Published online Aug 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i31.4338
Peer-review started: May 26, 2022
First decision: June 19, 2022
Revised: June 28, 2022
Accepted: July 25, 2022
Article in press: July 25, 2022
Published online: August 21, 2022
Processing time: 82 Days and 2.6 Hours
The mechanisms underlying diabetes remission after duodenal-jejunal bypass (DJB) remain elusive. In DJB surgery, the duodenum is excluded. However, the duodenum has emerged as an important regulator of glucose homeostasis, and elevated duodenal SIRT1 leads to improved hepatic insulin sensitivity. After DJB, bile acids (BAs) in the duodenum are not mixed and diluted by the ingested food. And activation of BA receptors promotes SIRT1 expression in many tissues. We hypothesized that BA-mediated upregulation of SIRT1 may contribute to diabetic control after DJB.
To investigate the surgical effects of DJB on duodenal SIRT1 expression and un
Twenty diabetic rats were randomly allocated to the sham (n = 10) and DJB (n = 10) groups. Body weight, food intake, fasting blood glucose (FBG), serum and intraduodenal total BA (TBA) levels were measured accordingly. Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) and intraperitoneal pyruvate tolerance test (ipPTT) were performed to evaluate the effects of surgeries on systemic glucose disposal and hepatic gluconeogenesis. The key genes of BA signaling pathway in the duodenal mucosa, including farnesoid X receptor (FXR), small heterodimer partner (SHP), and Takeda G-protein-coupled receptor 5 (TGR5) were evaluated by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction 8 wk postoperatively. The duodenal SIRT1, AMPK, and phosphorylated AMPK (p-AMPK) levels were evaluated by western blotting. Rat small intestine epithelial IEC-6 cells were treated with GW4064 and INT-777 to verify the effects of BAs on SIRT1 expression in enterocytes.
The DJB group exhibited body weight and food intake comparable to those of the sham group at all postoperative time points. The FBG level and area under the curve for the OGTT and ipPTT were significantly lower in the DJB group. The DJB group exhibited higher fasting and post
DJB elevates intraduodenal BA levels and activates the duodenal BA signaling pathway, which may upregulate duodenal SIRT1 and further contribute to improved glucose homeostasis after DJB.
Core Tip: The intrinsic mechanisms of diabetes remission after duodenal-jejunal bypass (DJB) surgery are complicated. Duodenal SIRT1 is a novel therapeutic target for diabetes, and increased duodenal SIRT1 is linked to improved hepatic insulin sensitivity and decreased hepatic glucose output. The animal study demonstrated that DJB increased intraduodenal bile acid (BA) levels, activated the BA signaling pathway, and upregulated SIRT1 expression in the duodenal mucosa. Our cell experiments proved that farnesoid X receptor and Takeda G-protein-coupled receptor 5 activation increased SIRT1 expression in rat small intestine epithelial cells, indicating that increased intraluminal BAs and activation of BA receptors contributed to increased duodenal SIRT1 after DJB.
- Citation: Han HF, Liu SZ, Zhang X, Wei M, Huang X, Yu WB. Duodenal-jejunal bypass increases intraduodenal bile acids and upregulates duodenal SIRT1 expression in high-fat diet and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(31): 4338-4350
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i31/4338.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i31.4338
Diabetes is one of the fastest-growing global health issues. The International Diabetes Federation reported that the global prevalence of diabetes in adults was approximately 10.5% in 2021, expected to rise to 12.2% in 2045[1]. Bariatric surgery is much more effective and persistent in diabetes control than conventional medical therapy[2]. Duodenal-jejunal bypass (DJB) is a well-designed experimental procedure investigating the weight-independent anti-diabetic mechanisms of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB). It can improve glucose homeostasis in both diabetic rats and patients[3-5], however, the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. A critical anatomical alteration of DJB is the exclusion of the duodenum. In addition, DJB liner, which mimics the duodenal-jejunal exclusion effects of RYGB, also improves glucose homeostasis[6]. Duodenal mucosal resurfacing, an endoscopic procedure that involves circumferential hydrothermal ablation and subsequent regeneration of the duodenal mucosa, elicits dramatic and durable glycemic improvements in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM)[7]. These findings suggest that the bypassed duodenum may play an important role in diabetic control after DJB.
The duodenum was primarily viewed as a digestive organ. However, accumulating evidence demonstrates that the duodenum has emerged as a key regulator of metabolic diseases, including diabetes[8]. The duodenal mucosa is exposed to various endogenous and exogenous chemical stimuli, such as macro- and micronutrients, gastric acid, bile acids (BAs), digestive enzymes, microorganisms, and drugs[9,10]. The duodenum is densely innervated by the enteric autonomous nervous system (ENS). Through chemical sensors located in the mucosa and ENS, the duodenum detects changes in luminal contents and further triggers a gut-brain negative feedback loop to inhibit exogenous nutrient intake and endogenous liver nutrient production[10,11]. In healthy rats, short-term intraduodenal intralipid infusion inhibits hepatic glucose production (HGP) via the gut-brain-liver neural axis. However, this suppressive effect is negated in insulin-resistant rats[12]. Metformin and resveratrol, two well-known anti-diabetic drugs, can activate specific duodenal energy sensors (AMPK and SIRT1, respectively) even before being absorbed into the systemic circulation, and further trigger the gut-brain-liver network to reverse insulin resistance and inhibit HGP[13,14].
SIRT1 is a conserved mammalian nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+)-dependent protein deacetylase that acts as a key metabolic sensor in various metabolic tissues, including the liver, skeletal muscle, adipose tissue, and pancreas. It directly links the cellular metabolic status to the regulation of gene expression, thus modulating various cellular processes, such as glucose metabolism, inflammation, and stress response[15,16]. SIRT1 is also expressed in the duodenal mucosa, which is significantly inhibited in high-fat diet (HFD)-fed insulin-resistant rats. Duodenum-specific knockdown of SIRT1 is sufficient to induce hepatic insulin resistance and increase hepatic glucose output in normal chow-fed rats[14]. To the best of our knowledge, the anti-diabetic effects of DJB surgery that could be linked to duodenal SIRT1 have not been investigated.
DJB hinders the duodenum from contacting the ingested chyme, therefore, the BAs released into the duodenum will not be mixed and diluted by food. In addition to their widely known roles in facilitating lipid absorption, BAs have recently been recognized as novel endocrine molecules that modulate glucose, lipids, and energy metabolism[17,18]. Activation of BA receptors, including the nuclear farnesoid X receptor (FXR) and membrane Takeda G-protein-coupled receptor 5 (TGR5), upregulates SIRT1 expression in the liver and brain, respectively[19,20]. These findings raise the possibility that DJB might upregulate duodenal SIRT1 by increasing intraluminal BAs, which might further contribute to the improved glucose homeostasis after DJB. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the impact of DJB on duodenal BA signaling and SIRT1 expression in HFD and streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats, and further explore the roles of BAs in modulating SIRT1 expression.
