Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 21, 2017; 23(43): 7657-7665
Published online Nov 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i43.7657
Published online Nov 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i43.7657
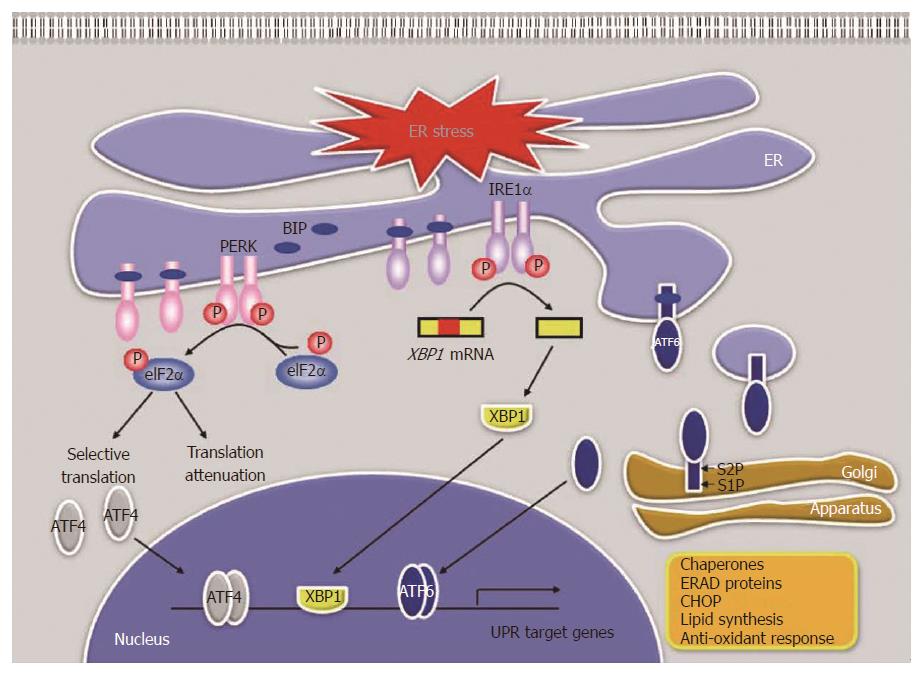
Figure 1 Endoplasmic reticulum stress and unfolded protein response signaling pathways.
ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; BIP: Binding immunoglobulin protein; PERK: Protein kinase RNA-like ER kinase; eIF2α: Eukaryotic translational initiation factor 2α; ATF4: Activating transcription factor 4; IRE1: Inositol-requiring protein 1; XBP1: X-box binding protein 1; ATF6: Activating transcription factor 6; S1P: Site 1 protease; S2P: Site 2 protease; UPR: Unfolded protein response; ERAD: ER associated degradation; CHOP: C/EBP homologous protein; P: Phosphate.
- Citation: Kim SY, Kyaw YY, Cheong J. Functional interaction of endoplasmic reticulum stress and hepatitis B virus in the pathogenesis of liver diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(43): 7657-7665
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i43/7657.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i43.7657