation have a higher probability of PVT, which should be prioritized for prophylactic anticoagulation.
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Gastroenterology and hepatology
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): A
Grade B (Very good): B
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Balakrishnan DS, India; El-Nakeep S, Egypt S-Editor: Fan JR L-Editor: Wang TQ P-Editor: Chen YX
| 1. | GBD 2017 Cirrhosis Collaborators. The global, regional, and national burden of cirrhosis by cause in 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;5:245-266. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1080] [Cited by in RCA: 1008] [Article Influence: 201.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (4)] |
| 2. | Wright AS, Rikkers LF. Current management of portal hypertension. J Gastrointest Surg. 2005;9:992-1005. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 51] [Cited by in RCA: 53] [Article Influence: 2.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Bancu S, Borz C, Popescu G, Torok A, Mureşan A, Bancu L, Turcu M. [Spleno-renal distal and proximal shunts for hypersplenism due to hepatic cirrhosis]. Chirurgia (Bucur). 2007;102:665-668. [PubMed] |
| 4. | Adam R, Karam V, Delvart V, O'Grady J, Mirza D, Klempnauer J, Castaing D, Neuhaus P, Jamieson N, Salizzoni M, Pollard S, Lerut J, Paul A, Garcia-Valdecasas JC, Rodríguez FS, Burroughs A; All contributing centers (www. eltr.org); European Liver and Intestine Transplant Association (ELITA). Evolution of indications and results of liver transplantation in Europe. A report from the European Liver Transplant Registry (ELTR). J Hepatol. 2012;57:675-688. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 606] [Cited by in RCA: 643] [Article Influence: 49.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (2)] |
| 5. | Bodzin AS, Baker TB. Liver Transplantation Today: Where We Are Now and Where We Are Going. Liver Transpl. 2018;24:1470-1475. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 76] [Cited by in RCA: 129] [Article Influence: 18.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Narahara Y, Kanazawa H, Fukuda T, Matsushita Y, Harimoto H, Kidokoro H, Katakura T, Atsukawa M, Taki Y, Kimura Y, Nakatsuka K, Sakamoto C. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt versus paracentesis plus albumin in patients with refractory ascites who have good hepatic and renal function: a prospective randomized trial. J Gastroenterol. 2011;46:78-85. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 107] [Cited by in RCA: 130] [Article Influence: 9.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Salerno F, Merli M, Riggio O, Cazzaniga M, Valeriano V, Pozzi M, Nicolini A, Salvatori F. Randomized controlled study of TIPS versus paracentesis plus albumin in cirrhosis with severe ascites. Hepatology. 2004;40:629-635. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 249] [Cited by in RCA: 236] [Article Influence: 11.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Lu S, Hu G, Chen S, Wang J. Risk Factors of Portal Vein Thrombosis after Devascularization Treatment in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis: A Nested Case-Control Study. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:9583706. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | de Cleva R, Herman P, D'albuquerque LA, Pugliese V, Santarem OL, Saad WA. Pre- and postoperative systemic hemodynamic evaluation in patients subjected to esophagogastric devascularization plus splenectomy and distal splenorenal shunt: a comparative study in schistomomal portal hypertension. World J Gastroenterol. 2007;13:5471-5475. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 33] [Cited by in RCA: 31] [Article Influence: 1.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Parikh S, Shah R, Kapoor P. Portal vein thrombosis. Am J Med. 2010;123:111-119. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 127] [Cited by in RCA: 134] [Article Influence: 8.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Hepatobiliary Disease Study Group; Chinese Society of Gastroenterology; Chinese Medical Association. [Consensus for management of portal vein thrombosis in liver cirrhosis (2020, Shanghai)]. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2020;28:999-1007. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | van't Riet M, Burger JW, van Muiswinkel JM, Kazemier G, Schipperus MR, Bonjer HJ. Diagnosis and treatment of portal vein thrombosis following splenectomy. Br J Surg. 2000;87:1229-1233. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 102] [Cited by in RCA: 106] [Article Influence: 4.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Ikeda M, Sekimoto M, Takiguchi S, Kubota M, Ikenaga M, Yamamoto H, Fujiwara Y, Ohue M, Yasuda T, Imamura H, Tatsuta M, Yano M, Furukawa H, Monden M. High incidence of thrombosis of the portal venous system after laparoscopic splenectomy: a prospective study with contrast-enhanced CT scan. Ann Surg. 2005;241:208-216. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 202] [Cited by in RCA: 186] [Article Influence: 9.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Krauth MT, Lechner K, Neugebauer EA, Pabinger I. The postoperative splenic/portal vein thrombosis after splenectomy and its prevention--an unresolved issue. Haematologica. 2008;93:1227-1232. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 92] [Cited by in RCA: 102] [Article Influence: 6.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Qi X, Bai M, Guo X, Fan D. Pharmacologic prophylaxis of portal venous system thrombosis after splenectomy: a meta-analysis. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2014;2014:292689. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 28] [Cited by in RCA: 27] [Article Influence: 2.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Zhang Y, Xu BY, Wang XB, Zheng X, Huang Y, Chen J, Meng ZJ, Gao YH, Qian ZP, Liu F, Lu XB, Shi Y, Shang J, Li H, Wang SY, Yin S, Sun SN, Hou YX, Xiong Y, Li BL, Lei Q, Gao N, Ji LJ, Li J, Jie FR, Zhao RH, Liu JP, Lin TF, Chen LY, Tan WT, Zhang Q, Zou CC, Huang ZB, Jiang XH, Luo S, Liu CY, Zhang YY, Li T, Ren HT, Wang SJ, Deng GH, Xiong SE, Liu XX, Wang C, Yuan W, Gu WY, Qiao L, Wang TY, Wu DD, Dong FC, Hua J. Prevalence and Clinical Significance of Portal Vein Thrombosis in Patients With Cirrhosis and Acute Decompensation. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;18:2564-2572.e1. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 67] [Cited by in RCA: 47] [Article Influence: 9.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Rossi S, Ghittoni G, Ravetta V, Torello Viera F, Rosa L, Serassi M, Scabini M, Vercelli A, Tinelli C, Dal Bello B, Burns PN, Calliada F. Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography and spiral computed tomography in the detection and characterization of portal vein thrombosis complicating hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur Radiol. 2008;18:1749-1756. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 98] [Cited by in RCA: 101] [Article Influence: 5.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Wang L, Liu GJ, Chen YX, Dong HP, Zhang YQ, Wang LX. Combined use of D-dimer and P-selectin for the diagnosis of splenic or portal vein thrombosis following splenectomy. Thromb Res. 2010;125:e206-e209. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Wu S, Wu Z, Zhang X, Wang R, Bai J. The incidence and risk factors of portal vein system thrombosis after splenectomy and pericardial devascularization. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2015;26:423-428. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 23] [Cited by in RCA: 29] [Article Influence: 3.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Zhang Y, Wen TF, Yan LN, Yang HJ, Deng XF, Li C, Wang C, Liang GL. Preoperative predictors of portal vein thrombosis after splenectomy with periesophagogastric devascularization. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18:1834-1839. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 25] [Cited by in RCA: 22] [Article Influence: 1.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Wu LF, Bai DS, Shi L, Jin SJ, Zhou BH, Jiang GQ. Predictors of portal vein thrombosis after laparoscopic splenectomy and azygoportal disconnection in hepatitis B cirrhosis: a prospective study. Surg Endosc. 2022;36:4090-4098. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Matsui T, Usui M, Wada H, Iizawa Y, Kato H, Tanemura A, Murata Y, Kuriyama N, Kishiwada M, Mizuno S, Sakurai H, Isaji S. Platelet Activation Assessed by Glycoprotein VI/Platelet Ratio Is Associated With Portal Vein Thrombosis After Hepatectomy and Splenectomy in Patients With Liver Cirrhosis. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2018;24:254-262. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Ushitora Y, Tashiro H, Takahashi S, Amano H, Oshita A, Kobayashi T, Chayama K, Ohdan H. Splenectomy in chronic hepatic disorders: portal vein thrombosis and improvement of liver function. Dig Surg. 2011;28:9-14. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 49] [Cited by in RCA: 59] [Article Influence: 4.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Zhang Y, Wen T, Yan L, Chen Z, Yang H, Deng X, Liang G, Li G, Zhang X, Ran S, Liao Z. The changes of hepatic hemodynamics and functional hepatic reserve after splenectomy with periesophagogastric devascularization. Hepatogastroenterology. 2009;56:835-839. [PubMed] |
