Published online Dec 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i46.8248
Peer-review started: June 22, 2017
First decision: July 13, 2017
Revised: July 27, 2017
Accepted: August 25, 2017
Article in press: August 25, 2017
Published online: December 14, 2017
Processing time: 174 Days and 16.7 Hours
Nested stromal-epithelial tumor (NSET) is a non-hepatocytic and non-biliary tumor of the liver consisting of nests of epithelial and spindled cells with associated myofibroblastic stroma and variable intra-lesional calcification and ossification, which represents a very rare and challenging disease. Most of the reported cases have been treated with surgery, obtaining a long survival outcome. Here, we report the case of a 31-year-old Caucasian man who underwent surgery at our institution for a large, lobulated, multinodular mass of the right hemi-liver. The histological exam confirmed the diagnosis of NSET. After 6 mo from surgery, a liver recurrence was described and a chemo-embolization was performed. After a further disease progression, based on the correlation between the histological features of the disease and those of the hepatoblastoma, a similar chemotherapy regimen (with cisplatin and ifosfamide/mesna chemotherapy, omitting doxorubicin due to liver impairment) was administered. However, infection of the biliary catheter required a dose modification of the treatment. No benefit was noted and a progression of disease was radiologically assessed after only four cycles. The worsening of the clinical status prevented further treatments, and the patient died a few months later. This case report documents how the NSET might have an aggressive and non-preventable behavior. No chemotherapy schedules with a proved efficacy are available, and new data are needed to shed light on this rare neoplasm.
Core tip: Nested stromal-epithelial tumor (NSET) of the liver is a very rare type of cancer, few cases have been reported in the world. Most of the literature described a low tendency of relapse, the majority of the reported cases have been treated with surgery, obtaining a long survival outcome. Our patient developed a more aggressive disease, which relapsed soon after surgery, and progressed after first line chemotherapy. We aimed to update the literature about NEST, especially in patients with either metastatic or recurrent disease, for whom no standard treatment is currently available.
- Citation: Meletani T, Cantini L, Lanese A, Nicolini D, Cimadamore A, Agostini A, Ricci G, Antognoli S, Mandolesi A, Guido M, Alaggio R, Giuseppetti GM, Scarpelli M, Vivarelli M, Berardi R. Are liver nested stromal epithelial tumors always low aggressive? World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(46): 8248-8255
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i46/8248.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i46.8248
Nested stromal-epithelial tumor (NSET) of the liver is a very rare type of cancer[1], with few cases diagnosed worldwide. It usually affects young people with age range from 1 to 34 years[2] and no sex preference. Cushing syndrome is often the presenting symptom of this neoplasm[2-4].
The right liver lobe is mostly involved, with a well-circumscribed, large mass characterized by calcification at the computer tomography (CT) scan imaging[1]. Histological features include circumscribed nests and islands of bland-appearing spindled to focally epithelioid cells, surrounded by a cellular desmoplastic stroma, with non-hepatocytic and non-biliary duct characteristics[5].
Here, we present a clinical case of a patient with NSET, with the aim of sharing our experience.
In March 2015, a 31-year-old Caucasian man presented at the Surgery Department complaining of weight loss (approximately 5% of body weight during the previous 2 mo) and abdominal pain. His father underwent liver resection for unspecified liver neoplasm 12 years before but no other significant family history of illness or tumor emerged. The patient had no history of alcohol abuse or hepatitis; he had been followed for arterial hypertension and treated with ramipril and nebivolol.
Physical examination revealed a palpable large abdominal mass in the right upper quadrant, with no evidence of ascites or splenomegaly. Laboratory findings revealed a high level of gamma-glutamyl transferase (349 U/L) and a mild leukocytosis (13.8 × 103 cells/mm3); serology findings for hepatitis B and C, autoimmune hepatitis and human immunodeficiency virus were negative. Serum findings for alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and carbohydrate antigen (CA) 19-9 were within normal range.
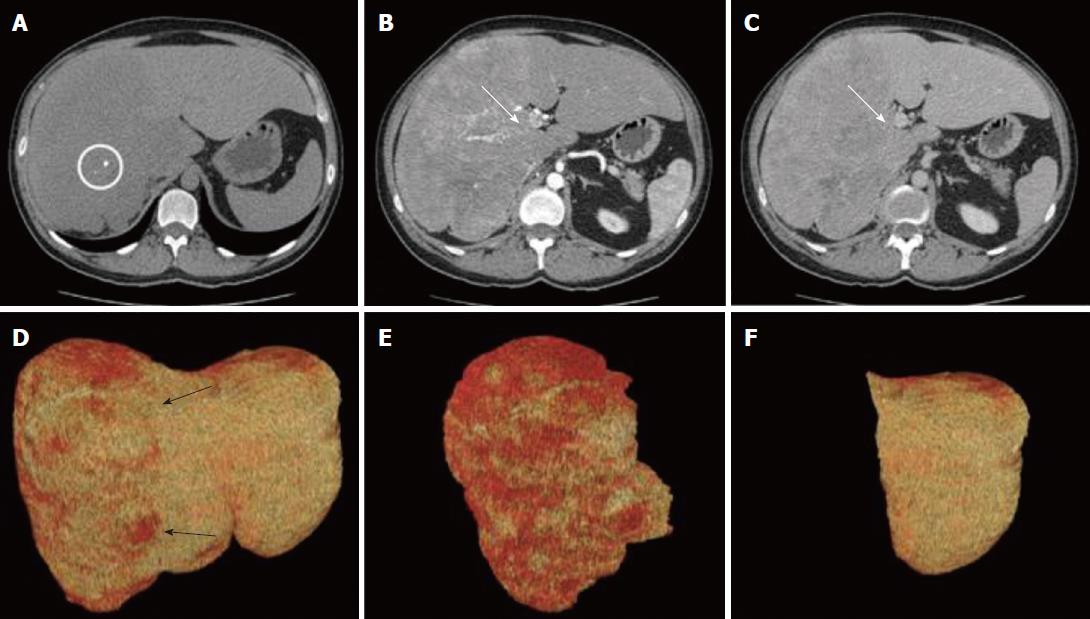
The CT scan showed a large, lobulated, multinodular mass (22 cm × 13 cm × 25 cm), with few round calcifications mainly in the central part, involving entirely the right hemi-liver, partially the Couinaud’s segment 4, and the caudate lobe. After administration of iodinated contrast material, the tumor showed non-homogeneous, early enhancement in the arterial phase, with subsequent washout in the portal and delayed phases. The CT images also demonstrated an extensive infiltration of the right portal branch and of the right and middle hepatic veins, with a consequent spontaneous hypertrophy of the left lobe (Figure 1).
The surgical procedure, consisting of a virtual resection, was planned[6]. The quantitative analysis of CT images showed a total liver volume of 5797 cm3 and a tumor volume of 3879 cm3 with a hypertrophic remnant left liver lobe (Couinaud’s segments II and III) of 1329 cm3. The future liver remnant, thus, was 69%, markedly over the safe cut-off[6]. Based on these radiological findings, a right trisectionectomy extending to the caudate lobe was proposed.
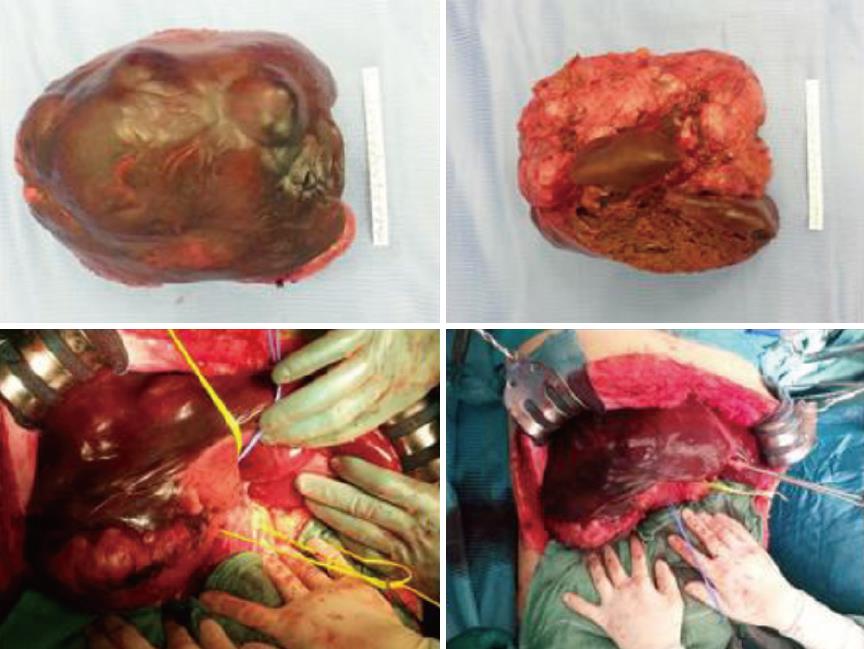
On laparotomy, careful exploration of the abdominal cavity ruled out no extra-hepatic manifestations; intraoperative ultrasound revealed another 2 cm nodule in segment II. The remaining left lobe did not show any histological alterations at intraoperative biopsy. Hepatoduodenal ligament was dissected to isolate and ligate the right hepatic artery, portal vein and bile duct as well as the biliary and vascular elements for segments IV and I (Figure 2). After transection of the right portal vein, that appeared infiltrated by the tumor, the hepatic parenchyma was dissected between segments II/III and segment IV by using Cavitron ultrasonic surgical aspirator and argon diathermy. Afterwards, the nodule at the hepatic segment II was treated by radiofrequency ablation.
Postoperative course was uneventful, except for a 4.5 cm fluid collection on the cut surface of the liver that was successfully treated by percutaneous drainage. The patient was discharged on postoperative day 21 with a completely preserved liver function.
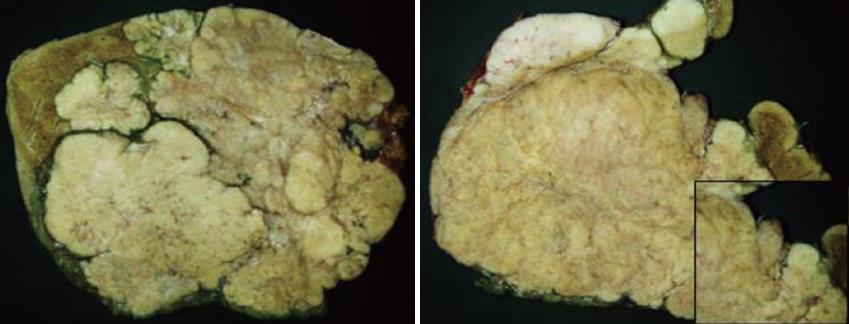
Gross appearance: The right hepatic lobe was almost entirely occupied by a multinodular mass with homogeneous whitish cut surface, partial necrosis and calcifications. The lesion had a greatest diameter of 19 cm and was 0.5 mm far from the surgical margin (Figure 3).
