Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2016; 22(45): 9954-9965
Published online Dec 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i45.9954
Published online Dec 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i45.9954
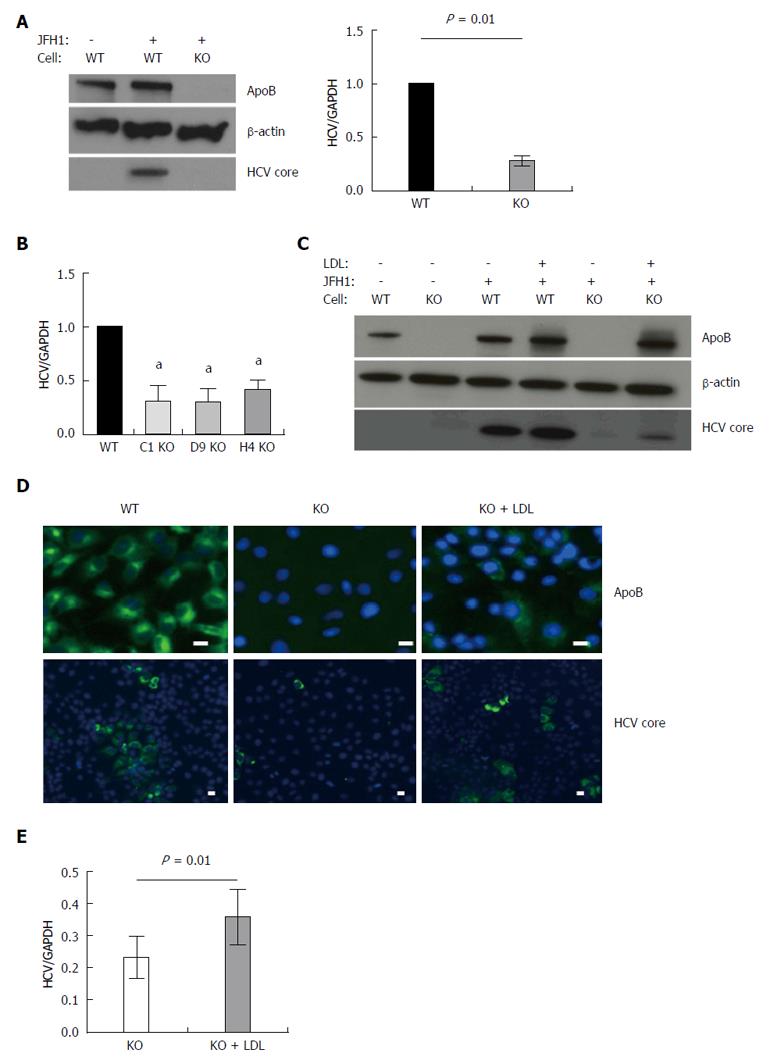
Figure 1 APOB genetic knockout Huh 7 hepatoma cells inefficiently support hepatitis C virus.
A: Using TALEN genetic deletion of APOB, knockout huh7/CD81 (high) cells were generated (APOB-/-, KO). We demonstrated that these cells inefficiently support hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection with the fully infectious tissue culture HCV virus, HCVcc (JFH1). There was markedly decreased JFH1 72 h following infection both at the level of HCV core protein and RNA. Data is shown as mean with 95% confidence interval, normalized to WT; B: To confirm this was not a clone-specific effect, three additional clones were infected with the JFH1 virus and intracellular HCV RNA assessed 72 h following infection. We again found a decrease in HCV RNA in the APOB KO clones (aP < 0.05); C, D: Rescue experiments were performed by treating cells with human LDL at the same time as infection with the JFH1 virus. We found partial restoration of intracellular apoB expression at 72 h following exposure (D), and there was a partial restoration of HCV infection, with increased expression of HCV core protein (C), HCV RNA (E), and IF demonstrating increased HCV core expression in the LDL-treated cells (D). Scale bar: 20 μm.
- Citation: Schaefer EAK, Meixiong J, Mark C, Deik A, Motola DL, Fusco D, Yang A, Brisac C, Salloum S, Lin W, Clish CB, Peng LF, Chung RT. Apolipoprotein B100 is required for hepatitis C infectivity and Mipomersen inhibits hepatitis C. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(45): 9954-9965
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i45/9954.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i45.9954