Eight-week-old male Wistar rats were purchased from the Laboratory Animal Center of Shandong University (Jinan, China) and individually housed in ventilated cages in a controlled environment (12 h light/dark cycle, 24 ± 2 °C, humidity 50%-60%). The rats had ad libitum access to rodent chow and water. The diabetic rat model was established by HFD (40% fat, Huafukang Biotech, China) feeding for 4 wk to induce insulin resistance, followed by subsequent intraperitoneal injection of low-dose STZ (35 mg/kg, Sigma, United States) to induce mild insulin deficiency and hyperglycemia. After 72 h of STZ administration, 20 diabetic rats with random blood glucose ≥ 16.7 mmol/L were selected and randomly allocated to the sham (n = 10) and DJB (n = 10) groups. All animal protocols were approved by the Ethics Committee on Experimental Animals of Cheeloo College of Medicine, Shandong University.
The rats were deprived of solid food but were given free access to water and 10% enteral nutrition powder (Ensure, Abbott Laboratories B.V., Netherlands) two days preoperatively. Complete fasting was initiated 12 h preoperatively. All operations were conducted under anesthesia with 10% chloral hydrate (3 mL/kg). DJB and sham surgeries were performed as previously described[21].
DJB: First, a midline incision was made in the upper abdomen and the duodenum was then transected 1 cm distal to the pylorus and the stump was sealed. Next, the jejunum was transected approximately 10 cm distal to the ligament of Treitz, and the distal limb of the jejunum was anastomosed to the proximal duodenum in an end-to-end manner. Finally, the biliopancreatic limb was anastomosed to the jejunum 15 cm distal to the duodenojejunal anastomosis in a Roux-en-Y manner.
Sham: Sham surgery was performed via an incision comparable to that of the DJB group. The intestines were transected at the same sites where enterotomies were performed in DJB, and re-anastomosis was made in situ. The operation time was prolonged equally to that of the DJB group to achieve similar surgical and anesthetic stress.
The rats were only given access to water during the first 24 h postoperatively, followed by 10% enteral nutrition powder for three days, and thereafter a standard rodent chow until the end of this study. Body weight and food intake were recorded preoperatively and once a week postoperatively. Fasting blood glucose (FBG) levels were measured at baseline and at 1, 2, 4, 6, and 8 wk postoperatively.
Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) was performed 2 and 8 wk postoperatively. The rats were administered with 20% glucose (1 g/kg body weight) by oral gavage after overnight fasting. Blood samples were collected from the tail vein at baseline and at 15, 30, 60, 120, and 180 min after glucose administration to measure blood glucose levels. The area under the curve for the OGTT (AUCOGTT) was calculated by trapezoidal integration.
The intraperitoneal pyruvate tolerance test (ipPTT) was conducted 2 and 8 wk postoperatively to evaluate hepatic gluconeogenic capacity and hepatic insulin resistance. After 12 h of fasting, 10% pyruvate solution (1 g/kg body weight) was administered intraperitoneally into conscious rats. Blood glucose levels were monitored at baseline and at 15, 30, 60, and 120 min after injection. The AUC for ipPTT (AUCipPTT) was calculated using trapezoidal integration.
Fasting and postprandial systemic total BAs (TBAs) were measured 2 and 8 wk postoperatively. The rats were fasted for 12 h and then administered with 10% Ensure (10 mL/kg body weight) via intragastric gavage. Blood samples were collected from the retrobulbar venous plexus into chilled SST tubes at baseline and 60 min after gavage to measure the systemic TBAs.
Eight weeks after the surgery, the rats were euthanized immediately after blood collection. Intestine segments of 0.5 cm length were excised from the descending and horizontal duodenum separately without rinsing. TBAs in the duodenum lumen were extracted by mixing the duodenal segments with 1 mL of 50% tert-butyl alcohol for 1 h at 37 °C. After centrifugation, the supernatant was collected and stored at -80 °C until analysis. BAs were measured with an automatic biochemistry analyzer (Roche Cobas 8000 system) using an enzyme cycling method.
Rat small intestine epithelial IEC-6 cells were purchased from Fuheng Biology (Shanghai, China), and cultured in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (Gibco, CA, United States) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Gibco, CA, United States), and maintained under standard culture conditions (in incubators at 37 °C in a 5% CO2/95% air atmosphere). To investigate the effects of FXR and TGR5 activation on SIRT1, AMPK, and phosphorylated AMPK (p-AMPK) expression, IEC-6 cells were treated with GW4064 (5 μM, 24 h) and INT-777 (10 μM, 1 h) respectively, and the control groups were treated with an equal volume of dimethyl sulfoxide. At the end of the study, cells were harvested for protein and gene expression analyses.
Total mRNA of the duodenal mucosa and IEC-6 cells were extracted using TRIzol Reagent (Cwbio, China). The total mRNA was then reverse-transcribed into cDNA using a HiFiScript cDNA Synthesis Kit (Cwbio, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The cDNA was subjected to real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) quantitation with UltraSYBR Mixture (Cwbio, China) on a RT-qPCR system (Hehui biotech, China). GAPDH was used as an internal control. Primers used in this study are listed in Table 1.
| Gene | Forward (5’-3’) | Reverse (5’-3’) |
| SIRT1 | GGGAACCTCTGCCTCATCTACAT | CGCCACCTAACCTATGACACAA |
| AMPK | GAAGATCGGACACTACGTGCT | ACTGCCACTTTATGGCCTGTC |
| FXR | CATTACAACGCGCTCACCTG | CCCATCTCTCTGCACTTCCT |
| TGR5 | TACTCACAGGGTTGGCACTG | CAAAAGTTGGGGGCCAAGTG |
| SHP | TCCGGTCCCCAGCATACTTA | GAAAGACTCCAGGCAGTGCT |
| GAPDH | GATTTGGCCGTATCGGAC | GAAGACGCCAGTAGACTC |
The duodenal mucosa was immediately flash-frozen in liquid nitrogen after the rats were euthanized. The cyclic adenosine 3’, 5’-monophosphate (cAMP) concentration in the duodenal mucosa was measured using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Sigma-Aldrich, United States).
Total proteins of the duodenal mucosa and IEC-6 cells were extracted with RIPA lysis buffer (Beyotime, China) and analyzed using a BCA protein assay kit (Beyotime, China). The primary antibodies used in western blotting were SIRT1 (Cell Signaling Technology, United States), AMPK (Cell Signaling Technology, United States), p-AMPK (Cell Signaling Technology, United States), and GAPDH (Proteintech, China). The protein bands were visualized using ECL solution (Millipore, United States), and band densitometry was assessed with ImageJ software.
Quantitative data were expressed as mean ± SD. The intergroups differences were evaluated by the Student’s t-test except for blood glucose levels in the OGTT and ipPTT studies, which were analyzed by two-way repeated measures ANOVA (mixed model ANOVA) followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test. All analyses were performed using SPSS (Version 26). The criterion for statistical significance was set at P < 0.05.
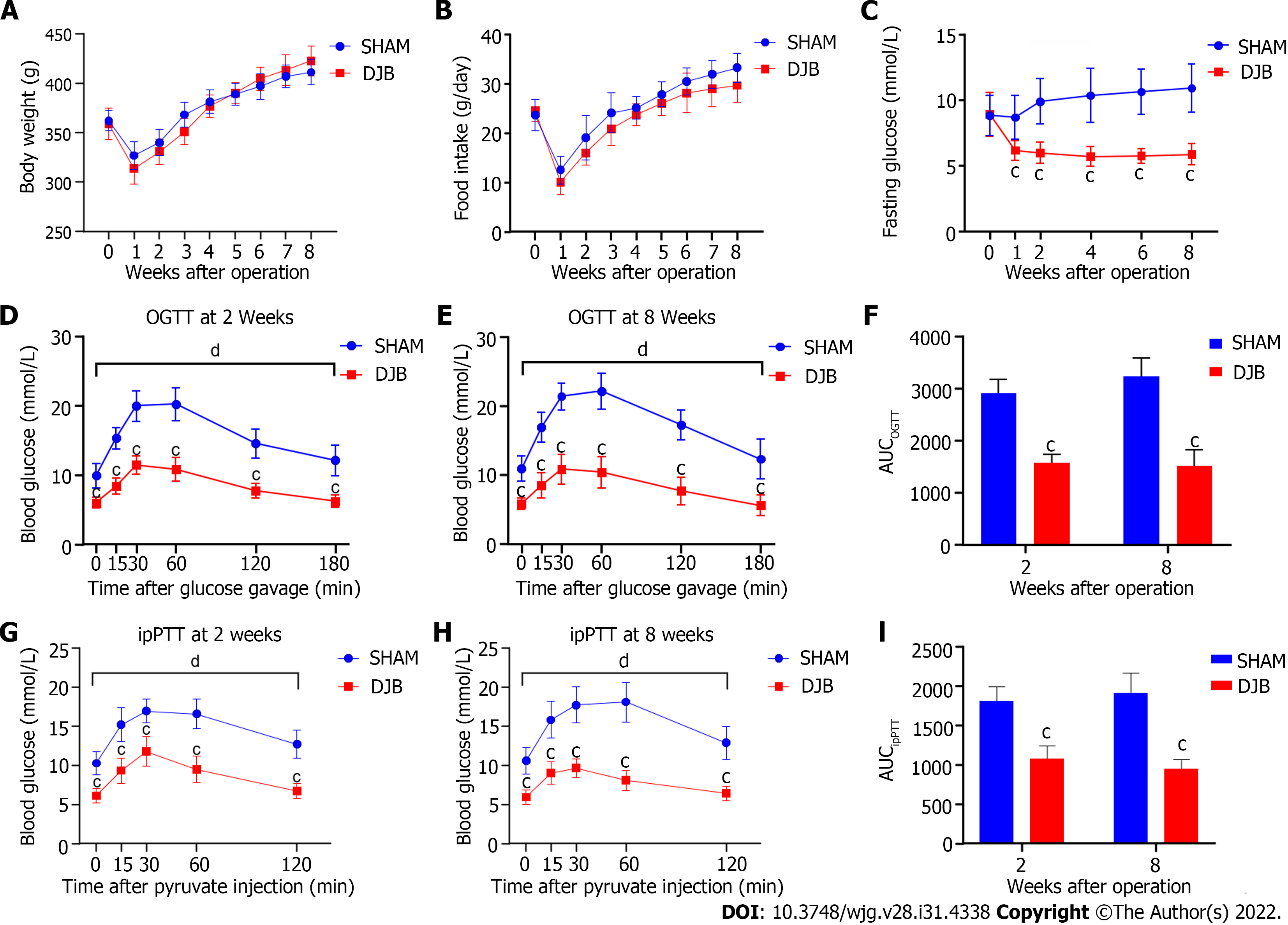
Body weight and food intake were comparable between the two groups before operation. Due to surgical stress, unrestored gastrointestinal function, and decreased food intake, the body weight of both groups fell to a minimum point in the first week after surgery. As food intake increased, the body weight of both groups gradually recovered to preoperative levels approximately 4 wk after operation. As a nonrestrictive surgery, the DJB group exhibited similar body weight and food intake as the sham group at all measured time points postoperatively (Figures 1A and B).
There were no significant differences in FBG levels between the two groups preoperatively. The FBG of the DJB group rapidly and significantly declined as early as one week postoperatively and was maintained at a relatively stable level. While the FBG of the sham group was not alleviated after operation and showed a tendency to deteriorate over time. Compared to the sham group, the DJB group exhibited lower FBG at all postoperative time points (Figure 1C).
Consistent with rapidly reduced FBG, the DJB group showed significantly lower blood glucose excursion and AUCOGTT during the OGTT studies at 2 and 8 wk postoperatively (Figures 1D-F), indicating improved glucose tolerance and increased systemic glucose disposal after DJB. To evaluate the impact of DJB on hepatic gluconeogenic capacity, ipPTT was conducted at 2 and 8 wk postoperatively. As shown in Figures 1G-I, the DJB group exhibited reduced glucose excursion and AUCipPTT in response to intraperitoneal pyruvate challenge, implying that DJB improved hepatic insulin sensitivity and decreased hepatic glucose output in diabetic rats early after surgery.
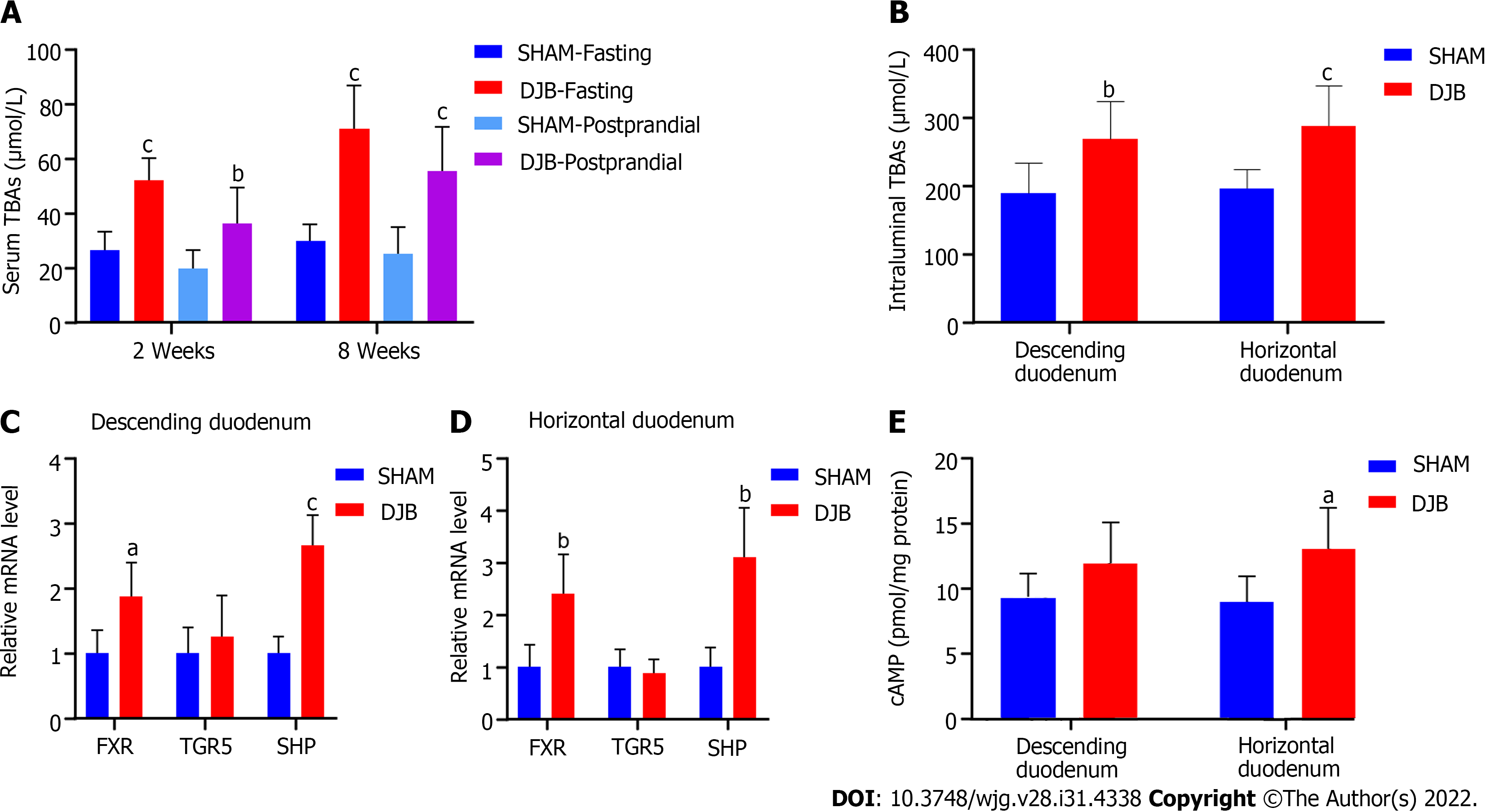
Compared with the sham group, the DJB-operated rats exhibited elevated fasting and postprandial serum TBAs at 2 and 8 wk postoperatively (Figure 2A). Altered food and digestive juice flow in the gastrointestinal tract also affected luminal TBAs after DJB. As shown in Figure 2B, the DJB group displayed elevated intraluminal TBAs in both the descending and horizontal duodenum 8 wk postoperatively.
To determine the effects of increased intraduodenal TBAs on duodenal BA signaling, the mRNA levels of FXR, TGR5, and small heterodimer partner (SHP) in the duodenal mucosa were evaluated by RT-qPCR eight weeks after surgery. The mRNA expression of FXR and its target gene SHP were concurrently increased in the duodenal mucosa of the DJB group (Figures 2C and D), indicating that the BAs-FXR-SHP pathway was activated. As a membrane bound receptor, TGR5 activation leads to cAMP accumulation in cells. Although DJB did not enhance TGR5 gene expression in the duodenal mucosa (Figures 2C and D), it increased the cAMP content in the horizontal duodenum (Figure 2E). cAMP also tended to increase in the descending duodenum of the DJB group despite no statistical significance (Figure 2E). These results suggest that the duodenal TGR5 receptor may also be activated after DJB.
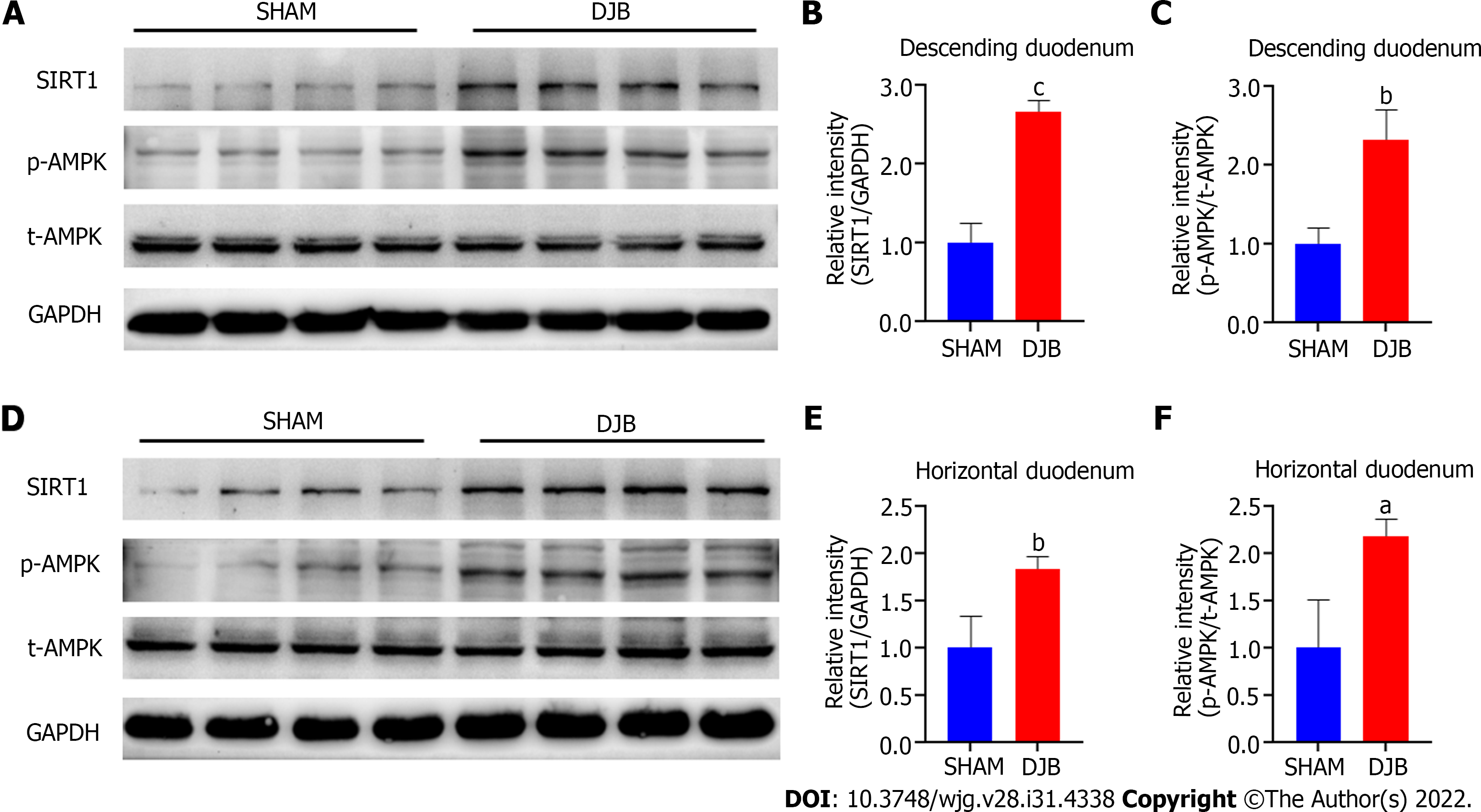
The ipPTT studies suggested that hepatic gluconeogenesis was reduced after DJB. Elevated duodenal SIRT1 and p-AMPK are associated with suppressed hepatic glucose output via the gut-brain-liver neural loop[13,14]. Therefore, to elucidate the underlying mechanism of improved hepatic insulin sensitivity and glucose homeostasis after DJB, duodenal SIRT1 and p-AMPK expression were investigated by western blotting eight weeks after surgery. As shown in Figure 3, DJB increased SIRT1 expression and promoted phosphorylation of AMPK in both the descending and horizontal parts of the duodenum.
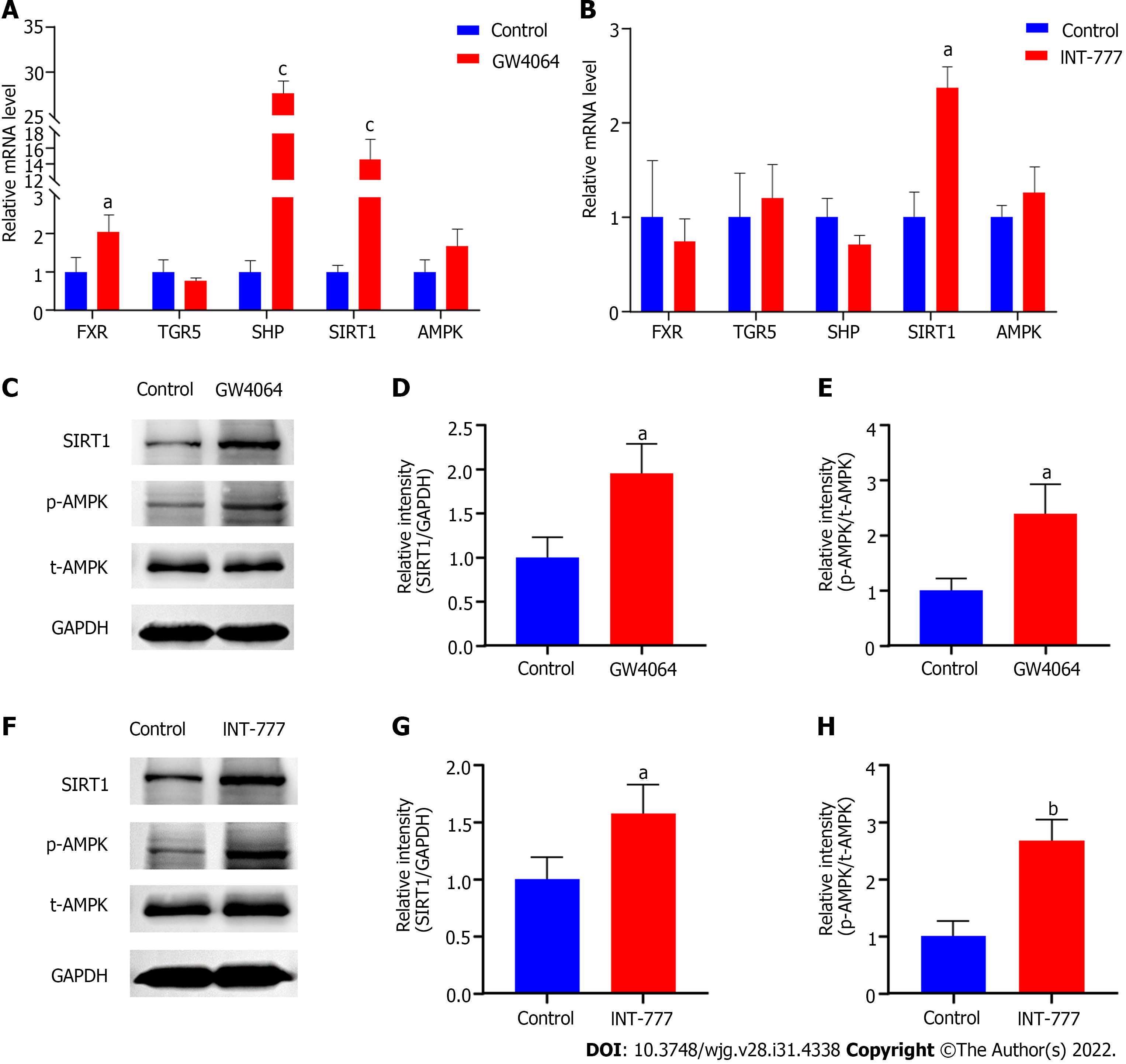
To verify whether increased SIRT1 and p-AMPK could be attributed to activated BA signaling in the duodenal mucosa, we treated rat small intestine epithelial IEC-6 cells with FXR and TGR5 agonists, respectively. Upon FXR activation by GW4064, the mRNA expression of FXR, SHP, and SIRT1 were all dramatically upregulated in IEC-6 cells (Figure 4A). Although INT-777 stimulation did not induce TGR5 transcription, it promoted the mRNA expression of SIRT1 (Figure 4B). In line with the increased mRNA expression, the protein levels of SIRT1 were also significantly elevated upon the activation of both BAs receptors (Figures 4C, D, F and G). Although FXR and TGR5 agonists did not increase the gene and protein expression of AMPK, they both promoted AMPK phosphorylation in IEC-6 cells (Figures 4C, E, F and H). These results indicate that the activated BA signaling pathway contributes to the upregulation of SIRT1 and the phosphorylation of AMPK.
In this study, we performed DJB and sham surgeries on diabetic rats induced by HFD and STZ, and demonstrated that DJB elevated intraduodenal TBAs, activated the BA signaling pathway and upregulated SIRT1 expression in the duodenal mucosa. By using specific BA receptor agonists, we proved that FXR and TGR5 activation increased SIRT1 expression and promoted phosphorylation of AMPK in rat small intestine epithelial cells, indicating that increased intraluminal BAs and activation of BA receptors contributed to the increased duodenal SIRT1 after DJB.
SIRT1 is an evolutionarily conserved NAD+-dependent deacetylase that belongs to the Sirtuins family (SIRT1-SIRT7)[22]. SIRT1 acts as a key metabolic sensor in the liver, skeletal muscles, adipose tissues, pancreatic islets, and other metabolic tissues. It plays an important role in various aging-related diseases, including insulin resistance, diabetes, obesity, hepatic steatosis, and cardiovascular diseases[22,23]. Liver-specific deletion of SIRT1 impairs hepatic and systemic insulin sensitivity in mice[24]. Muscular SIRT1 levels are decreased in patients with T2DM and HFD-induced insulin-resistant rats, and overexpression of SIRT1 in skeletal muscle improves muscular insulin sensitivity[25,26]. Adipose tissue-specific ablation of SIRT1 results in increased fat deposition, impaired glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity in mice[27]. SIRT1 activation protects the function and morphology of residual pancreatic β-cells and induces β-cell regeneration from progenitor cells, thus improving glucose homeostasis[28].
Sleeve gastrectomy (SG) upregulates hepatic SIRT1 and dramatically ameliorates hepatic steatosis in HFD-fed obese mice[29]. RYGB activates the AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1α pathway in the skeletal muscle of diabetic Zucker fatty rats, which contributes to diabetes remission[30]. Laparoscopic bariatric surgery increases SIRT1 levels in the peripheral blood of patients with obesity and T2DM, which is higher in the effective than in the ineffective group[31]. The effects of bariatric surgeries on duodenal SIRT1 expression have not been investigated previously. Duodenal SIRT1 is a novel therapeutic target for insulin resistance and diabetes. HFD-fed insulin-resistant rats exhibit significantly downregulated SIRT1 in the duodenal mucosa, and duodenum-specific knockdown of SIRT1 is sufficient to induce hepatic insulin resistance in normal chow-fed rats[14]. Our study is the first to demonstrate that DJB promotes SIRT1 expression in the duodenal mucosa. As duodenal SIRT1 activation further inhibits HGP and improves hepatic insulin sensitivity by triggering the gut-hypothalamus-liver neural network[14], we postulate that increased duodenal SIRT1 at least partly accounts for the improved hepatic insulin resistance and glucose homeostasis after DJB.
As an indispensable energy sensor, SIRT1 expression is closely related to energy status and environmental stress[32]. The SIRT1 transcription is usually activated during fasting, which transforms the metabolic status from gluconeogenesis to fat mobilization and fatty acid oxidation[32]. Chen et al[33] demonstrated that calorie restriction (CR) increased both pancreatic and hepatic SIRT1 expression in rats. Additionally, Civitarese et al[34] reported that CR for 6 mo promoted muscular SIRT1 expression in healthy overweight individuals. In mammalian cells, acute nutrient deprivation increases SIRT1 transcription by activating the Forkhead transcription factor Foxo3a[35]. Although food intake is not reduced after DJB, the duodenum is hindered from contact with ingested food, which might result in a duodenum-specific CR status, thus further inducing duodenal SIRT1 expression. Furthermore, gastric acids are not expelled into the duodenum after DJB, which increases the pH of duodenal content. The deacetylation activity of SIRT1 is pH-dependent, and higher pH attenuates the inhibition of SIRT1 by nicotinamide[36].
Increased intraduodenal BAs might be another key contributor to elevated duodenal SIRT1 after DJB. It is well documented that circulating BAs are increased after numerous metabolic surgeries, including DJB, SG, and RYGB[3,37,38]. By using genetically modified animal models, it has been proven that both FXR and TGR5 are required for the metabolic benefits of SG[39,40]. As demonstrated by our study, DJB not only elevated serum TBAs, but also significantly increased intraduodenal TBAs. Similarly, Ueno et al[41] demonstrated that DJB increased conjugated BAs in the bypassed jejunum just distal to the ligament of Treitz. Furthermore, we observed higher SHP mRNA and cAMP concentrations in the duodenal mucosa of DJB-operated rats, indicating that FXR and TGR5 signaling were activated after DJB. Whether causality exists between activated BA signaling and increased SIRT1 in enterocytes has not been investigated.
Numerous studies have suggested that BAs serve as upstream signaling molecules for SIRT1 in various tissues. FXR activation upregulates SIRT1 expression by promoting the transcription of SHP and repressing the transcription of p53 and miR34a in the livers of normal mice[19]. In diabetic db/db mice, TGR5 activation increases both the mRNA and protein levels of SIRT1 in the kidneys[42]. Similarly, TGR5 activation upregulates SIRT1 expression in the brains of Sprague Dawley rats[20]. These studies suggest that activation of duodenal FXR and/or TGR5 might account for the increased duodenal SIRT1 after DJB. To verify our hypothesis, we used GW4064 and INT-777 to activate FXR and TGR5 in IEC-6 cells and showed that both agonists increased SIRT1 expression in enterocytes. We also found that GW4064 increased FXR gene expression in IEC-6 cells in accordance with the elevated FXR mRNA in the duodenal mucosa after DJB. Similar changes in FXR mRNA were also observed in mouse mesangial cells after GW4064 stimulation[43].
In addition, we demonstrated that DJB promoted phosphorylation of AMPK in the duodenal mucosa, which might also contribute to improved glucose homeostasis after DJB, as duodenal AMPK activation improves hepatic insulin sensitivity and inhibits hepatic glucose output via the gut-hypothalamus-liver neural axis[13]. Jiao et al[4] reported that DJB promoted phosphorylation of AMPK in both the liver and skeletal muscle, which contributed to the restoration of normoglycemia after surgery. Likewise, SG enhances AMPK phosphorylation in both the liver and monocytes[44]. Similarly, RYGB exhibits anti-diabetic properties via AMPK activation in the liver and Kupffer cells[45]. Actually, as two important energy sensors in cells, AMPK and SIRT1 mutually regulate each other, share many common target molecules, and have similar effects on diverse processes such as glucose and energy metabolism[46]. Our study suggests that activated duodenal AMPK might also be attributed to elevated duodenal BAs because both FXR and TGR5 activation promoted phosphorylation of AMPK in IEC-6 cells.
There are some limitations in our study. First, we only investigated changes in TBAs in the duodenum after DJB. There are numerous components in the BA pool, and different components may exert different metabolic effects. Second, our study did not provide sufficient information on whether duodenal SIRT1 is indispensable for DJB-induced diabetic control, therefore, duodenum-specific SIRT1 loss- and gain-of-function animal models would be necessary for future studies.
DJB upregulates SIRT1 expression in the duodenal mucosa, which may partly account for surgery-induced diabetic control. Increased intraduodenal TBA levels and activated duodenal BA signaling pathway may contribute to the upregulation of duodenal SIRT1 after DJB.
Duodenal-jejunal bypass (DJB) induces rapid and significant amelioration of type 2 diabetes mellitus in various diabetic rat models, while the mechanisms have not been fully elucidated. Duodenal SIRT1 regulates hepatic glucose production and hepatic insulin sensitivity through a gut-brain-liver axis, and activation of bile acid (BA) receptors promotes SIRT1 expression in many tissues. This study aimed at uncovering the roles of duodenal BAs and SIRT1 in the diabetic control after DJB.
To expand and deepen our understanding on the mechanisms underlying diabetes control after DJB, and to provide new ideas and targets for the non-surgical treatment of diabetes in the future.
To investigate the effects of DJB on the duodenal BA signaling pathway and SIRT1 expression in a diabetic rat model, and further reveal the roles of BAs in modulating SIRT1 expression in enterocytes.
DJB and sham surgeries were performed on rats with diabetes induced by high-fat diet and low-dose streptozotocin. The effects of surgeries on metabolic parameters were compared accordingly. The intraduodenal BA concentration, the key genes of BA signaling pathway and SIRT1 in the duodenal mucosa were evaluated 8 wk postoperatively. Rat small intestine epithelial IEC-6 cells were treated with GW4064 and INT-777 to verify the effects of BA receptor activation on SIRT1 expression in enterocytes.
DJB rapidly and dramatically improved glucose homeostasis in the diabetic rats independently of body weight and food intake. DJB increased both systemic and intraduodenal total BAs, activated the BA signaling pathway and promoted SIRT1 expression in the duodenum mucosa. Activation of BA receptors including farnesoid X receptor and Takeda G-protein-coupled receptor 5 increased the mRNA and protein expression of SIRT1 in IEC-6 cells.
DJB increases intraduodenal BA levels and activates the duodenal BA signaling pathway, which may further contribute to the improved hepatic insulin resistance and glucose homeostasis by upregulating SIRT1 expression in the duodenal mucosa.
Our findings provide evidence that BA-mediated upregulation of SIRT1 in the duodenum contributes to the diabetic control after DJB. This study also implicates that duodenal BAs and SIRT1 might be potential targets for improving hepatic insulin sensitivity and systemic glucose homeostasis, which lays the groundwork for developing duodenal BA and SIRT1-specific treatments to alleviate diabetes.
The authors would like to acknowledge Sun M and Liu XM for their skillful technical assistance.
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Gastroenterology and hepatology
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B, B, B
Grade C (Good): 0
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Kim M, South Korea; Madadi-Sanjani O, Germany; Nio M, Japan S-Editor: Wang JJ L-Editor: A P-Editor: Cai YX
| 1. | Sun H, Saeedi P, Karuranga S, Pinkepank M, Ogurtsova K, Duncan BB, Stein C, Basit A, Chan JCN, Mbanya JC, Pavkov ME, Ramachandaran A, Wild SH, James S, Herman WH, Zhang P, Bommer C, Kuo S, Boyko EJ, Magliano DJ. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022;183:109119. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3033] [Cited by in RCA: 4813] [Article Influence: 1604.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (36)] |
| 2. | Khorgami Z, Shoar S, Saber AA, Howard CA, Danaei G, Sclabas GM. Outcomes of Bariatric Surgery Versus Medical Management for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: a Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Obes Surg. 2019;29:964-974. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 49] [Cited by in RCA: 67] [Article Influence: 13.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Zhang X, Wang Y, Zhong M, Liu T, Han H, Zhang G, Liu S, Wei M, Wu Q, Hu S. Duodenal-Jejunal Bypass Preferentially Elevates Serum Taurine-Conjugated Bile Acids and Alters Gut Microbiota in a Diabetic Rat Model. Obes Surg. 2016;26:1890-1899. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 1.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Jiao J, Bae EJ, Bandyopadhyay G, Oliver J, Marathe C, Chen M, Hsu JY, Chen Y, Tian H, Olefsky JM, Saberi M. Restoration of euglycemia after duodenal bypass surgery is reliant on central and peripheral inputs in Zucker fa/fa rats. Diabetes. 2013;62:1074-1083. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 29] [Cited by in RCA: 30] [Article Influence: 2.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Klein S, Fabbrini E, Patterson BW, Polonsky KS, Schiavon CA, Correa JL, Salles JE, Wajchenberg BL, Cohen R. Moderate effect of duodenal-jejunal bypass surgery on glucose homeostasis in patients with type 2 diabetes. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2012;20:1266-1272. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 51] [Cited by in RCA: 52] [Article Influence: 4.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | de Jonge C, Rensen SS, Verdam FJ, Vincent RP, Bloom SR, Buurman WA, le Roux CW, Schaper NC, Bouvy ND, Greve JW. Endoscopic duodenal-jejunal bypass liner rapidly improves type 2 diabetes. Obes Surg. 2013;23:1354-1360. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 101] [Cited by in RCA: 108] [Article Influence: 9.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | van Baar ACG, Holleman F, Crenier L, Haidry R, Magee C, Hopkins D, Rodriguez Grunert L, Galvao Neto M, Vignolo P, Hayee B, Mertens A, Bisschops R, Tijssen J, Nieuwdorp M, Guidone C, Costamagna G, Devière J, Bergman JJGHM. Endoscopic duodenal mucosal resurfacing for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: one year results from the first international, open-label, prospective, multicentre study. Gut. 2020;69:295-303. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 97] [Cited by in RCA: 133] [Article Influence: 26.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | van Baar ACG, Nieuwdorp M, Holleman F, Soeters MR, Groen AK, Bergman JJGHM. The Duodenum harbors a Broad Untapped Therapeutic Potential. Gastroenterology. 2018;154:773-777. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 26] [Cited by in RCA: 36] [Article Influence: 5.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Akiba Y, Kaunitz JD. Duodenal chemosensing and mucosal defenses. Digestion. 2011;83 Suppl 1:25-31. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 21] [Cited by in RCA: 21] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Rønnestad I, Akiba Y, Kaji I, Kaunitz JD. Duodenal luminal nutrient sensing. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2014;19:67-75. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 30] [Cited by in RCA: 33] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Lam TK. Neuronal regulation of homeostasis by nutrient sensing. Nat Med. 2010;16:392-395. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 101] [Cited by in RCA: 99] [Article Influence: 6.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Wang PY, Caspi L, Lam CK, Chari M, Li X, Light PE, Gutierrez-Juarez R, Ang M, Schwartz GJ, Lam TK. Upper intestinal lipids trigger a gut-brain-liver axis to regulate glucose production. Nature. 2008;452:1012-1016. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 205] [Cited by in RCA: 221] [Article Influence: 13.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Duca FA, Côté CD, Rasmussen BA, Zadeh-Tahmasebi M, Rutter GA, Filippi BM, Lam TK. Metformin activates a duodenal Ampk-dependent pathway to lower hepatic glucose production in rats. Nat Med. 2015;21:506-511. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 254] [Cited by in RCA: 328] [Article Influence: 32.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Côté CD, Rasmussen BA, Duca FA, Zadeh-Tahmasebi M, Baur JA, Daljeet M, Breen DM, Filippi BM, Lam TK. Resveratrol activates duodenal Sirt1 to reverse insulin resistance in rats through a neuronal network. Nat Med. 2015;21:498-505. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 101] [Cited by in RCA: 122] [Article Influence: 12.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Cao Y, Jiang X, Ma H, Wang Y, Xue P, Liu Y. SIRT1 and insulin resistance. J Diabetes Complications. 2016;30:178-183. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 85] [Cited by in RCA: 111] [Article Influence: 12.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Li X. SIRT1 and energy metabolism. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2013;45:51-60. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 196] [Cited by in RCA: 262] [Article Influence: 21.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Molinaro A, Wahlström A, Marschall HU. Role of Bile Acids in Metabolic Control. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2018;29:31-41. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 230] [Cited by in RCA: 318] [Article Influence: 45.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Ahmad TR, Haeusler RA. Bile acids in glucose metabolism and insulin signalling - mechanisms and research needs. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2019;15:701-712. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 132] [Cited by in RCA: 228] [Article Influence: 38.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Lee J, Padhye A, Sharma A, Song G, Miao J, Mo YY, Wang L, Kemper JK. A pathway involving farnesoid X receptor and small heterodimer partner positively regulates hepatic sirtuin 1 Levels via microRNA-34a inhibition. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:12604-12611. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 183] [Cited by in RCA: 222] [Article Influence: 14.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Liang H, Matei N, McBride DW, Xu Y, Tang J, Luo B, Zhang JH. Activation of TGR5 protects blood brain barrier via the BRCA1/Sirt1 pathway after middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. J Biomed Sci. 2020;27:61. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 26] [Cited by in RCA: 33] [Article Influence: 6.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Liu S, Zhang G, Wang L, Sun D, Chen W, Yan Z, Sun Y, Hu S. The entire small intestine mediates the changes in glucose homeostasis after intestinal surgery in Goto-Kakizaki rats. Ann Surg. 2012;256:1049-1058. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 25] [Cited by in RCA: 25] [Article Influence: 2.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Zhou S, Tang X, Chen HZ. Sirtuins and Insulin Resistance. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018;9:748. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 68] [Cited by in RCA: 98] [Article Influence: 14.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Morris BJ. Seven sirtuins for seven deadly diseases of aging. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013;56:133-171. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 281] [Cited by in RCA: 293] [Article Influence: 24.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Wang RH, Kim HS, Xiao C, Xu X, Gavrilova O, Deng CX. Hepatic Sirt1 deficiency in mice impairs mTorc2/Akt signaling and results in hyperglycemia, oxidative damage, and insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 2011;121:4477-4490. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 221] [Cited by in RCA: 251] [Article Influence: 17.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Fröjdö S, Durand C, Molin L, Carey AL, El-Osta A, Kingwell BA, Febbraio MA, Solari F, Vidal H, Pirola L. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase as a novel functional target for the regulation of the insulin signaling pathway by SIRT1. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2011;335:166-176. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 85] [Cited by in RCA: 98] [Article Influence: 7.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Zhang HH, Qin GJ, Li XL, Zhang YH, Du PJ, Zhang PY, Zhao YY, Wu J. SIRT1 overexpression in skeletal muscle in vivo induces increased insulin sensitivity and enhanced complex I but not complex II-V functions in individual subsarcolemmal and intermyofibrillar mitochondria. J Physiol Biochem. 2015;71:177-190. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Article Influence: 1.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Li F, Li H, Jin X, Zhang Y, Kang X, Zhang Z, Xu M, Qian Z, Ma Z, Gao X, Zhao L, Wu S, Sun H. Adipose-specific knockdown of Sirt1 results in obesity and insulin resistance by promoting exosomes release. Cell Cycle. 2019;18:2067-2082. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 27] [Cited by in RCA: 47] [Article Influence: 7.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Wu SY, Liang J, Yang BC, Leung PS. SIRT1 Activation Promotes β-Cell Regeneration by Activating Endocrine Progenitor Cells via AMPK Signaling-Mediated Fatty Acid Oxidation. Stem Cells. 2019;37:1416-1428. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 3.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Hua R, Wang GZ, Shen QW, Yang YP, Wang M, Wu M, Shao YK, He M, Zang Y, Yao QY, Zhang ZY. Sleeve gastrectomy ameliorated high-fat diet (HFD)-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and upregulated the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide +/ Sirtuin-1 pathway in mice. Asian J Surg. 2021;44:213-220. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 2.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Huang H, Aminian A, Hassan M, Dan O, Axelrod CL, Schauer PR, Brethauer SA, Kirwan JP. Gastric Bypass Surgery Improves the Skeletal Muscle Ceramide/S1P Ratio and Upregulates the AMPK/ SIRT1/ PGC-1α Pathway in Zucker Diabetic Fatty Rats. Obes Surg. 2019;29:2158-2165. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 2.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Wang Y, Wang DS, Cheng YS, Jia BL, Yu G, Yin XQ, Wang Y. Expression of MicroRNA-448 and SIRT1 and Prognosis of Obese Type 2 Diabetic Mellitus Patients After Laparoscopic Bariatric Surgery. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;45:935-950. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 18] [Article Influence: 2.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Pardo PS, Boriek AM. SIRT1 Regulation in Ageing and Obesity. Mech Ageing Dev. 2020;188:111249. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 51] [Article Influence: 10.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 33. | Chen YR, Fang SR, Fu YC, Zhou XH, Xu MY, Xu WC. Calorie restriction on insulin resistance and expression of SIRT1 and SIRT4 in rats. Biochem Cell Biol. 2010;88:715-722. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 40] [Cited by in RCA: 46] [Article Influence: 3.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 34. | Civitarese AE, Carling S, Heilbronn LK, Hulver MH, Ukropcova B, Deutsch WA, Smith SR, Ravussin E; CALERIE Pennington Team. Calorie restriction increases muscle mitochondrial biogenesis in healthy humans. PLoS Med. 2007;4:e76. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 634] [Cited by in RCA: 574] [Article Influence: 31.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 35. | Nemoto S, Fergusson MM, Finkel T. Nutrient availability regulates SIRT1 through a forkhead-dependent pathway. Science. 2004;306:2105-2108. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 517] [Cited by in RCA: 543] [Article Influence: 27.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 36. | Rymarchyk S, Kang W, Cen Y. Substrate-Dependent Sensitivity of SIRT1 to Nicotinamide Inhibition. Biomolecules. 2021;11. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 37. | Wu Q, Zhang X, Zhong M, Han H, Liu S, Liu T, Wei M, Guo W, Xie H, Hu S, Zhang G. Effects of Bariatric Surgery on Serum Bile Acid Composition and Conjugation in a Diabetic Rat Model. Obes Surg. 2016;26:2384-2392. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 22] [Cited by in RCA: 24] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 38. | Patti ME, Houten SM, Bianco AC, Bernier R, Larsen PR, Holst JJ, Badman MK, Maratos-Flier E, Mun EC, Pihlajamaki J, Auwerx J, Goldfine AB. Serum bile acids are higher in humans with prior gastric bypass: potential contribution to improved glucose and lipid metabolism. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2009;17:1671-1677. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 504] [Cited by in RCA: 455] [Article Influence: 28.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 39. | Ryan KK, Tremaroli V, Clemmensen C, Kovatcheva-Datchary P, Myronovych A, Karns R, Wilson-Pérez HE, Sandoval DA, Kohli R, Bäckhed F, Seeley RJ. FXR is a molecular target for the effects of vertical sleeve gastrectomy. Nature. 2014;509:183-188. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 694] [Cited by in RCA: 749] [Article Influence: 68.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 40. | Ding L, Sousa KM, Jin L, Dong B, Kim BW, Ramirez R, Xiao Z, Gu Y, Yang Q, Wang J, Yu D, Pigazzi A, Schones D, Yang L, Moore D, Wang Z, Huang W. Vertical sleeve gastrectomy activates GPBAR-1/TGR5 to sustain weight loss, improve fatty liver, and remit insulin resistance in mice. Hepatology. 2016;64:760-773. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 122] [Cited by in RCA: 150] [Article Influence: 16.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 41. | Ueno T, Tanaka N, Imoto H, Maekawa M, Kohyama A, Watanabe K, Motoi F, Kamei T, Unno M, Naitoh T. Mechanism of Bile Acid Reabsorption in the Biliopancreatic Limb After Duodenal-Jejunal Bypass in Rats. Obes Surg. 2020;30:2528-2537. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 42. | Wang XX, Edelstein MH, Gafter U, Qiu L, Luo Y, Dobrinskikh E, Lucia S, Adorini L, D'Agati VD, Levi J, Rosenberg A, Kopp JB, Gius DR, Saleem MA, Levi M. G Protein-Coupled Bile Acid Receptor TGR5 Activation Inhibits Kidney Disease in Obesity and Diabetes. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016;27:1362-1378. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 82] [Cited by in RCA: 152] [Article Influence: 15.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 43. | Jiang T, Wang XX, Scherzer P, Wilson P, Tallman J, Takahashi H, Li J, Iwahashi M, Sutherland E, Arend L, Levi M. Farnesoid X receptor modulates renal lipid metabolism, fibrosis, and diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes. 2007;56:2485-2493. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 156] [Cited by in RCA: 185] [Article Influence: 10.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 44. | Angelini G, Castagneto Gissey L, Del Corpo G, Giordano C, Cerbelli B, Severino A, Manco M, Basso N, Birkenfeld AL, Bornstein SR, Genco A, Mingrone G, Casella G. New insight into the mechanisms of ectopic fat deposition improvement after bariatric surgery. Sci Rep. 2019;9:17315. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 24] [Article Influence: 4.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 45. | Peng Y, Li JZ, You M, Murr MM. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass improves glucose homeostasis, reduces oxidative stress and inflammation in livers of obese rats and in Kupffer cells via an AMPK-dependent pathway. Surgery. 2017;162:59-67. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 46. | Ruderman NB, Xu XJ, Nelson L, Cacicedo JM, Saha AK, Lan F, Ido Y. AMPK and SIRT1: a long-standing partnership? Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2010;298:E751-E760. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 600] [Cited by in RCA: 706] [Article Influence: 47.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |