Published online Mar 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i11.1043
Peer-review started: November 7, 2020
First decision: January 23, 2021
Revised: January 27, 2021
Accepted: March 7, 2021
Article in press: March 7, 2021
Published online: March 21, 2021
Processing time: 129 Days and 22.7 Hours
Recent improvements in the prognosis of patients with esophageal cancer have led to the increased occurrence of gastric tube cancer (GTC) in the reconstructed gastric tube. However, there are few reports on the treatment results of endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) for GTC.
To evaluate the efficacy and safety of ESD for GTC after esophagectomy in a multicenter trial.
We retrospectively investigated 48 GTC lesions in 38 consecutive patients with GTC in the reconstructed gastric tube after esophagectomy who had undergone ESD between January 2005 and December 2019 at 8 institutions participating in the Okayama Gut Study group. The clinical indications of ESD for early gastric cancer were similarly applied for GTC after esophagectomy. ESD specimens were evaluated in 2-mm slices according to the Japanese Classification of Gastric Carcinoma with curability assessments divided into curative and non-curative resection based on the Gastric Cancer Treatment Guidelines. Patient characteristics, treatment results, clinical course, and treatment outcomes were analyzed.
The median age of patients was 71.5 years (range, 57-84years), and there were 34 men and 4 women. The median observation period after ESD was 884 d (range, 8-4040 d). The median procedure time was 81 min (range, 29-334 min), the en bloc resection rate was 91.7% (44/48), and the curative resection rate was 79% (38/48). Complications during ESD were seen in 4% (2/48) of case, and those after ESD were seen in 10% (5/48) of case. The survival rate at 5 years was 59.5%. During the observation period after ESD, 10 patients died of other diseases. Although there were differences in the procedure time between institutions, a multivariate analysis showed that tumor size was the only factor associated with prolonged procedure time.
ESD for GTC after esophagectomy was shown to be safe and effective.
Core Tip: Despite increasing occurrence of gastric tube cancer (GTC) after esophagectomy, there are few reports on the treatment results of endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) for GTC. This multicenter study showed that treatment results and complications of ESD for GTC were similar to those of standard ESD and there were not significantly difference between institutions except for procedure time. ESD for GTC after esophagectomy is a safe and effective treatment.
- Citation: Satomi T, Kawano S, Inaba T, Nakagawa M, Mouri H, Yoshioka M, Tanaka S, Toyokawa T, Kobayashi S, Tanaka T, Kanzaki H, Iwamuro M, Kawahara Y, Okada H. Efficacy and safety of endoscopic submucosal dissection for gastric tube cancer: A multicenter retrospective study. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(11): 1043-1054
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i11/1043.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i11.1043
Recently, the survival of patients with esophageal cancer after esophagectomy has improved[1-5]. However, the risk of a subsequent occurrence of primary cancer is high in these patients. The most frequent cancer that overlaps with esophageal cancer is head and neck cancer, while the second most common is gastric cancer, including gastric tube cancer (GTC)[6-9]. Therefore, the improved prognosis of esophageal cancer patients has led to an increase in the occurrence of GTC in the reconstructed gastric tube.
For the treatment of GTC after esophagectomy, total gastric tube resection (TGTR) or partial gastric tube resection (PGTR) has been proposed. However, surgical resection for GTC, being a secondary operation following esophagectomy, may lead to high mortality and morbidity[10,11]. On the other hand, in recent years, endoscopic therapy for early gastric cancer (EGC) has developed and become widespread[12]. Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) enables the treatment of large lesions with a higher rate of en bloc resection that cannot be achieved by using conventional endoscopic mucosal resection. In addition, ESD is less invasive than surgery. For this reason, ESD has become widely used as a standard treatment for EGC, and ESD is often performed for GTC.
However, ESD for GTC after esophagectomy is a technically difficult procedure compared with that for an unresected stomach because of the limited working space, unusual fluid-pooling area, food residue, bile reflux, fibrosis, and staples under the suture line[13]. Therefore, a high degree of skill is required for ESD of GTC. There are few reports about ESD for GTC after esophagectomy, and most are case reports and case series of a small number of patients[13-17]. A study by Nonaka et al[18] reported the effectiveness and safety of ESD for GTC in a high-volume national center, which had largest number of cases but was nonetheless a single-center study. Therefore, the aim of this study was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of ESD for GTC after esophagectomy in a multicenter context.
We retrospectively investigated patients with GTC in the reconstructed gastric tube after esophagectomy for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma who had undergone ESD between January 2005 and December 2019 at 8 institutions participating in the Okayama Gut Study group (O-GUTS). All of the participating institutions in O-GUTS, except Okayama University Hospital (OUH), were considered core hospitals in each area. During the study period, 48 GTC lesions in 38 consecutive patients were treated. The clinical indications of ESD for EGC were based on the Gastric Cancer Treatment Guidelines[19]. These indications were similarly applied for GTC after esophagectomy with gastric tube reconstruction.