| 25. | Xu W, Cheng Y, Tu B. [Construction and validation of a nomogram for predicting the risk of portal vein thrombosis after splenectomy in patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis]. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2020;40:1265-1272. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Yuan HL, Wang M, Chu WW, Li FX, Lu JJ, Li Y. Nomogram Model for Prediction of Portal Vein Thrombosis in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis After Splenectomy: A Retrospective Analysis of 2 Independent Cohorts. Med Sci Monit. 2021;27:e929844. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Dong Z, Lin Y, Lin F, Luo X, Lin Z, Zhang Y, Li L, Li ZP, Feng ST, Cai H, Peng Z. Prediction of Early Treatment Response to Initial Conventional Transarterial Chemoembolization Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Machine-Learning Model Based on Computed Tomography. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2021;8:1473-1484. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Gao Y, Cai GY, Fang W, Li HY, Wang SY, Chen L, Yu Y, Liu D, Xu S, Cui PF, Zeng SQ, Feng XX, Yu RD, Wang Y, Yuan Y, Jiao XF, Chi JH, Liu JH, Li RY, Zheng X, Song CY, Jin N, Gong WJ, Liu XY, Huang L, Tian X, Li L, Xing H, Ma D, Li CR, Ye F, Gao QL. Machine learning based early warning system enables accurate mortality risk prediction for COVID-19. Nat Commun. 2020;11:5033. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 177] [Cited by in RCA: 173] [Article Influence: 34.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Kawakami E, Tabata J, Yanaihara N, Ishikawa T, Koseki K, Iida Y, Saito M, Komazaki H, Shapiro JS, Goto C, Akiyama Y, Saito R, Takano H, Yamada K, Okamoto A. Application of Artificial Intelligence for Preoperative Diagnostic and Prognostic Prediction in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Based on Blood Biomarkers. Clin Cancer Res. 2019;25:3006-3015. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 58] [Cited by in RCA: 121] [Article Influence: 20.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Ganggayah MD, Taib NA, Har YC, Lio P, Dhillon SK. Predicting factors for survival of breast cancer patients using machine learning techniques. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2019;19:48. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 83] [Cited by in RCA: 95] [Article Influence: 15.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Heo J, Yoon JG, Park H, Kim YD, Nam HS, Heo JH. Machine Learning-Based Model for Prediction of Outcomes in Acute Stroke. Stroke. 2019;50:1263-1265. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 156] [Cited by in RCA: 340] [Article Influence: 68.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Churpek MM, Yuen TC, Winslow C, Meltzer DO, Kattan MW, Edelson DP. Multicenter Comparison of Machine Learning Methods and Conventional Regression for Predicting Clinical Deterioration on the Wards. Crit Care Med. 2016;44:368-374. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 293] [Cited by in RCA: 406] [Article Influence: 45.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 33. | Wang M, Ding L, Xu M, Xie J, Wu S, Xu S, Yao Y, Liu Q. A novel method detecting the key clinic factors of portal vein system thrombosis of splenectomy & cardia devascularization patients for cirrhosis & portal hypertension. BMC Bioinformatics. 2019;20:720. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 34. | Pugh RN, Murray-Lyon IM, Dawson JL, Pietroni MC, Williams R. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg. 1973;60:646-649. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5490] [Cited by in RCA: 5734] [Article Influence: 110.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (2)] |
| 35. | Tran T, Demyttenaere SV, Polyhronopoulos G, Séguin C, Artho GP, Kaneva P, Fried GM, Feldman LS. Recommended timing for surveillance ultrasonography to diagnose portal splenic vein thrombosis after laparoscopic splenectomy. Surg Endosc. 2010;24:1670-1678. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 24] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 36. | Anton A, Campreciós G, Pérez-Campuzano V, Orts L, García-Pagán JC, Hernández-Gea V. The Pathophysiology of Portal Vein Thrombosis in Cirrhosis: Getting Deeper into Virchow's Triad. J Clin Med. 2022;11. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 30] [Article Influence: 10.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 37. | Gaiani S, Gramantieri L, Venturoli N, Piscaglia F, Siringo S, D'Errico A, Zironi G, Grigioni W, Bolondi L. What is the criterion for differentiating chronic hepatitis from compensated cirrhosis? J Hepatol. 1997;27:979-985. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 196] [Cited by in RCA: 173] [Article Influence: 6.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 38. | McEligot AJ, Poynor V, Sharma R, Panangadan A. Logistic LASSO Regression for Dietary Intakes and Breast Cancer. Nutrients. 2020;12. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 57] [Cited by in RCA: 180] [Article Influence: 36.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 39. | Majhi R, Thangeda R, Sugasi RP, Kumar N. Analysis and prediction of COVID-19 trajectory: A machine learning approach. J Public Aff. 2020;e2537. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 21] [Cited by in RCA: 16] [Article Influence: 4.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 40. | Strobl C, Boulesteix AL, Zeileis A, Hothorn T. Bias in random forest variable importance measures: illustrations, sources and a solution. BMC Bioinformatics. 2007;8:25. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1744] [Cited by in RCA: 1290] [Article Influence: 71.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 41. | Anstee QM, Dhar A, Thursz MR. The role of hypercoagulability in liver fibrogenesis. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2011;35:526-533. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 74] [Cited by in RCA: 74] [Article Influence: 5.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 42. | D'Amico G, De Franchis R; Cooperative Study Group. Upper digestive bleeding in cirrhosis. Post-therapeutic outcome and prognostic indicators. Hepatology. 2003;38:599-612. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 585] [Cited by in RCA: 597] [Article Influence: 27.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 43. | Song L, Langfelder P, Horvath S. Random generalized linear model: a highly accurate and interpretable ensemble predictor. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013;14:5. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 62] [Cited by in RCA: 64] [Article Influence: 5.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 44. | Amin MB, Greene FL, Edge SB, Compton CC, Gershenwald JE, Brookland RK, Meyer L, Gress DM, Byrd DR, Winchester DP. The Eighth Edition AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: Continuing to build a bridge from a population-based to a more "personalized" approach to cancer staging. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67:93-99. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2341] [Cited by in RCA: 4397] [Article Influence: 549.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (4)] |
| 45. | Chen H, Trilok G, Wang F, Qi X, Xiao J, Yang C. A single hospital study on portal vein thrombosis in cirrhotic patients - clinical characteristics & risk factors. Indian J Med Res. 2014;139:260-266. [PubMed] |
| 46. | Li MX, Zhang XF, Liu ZW, Lv Y. Risk factors and clinical characteristics of portal vein thrombosis after splenectomy in patients with liver cirrhosis. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2013;12:512-519. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 35] [Cited by in RCA: 37] [Article Influence: 3.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 47. | Kinjo N, Kawanaka H, Akahoshi T, Tomikawa M, Yamashita N, Konishi K, Tanoue K, Shirabe K, Hashizume M, Maehara Y. Risk factors for portal venous thrombosis after splenectomy in patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Br J Surg. 2010;97:910-916. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 86] [Cited by in RCA: 103] [Article Influence: 6.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 48. | Stamou KM, Toutouzas KG, Kekis PB, Nakos S, Gafou A, Manouras A, Krespis E, Katsaragakis S, Bramis J. Prospective study of the incidence and risk factors of postsplenectomy thrombosis of the portal, mesenteric, and splenic veins. Arch Surg. 2006;141:663-669. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 134] [Cited by in RCA: 123] [Article Influence: 6.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 49. | Kawanaka H, Akahoshi T, Kinjo N, Konishi K, Yoshida D, Anegawa G, Yamaguchi S, Uehara H, Hashimoto N, Tsutsumi N, Tomikawa M, Maehara Y. Impact of antithrombin III concentrates on portal vein thrombosis after splenectomy in patients with liver cirrhosis and hypersplenism. Ann Surg. 2010;251:76-83. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 81] [Cited by in RCA: 83] [Article Influence: 5.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 50. | Yao W, Feng Y, Liu T, Li W, Zhang M, Yao Y, Wu S. Rivaroxaban versus low-molecular weight heparin plus warfarin prevents portal vein system thrombosis after splenectomy and pericardial devascularization: A randomized clinical trial. EXCLI J. 2021;20:537-549. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 51. | Ding H, Zhang Y, Zhao L, Wu S, Liu J, Wang C, Pei T, Su Y. What intervention regimen is most effective prevention for Portal venous system thrombosis after splenectomy in cirrhotics patients with Portal hypertension? Pharmacol Res. 2020;157:104825. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 2.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |