Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2019; 25(25): 3151-3167
Published online Jul 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i25.3151
Published online Jul 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i25.3151
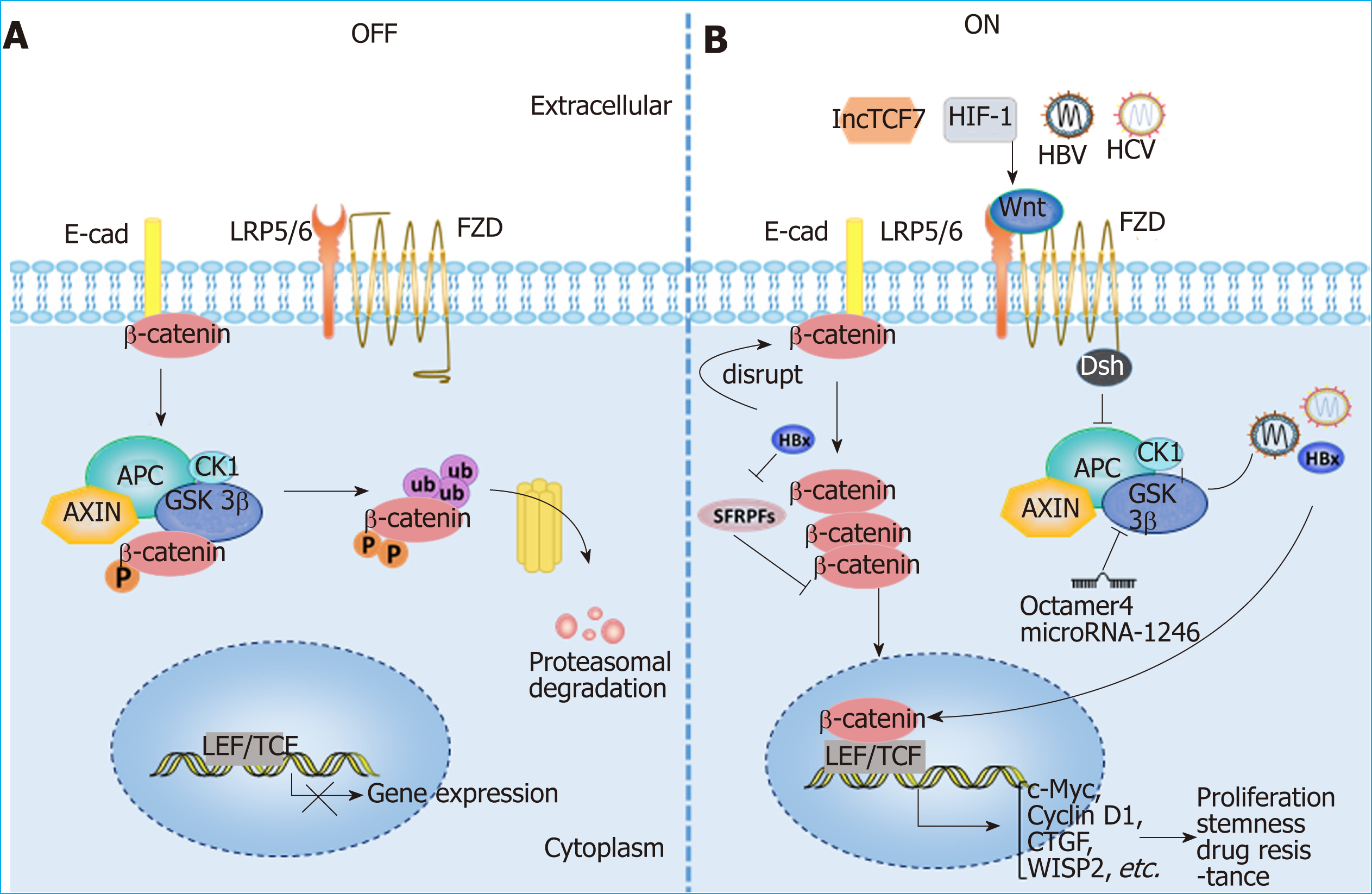
Figure 3 Aberrant activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma.
A: Wnt signaling is inactive in the absence of Wnt ligands (OFF); B: Wnt signaling can be activated by various molecules in HCC (ON). HBV and HCV can active Wnt/β-catenin signaling by activating TCF or inhibiting GSK3β; HBx can silence SFRPs to activate Wnt signaling; LncTCF7 triggers Wnt7a and TCF7 expression to activate Wnt signaling. Lines ending with arrows or bars indicate activating or inhibitory effects, respectively. HIF1α: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1α; LEF: Lymphoid enhancer-binding factor; LRP: Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein; TCF: T cell factor; FZD: Frizzled; E-cad: E-cadherin; SFRPs: Secreted frizzled-related proteins; CTGF: Connective tissue growth factor; WISP2: Wnt1 inducible signaling pathway protein 2.
- Citation: Jiang Y, Han QJ, Zhang J. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Mechanisms of progression and immunotherapy. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(25): 3151-3167
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i25/3151.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i25.3151