Study measurements were as follows: patient characteristics, endoscopic findings, treatment results, adverse events, histopathological results, and clinical courses. In addition, we defined OUH as a high-volume center and compared the patients’ background and clinical outcomes between OUH and other facilities.
The institutional review board of each hospital approved this study, and informed consent was obtained from all patients.
All endoscopic procedures were performed by experts in ESD who had experience with more than 500 clinical cases. There were no restrictions on the scopes and devices used by each endoscopist for ESD. The scopes used were GIF-Q260J or GIF-H260 (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan), and the devices were an insulation-tipped diathermic knife (IT Knife), IT Knife 2, IT Knife nano, or Dual Knife J (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan). Other devices, such as an argon plasma coagulation probe (ERBE, Tubingen, Germany) for marking dots or a needle knife (ZEON MEDICAL, Tokyo, Japan) for the initial incision, were occasionally used.
First, marking dots for the incision lines were placed around the lesion. Next, fructose-added glycerol (Glyceol; TAIYO Pharma CO, Tokyo, Japan) with a minute amount of indigo carmine dye was injected into the submucosal layer. In some cases, 0.4% sodium hyaluronate (MucoUp; Boston Scientific, Tokyo, Japan) was used. After submucosal injection, a precut was made with the Dual Knife J or needle knife, followed by a circumferential mucosal incision around the lesion using the dots as a landmark and submucosal dissection with the IT Knife, IT Knife 2, IT Knife nano, or Dual Knife J. The resected specimens were evaluated pathologically.
ESD specimens were evaluated in 2-mm slices according to the Japanese Classification of Gastric Carcinoma with curability assessments divided into curative and non-curative resection based on the Gastric Cancer Treatment Guidelines[20]. R0 resection indicated that the lesion was resected en bloc with both the horizontal and vertical margins tumor-free histopathologically, but did not include findings regarding lymphovascular infiltration, the type of adenocarcinoma, or an assessment of the depth of invasion for curability. A curative resection was divided into eCura A and eCura B. A non-curative resection was defined as not meeting the criteria of curative resection and was further separated into 2 groups, eCura C-1 and eCura C-2, based on histopathological results per the Gastric Cancer Treatment Guidelines[19].
Continuous and categorical variables are expressed as median (range) and n (%), respectively. Overall survival was calculated according to the Kaplan-Meier method. Differences in the clinical outcomes of ESD for GTC between institutions were evaluated using the Mann-Whitney U test for continuous data and the Chi-squared test for categorical variables. The risk factors for long procedure time were evaluated using logistic regression analysis. All statistical analyses were performed using the statistical analysis software JMP Pro, version 15 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, United States). P values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
A total of 38 consecutive patients with 48 GTC lesions were treated with ESD between January 2005 and December 2019 (Table 1). The median age of these patients was 71.5 years (range, 57-84 years), and they included 34 men and 4 women. The median period from esophagectomy to the treatment of GTC was 2106 d (range, 38-9523 d). This included patients who had a diagnosis of EGC before surgery for esophageal cancer and had undergone ESD after esophagectomy (5 patients). The reconstruction routes were antethoracic, retrosternal, and posterior mediastinal in 7, 11, and 20 patients, respectively. The location of the GTC lesion was upper, middle, and low in 2, 18, and 28 patients, respectively. Regarding the macroscopic type, there were 21 lesions of 0-IIa, 22 lesions of 0-IIc, 2 lesions of 0-IIb, 1 lesion of 0-III, and 2 combined lesions. The median observation period after ESD was 884 d (range, 8-4040 d).
| Characteristics | |
| Patients/lesions, n | 38/48 |
| Median age, yr (range) | 71.5 (57-84) |
| Sex, n (%) | |
| Male | 34 (89) |
| Female | 4 (11) |
| Median period from esophagectomy to ESD for GTC, d (range) | 2106 (38-9523) |
| Reconstruction route of gastric tube, n (%) | |
| Antethoracic | 7 (18) |
| Retrosternal | 11 (29) |
| Posterior mediastinal | 20 (53) |
| Median observation period after ESD, d (range) | 884 (8-4040) |
| Location of lesion, n (%) | |
| U | 2 (4) |
| M | 18 (38) |
| L | 28 (58) |
| Macroscopic type, n (%) | |
| 0-IIa | 21 (44) |
| 0-IIb | 2 (4) |
| 0-IIc | 22 (46) |
| 0-III | 1 (2) |
| Combined | 2 (4) |
Treatment results of ESD for GTC after esophagectomy and pathological findings are shown in Table 2. The median procedure time was 81 min (range, 29-334 min). En bloc resection was performed in 44 of 48 lesions (91.7%). The median tumor size of the resected specimen was 15 mm (range, 4-60 mm). Among the 48 lesions, 43 were differentiated (90%) and 5 were undifferentiated (10%). Regarding the tumor depth, 40 lesions were intramucosal carcinoma (M, 84%), 4 were submucosal superficial carcinoma (SM1, 8%), and 4 were submucosal deep invasive carcinoma (SM2 or deeper, 8%). Ulcerative findings were seen in 6 lesions (13%). Lymphatic infiltration was seen in 3 lesions (6%), and vascular infiltration was seen in 1 lesion (2%). According to the Japanese Gastric Cancer Treatment Guidelines, 38 lesions (79%) achieved curative resection (eCura A) and 10 lesions (21%) were classified as non-curative resection. The reasons for non-curative resection were as follows: 3 lesions were horizontal margin positive (HM1) or cutting into the lesion (eCura C-1), 2 were undifferentiated and showed SM invasion, 2 showed lymphatic infiltration, 2 showed SM invasion with ulcerative findings, and 1 was undifferentiated and showed SM invasion and lymphatic and vascular infiltration (eCura C-2).
