Published online Jul 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i27.3952
Peer-review started: March 17, 2020
First decision: April 25, 2020
Revised: May 6, 2020
Accepted: June 30, 2020
Article in press: June 30, 2020
Published online: July 21, 2020
Processing time: 126 Days and 1.3 Hours
The presence of significant liver fibrosis in hepatitis B virus (HBV)-infected individuals with persistently normal serum alanine aminotransferase (PNALT) levels is a strong indicator for initiating antiviral therapy. Serum ceruloplasmin (CP) is negatively correlated with liver fibrosis in HBV-infected individuals.
To examine the potential value of serum CP and develop a noninvasive index including CP to assess significant fibrosis among HBV-infected individuals with PNALT.
Two hundred and seventy-five HBV-infected individuals with PNALT were retrospectively evaluated. The association between CP and fibrotic stages was statistically analyzed. A predictive index including CP [Ceruloplasmin hepatitis B virus (CPHBV)] was constructed to predict significant fibrosis and compared to previously reported models.
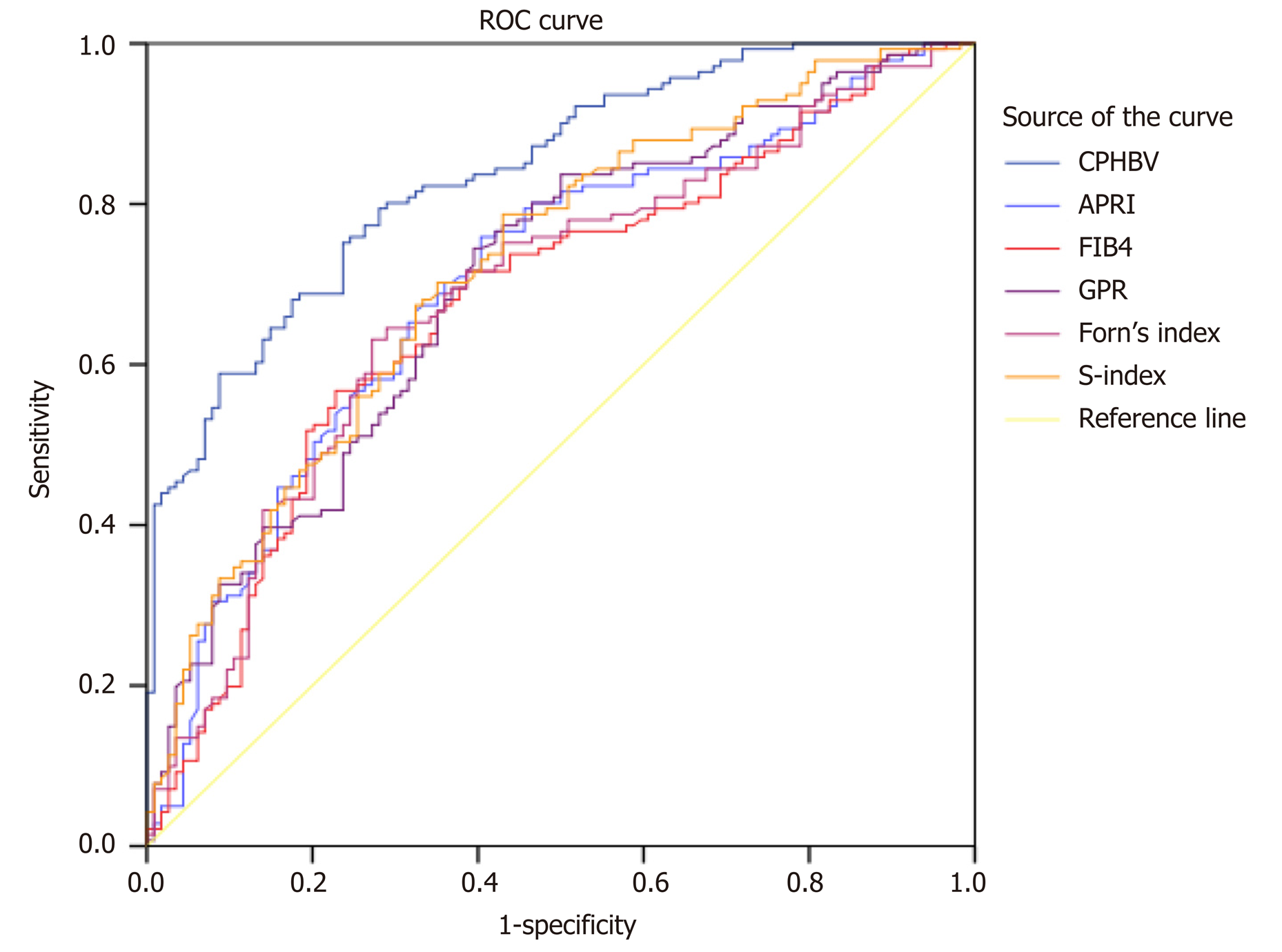
Serum CP had an inverse correlation with liver fibrosis (r = -0.600). Using CP, the areas under the curves (AUCs) to predict significant fibrosis, advanced fibrosis, and cirrhosis were 0.774, 0.812, and 0.853, respectively. The CPHBV model was developed using CP, platelets (PLT), and HBsAg levels to predict significant fibrosis. The AUCs of this model to predict significant fibrosis, advanced fibrosis, and cirrhosis were 0.842, 0.920, and 0.904, respectively. CPHBV was superior to previous models like the aspartate aminotransferase (AST)-to-PLT ratio index, Fibrosis-4 score, gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase-to-PLT ratio, Forn’s score, and S-index in predicting significant fibrosis in HBV-infected individuals with PNALT.
