Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2019; 25(30): 4092-4104
Published online Aug 14, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i30.4092
Published online Aug 14, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i30.4092
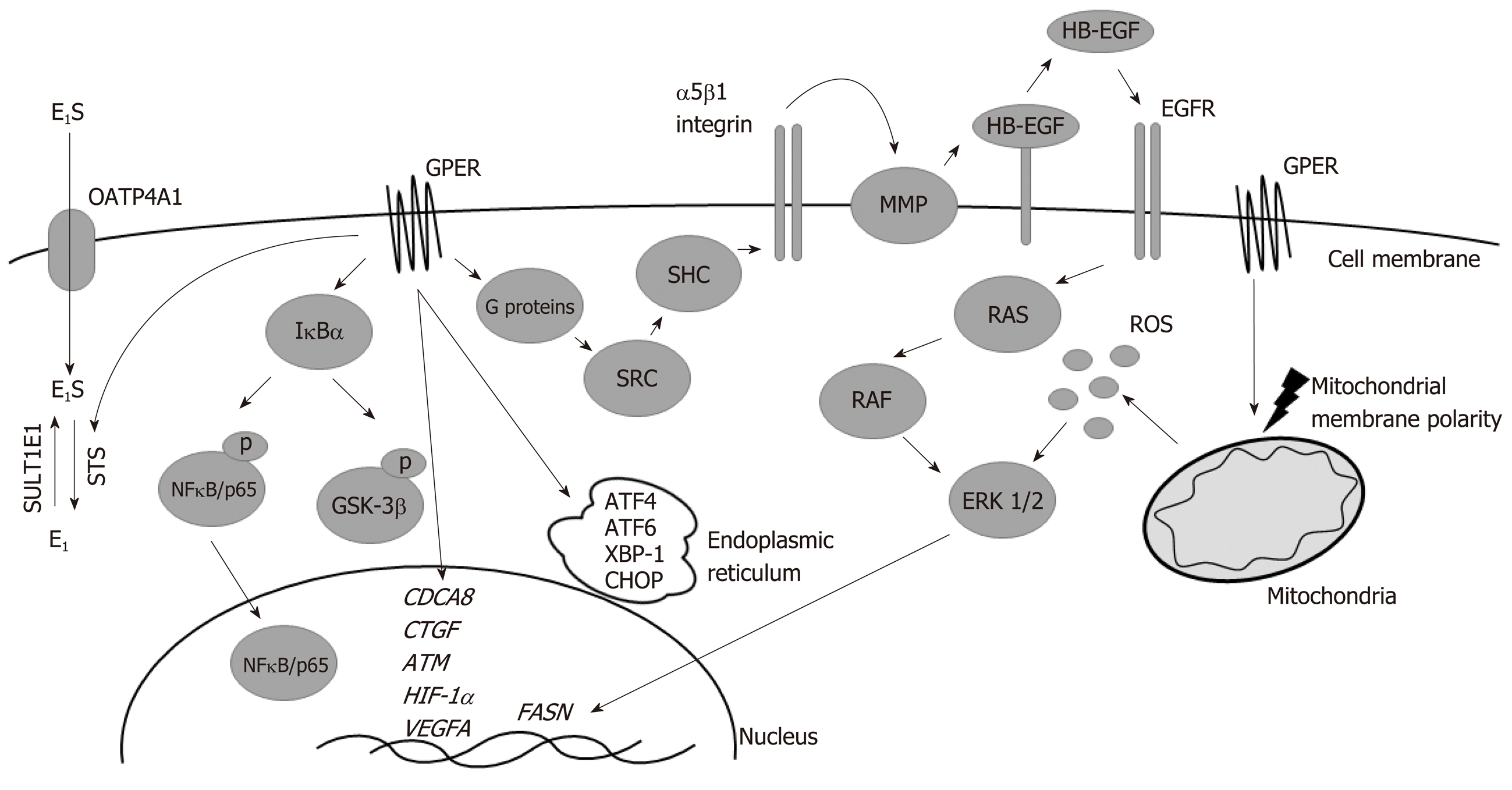
Figure 1 Signaling pathways modulated by G protein-coupled estrogen receptor in colorectal cancer cells.
ATF4: Activating transcription factor 4; ATF6: Activating transcription factor 6; ATM: Ataxia telangiectasia mutated; CDCA8: Cell division cycle A8; CHOP: C/EBP-homologous protein; CTGF: Connective tissue growth factor; E1: Estrone; E1S: Estrone sulfate; EGFR: Epithelial growth factor receptor; ERK 1/2: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2; FASN: Fatty acid synthase; GPER: G protein-coupled estrogen receptor; HB-EGF: Heparin-binding epidermal growth factor; HIF-1α: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; IκBα: NFκB inhibitor α; MMP: Matrix metalloproteinase; NFκB/p65: Nuclear factor κ-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; OATP4A1: Organic anion transporter polypeptide 4A1; P: Phosphorylation; RAF: Rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma, serine-threonine kinase; RAS: Rat sarcoma, small GTPase; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; SHC: Adapter protein containing SRC homology 2 domain; SRC: Non-receptor tyrosine kinase; STS: Steroid sulfatase; SULT1E1: Sulfotransferase family 1E member 1; VEGFA: Vascular endothelial growth factor A; XBP-1: X-box binding protein 1.
- Citation: Jacenik D, Beswick EJ, Krajewska WM, Prossnitz ER. G protein-coupled estrogen receptor in colon function, immune regulation and carcinogenesis. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(30): 4092-4104
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i30/4092.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i30.4092