| Lesions, n | 48 |
| Median procedure time, min (range) | 81 (29-334) |
| En bloc resection, n (%) | 44 (91.7) |
| Adverse events during ESD, n (%) | |
| Bleeding | 1(2) |
| Perforation | 1(2) |
| Adverse events post ESD, n (%) | |
| Bleeding | 2 (4) |
| Subcutaneous abscess | 1 (2) |
| Liver failure | 1 (2) |
| Respiratory failure | 1 (2) |
| Median tumor size, mm (range) | 15 (4-60) |
| Histrogical type, n | |
| Differentiated | 43 |
| Undifferentiated | 5 |
| Tumor depth, n | |
| M | 40 |
| SM1 | 4 |
| SM2 | 4 |
| Ulcerative findings, n | |
| Absent | 41 |
| Present | 7 |
| Lymphatic infiltration, n | |
| Negative | 3 |
| Positive | 45 |
| Lymphatic infiltration, n | |
| Negative | 1 |
| Positive | 47 |
| Horizontal margin, n | |
| Negative | 45 |
| Positive | 3 |
| Vertical margin, n | |
| Negative | 47 |
| Positive | 1 |
| eCura, n (%) | |
| A | 38 (79) |
| C-1 | 3 (6) |
| C-2 | 7 (15) |
Complications during ESD were seen in 2 cases (4%), with 1 case of perforation, and 1 case of bleeding. Complications after ESD were seen in 5 cases (10%), with 2 cases of bleeding, 1 case of subcutaneous abscess, 1 case of liver failure, and 1 case of respiratory failure (Table 2).
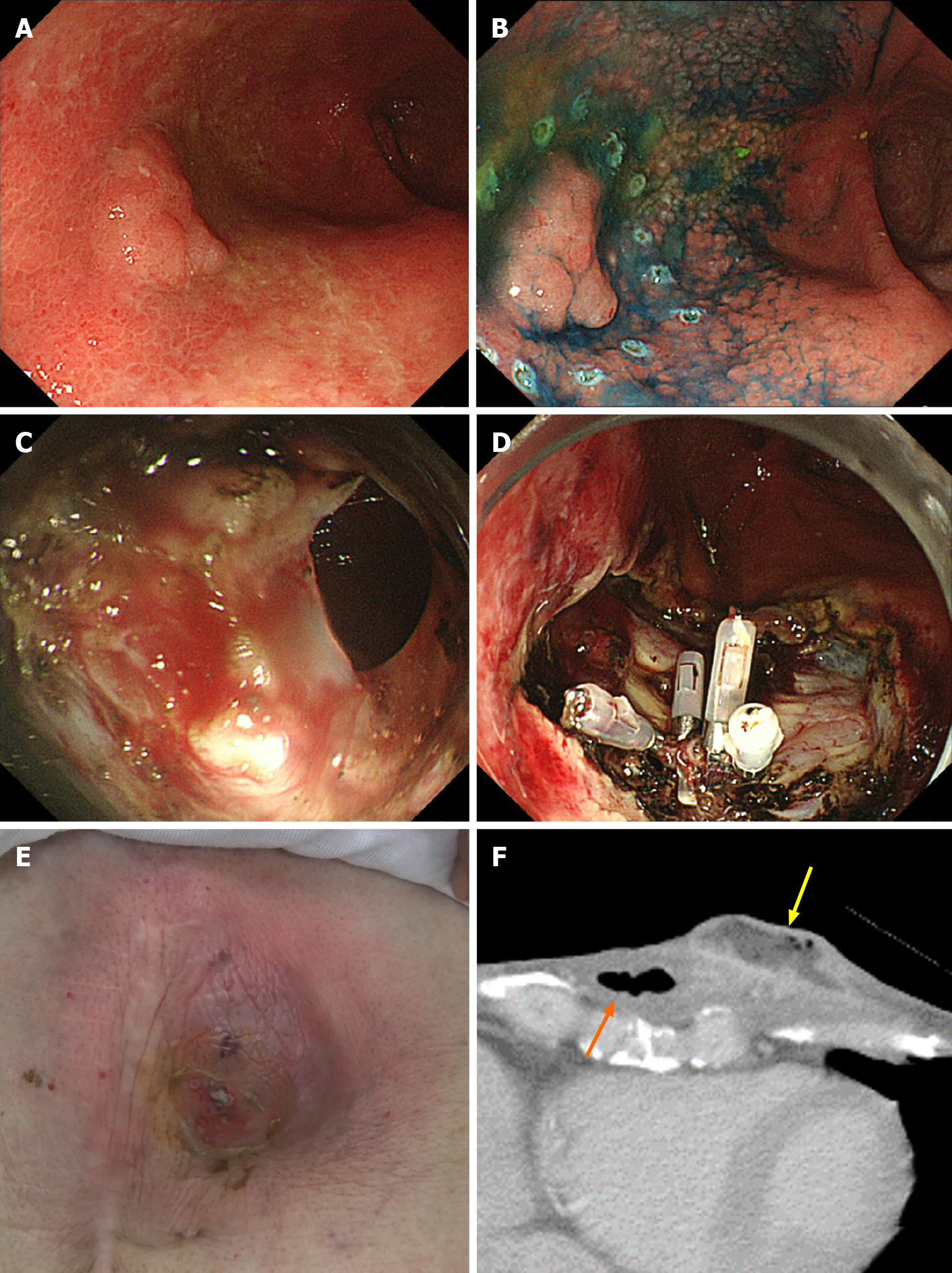
