Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2016; 22(45): 9954-9965
Published online Dec 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i45.9954
Published online Dec 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i45.9954
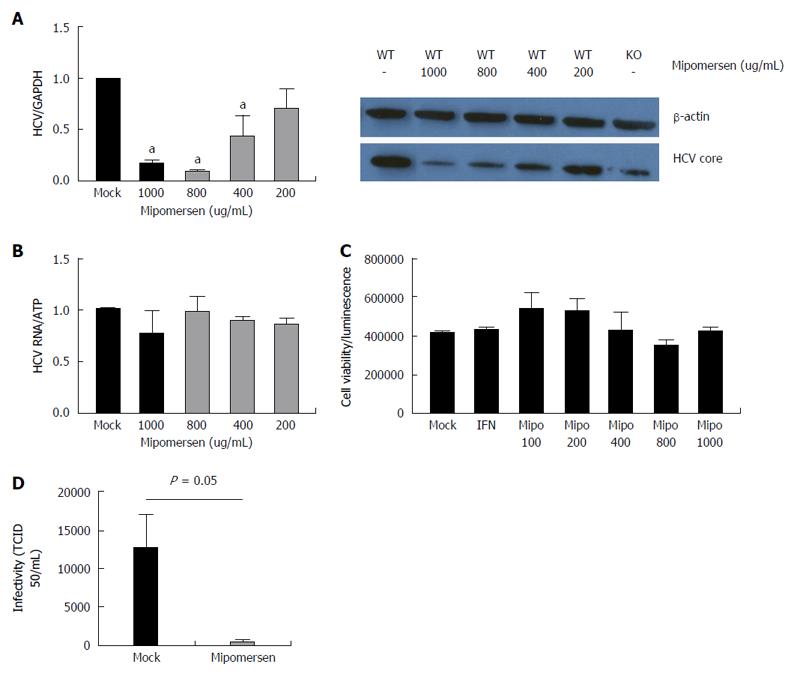
Figure 6 Mipomersen exerts a dose-dependent and potent anti-hepatitis C virus effect.
A: Huh7/CD81 high cells were treated with escalating doses of mipomersen from 200 ug/mL to 1000 ug/mL and then infected with JFH1. At 72 h following infection, there was a dose-dependent inhibition of hepatitis C virus (HCV), demonstrated at both the RNA and protein (HCV core) level. Data are shown as means with 95%CI (aP < 0.05); B: OR6 genotype 1b replicon cells were treated with mipomersen for 72 h and no effect was observed on HCV replication; C: There was no negative impact of escalating doses of mipomersen on cell viability; D: Infectivity of the virus was assessed using the TCID50 method. Virus generated in cells treated with mipomersen had a significant reduction in infectivity compared with virus generated in mock-treated cells. Data shown as mean TCID50/mL ± SEM.
- Citation: Schaefer EAK, Meixiong J, Mark C, Deik A, Motola DL, Fusco D, Yang A, Brisac C, Salloum S, Lin W, Clish CB, Peng LF, Chung RT. Apolipoprotein B100 is required for hepatitis C infectivity and Mipomersen inhibits hepatitis C. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(45): 9954-9965
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i45/9954.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i45.9954