CPHBV could accurately predict liver fibrosis in HBV-infected individuals with PNALT. Therefore, CPHBV can be a valuable tool for antiviral treatment decisions.
Core tip: Chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV)-infected individuals with persistently normal serum alanine aminotransferase (PNALT) levels may develop severe liver fibrosis, which requires antiviral therapy. Following up on our previous findings, this multicenter, cross-sectional study showed that ceruloplasmin (CP) has an inverse correlation with liver fibrosis and is a promising predictive marker for liver fibrosis among HBV-infected individuals with PNALT. We developed a noninvasive model (ceruloplasmin hepatitis B virus) using CP, platelets, and HBsAg levels to identify various stages of fibrosis among HBV-infected individuals with PNALT. Our model could reduce the need for liver biopsy before antiviral treatment.
- Citation: Kang NL, Zhang JM, Lin MX, Chen XD, Huang ZX, Zhu YY, Liu YR, Zeng DW. Serum ceruloplasmin can predict liver fibrosis in hepatitis B virus-infected patients. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(27): 3952-3962
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i27/3952.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i27.3952
Approximately 292 million people have experienced hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection worldwide; nonetheless, less than 5% of those infected received antiviral therapy[1]. Chronic HBV infection can cause fibrosis, which can eventually develop into hepatocellular carcinoma[2]. Therefore, timely diagnosis of liver fibrosis is instrumental for commencing anti-HBV treatment, which will ultimately control the progression of liver injury and improve the patient prognosis[3]. Assessment of serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) level is a relatively inexpensive biochemical test that is widely used to detect liver injury. However, recent evidence suggests that some patients with normal ALT can also suffer from severe liver fibrosis[4-6].
Published guidelines for HBV management recommend that antiviral therapy be offered to chronic HBV-infected individuals with persistently normal ALT (PNALT) upon significant histological alterations[7-9]. Liver biopsy (LB) is a standard procedure in diagnosing hepatic fibrosis; however, its invasiveness increases the risk of complications[10-12]. FibroScan is another feasible alternative to LB due to its excellent diagnostic value in liver fibrosis[13-15]. However, its high cost and limitations in immune-tolerant HBV-infected individuals hinder its wide clinical application. The aspartate aminotransferase (AST)-to-platelet (PLT) ratio index (APRI) and fibrosis-4 score (FIB-4) have been recommended as noninvasive predictive indexes to assess liver fibrosis[16]. However, recent research showed that APRI and FIB-4 had poor diagnostic value for assessing the improvement of liver fibrosis during anti-HBV therapy[17]. Further, APRI and FIB-4 could not precisely estimate the stages of fibrosis in HBV-infected individuals with PNALT[18]. Therefore, it is essential to develop a novel predictive index to diagnose hepatic fibrosis in HBV-infected individuals with PNALT.
Serum ceruloplasmin (CP), a glycoprotein secreted by hepatocytes, carries more than 95% of the circulating copper in a healthy human. Studies have shown that CP has a strong antioxidant function and suppresses lipid peroxidation by eliminating superoxide anions[19,20]. Further, abnormal CP levels have been implicated in other pathological conditions[21]. Our previous data showed that CP was negatively correlated with liver fibrosis, suggesting that CP is a useful marker to diagnose liver fibrosis in CHB individuals[22-24]. Nonetheless, the association between CP and hepatic fibrosis among HBV-infected individuals with PNALT remains poorly understood[23]. Therefore, our purpose was to develop a novel panel to noninvasively predict hepatic fibrosis among HBV-infected individuals with PNALT using the CP levels. For this purpose, we routinely collected clinical data in a multicenter and cross-sectional study to develop such a model [ceruloplasmin hepatitis B virus (CPHBV)]. Next, we compared the diagnostic value of the new panel with that of previously established parameters like APRI, FIB-4, the gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase-to-PLT ratio (GPR), S-index, and Forn’s index[25-29].
Two hundred and seventy-five HBV-infected individuals with PNALT were retrospectively assessed between June 2010 and November 2019 from three affiliated hospitals of Fujian Medical University [First Affiliated Hospital, Mengchao Hepatobiliary Hospital (Xihong Branch of the First Affiliated Hospital), and The First Hospital of Quanzhou]. A portion of our patient cohort was previously investigated in former studies. In particular, 15.1% of the patients were investigated in Zeng et al[22], 2013 and 31.1% of the patients were investigated in Zeng et al[23], 2016. All treatment-naive patients had been HBsAg-positive for more than 6 mo. All exclusion criteria presented in our previous paper were applied in this study[23]. All individuals were randomly stratified into a training and validation group. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Fujian Medical University, and the need for informed consent was waived due to the retrospective nature of the study.
Liver specimens were obtained using 16-gauge modified aspiration needles (TSK Laboratory, Tochigi, Japan). Qualified liver specimens (a length of more than 1.5 cm and 6 portal tracts) were obtained, fixed in 4% formalin, embedded in paraffin, and processed with hematoxylin-eosin-safran, and Masson’s trichrome according to the standard protocols. Liver fibrosis staging (F0-F4) was carried out according to the METAVIR scoring system by a pathologist blinded to the patients’ data. Significant fibrosis was defined as F ≥ 2, advanced fibrosis as F ≥ 3, and cirrhosis as F = 4, as detailed previously[30].
The serum CP was examined by use of the nephelometric immunoassay kit (BN II System, Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics GmbH, Eschborn, Germany). Quantitative HBsAg was tested by use of the Elecsys HBsAg II quant assay (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) or the Abbott ARCHITECT assay (Abbott Laboratories, Chicago), and HBV-DNA was examined by use of quantitative polymerase chain reaction assay (PG Co, Shenzhen, China). Other routine biochemical parameters were assayed using an automatic biochemistry analyzer. Laboratory tests were assessed 1 wk prior to the LB procedure.
The Student’s t-test was utilized to investigate differences in continuous variables with a normal distribution. We performed the Mann–Whitney test to investigate the differences in continuous variables with a non-normal distribution. The chi-square test was used to detect differences in categorical data. The Spearman test for correlation analyses was applied. Univariate and multivariate regression analyses were applied to select independent parameters linked with significant liver fibrosis. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis was carried out to obtain the best cut-off value of CP for liver fibrosis. Diagnostic accuracy was obtained by the area under the curve (AUC). To compare the AUC of CPHBV with that of five noninvasive models (APRI, FIB-4, GPR, Forn’s index, and S index), the Z test was applied. Statistical analyses were applied by use of SPSS v23.0.
Among a total of 275 enrolled patients (mean age = 40.25 ± 9.65 years), 194 (70.5%) were men and 81 (29.5%) were women (Table 1). Further, 54.5% of the patients presented with at least moderate fibrosis (F ≥ 2) and 19.3% had liver cirrhosis (F4). Analysis of the demographic and clinical features did not reveal significant differences between the training and validation groups (P > 0.05, Table 1).
| ALL (n = 275) | Training group (n = 138) | Validation group (n = 137) | P value | ||
| Age (yr) | 40.25 ± 9.65 | 40.90 ± 9.90 | 39.61 ± 9.37 | 0.267 | |
| Gender | Male | 194 (70.5%) | 101 (73.2%) | 93 (67.9%) | 0.335 |
| Female | 81 (29.5%) | 37 (26.8%) | 44 (32.1%) | ||
| CP (mg/L) | 213.01 ± 43.28 | 212.72 ± 42.68 | 213.29 ± 44.03 | 0.914 | |
| Total bilirubin (μmol/L) | 13.51± 7.16 | 13.31 ± 6.46 | 13.71 ± 7.80 | 0.652 | |
| Albumin (g/L) | 42.84 ± 3.68 | 42.93 ± 3.74 | 42.75 ± 3.63 | 0.692 | |
| Globulin (g/L) | 28.19 ± 18.49 | 29.43 ± 6.04 | 27.01 ± 4.28 | 0.291 | |
| ALT (IU/L) | 29.56 ± 9.86 | 29.65 ± 9.69 | 29.46 ± 10.07 | 0.872 | |
| AST (IU/L) | 26.91 ± 7.17 | 26.71 ± 7.19 | 27.11 ± 7.16 | 0.645 | |
| GGT (IU/L) | 29.48 ± 21.87 | 29.23 ± 24.34 | 29.71 ± 19.28 | 0.860 | |
| TCHO (mmol/L) | 4.69 ± 0.89 | 4.61 ± 0.75 | 4.77 ± 1.00 | 0.149 | |
| TG (mmol/L) | 1.15 ± 0.68 | 1.25 ± 0.80 | 1.05 ± 0.50 | 0.113 | |
| CHE (IU/mL) | 8215.20 ± 2312.22 | 8409.96 ± 2358.01 | 8027.75 ± 2260.29 | 0.182 | |
| WBC (109/L) | 5.68 ± 1.48 | 5.74 ± 1.48 | 5.62 ± 1.49 | 0.509 | |
| PLT (109/L) | 191.96 ± 51.77 | 193.78 ± 51.91 | 190.11 ± 51.76 | 0.558 | |
| HBsAg (Log IU/mL) | 3.95 ± 0.95 | 3.89 ± 0.99 | 3.40 ± 0.90 | 0.346 | |
| HBV-DNA (Log IU/mL) | 5.13 ± 2.02 | 5.08 ± 2.01 | 5.19 ± 2.03 | 0.666 | |
| PT (s) | 12.11 ± 2.31 | 12.04 ± 2.56 | 12.18 ± 2.04 | 0.626 | |
| INR | 1.00 ± 0.19 | 0.99 ± 0.21 | 1.01 ± 0.17 | 0.662 | |
| Fibrosis stage, n (%) | 0.670 | ||||
| F0 | 19 (6.9) | 12 (8.7) | 7 (5.1) | ||
| F1 | 106 (38.5) | 52 (37.7) | 54 (39.4) | ||
| F2 | 57 (20.7) | 26 (18.8) | 31 (22.6) | ||
| F3 | 40 (14.5) | 19 (13.8) | 21 (15.3) | ||
| F4 | 53 (19.3) | 29 (21.0) | 24 (17.5) | ||
Serum CP levels revealed an inverse correlation with hepatic fibrosis (r = -0.6). The AUCs were 0.774 for F ≥ 2, 0.812 for F ≥ 3, and 0.853 for F4 (Table 2). Further, the best diagnostic CP values were 203.5 mg/L for F ≥ 2, 190.5 mg/L for F ≥ 3, and 182.5 mg/L for F4 (Table 2).
| Steatosis degree | AUC (95%CI) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | PPV (%) | NPV (%) | Cut-off point |
| F ≥ 2 | 0.774 (0.696-0.851) | 81.3 | 64.9 | 66.7 | 80 | ≤ 203.5 |
| F ≥ 3 | 0.812 (0.732-0.892) | 82.8 | 65.9 | 83.7 | 64.4 | ≤ 190.5 |
| F = 4 | 0.853 (0.781-0.925) | 89.3 | 65.4 | 91.7 | 58.6 | ≤ 182.5 |
Next, we analyzed the correlation between various biochemical parameters and significant fibrosis (Table 3). Univariate analysis revealed that the CP, albumin, gamma glutamyl transpeptidase, total cholesterol, cholinesterase, HBsAg, and PLT levels were different between individuals with non-significant and significant fibrosis (P < 0.05). These variables were then subjected to multivariate regression. CP, PLT, and HBsAg were identified as independent predictors. Using these parameters, a novel diagnostic model named CPHBV was developed to evaluate significant fibrosis in HBV-infected individuals with PNALT as follows: 37.122-10.072 × log CP (mg/L) - 4.291 × log PLT (109/L) - 0.958 × log HBsAg (IU/mL).