It was the same patient who had perforation during ESD and who formed subcutaneous abscess after ESD (Figure 1). In this case, perforation during ESD was sealed immediately with endoclips. Nevertheless, 20 d after ESD, the patient was admitted to the hospital with redness of the skin in the precordial area and excretion of pus from the skin. Computed tomography showed formation of a subcutaneous abscess around the gastric tube of the antethoracic reconstruction route. The patient was treated conservatively with antibiotics and percutaneous drainage and was discharged on the 16th day after the start of re-admission.
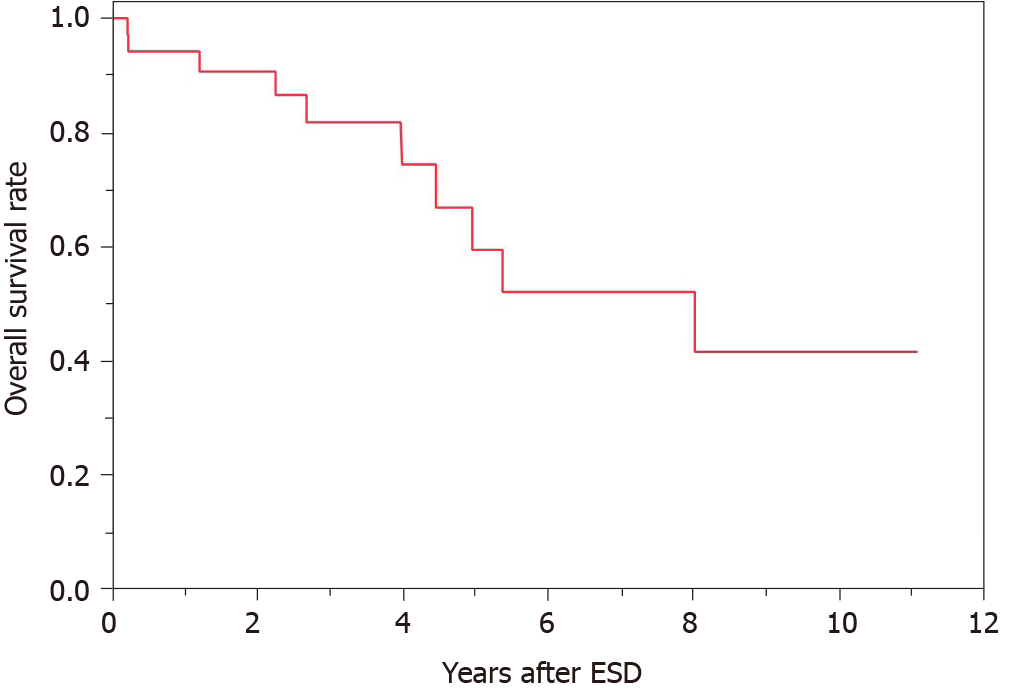
Of the 38 cases, 2 had local recurrence and 3 had metachronous recurrence. In the 2 cases with local recurrence, 1 received additional surgery and the other received additional ESD. In the 3 cases with metachronous recurrence, 1 received additional surgery and the others received additional ESD. The patients’ overall survival curve is shown in Figure 2. The survival rate at 5 years was 59.5%. During the observation period after ESD, no patient died of GTC. However, 10 patients died of other diseases, including pneumonia, which was the most common and occurred in 4 patients, heart failure and hepatocellular carcinoma in 1 patient each, and other unknown diseases.
A comparison of the patients’ background and clinical outcomes between OUH and other hospitals is shown in Table 3. In terms of the patients’ backgrounds, the posterior mediastinal route was used as a reconstruction route in more cases at other hospitals. Treatment results were generally similar in both groups; however, procedure time was significantly longer at other hospitals.
| Institution (patients/lesions) | OUH (17/20) | Other hospitals (21/28) | P value |
| Median age, yr (range) | 70 (57-83) | 73 (58-84) | 0.28 |
| Male, n (%) | 15 (88) | 19 (79) | 0.72 |
| Reconstruction route of gastric tube, n | < 0.01 | ||
| Antethoracic | 7 | 0 | |
| Retrosternal | 7 | 4 | |
| Posterior mediastinal | 3 | 17 | |
| Median tumor size, mm (range) | 18 (8-60) | 15 (4-40) | 0.21 |
| depth, M/SM, n | 16/4 | 24/4 | 0.6 |
| Ulcerative findings positive, n (%) | 3 (15) | 4 (14) | 0.94 |
| Median procedure time, min (range) | 50 (20-180) | 108 (32-334) | < 0.01 |
| En bloc resection, n (%) | 19 (95) | 25 (89) | 0.48 |
| Curative resection (eCura A or B), n (%) | 17 (85) | 21 (75) | 0.4 |
| Adverse events during ESD, n (%) | 1 (5.0) | 1 (3.6) | 0.8 |
| Adverse events post ESD, n (%) | 3 (15) | 2 (7.1) | 0.37 |
Since there were differences in procedure time between institutions, we divided patients into two groups, a short procedure time group (< 90 min) and a long procedure time group (≥ 90 min), and examined the factors affecting the procedure time. In univariate analysis (Table 4), the treatment institution and tumor size showed significant differences between the two groups. However, in multivariate analysis (Table 5), tumor size was the only factor associated with a long procedure time.
| < 90 min, n = 26 | ≥ 90 min, n = 22 | P value | |
| Okayama University Hospital/other hospitals, n | 15/11 | 5/17 | 0.01 |
| Reconstruction route of gastric tube, n | |||
| Antethoracic/retrosternal/posterior mediastinal | 6/11/9 | 3/4/15 | 0.06 |
| Location of lesion, n | |||
| U/L/M | 0/8/18 | 2/10/10 | 0.08 |
| Median tumor size, mm (range) | 13 (4-26) | 15 (6-60) | 0.06 |
| Tumor depth, n | |||
| M/SM | 23/3 | 17/5 | 0.30 |
| Ulcerative findings positive, n | 2 | 5 | 0.14 |
| Risk ratio (95%CI) | P value | |
| Other hospitals | 3.18 (0.59-19.6) | NS |
| Posterior mediastinal route | 3.18 (0.61-19.4) | NS |
| Location of lesion, U/M | 2.12 (0.52-8.84) | NS |
| Median tumor size ≥ 20 mm | 4.90 (1.09-29.6) | 0.04 |
This study was the first multicenter study on ESD for GTC in the reconstructed gastric tube after esophagectomy, and it included the second largest number of patients. According to a systematic review of GTC after esophagectomy, there are two surgical options for the treatment of GTC: PGTR or TGTR plus lymphadenectomy with colon or jejunal reconstruction[21]. However, surgical treatment for GTC is highly invasive and carries a certain degree of risk. Sugiura et al[10] reported that 5 of 7 cases of TGTR had surgical complications (leakage) and 2 died. In addition, 1 of 3 cases of PTGR had fatal complications. Akita et al[11] reported that 1 of 5 cases of TGTR died of postoperative complications. On the other hand, in previous studies on ESD for GTC, the proportions of R0 resection and curative resection were 87.5%-92% and 65%-85%, respectively, and complications were seen in 12.5%-18% of patients[13-18]. In the present study, the proportions of R0 resection and curative resection were 91.7% and 79%, respectively, and complications were seen in 10%. Overall, the treatment results of ESD for GTC in this study were similar to those of previous studies. In a previous study on gastric ESD of the unresected stomach, the proportions of R0 resection, curative resections, and complications were 92%-94.9%, 80.4%-94.7%, and 5.9%-6.3%, respectively[22,23]. Furthermore, in gastric ESD of the remnant stomach after gastrectomy, the proportions of R0 resection, curative resection, and complications were 84.7%-85%, 70.9%-78%, and 2.8%-21.1%, respectively[24,25]. ESD for GTC was considered a minimally invasive, effective, and relatively safe treatment.
There are some points of note in GTC. First, detection of early GTC requires long-term regular endoscopic surveillance after esophagectomy. GTC is often found long after esophagectomy; in some cases, GTC is detected after more than 10 years and the risk of metachronous GTC is high[15-18]. Second, GTC may be difficult to diagnose. The reasons are as follows: Food residue and bile reflux are often seen in the gastric tube, and the lumen of the gastric tube is long and narrow and can constrain endoscopic observation[13]. Therefore, it is necessary to pay attention to these points during endoscopy for patients with gastric tube reconstruction after esophagectomy. Third, when performing ESD for GTC, it is necessary to pay attention to complications specific to GTC. For example, in our study, a subcutaneous abscess formed after treatment in a case with perforation during ESD for GTC in the antethoracic reconstruction route. This case was cured by conservative treatment with antibiotics and percutaneous drainage. Moreover, Miyagi et al[26] reported that post-treatment precordial skin burns occurred in 5 of 8 patients with GTC in the antethoracic reconstruction route. In this report, all burns were diagnosed as first-degree burns based on the clinical classification of burn depth, developed on postoperative day 1-2, and took 4-7 d to heal.
In this study, since approximately half of the patients were treated at OUH, we defined it as a high-volume center and compared clinical outcomes with those of other institutions. As a result, there were no significant differences in the clinical outcomes of ESD between institutions. In addition, lesion size was the only factor related to long procedure time in multivariate analysis. We believe these results were attributable to the fact that all of the participating institutions specialized in gastrointestinal diseases with more than 500 cases of ESD for EGC. Moreover, ESD for GTC may have been performed by leading specialists given the relative rarity of GTC. For these reasons, ESD for GTC seems safe if performed by specialists with sufficient ESD experience.
Previously, not a few patients had complications or died of other diseases during the course after esophagectomy[27,28]. However, due to the widespread use of minimally invasive esophagectomy, such as thoracoscopic and laparoscopic surgery, the incidence of postoperative complications, including respiratory complications, has decreased and the general condition of patients after esophagectomy has improved in recent years[29-32]. With continued improvements in the prognosis of esophageal cancer, the number of cases of GTC after esophagectomy will likely increase in the future and the demand for ESD for GTC is expected to increase further.
There were several limitations to this study. First, as this was a retrospective study, the ESD indications and devices used for treatment were not standardized. However, treatment was performed according to the typical standards. Second, since data on Helicobacter pylori infection status were missing in some patients, the association between GTC and Helicobacter pylori could not be evaluated. Third, as some patients were observed for only a short time, the assessment of long-term prognosis after ESD for GTC was insufficient. Further follow-up studies are needed in the future.
In conclusion, ESD for GTC after esophagectomy is a safe and effective treatment that can be performed without significant variability in treatment results at any specialized institution where standard gastric ESD can be performed with sufficient expertise. Further accumulation and follow-up of cases of GTC are necessary in the future.
Recent improvements in the prognosis of patients with esophageal cancer have led to the increased occurrence of gastric tube cancer (GTC) in the reconstructed gastric tube.
There are few reports on the treatment results of endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) for GTC.
This retrospective study aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of ESD for GTC after esophagectomy in a multicenter trial.
We retrospectively investigated 48 GTC lesions in 38 consecutive patients with GTC in the reconstructed gastric tube after esophagectomy who had undergone ESD between January 2005 and December 2019 at 8 institutions participating in the Okayama Gut Study group. Patient characteristics, treatment results, clinical course, and treatment outcomes were analyzed.
The median age of patients was 71.5 years (range, 57-84years), and there were 34 men and 4 women. The median observation period after ESD was 884 d (range, 8-4040 d). The median procedure time was 81 min (range, 29-334 min), the en bloc resection rate was 91.7% (44/48), and the curative resection rate was 79% (38/48). Complications during ESD were seen in 4% (2/48) of case, and those after ESD were seen in 10% (5/48) of case. The survival rate at 5 years was 59.5%. During the observation period after ESD, 10 patients died of other diseases. Although there were differences in the procedure time between institutions, a multivariate analysis showed that tumor size was the only factor associated with prolonged procedure time.
ESD for GTC after esophagectomy was shown to be safe and effective.
As some patients were observed for only a short time, the assessment of long-term prognosis after ESD for GTC was insufficient. Further accumulation and follow-up of cases of GTC are necessary in the future.
