Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2021; 27(14): 1369-1391
Published online Apr 14, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i14.1369
Published online Apr 14, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i14.1369
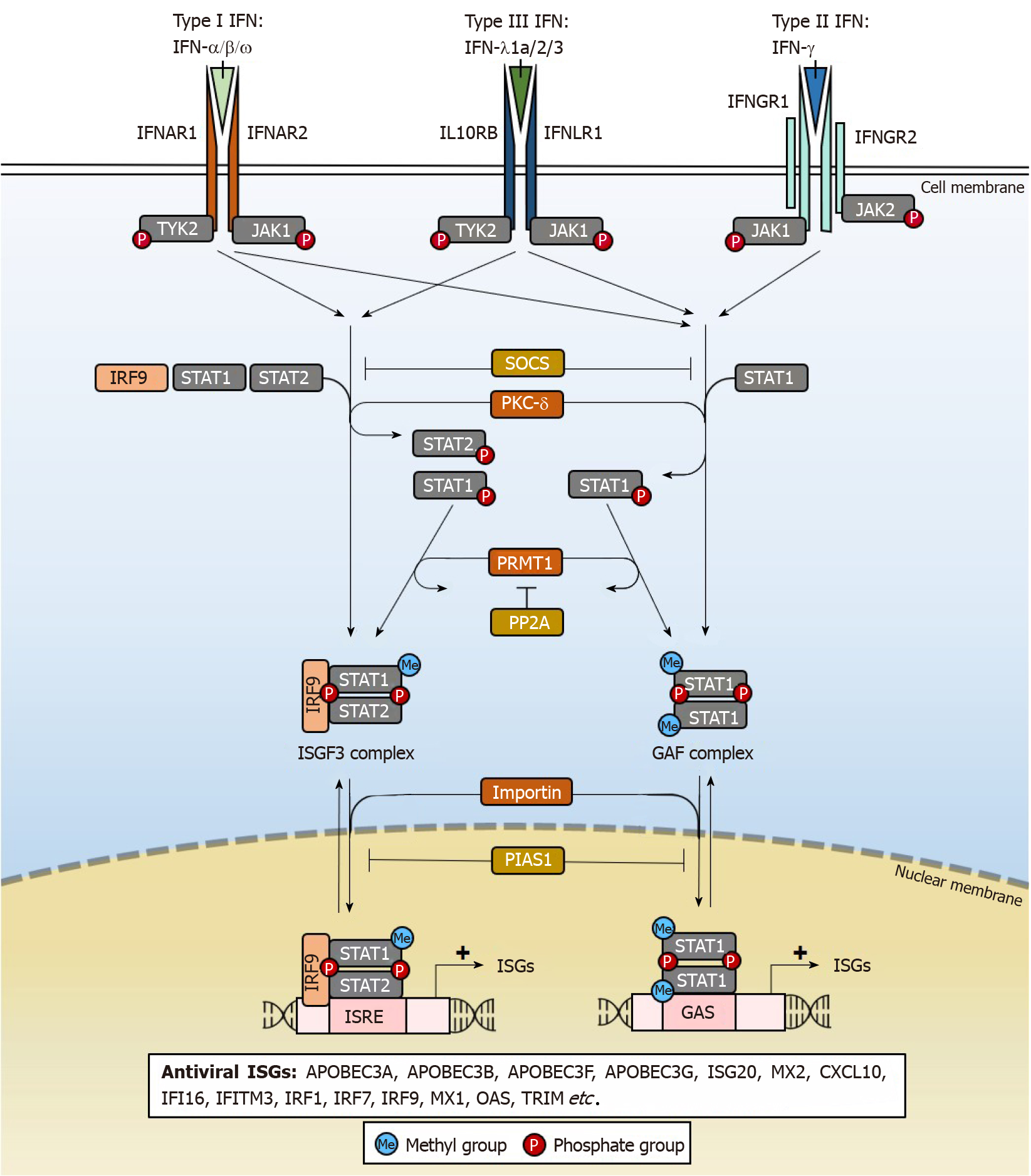
Figure 1 Activation of antiviral interferon-stimulated genes by different interferon subtypes.
Different subtypes of interferons (IFNs) bind to their cognate receptors to trigger IFN signalling pathways. The activate janus kinase/signal transducers and activators of transcription-dependent signalling results in the formation of transcription complexes that induce the expression several IFN-stimulated response elements-dependent and gamma activated site-dependent antiviral IFN-stimulated genes (ISGs), which target covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA) stability and function through a variety of mechanisms. The potency of IFN sub-type for cccDNA degradation or silencing is dependent on the types and number of ISGs induced. IFN: Interferon; TYK2: Tyrosine kinase 2; SOCS: Suppressor of cytokine signalling; PKC-δ: Protein kinase C-delta; IRF: Interferon regulatory factor; JAK: Activate janus kinase; STAT: Signal transducers and activators of transcription; ISGF: Interferon-stimulated gene factor; GAF: Gamma-activated factor; ISGs: Interferon-stimulated genes; ISRE: Interferon-stimulated response elements; GAS: Gamma activated site.
- Citation: Goh ZY, Ren EC, Ko HL. Intracellular interferon signalling pathways as potential regulators of covalently closed circular DNA in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(14): 1369-1391
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i14/1369.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i14.1369