Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2022; 28(31): 4328-4337
Published online Aug 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i31.4328
Published online Aug 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i31.4328
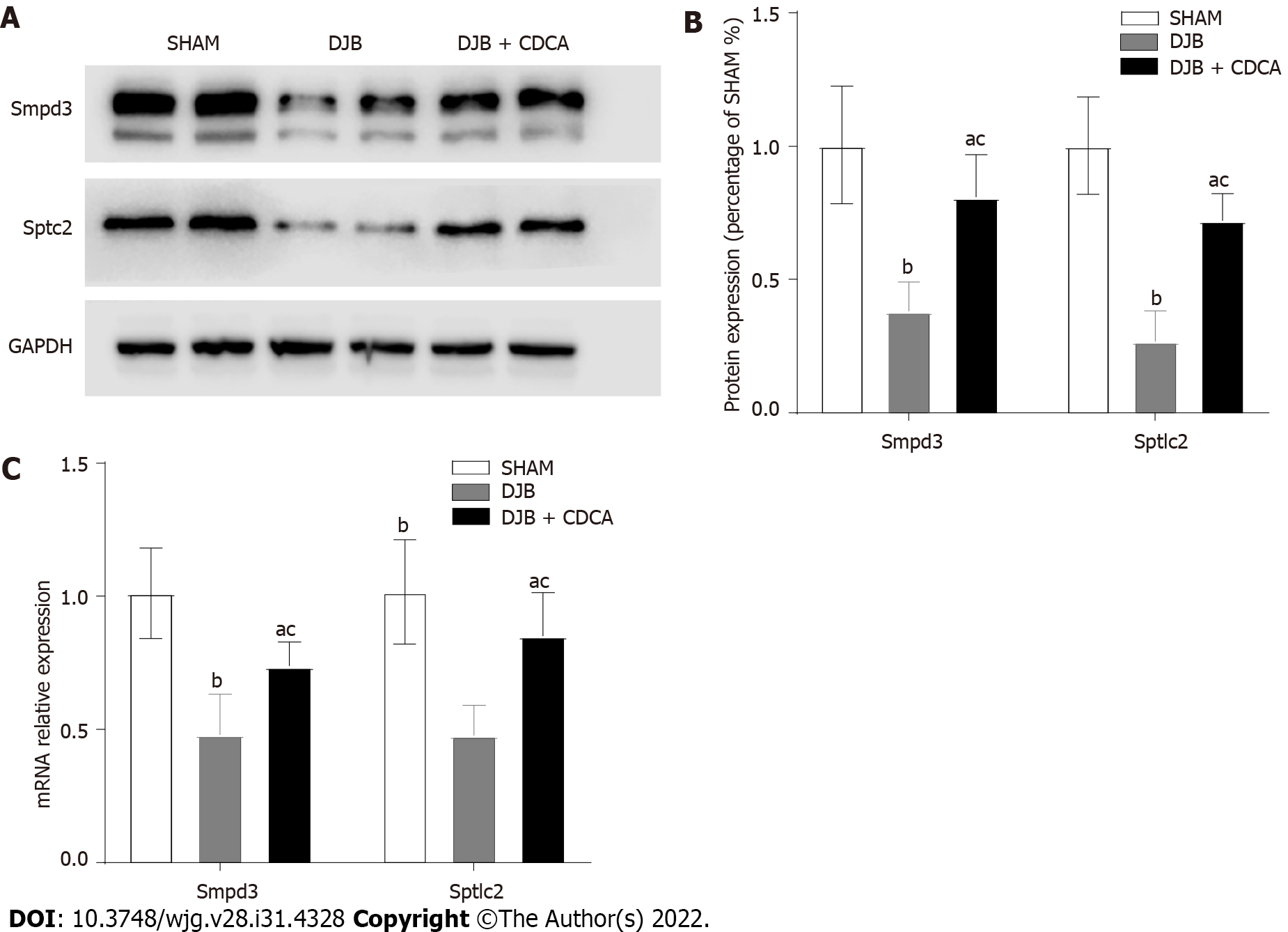
Figure 3 Expression of ceramide synthesis-related enzyme sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase 3 and serine palmitoyltransferase long chain base subunit 2 at protein and mRNA levels.
A: Expression of sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase 3 (Smpd3), serine palmitoyltransferase long chain base subunit 2 (Sptlc2) and GAPDH; B: Expression of Smpd3, Sptlc2 at protein; C: Expression of Smpd3, Sptlc2 mRNA levels. aP < 0.05, salicylhydroxamic acid vs duodenal-jejunal bypass + chenodeoxycholic acid; bP < 0.05, salicylhydroxamic acid vs duodenal-jejunal bypass; cP < 0.05, duodenal-jejunal bypass vs duodenal-jejunal bypass + chenodeoxycholic acid. SHAM: Salicylhydroxamic acid; DJB: Duodenal-jejunal bypass; CDCA: Chenodeoxycholic acid; Smpd3: Sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase 3; Sptlc2: Serine palmitoyltransferase long chain base subunit 2.
- Citation: Cheng ZQ, Liu TM, Ren PF, Chen C, Wang YL, Dai Y, Zhang X. Duodenal-jejunal bypass reduces serum ceramides via inhibiting intestinal bile acid-farnesoid X receptor pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(31): 4328-4337
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i31/4328.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i31.4328