Manuscript source: Unsolicited manuscript
Specialty type: Gastroenterology and hepatology
Country/Territory of origin: Japan
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Sandhu DS S-Editor: Gao CC L-Editor: A P-Editor: Liu JH
| 1. | Medical Research Council Oesophageal Cancer Working Group. Surgical resection with or without preoperative chemotherapy in oesophageal cancer: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2002;359:1727-1733. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1121] [Cited by in RCA: 1084] [Article Influence: 47.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Allum WH, Stenning SP, Bancewicz J, Clark PI, Langley RE. Long-term results of a randomized trial of surgery with or without preoperative chemotherapy in esophageal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:5062-5067. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 662] [Cited by in RCA: 754] [Article Influence: 47.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Ozawa S, Tachimori Y, Baba H, Matsubara H, Muro K, Numasaki H, Oyama T, Shinoda M, Takeuchi H, Tanaka O, Teshima T, Udagawa H, Uno T, Barron JP. Comprehensive registry of esophageal cancer in Japan, 2002. Esophagus. 2010;7:7-22. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 4. | Ando N, Kato H, Igaki H, Shinoda M, Ozawa S, Shimizu H, Nakamura T, Yabusaki H, Aoyama N, Kurita A, Ikeda K, Kanda T, Tsujinaka T, Nakamura K, Fukuda H. A randomized trial comparing postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy with cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil vs preoperative chemotherapy for localized advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the thoracic esophagus (JCOG9907). Ann Surg Oncol. 2012;19:68-74. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 788] [Cited by in RCA: 1052] [Article Influence: 75.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Toxopeus E, van der Schaaf M, van Lanschot J, Lagergren J, Lagergren P, van der Gaast A, Wijnhoven B. Outcome of Patients Treated Within and Outside a Randomized Clinical Trial on Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy Plus Surgery for Esophageal Cancer: Extrapolation of a Randomized Clinical Trial (CROSS). Ann Surg Oncol. 2018;25:2441-2448. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 21] [Cited by in RCA: 34] [Article Influence: 4.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Kokawa A, Yamaguchi H, Tachimori Y, Kato H, Watanabe H, Nakanishi Y. Other primary cancers occurring after treatment of superficial oesophageal cancer. Br J Surg. 2001;88:439-443. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 28] [Cited by in RCA: 30] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Noguchi T, Kato T, Takeno S, Wada S, Yanagisawa S, Suzuki M. Necessity of screening for multiple primary cancers in patients with esophageal cancer. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2002;8:336-342. [PubMed] |
| 8. | Natsugoe S, Matsumoto M, Okumura H, Ishigami S, Uenosono Y, Owaki T, Takao S, Aikou T. Multiple primary carcinomas with esophageal squamous cell cancer: clinicopathologic outcome. World J Surg. 2005;29:46-49. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 43] [Cited by in RCA: 45] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Chuang SC, Hashibe M, Scelo G, Brewster DH, Pukkala E, Friis S, Tracey E, Weiderpass E, Hemminki K, Tamaro S, Chia KS, Pompe-Kirn V, Kliewer EV, Tonita JM, Martos C, Jonasson JG, Dresler CM, Boffetta P, Brennan P. Risk of second primary cancer among esophageal cancer patients: a pooled analysis of 13 cancer registries. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2008;17:1543-1549. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 65] [Cited by in RCA: 78] [Article Influence: 4.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Sugiura T, Kato H, Tachimori Y, Igaki H, Yamaguchi H, Nakanishi Y. Second primary carcinoma in the gastric tube constructed as an esophageal substitute after esophagectomy. J Am Coll Surg. 2002;194:578-583. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 58] [Cited by in RCA: 60] [Article Influence: 2.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Akita H, Doki Y, Ishikawa O, Takachi K, Miyashiro I, Sasaki Y, Ohigashi H, Murata K, Noura S, Yamada T, Eguchi H, Imaoka S. Total removal of the posterior mediastinal gastric conduit due to gastric cancer after esophagectomy. J Surg Oncol. 2004;85:204-208. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Gotoda T. Endoscopic resection of early gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 2007;10:1-11. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 479] [Cited by in RCA: 495] [Article Influence: 27.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 13. | Mukasa M, Takedatsu H, Matsuo K, Sumie H, Yoshida H, Hinosaka A, Watanabe Y, Tsuruta O, Torimura T. Clinical characteristics and management of gastric tube cancer with endoscopic submucosal dissection. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21:919-925. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 2.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Osumi W, Fujita Y, Hiramatsu M, Kawai M, Sumiyoshi K, Umegaki E, Tokioka S, Yoda Y, Egashira Y, Abe S, Higuchi K, Tanigawa N. Endoscopic submucosal dissection allows less-invasive curative resection for gastric tube cancer after esophagectomy - a case series. Endoscopy. 2009;41:777-780. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 20] [Cited by in RCA: 24] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Bamba T, Kosugi S, Takeuchi M, Kobayashi M, Kanda T, Matsuki A, Hatakeyama K. Surveillance and treatment for second primary cancer in the gastric tube after radical esophagectomy. Surg Endosc. 2010;24:1310-1317. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 38] [Cited by in RCA: 42] [Article Influence: 2.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Tawaraya S, Jin M, Matsuhashi T, Suzuki Y, Sawaguchi M, Watanabe N, Onochi K, Koizumi S, Hatakeyama N, Ohba R, Mashima H, Ohnishi H. Advanced feasibility of endoscopic submucosal dissection for the treatment of gastric tube cancer after esophagectomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2014;79:525-530. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 0.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Hirayama Y, Fujisaki J, Yoshimizu S, Horiuchi Y, Yoshio T, Ishiyama A, Hirasawa T, Imamura Y, Mine S, Watanabe M, Tsuchida T. Efficacy and safety of endoscopic resection for gastric tube cancer after surgical resection of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Esophagus. 2019;16:194-200. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 2.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Nonaka S, Oda I, Sato C, Abe S, Suzuki H, Yoshinaga S, Hokamura N, Igaki H, Tachimori Y, Taniguchi H, Kushima R, Saito Y. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for gastric tube cancer after esophagectomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2014;79:260-270. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 25] [Cited by in RCA: 30] [Article Influence: 2.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Japanese Gastric Cancer Association. Japanese gastric cancer treatment guidelines 2018 (5th edition). Gastric Cancer. 2021;24:1-21. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 735] [Cited by in RCA: 1337] [Article Influence: 334.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (2)] |
| 20. | Japanese Gastric Cancer Association. Japanese classification of gastric carcinoma: 3rd English edition. Gastric Cancer. 2011;14:101-112. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2390] [Cited by in RCA: 2872] [Article Influence: 205.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Gentile D, Riva P, Da Roit A, Basato S, Marano S, Castoro C. Gastric tube cancer after esophagectomy for cancer: a systematic review. Dis Esophagus. 2019;32. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 18] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Takenaka R, Kawahara Y, Okada H, Hori K, Inoue M, Kawano S, Tanioka D, Tsuzuki T, Yagi S, Kato J, Uemura M, Ohara N, Yoshino T, Imagawa A, Fujiki S, Takata R, Yamamoto K. Risk factors associated with local recurrence of early gastric cancers after endoscopic submucosal dissection. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008;68:887-894. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 116] [Cited by in RCA: 112] [Article Influence: 6.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Isomoto H, Shikuwa S, Yamaguchi N, Fukuda E, Ikeda K, Nishiyama H, Ohnita K, Mizuta Y, Shiozawa J, Kohno S. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer: a large-scale feasibility study. Gut. 2009;58:331-336. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 470] [Cited by in RCA: 520] [Article Influence: 32.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 24. | Nonaka S, Oda I, Makazu M, Haruyama S, Abe S, Suzuki H, Yoshinaga S, Nakajima T, Kushima R, Saito Y. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer in the remnant stomach after gastrectomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013;78:63-72. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 39] [Cited by in RCA: 45] [Article Influence: 3.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Yabuuchi Y, Kakushima N, Takizawa K, Tanaka M, Kawata N, Yoshida M, Kishida Y, Ito S, Imai K, Ishiwatari H, Hotta K, Matsubayashi H, Ono H. Short- and long-term outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer in the remnant stomach after gastrectomy. J Gastroenterol. 2019;54:511-520. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 23] [Article Influence: 3.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Miyagi M, Yoshio T, Hirasawa T, Ishiyama A, Yamamoto Y, Tsuchida T, Fujisaki J, Igarashi M. Precordial skin burns after endoscopic submucosal dissection for gastric tube cancer. Dig Endosc. 2015;27:742-746. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Griffin SM, Shaw IH, Dresner SM. Early complications after Ivor Lewis subtotal esophagectomy with two-field lymphadenectomy: risk factors and management. J Am Coll Surg. 2002;194:285-297. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 156] [Cited by in RCA: 145] [Article Influence: 6.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Ando N, Ozawa S, Kitagawa Y, Shinozawa Y, Kitajima M. Improvement in the results of surgical treatment of advanced squamous esophageal carcinoma during 15 consecutive years. Ann Surg. 2000;232:225-232. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 410] [Cited by in RCA: 408] [Article Influence: 16.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Akaishi T, Kaneda I, Higuchi N, Kuriya Y, Kuramoto J, Toyoda T, Wakabayashi A. Thoracoscopic en bloc total esophagectomy with radical mediastinal lymphadenectomy. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1996;112:1533-40; discussion 1540. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 142] [Cited by in RCA: 117] [Article Influence: 4.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Osugi H, Takemura M, Higashino M, Takada N, Lee S, Kinoshita H. A comparison of video-assisted thoracoscopic oesophagectomy and radical lymph node dissection for squamous cell cancer of the oesophagus with open operation. Br J Surg. 2003;90:108-113. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 178] [Cited by in RCA: 164] [Article Influence: 7.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Luketich JD, Alvelo-Rivera M, Buenaventura PO, Christie NA, McCaughan JS, Litle VR, Schauer PR, Close JM, Fernando HC. Minimally invasive esophagectomy: outcomes in 222 patients. Ann Surg. 2003;238:486-94; discussion 494. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 707] [Cited by in RCA: 640] [Article Influence: 29.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Zingg U, McQuinn A, DiValentino D, Esterman AJ, Bessell JR, Thompson SK, Jamieson GG, Watson DI. Minimally invasive vs open esophagectomy for patients with esophageal cancer. Ann Thorac Surg. 2009;87:911-919. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 110] [Cited by in RCA: 103] [Article Influence: 6.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |