Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2017; 23(27): 4935-4941
Published online Jul 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i27.4935
Published online Jul 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i27.4935
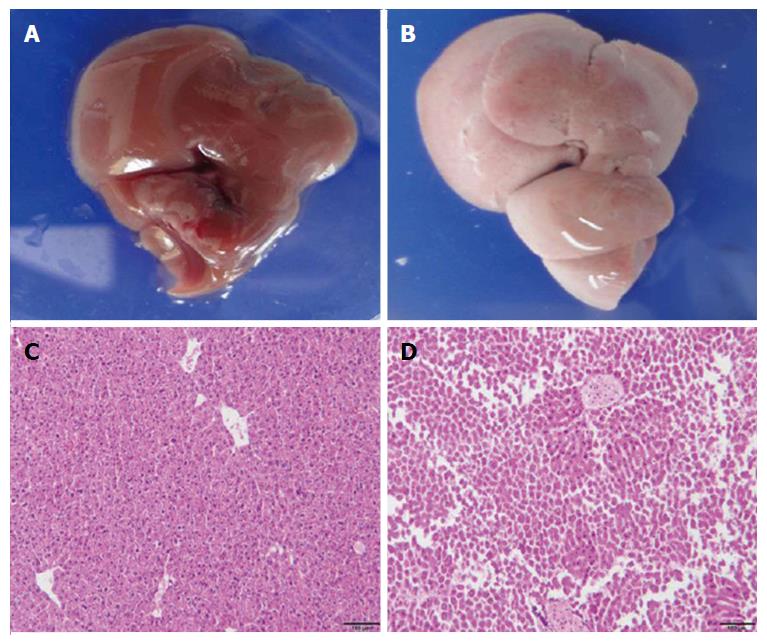
Figure 2 Histological analysis of liver injury.
Two days after DT treatment, liver sections from non-transgenic mice and ADSB mice were stained with H and E. A: The liver from non-transgenic mice (C57BL/6); B: The liver from ADSB mouse; C: A representative liver section from non-transgenic mice showing normal histological appearance; D: A representative liver section from ADSB mice showing liver injury. ADSB: Triple-crossed albumin (Alb)-cre transgenic mice, inducible diphtheria toxin receptor (DTR) transgenic mice and severe combined immune deficient-beige mice; DT: Diphtheria toxin; H and E: Hematoxylin and eosin.
- Citation: Ren XN, Ren RR, Yang H, Qin BY, Peng XH, Chen LX, Li S, Yuan MJ, Wang C, Zhou XH. Human liver chimeric mouse model based on diphtheria toxin-induced liver injury. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(27): 4935-4941
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i27/4935.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i27.4935