| No significant fibrosis (n = 64) | Significant fibrosis (n = 74) | P value | ||
| Age (yr) | 39.88 ± 9.68 | 39.61 ± 9.37 | 0.260 | |
| Gender | Male | 47 (73.4%) | 54 (73.0%) | 0.951 |
| Female | 17 (26.6%) | 20 (27.0%) | ||
| CP (mg/L) | 231.22 ± 35.26 | 196.73 ± 42.27 | < 0.0001 | |
| Total bilirubin (μmol/L) | 13.11 ± 6.97 | 13.48 ± 6.05 | 0.747 | |
| Albumin (g/L) | 44.27 ± 3.29 | 41.79 ± 3.75 | <0.0001 | |
| Globulin (g/L) | 27.15 ± 5.15 | 31.35 ± 5.03 | 0.363 | |
| ALT (IU/L) | 29.25 ± 10.32 | 30.00 ± 9.17 | 0.652 | |
| AST (IU/L) | 25.77 ± 7.21 | 27.53 ± 7.11 | 0.152 | |
| GGT (IU/L) | 23.69 ± 13.96 | 33.90 ± 29.78 | 0.017 | |
| TCHO (mmol/L) | 4.82 ± 0.83 | 4.44 ± 0.62 | 0.004 | |
| TG (mmol/L) | 1.31 ± 0.74 | 1.21 ± 0.85 | 0.474 | |
| CHE (IU/mL) | 9254.48 ± 2583.76 | 7710.21 ± 1903.41 | < 0.0001 | |
| WBC (109/L) | 5.78 ± 1.36 | 5.71 ± 1.59 | 0.766 | |
| PLT (109/L) | 212.63 ± 50.24 | 177.49 ± 47.94 | < 0.0001 | |
| HBsAg (Log IU/mL) | 4.40 ± 0.78 | 3.45 ± 0.96 | < 0.0001 | |
| HBV-DNA (Log IU/mL) | 5.17 ± 2.33 | 5.00 ± 1.70 | 0.614 | |
| PT (s) | 11.71 ± 2.81 | 12.33 ± 2.31 | 0.161 | |
| INR | 0.96 ± 0.23 | 1.02 ± 0.19 | 0.103 | |
We then analyzed the diagnostic value of the CPHBV model for detecting F ≥ 2, F ≥ 3, and F4 (Table 4). The AUC of CPHBV for predicting F ≥ 2 was 0.842. The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV) were 81.1%, 71.9%, 76.9%, and 76.7%, respectively, in the training group, and 72.4%, 80.3%, 82.1%, and 70.0% in the validation group. The AUC of CPHBV for the evaluation of significant fibrosis showed a comparable predictive value between the training and validation groups (Z = 0.746, P = 0.46). Upon using our model to assess advanced fibrosis and cirrhosis, the AUC, sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and NPV were 0.92, 90.9%, 78.7%, 66.7%, and 94.9%, respectively, for F ≥ 3, and 0.904, 96.2%, 71.4%, 43.9%, and 98.8% for F4 in the training group (Table 4).
| Variable | Training group (n = 138) | Validation group (n = 137) | ||||
| F ≥ 2 | F ≥ 3 | F = 4 | F ≥ 2 | F ≥ 3 | F = 4 | |
| AUC | 0.842 | 0.920 | 0.904 | 0.805 | 0.886 | 0.863 |
| 95%CI | 0.777-0.907 | 0.872-0.967 | 0.842-0.955 | 0.733-0.877 | 0.827-0.946 | 0.784-0.943 |
| Cut-off | 0.0304 | 0.496 | 0.553 | 0.174 | 0.176 | 0.206 |
| Sensitivity, % | 81.1 | 90.9 | 96.2 | 72.4 | 89.1 | 97.1 |
| Specificity | 71.9 | 78.7 | 71.4 | 80.3 | 72.5 | 70.6 |
| Youden’s index | 0.530 | 0.696 | 0.676 | 0.527 | 0.616 | 0.677 |
| PPV | 76.9 | 66.7 | 43.9 | 82.1 | 62.1 | 53.1 |
| NPV | 76.7 | 94.9 | 98.8 | 70.0 | 93.0 | 98.6 |
We compared the AUCs among six panels for the evaluation of significant fibrosis (Table 5, Figure 1). The CPHBV model had a significantly higher AUC value for significant fibrosis in HBV-infected individuals with PNALT than APRI, FIB-4, GPR, Forn’s index, and S-index (Table 5).
| Model | AUC (95%CI) | Youden index | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | PPV (%) | NPV (%) | P value |
| CPHBV | 0.839 (0.792-0.886) | 0.512 | 80.1 | 71.1 | 76.2 | 72.4 | |
| APRI | 0.704 (0.639-0.768) | 0.355 | 75.9 | 59.6 | 68.5 | 66.1 | < 0.001 |
| FIB-4 | 0.678 (0.612-0.745) | 0.330 | 71.9 | 61.4 | 68.8 | 64.2 | < 0.001 |
| GPR | 0.704 (0.640-0.768) | 0.350 | 74.5 | 60.5 | 70.1 | 66.7 | < 0.001 |
| Forn’s index | 0.687 (0.622-0.753) | 0.359 | 63.1 | 72.8 | 74.2 | 61.5 | < 0.001 |
| S-index | 0.722 (0.659-0.784) | 0.357 | 78.7 | 57.0 | 69.9 | 69.7 | 0.0034 |
We previously demonstrated that serum CP was a potential biomarker to predict hepatic fibrosis in HBV-infected individuals[22,23]. In this multi-center study, we further confirmed the valuable role of CP as a strong indicator to assess hepatic fibrosis in HBV-infected individuals with PNALT. In particular, our results demonstrated that serum CP had an inverse correlation with liver fibrosis. Therefore, we were able to develop the CPHBV index to predict different stages of fibrosis (i.e., significant, advanced, and cirrhosis). Further, we validated the specificity and sensitivity of the CPHBV model and compared its prognostic value to that of previously established models. Remarkably, the newly developed CPHBV model had a significantly better predictive value for significant fibrosis than the APRI, FIB-4, and GPR, scores as well as Forn’s index and the S-index. To our knowledge, this is the first effort to develop such a model and validate its valuable role for assessing significant fibrosis in HBV-infected individuals with PNALT.
ALT is a valuable biomarker for the detection of hepatic damage, i.e., normal serum ALT typically indicates the absence of liver injury. However, this is not the case in chronic HBV patients with PNALT. Previous studies demonstrated that more than 30% of HBV-infected individuals with PNALT present with significant liver fibrosis[31,32]. Indeed, our results demonstrated that 54.5% of HBV-infected individuals with PNALT had significant fibrosis, and their CP levels had an inverse correlation with hepatic fibrosis. In addition, multivariate analyses identified CP, HBsAg, and PLT as potential biomarkers that were independently correlated to liver fibrosis. In HBV-infected individuals with PNALT, analysis of the AUCs indicated that the serum CP had a reasonable diagnostic value to assess F ≥ 2, F ≥ 3, and F4. These results were in accordance with previous studies that suggested the potential function of CP for diagnosing fibrosis among HBV-infected individuals[22,23]. The detection of PLT levels has repeatedly been used to predict liver fibrosis[33]. Further, our previous research demonstrated that quantitative measurement of the HBsAg level can distinguish patients with active liver injury from immune tolerant HBV-infected individuals[34]. Although the mechanisms underlying the negative correlation between the serum HBsAg and fibrosis stages remain unclear, it is reasonable to speculate that host immune responses to HBV may result in liver damage, which can lead to a reduction in the HBsAg level. Taken together, our study enabled the identification of three serum biomarkers that were negatively associated with liver fibrosis, which enabled us to develop the CPHBV model.
The CPHBV model consists of three routinely assessed and relatively inexpensive biochemical parameters (CP, HBsAg, and PLT), which can be beneficial for resource-limited institutions to accurately detect liver fibrosis. CPHBV enabled the correct identification of patients with significant fibrosis and cirrhosis with an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.842 and 0.920, respectively. A CPHBV value less than 0.034 had an NPV of 76.7% to exclude significant fibrosis with a sensitivity of 81.1%. Among the 64 patients who did not have significant fibrosis, 18 (28.1%) will present with a CPHBV value higher than 0.0304. For patients with a score below 0.553, 80 (98.8%) out of 81 patients will not develop cirrhosis. Applying a higher cutoff value of 0.553, 32 (28.6%) of 112 without cirrhosis would be classified incorrectly (Supplementary Table 1 and 2). So, our study showed that the use of the CPHBV model will enable the accurate determination of patients in urgent need of antiviral treatment. Although this novel model was developed to diagnose significant fibrosis, it can also be used for diagnosing advanced fibrosis and cirrhosis.
Numerous novel noninvasive models to diagnose liver fibrosis have emerged. The APRI and FIB-4 scores were recommended to evaluate hepatic fibrosis by the HBV practice clinical guidelines. However, recent research showed that APRI and FIB-4 had low predictive performance in chronic HBV patients with PNALT (AUCs of 0.518 and 0.597, respectively)[18]. In this study, the AUC of FIB-4 or APRI for F ≥ 2 in HBV-infected individuals with PNALT was lower than that for the CPHBV model (P < 0.001). GPR is another novel predictive index for significant fibrosis in HBV-infected patients in the West African population[27]. GPR was found to be useful in our Chinese patient cohort but the predictive value of the novel CPHBV panel significantly surpassed that of GPR. Forn’s index was applied to diagnose liver fibrosis in CHB individuals[35]. However, the diagnostic value of Forn’s index for significant fibrosis in HBV-infected individuals with PNALT was rather limited (AUC = 0.687). The S-index was specifically designed to assess significant fibrosis in CHB individuals and had superior diagnostic accuracy compared to the APRI and FIB-4[36]. Nevertheless, CPHBV was superior to the S index in our patient cohort (0.839 vs 0.722, P = 0.0034). Taken together, the newly developed CPHBV model had better performance in identifying significant fibrosis than APRI, FIB-4, GPR, Forn’s index, and S index, at least in our patient cohort.
This study had a few limitations. First, CPHBV was developed and evaluated in a multicenter cross-sectional study. Therefore, future prospective multicenter studies will be needed to verify the diagnostic value of CPHBV. Second, we used cutoff ALT values < 40 IU/mL as the upper limit of normal for ALT in this study. However, in accordance with the current guidelines, ALT is estimated to be 35 IU/mL in healthy men and 25 IU/mL in healthy women[7]. Third, we used CP values tested at one time point to construct our model. Future studies should follow up with the participants to validate our results at different time points. Fourth, transient elastography (Fibroscan), the enhanced liver fibrosis test, and Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-positive Mac-2 binding protein(WFA + -M2BP) were as well accurate diagnostic tests for monitoring regression of fibrosis in patients with chronic HBV infection[37-41]. However, we did not perform the comparison because of the unavailable equipment at the time of data collection and serum indicators, such as hyaluronic acid, procollagen III amino-terminal peptide, metalloproteinase 1, and WFA + -M2BP are not routinely tested in our hospital.
In conclusion, serum CP is a routinely investigated biochemical index that negatively correlates with hepatic fibrosis and a potential marker to diagnose liver fibrosis in HBV-infected individuals with PNALT. The CPHBV model was found to be more efficient than the previously reported noninvasive models in diagnosing significant fibrosis among HBV-infected individuals with PNALT. The use of CPHBV might reduce the clinical need for LB in the future.
Chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV)-infected individuals with persistently normal serum ALT (PNALT) levels can suffer from severe liver fibrosis. Therefore, those patients can be prioritized in commencing the antiviral therapy. The timely diagnosis of liver fibrosis and initiation of anti-HBV treatment can control the disease progression and improve the patient prognosis. Serum ceruloplasmin (CP) is negatively correlated with liver fibrosis and thus it may serve as a predictive marker for liver fibrosis among HBV-infected individuals with PNALT.
Our previous data demonstrated that CP was negatively correlated with liver fibrosis in CHB individuals. Nonetheless, the association between CP and hepatic fibrosis among HBV-infected individuals with PNALT remains poorly understood.
We aimed to develop a predictive model combining serum CP to predict hepatic fibrosis among HBV-infected individuals with PNALT.
Two hundred and seventy-five HBV-infected individuals with PNALT were retrospectively assessed between June 2010 and November 2019 from three affiliated hospitals of Fujian Medical University [First Affiliated Hospital, Mengchao Hepatobiliary Hospital, and The First Hospital of Quanzhou]. The association between CP and fibrotic stages was statistically analyzed. A predictive index that included CP was constructed to predict significant fibrosis and compared to previously established parameters like the aspartate aminotransferase (AST)-to-platelet (PLT) ratio index (APRI), Fibrosis-4 score (FIB-4), gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase-to-PLT ratio (GPR), Forn’s score, and S-index.
We found that serum CP had an inverse correlation with liver fibrosis among HBV-infected individuals with PNALT. The CPHBV model was developed using CP, PLT, and HBsAg levels to predict various stages of fibrosis among HBV-infected individuals with PNALT. CPHBV was superior to previously reported models like APRI, FIB-4, GPR, Forn’s index, and S index.
Serum CP is a routinely investigated biochemical parameter that negatively correlates with hepatic fibrosis and can be a potential marker to diagnose liver fibrosis in HBV-infected individuals with PNALT. The CPHBV model could accurately predict liver fibrosis in HBV-infected individuals with PNALT. Therefore, CPHBV may efficiently predict liver fibrosis, which can reduce the need for liver biopsy before commencing antiviral treatment.
CPHBV was developed and evaluated in this multicenter cross-sectional study, thus providing a solid foundation for future prospective studies to validate the diagnostic value of this model.
Manuscript source: Unsolicited manuscript
Specialty type: Gastroenterology and hepatology
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): D
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: El-Shabrawi MHF, Fujita K, Lendvai G S-Editor: Dou Y L-Editor: Wang TQ E-Editor: Zhang YL
| 1. | Polaris Observatory Collaborators. Global prevalence, treatment, and prevention of hepatitis B virus infection in 2016: a modelling study. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;3:383-403. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1260] [Cited by in RCA: 1215] [Article Influence: 173.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (2)] |
| 2. | Wu JF, Chang MH. Natural history of chronic hepatitis B virus infection from infancy to adult life - the mechanism of inflammation triggering and long-term impacts. J Biomed Sci. 2015;22:92. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 53] [Cited by in RCA: 64] [Article Influence: 6.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Xiao G, Yang J, Yan L. Comparison of diagnostic accuracy of aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index and fibrosis-4 index for detecting liver fibrosis in adult patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection: a systemic review and meta-analysis. Hepatology. 2015;61:292-302. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 338] [Cited by in RCA: 391] [Article Influence: 39.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Weemhoff JL, Woolbright BL, Jenkins RE, McGill MR, Sharpe MR, Olson JC, Antoine DJ, Curry SC, Jaeschke H. Plasma biomarkers to study mechanisms of liver injury in patients with hypoxic hepatitis. Liver Int. 2017;37:377-384. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 30] [Cited by in RCA: 34] [Article Influence: 4.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Gong Y, Liu Z, Liao Y, Mai C, Chen T, Tang H, Tang Y. Effectiveness of ω-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Based Lipid Emulsions for Treatment of Patients after Hepatectomy: A Prospective Clinical Trial. Nutrients. 2016;8. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 27] [Cited by in RCA: 34] [Article Influence: 3.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Kelleni MT, Ibrahim SA, Abdelrahman AM. Effect of captopril and telmisartan on methotrexate-induced hepatotoxicity in rats: impact of oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. Toxicol Mech Methods. 2016;26:371-377. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 28] [Cited by in RCA: 27] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Terrault NA, Lok ASF, McMahon BJ, Chang KM, Hwang JP, Jonas MM, Brown RS, Bzowej NH, Wong JB. Update on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic hepatitis B: AASLD 2018 hepatitis B guidance. Hepatology. 2018;67:1560-1599. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2290] [Cited by in RCA: 2840] [Article Influence: 405.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol. 2017;67:370-398. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3745] [Cited by in RCA: 3799] [Article Influence: 474.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 9. | Sarin SK, Kumar M, Lau GK, Abbas Z, Chan HL, Chen CJ, Chen DS, Chen HL, Chen PJ, Chien RN, Dokmeci AK, Gane E, Hou JL, Jafri W, Jia J, Kim JH, Lai CL, Lee HC, Lim SG, Liu CJ, Locarnini S, Al Mahtab M, Mohamed R, Omata M, Park J, Piratvisuth T, Sharma BC, Sollano J, Wang FS, Wei L, Yuen MF, Zheng SS, Kao JH. Asian-Pacific clinical practice guidelines on the management of hepatitis B: a 2015 update. Hepatol Int. 2016;10:1-98. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1985] [Cited by in RCA: 1958] [Article Influence: 217.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Rockey DC, Caldwell SH, Goodman ZD, Nelson RC, Smith AD; American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Liver biopsy. Hepatology. 2009;49:1017-1044. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1449] [Cited by in RCA: 1580] [Article Influence: 98.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 11. | Schuppan D, Kim YO. Evolving therapies for liver fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 2013;123:1887-1901. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 502] [Cited by in RCA: 489] [Article Influence: 40.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Udell JA, Wang CS, Tinmouth J, FitzGerald JM, Ayas NT, Simel DL, Schulzer M, Mak E, Yoshida EM. Does this patient with liver disease have cirrhosis? JAMA. 2012;307:832-842. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 113] [Cited by in RCA: 124] [Article Influence: 9.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Jia J, Hou J, Ding H, Chen G, Xie Q, Wang Y, Zeng M, Zhao J, Wang T, Hu X, Schuppan D. Transient elastography compared to serum markers to predict liver fibrosis in a cohort of Chinese patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;30:756-762. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 65] [Cited by in RCA: 63] [Article Influence: 6.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Dong DR, Hao MN, Li C, Peng Z, Liu X, Wang GP, Ma AL. Acoustic radiation force impulse elastography, FibroScan®, Forns' index and their combination in the assessment of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B, and the impact of inflammatory activity and steatosis on these diagnostic methods. Mol Med Rep. 2015;11:4174-4182. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 32] [Cited by in RCA: 35] [Article Influence: 3.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Meng F, Zheng Y, Zhang Q, Mu X, Xu X, Zhang H, Ding L. Noninvasive evaluation of liver fibrosis using real-time tissue elastography and transient elastography (FibroScan). J Ultrasound Med. 2015;34:403-410. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 27] [Cited by in RCA: 25] [Article Influence: 2.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. |
Guidelines for the Prevention, Care and Treatment of Persons with Chronic Hepatitis B Infection.
Geneva; World Health Organization 2015; |
| 17. | Kim WR, Berg T, Asselah T, Flisiak R, Fung S, Gordon SC, Janssen HL, Lampertico P, Lau D, Bornstein JD, Schall RE, Dinh P, Yee LJ, Martins EB, Lim SG, Loomba R, Petersen J, Buti M, Marcellin P. Evaluation of APRI and FIB-4 scoring systems for non-invasive assessment of hepatic fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B patients. J Hepatol. 2016;64:773-780. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 170] [Cited by in RCA: 224] [Article Influence: 24.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Tan YW, Zhou XB, Ye Y, He C, Ge GH. Diagnostic value of FIB-4, aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index and liver stiffness measurement in hepatitis B virus-infected patients with persistently normal alanine aminotransferase. World J Gastroenterol. 2017;23:5746-5754. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 25] [Cited by in RCA: 27] [Article Influence: 3.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Ehrenwald E, Chisolm GM, Fox PL. Intact human ceruloplasmin oxidatively modifies low density lipoprotein. J Clin Invest. 1994;93:1493-1501. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 200] [Cited by in RCA: 189] [Article Influence: 6.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Linder MC. Ceruloplasmin and other copper binding components of blood plasma and their functions: an update. Metallomics. 2016;8:887-905. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 129] [Cited by in RCA: 197] [Article Influence: 21.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Yu L, Liou IW, Biggins SW, Yeh M, Jalikis F, Chan LN, Burkhead J. Copper Deficiency in Liver Diseases: A Case Series and Pathophysiological Considerations. Hepatol Commun. 2019;3:1159-1165. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 25] [Article Influence: 4.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Zeng DW, Liu YR, Zhang JM, Zhu YY, Lin S, You J, Li YB, Chen J, Zheng Q, Jiang JJ, Dong J. Serum ceruloplasmin levels correlate negatively with liver fibrosis in males with chronic hepatitis B: a new noninvasive model for predicting liver fibrosis in HBV-related liver disease. PLoS One. 2013;8:e77942. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 21] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 1.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Zeng DW, Dong J, Jiang JJ, Zhu YY, Liu YR. Ceruloplasmin, a reliable marker of fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B virus patients with normal or minimally raised alanine aminotransferase. World J Gastroenterol. 2016;22:9586-9594. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 14] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Kang NL, Zhang JM, Liu YR, Lin S, Dong J, Jiang JJ, Zhu YY, Zeng DW. Novel predictive models using serum ceruloplasmin levels for hepatic steatosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B infection. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2020;44:57-65. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Wai CT, Greenson JK, Fontana RJ, Kalbfleisch JD, Marrero JA, Conjeevaram HS, Lok AS. A simple noninvasive index can predict both significant fibrosis and cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2003;38:518-526. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2762] [Cited by in RCA: 3245] [Article Influence: 147.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Vallet-Pichard A, Mallet V, Nalpas B, Verkarre V, Nalpas A, Dhalluin-Venier V, Fontaine H, Pol S. FIB-4: an inexpensive and accurate marker of fibrosis in HCV infection. comparison with liver biopsy and fibrotest. Hepatology. 2007;46:32-36. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1288] [Cited by in RCA: 1609] [Article Influence: 89.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Lemoine M, Shimakawa Y, Nayagam S, Khalil M, Suso P, Lloyd J, Goldin R, Njai HF, Ndow G, Taal M, Cooke G, D'Alessandro U, Vray M, Mbaye PS, Njie R, Mallet V, Thursz M. The gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase to platelet ratio (GPR) predicts significant liver fibrosis and cirrhosis in patients with chronic HBV infection in West Africa. Gut. 2016;65:1369-1376. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 210] [Cited by in RCA: 276] [Article Influence: 30.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 28. | Forns X, Ampurdanès S, Llovet JM, Aponte J, Quintó L, Martínez-Bauer E, Bruguera M, Sánchez-Tapias JM, Rodés J. Identification of chronic hepatitis C patients without hepatic fibrosis by a simple predictive model. Hepatology. 2002;36:986-992. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 672] [Cited by in RCA: 721] [Article Influence: 31.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Zhou K, Gao CF, Zhao YP, Liu HL, Zheng RD, Xian JC, Xu HT, Mao YM, Zeng MD, Lu LG. Simpler score of routine laboratory tests predicts liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;25:1569-1577. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 76] [Cited by in RCA: 86] [Article Influence: 5.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | European Association For The Study Of The Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: management of chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol. 2009;50:227-242. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1152] [Cited by in RCA: 1155] [Article Influence: 72.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Andreani T, Serfaty L, Mohand D, Dernaika S, Wendum D, Chazouillères O, Poupon R. Chronic hepatitis B virus carriers in the immunotolerant phase of infection: histologic findings and outcome. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;5:636-641. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 86] [Cited by in RCA: 92] [Article Influence: 5.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Kumar M, Sarin SK, Hissar S, Pande C, Sakhuja P, Sharma BC, Chauhan R, Bose S. Virologic and histologic features of chronic hepatitis B virus-infected asymptomatic patients with persistently normal ALT. Gastroenterology. 2008;134:1376-1384. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 284] [Cited by in RCA: 320] [Article Influence: 18.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 33. | Sterling RK, Lissen E, Clumeck N, Sola R, Correa MC, Montaner J, S Sulkowski M, Torriani FJ, Dieterich DT, Thomas DL, Messinger D, Nelson M; APRICOT Clinical Investigators. Development of a simple noninvasive index to predict significant fibrosis in patients with HIV/HCV coinfection. Hepatology. 2006;43:1317-1325. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2633] [Cited by in RCA: 3561] [Article Influence: 187.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 34. | Zeng DW, Zhang JM, Liu YR, Dong J, Jiang JJ, Zhu YY. A Retrospective Study on the Significance of Liver Biopsy and Hepatitis B Surface Antigen in Chronic Hepatitis B Infection. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95:e2503. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 35. | Ucar F, Sezer S, Ginis Z, Ozturk G, Albayrak A, Basar O, Ekiz F, Coban S, Yuksel O, Armutcu F, Akbal E. APRI, the FIB-4 score, and Forn's index have noninvasive diagnostic value for liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;25:1076-1081. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 57] [Cited by in RCA: 73] [Article Influence: 6.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 36. | Zeng X, Xu C, He D, Li M, Zhang H, Wu Q, Xiang D, Wang Y. Performance of several simple, noninvasive models for assessing significant liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Croat Med J. 2015;56:272-279. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 22] [Cited by in RCA: 21] [Article Influence: 2.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 37. | Seo YS, Kim MY, Kim SU, Hyun BS, Jang JY, Lee JW, Lee JI, Suh SJ, Park SY, Park H, Jung EU, Kim BS, Kim IH, Lee TH, Um SH, Han KH, Kim SG, Paik SK, Choi JY, Jeong SW, Jin YJ, Lee KS, Yim HJ, Tak WY, Hwang SG, Lee YJ, Lee CH, Kim DG, Kang YW, Kim YS; Korean Transient Elastography Study Group. Accuracy of transient elastography in assessing liver fibrosis in chronic viral hepatitis: A multicentre, retrospective study. Liver Int. 2015;35:2246-2255. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 68] [Cited by in RCA: 64] [Article Influence: 6.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 38. | Fagan KJ, Pretorius CJ, Horsfall LU, Irvine KM, Wilgen U, Choi K, Fletcher LM, Tate J, Melino M, Nusrat S, Miller GC, Clouston AD, Ballard E, O'Rourke P, Lampe G, Ungerer JP, Powell EE. ELF score ≥9.8 indicates advanced hepatic fibrosis and is influenced by age, steatosis and histological activity. Liver Int. 2015;35:1673-1681. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 51] [Cited by in RCA: 59] [Article Influence: 5.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 39. | Rosenberg WM, Voelker M, Thiel R, Becka M, Burt A, Schuppan D, Hubscher S, Roskams T, Pinzani M, Arthur MJ; European Liver Fibrosis Group. Serum markers detect the presence of liver fibrosis: a cohort study. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:1704-1713. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 756] [Cited by in RCA: 759] [Article Influence: 36.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 40. | Kuno A, Ikehara Y, Tanaka Y, Ito K, Matsuda A, Sekiya S, Hige S, Sakamoto M, Kage M, Mizokami M, Narimatsu H. A serum "sweet-doughnut" protein facilitates fibrosis evaluation and therapy assessment in patients with viral hepatitis. Sci Rep. 2013;3:1065. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 295] [Cited by in RCA: 282] [Article Influence: 23.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 41. | Jekarl DW, Choi H, Lee S, Kwon JH, Lee SW, Yu H, Kim M, Kim Y, Sung PS, Yoon SK. Diagnosis of Liver Fibrosis With Wisteria floribunda Agglutinin-Positive Mac-2 Binding Protein (WFA-M2BP) Among Chronic Hepatitis B Patients. Ann Lab Med. 2018;38:348-354. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 21] [Cited by in RCA: 25] [Article Influence: 3.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |