Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2022; 28(11): 1139-1158
Published online Mar 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i11.1139
Published online Mar 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i11.1139
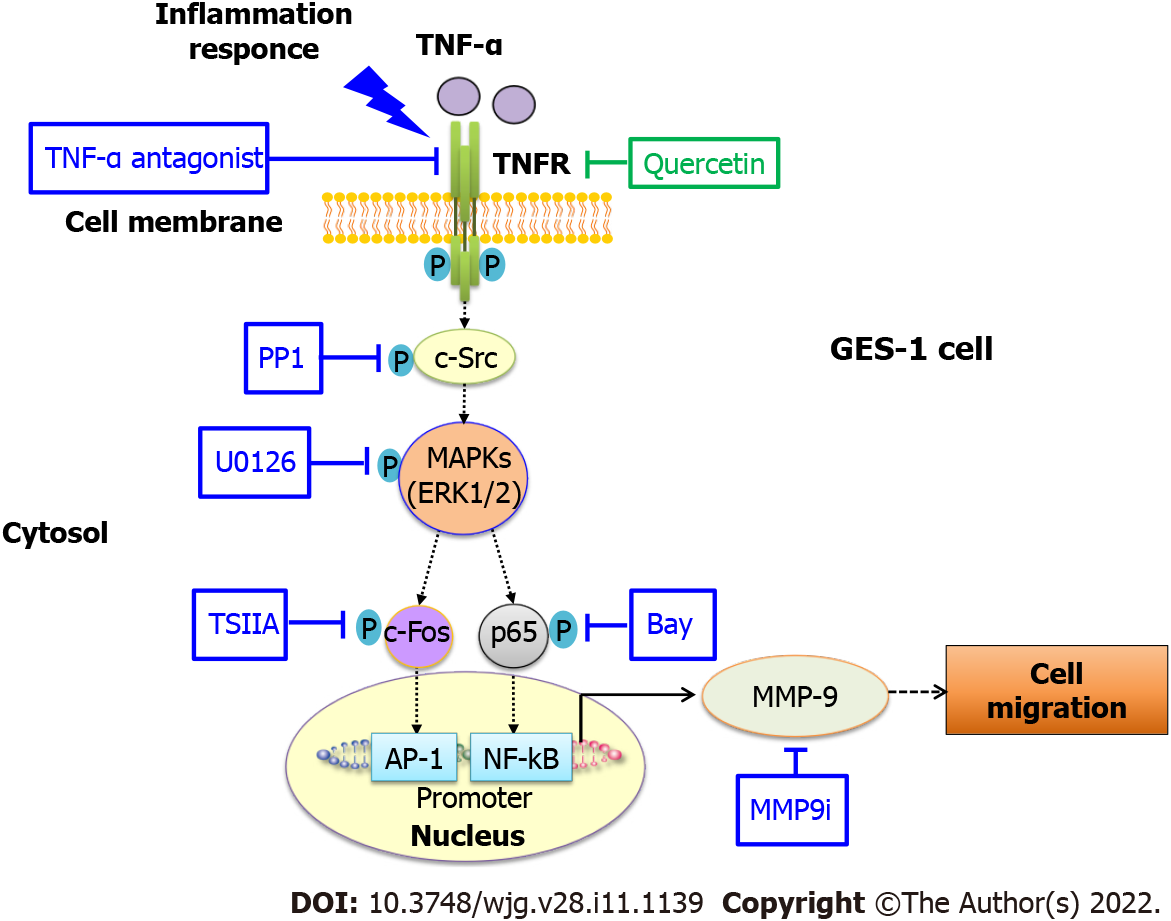
Figure 9 Schematic representation of the effects of quercetin on tumor necrosis factor-α-induced matrix metallopeptidase-9 expression and cell migration in normal human gastric mucosa epithelial cells.
Schematic diagram of the signaling pathways for quercetin-mediated attenuation of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α)-induced inflammation via downregulation of matrix metallopeptidase-9 (MMP-9) expression in normal human gastric mucosa epithelial cells. Quercetin attenuates TNF-α-induced MMP-9 expression in normal human gastric mucosa epithelial cells through the proinflammatory TNFR-c-Src–extracellular-signal-regulated kinase 1/2–c-Fos and nuclear factor kappa B pathways. AP-1: Activator protein-1; c-Src: Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src; ERK: Extracellular-signal-regulated kinase; GES-1: Normal human gastric mucosa epithelial cell line; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; MMP-9: Matrix metallopeptidase-9; MMP9i: MMP-9 inhibitor; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa B; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; TSIIA: Tanshinone IIA.
- Citation: Hsieh HL, Yu MC, Cheng LC, Chu MY, Huang TH, Yeh TS, Tsai MM. Quercetin exerts anti-inflammatory effects via inhibiting tumor necrosis factor-α-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in normal human gastric epithelial cells. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(11): 1139-1158
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i11/1139.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i11.1139