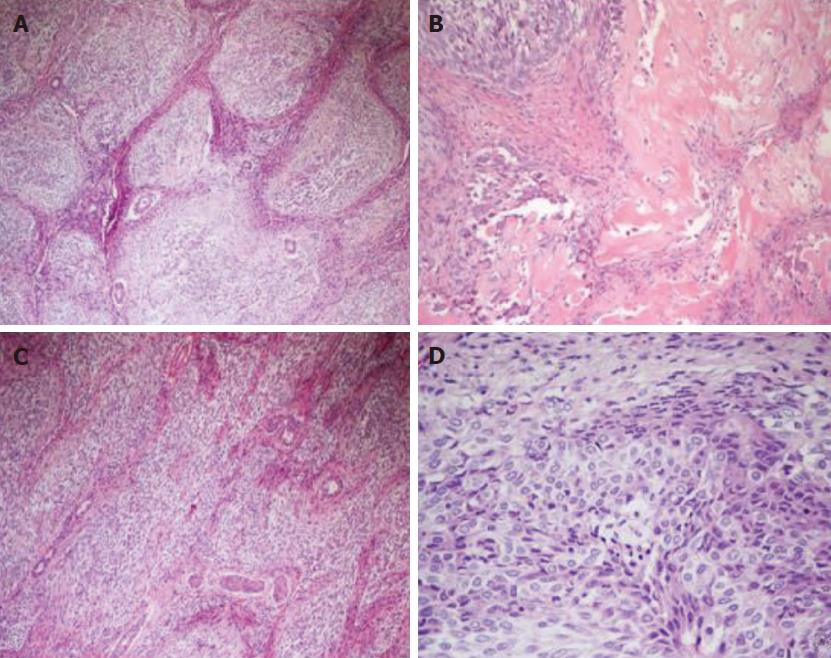
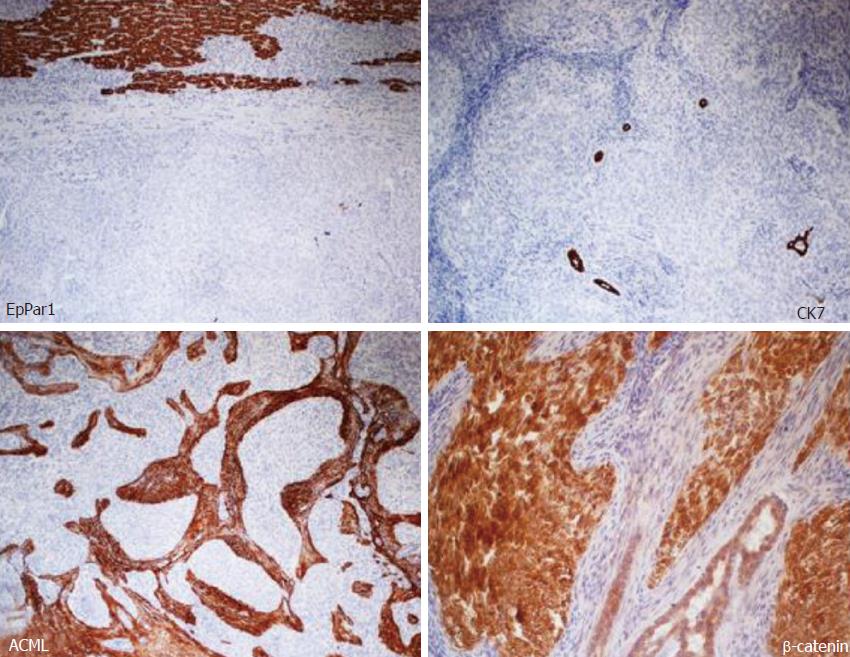
Microscopic and immunohistochemical features: Histologically, the neoplasm showed an organoid arranged tumor of well-defined nests of epithelioid and spindle cells with focal necrosis, surrounded by hypercellular stroma with areas of osseous metaplasia and calcifications. The cellular nests were oval, elongated, and irregular with rounded edges. The epithelioid part of the tumor was composed of monomorphous polygonal and spindle-shaped cells, round to oval nuclei with finely stippled chromatin and no appearance of nucleoli. The cytoplasm was eosinophilic in most areas, with few cells containing clear cytoplasm (Figure 4). The cellular nests showed positive staining for markers of epithelial differentiation (CAM 5.2, AE1/AE3, EMA (focal), β-catenin (both membrane and nuclear), WT1 (both membrane and cytoplasmatic), GPC3 (focally cytoplasmatic) and CD56 (diffuse) and negative staining for hepatocyte antigen EpPar1 (hepatocyte paraffin 1), CK7, CK19, CD34, CD99, chromogranin and desmin.
The calcifications were most commonly within or adjacent to cellular nests. The mitotic index was 10 mitotes/10 high power field (40 × objective). The stroma surrounding the cellular nests showed a myofibroblastic nature, with spindled cells with long tapered cytoplasmic processes, positive staining for smooth muscle actin and negative staining for citokeratins and EpPar1. Bile ducts entrapped in the fibrous stroma were normal and were highlighted by CK7 and CK19 immunohistochemical stains (Figure 5). The neoplastic cells infiltrated the surrounding hepatic parenchyma and peri-hepatic soft tissue. Vascular invasion of a portal vein branch was demonstrated.
Differential diagnosis: The differential diagnosis of a biphasic tumor, with a spindled and epithelioid component, variable calcifications and osseous metaplasia includes in the first instance synovial sarcoma, mixed epithelial and mesenchymal hepatoblastoma and calcifying NSET. Desmoplastic small round cell tumor (DSRCT) is also a diagnostic consideration in a young patient. In addition, the possibility of sarcomatous variants of hepatocellular carcinoma or cholangiocarcinoma should be considered. However, these tumors lack the nested, organoid architecture of NSET, typically showing a greater cytological atypia.
Areas predominantly composed of epithelioid nests may resemble islands of fetal hepatoblastoma cells. However, the neoplasm in this report lacked the fetal and/or embryonic hepatoid features of the epithelial component of mixed hepatoblastoma, and neither the spindled nor the epithelioid lesional cells stained with the hepatocyte-specific tissue stain EpPar1.
The overall histology and immunohistochemical features supported the diagnosis of NSET, a very rare tumor defined as a non-hepatocytic and non-biliary tumor of the liver consisting of nests of epithelial and spindled cells with associated myofibroblastic stroma and variable intralesional calcification and ossification[4,7,8].
For a comprehensive report, molecular analysis was performed. Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reactions for SYT-SSX and EWS-WT1 were negative in our case. Such findings, combined with the histological appearance, allowed us to rule out the hypothesis of synovial sarcoma and DSRCT, respectively.
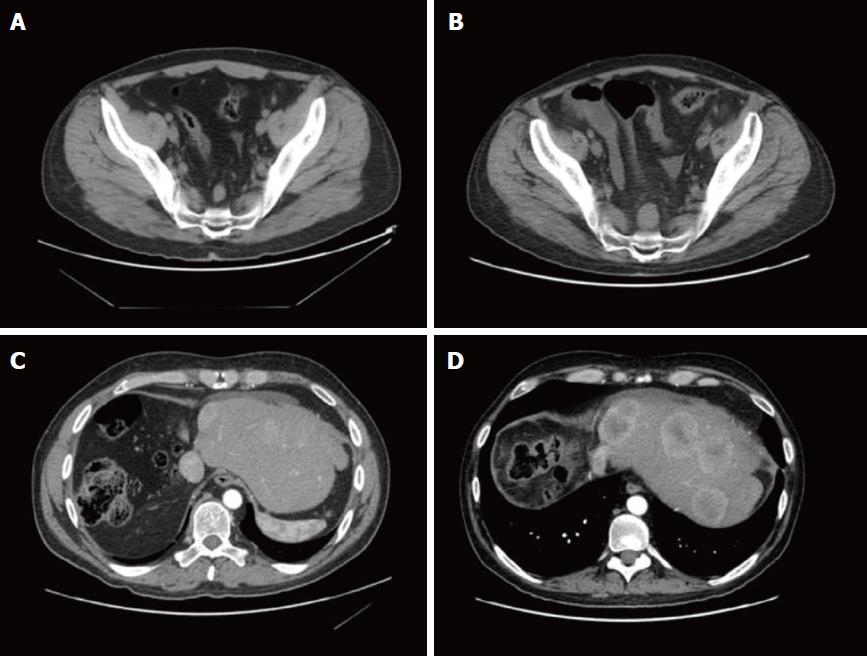
In September 2015, the patient underwent a CT scan, which showed several liver lesions (maximum diameter of 17 mm), and also a positron emission tomography (PET) that documented a pre-sacral nodule (SUV = 5). After discussion within the Multidisciplinary Tumor Board (MTB), since surgery was judged not feasible, a liver chemo-embolization (DCBeads + doxorubin) was performed. Although the arteriography showed a higher number of the lesions, only five nodules were treated with the chemoembolization. Due to an increase in the gamma-glutamyl transferase level (944 U/L), no further treatment was practicable.
In November 2015, a re-assessment with a CT scan showed a local progression and an increased number of abdominal lymphoadenopathies. Hyperbilirubinemy (10.2 mg/dL) was also observed with a dilatation of the intrahepatic biliary duct. Therefore, a trans-cutaneous biliary catheter was positioned, with consequent improvement of the hepatic and biliary function. The patient was re-evaluated within the MTB and we hypothesized a regimen with ifosfamide/mesna, platin and anthracycline according to ifosfamide/cisplatin/pirarubicine (commonly known as the IPA) schedule. Due to the correlation of the histological features of the disease with the hepatoblastoma, as described in literature[9-12], four courses of cisplatin (100 mg/m2) and ifosfamide/mesna (3 g/mq) were administered, omitting doxorubicin because of the liver impairment.
Anyway, infections of the biliary catheter, with fever and abdominal pain, affected the treatment, and required both antibiotics and a dose modification of the chemotherapy schedule. In fact, cisplatin alone was administered in the second course and ifosfamide/mesna was added again from the third course, reducing by 50% of its total dose. The patient received a total of four cycles of chemotherapy.
In April 2016, a restaging CT scan showed a progressive disease, represented by an increase of the hepatic lesion (5 cm vs 2.4 cm) and of the pre-sacral nodule (2.6 cm vs 1.7 cm). Ascites was also documented (Figure 6). Unfortunately, the worsening of the clinical status, the rise in total bilirubin up to 27.4 mg/dL and alterations of sodium and potassium prevented further administration of chemotherapy and the patient died in June 2016.
NSETs are a very rare type of cancer, and few data about their treatment are available. As far as we know, there are no predisposing factors increasing the risk of occurrence of this rare type of tumor. In the literature a few cases of NSET associated with Cushing syndrome at diagnosis have been described. In these cases, after excision of the tumors, the Cushing syndrome was abated, but the correlation remained unknown[2-4].
Considering the low tendency of relapse, the majority of the reported cases have been treated with surgery, obtaining a long survival outcome (up to a complete response) in most[2,12]. Liver transplantation is a further treatment that should be taken in account in patients with unresectable and not extra-hepatic disease, although not as a first choice[1,13]. Hommann et al[13] treated a 19-year-old patient who underwent liver surgery for a NSET and developed liver metastasis a few years later, with liver transplantation achieving 37 mo of overall survival (OS).
Our patient relapsed within 6 mo after surgery, with several focal lesions in the residual liver, showing an aggressive and unusual behavior of the disease. Necrosis, high mitotic rate, invasion of the surrounding parenchyma and vascular invasion are the features that might explain the malignant potential and the aggressive behavior of this rare neoplasm. Furthermore, a liver transplantation was not performed because of the presence of the extra-hepatic pre-sacral nodule. Consequently, chemotherapy seemed to be the only feasible therapeutic approach, although no guidelines, nor prognostic or predictive factors are currently known to choose the most appropriate treatment.
The analogies between NSET tumors and hepatoblastoma led us to use a hepatoblastoma chemotherapy protocol to treat our patient. This decision was also supported by the literature. In fact cases of both recurrent and metastatic disease have been treated with a good outcome[12]. Among the others, a 3-year-old child was treated both before and after resection, achieving a minimal shrinkage of the tumor[4]. The other two patients, of about 14-years-old and 2-years-old, were treated after surgery with the same chemotherapy protocol, with a disease-free survival of 90 mo and 84 mo, respectively[1]. It should be noted that all these cases were younger than our patient.
Nevertheless, our patient developed a more aggressive disease with a worse prognosis compared to the other case reports, and also several issues prevented a good compliance to the treatment. No tumor shrinkage was noted, but a progression of the disease in both liver and pre-sacral sites was observed. Other cases in the literature had a poor prognosis[1,14], with OS around 37 mo to 40 mo, which was better than our patient outcome (OS of 15 mo), probably because they underwent liver transplantation.
In conclusion, in sharing our experience, we aimed to enhance the knowledge of NSET in the literature, especially for patients with either metastatic or recurrent disease, when a chemotherapeutic rather than a surgical approach is requested and where prognostic and predictive factors are not still available.
A 31-year-old Caucasian man presented at our institution for a large, lobulated, multinodular mass of the right hemi-liver.
Distended abdomen with diffuse tenderness, palpable large abdominal mass in the right upper quadrant, with no evidence of ascites or splenomegaly.
Hepatocellular carcinoma, metastatic adenocarcinoma, cirrhosis, hepatoblastoma.
Increased gamma-glutamyl transferase (349 U/L) and a mild leukocytosis (13.8 × 103 cells/mm3). Negative serology for hepatitis B and C, autoimmune hepatitis and human immunodeficiency virus. Serum alpha-fetoprotein, carcinoembryonic antigen and CA 19-9 within normal range.
The computed tomography (CT) scan showed a large, lobulated, multinodular mass (22 cm × 13 cm × 25 cm) with few round calcifications, mainly in the central part and involving the right hemi-liver entirely, and partially involving the Couinaud’s segment 4 and the caudate lobe. The CT images also demonstrated an extensive infiltration of the right portal branch and of the right and middle hepatic veins, with a consequent spontaneous hypertrophy of the left lobe.
The histological exam confirmed the diagnosis of nested stromal-epithelial tumor (NSET).
The first approach was surgery. After relapse, four courses of cisplatin (100 mg/m2) and ifosfamide/mesna (3 g/mq) were administered, omitting doxorubicin because of the liver impairment.
NSET of the liver is a very rare type of cancer, that affects young people without sex preference. Cushing syndrome is often the presenting symptom of this neoplasm.
NSET is usually a large hepatic lesion, partially necrotic and with calcifications. Upon histological analysis, it appears as well-defined nests of epithelioid and spindle cells with focal necrosis, surrounded by hypercellular stroma.
This entity is usually associated with a good prognosis after surgery. Nevertheless, our patient’s prognosis was poor, and the disease showed an aggressive behavior. No standard therapy is approved for the metastatic disease.
This case report showed the uncommon situation of a patient with a metastatic NSET, and the chemotherapy administered which had provided no benefit. The authors present very precisely the case of very rare type of liver cancer which had a very aggressive form and progressed after surgery and first-line chemotherapy.
Manuscript source: Unsolicited manuscript
Specialty type: Gastroenterology and hepatology
Country of origin: Italy
Peer-review report classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B, B
Grade C (Good): 0
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P- Reviewer: Inoue K, Vorobjova T S- Editor: Gong ZM L- Editor: Filipodia E- Editor: Huang Y
| 1. | Schaffer LR, Shehata BM, Yin J, Schemankewitz E, Alazraki A. Calcifying nested stromal-epithelial tumor (CNSET) of the liver: a newly recognized entity to be considered in the radiologist’s differential diagnosis. Clin Imaging. 2016;40:137-139. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 0.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Makhlouf HR, Abdul-Al HM, Wang G, Goodman ZD. Calcifying nested stromal-epithelial tumors of the liver: a clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical, and molecular genetic study of 9 cases with a long-term follow-up. Am J Surg Pathol. 2009;33:976-983. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 48] [Cited by in RCA: 44] [Article Influence: 2.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Weeda VB, de Reuver PR, Bras H, Zsíros J, Lamers WH, Aronson DC. Cushing syndrome as presenting symptom of calcifying nested stromal-epithelial tumor of the liver in an adolescent boy: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2016;10:160. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Heerema-McKenney A, Leuschner I, Smith N, Sennesh J, Finegold MJ. Nested stromal epithelial tumor of the liver: six cases of a distinctive pediatric neoplasm with frequent calcifications and association with cushing syndrome. Am J Surg Pathol. 2005;29:10-20. [PubMed] |
| 5. | Grazi GL, Vetrone G, d’Errico A, Caprara G, Ercolani G, Cescon M, Ravaioli M, Del Gaudio M, Vivarelli M, Zanello M. Nested stromal-epithelial tumor (NSET) of the liver: a case report of an extremely rare tumor. Pathol Res Pract. 2010;206:282-286. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Schindl MJ, Redhead DN, Fearon KC, Garden OJ, Wigmore SJ; Edinburgh Liver Surgery and Transplantation Experimental Research Group (eLISTER). The value of residual liver volume as a predictor of hepatic dysfunction and infection after major liver resection. Gut. 2005;54:289-296. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 430] [Cited by in RCA: 416] [Article Influence: 20.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Heywood G, Burgart LJ, Nagorney DM. Ossifying malignant mixed epithelial and stromal tumor of the liver: a case report of a previously undescribed tumor. Cancer. 2002;94:1018-1022. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 31] [Cited by in RCA: 24] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Hill DA, Swanson PE, Anderson K, Covinsky MH, Finn LS, Ruchelli ED, Nascimento AG, Langer JC, Minkes RK, McAlister W. Desmoplastic nested spindle cell tumor of liver: report of four cases of a proposed new entity. Am J Surg Pathol. 2005;29:1-9. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 43] [Cited by in RCA: 27] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Assmann G, Kappler R, Zeindl-Eberhart E, Schmid I, Häberle B, Graeb C, Jung A, Müller-Höcker J. β-Catenin mutations in 2 nested stromal epithelial tumors of the liver--a neoplasia with defective mesenchymal-epithelial transition. Hum Pathol. 2012;43:1815-1827. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 33] [Cited by in RCA: 26] [Article Influence: 2.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Häberle B, Bode U, von Schweinitz D. [Differentiated treatment protocols for high- and standard-risk hepatoblastoma--an interim report of the German Liver Tumor Study HB99]. Klin Padiatr. 2003;215:159-165. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 32] [Cited by in RCA: 25] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Procopio F, Di Tommaso L, Armenia S, Quagliuolo V, Roncalli M, Torzilli G. Nested stromal-epithelial tumour of the liver: An unusual liver entity. World J Hepatol. 2014;6:155-159. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 0.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Brodsky SV, Sandoval C, Sharma N, Yusuf Y, Facciuto ME, Humphrey M, Yeh YA, Braun A, Melamed M, Finegold MJ. Recurrent nested stromal epithelial tumor of the liver with extrahepatic metastasis: case report and review of literature. Pediatr Dev Pathol. 2008;11:469-473. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 30] [Cited by in RCA: 27] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Hommann M, Kaemmerer D, Daffner W, Prasad V, Baum RP, Petrovitch A, Sauerbrey A, Katenkamp K, Kaufmann R, Settmacher U. Nested stromal epithelial tumor of the liver--liver transplantation and follow-up. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2011;42:292-295. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 20] [Cited by in RCA: 21] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Misra S, Bihari C. Desmoplastic nested spindle cell tumours and nested stromal epithelial tumours of the liver. A. PMIS. 2016;124:245-251. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |