Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2015; 21(10): 2988-2996
Published online Mar 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i10.2988
Published online Mar 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i10.2988
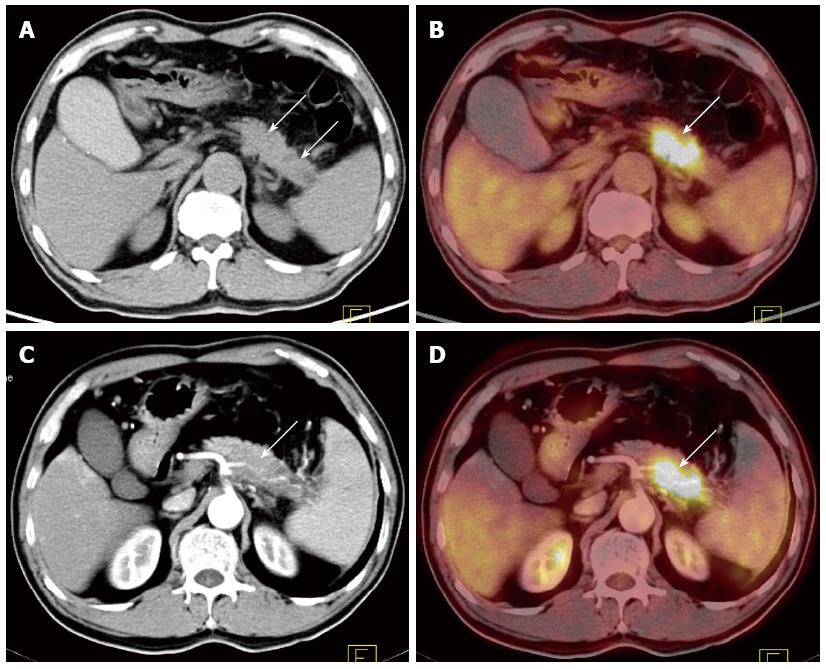
Figure 2 A 61-old male patient with upper abdominal pain for more than 3 mo.
A-B: PET/CT image [A: Enlargement at the junction of the pancreatic body and tail (depicted by plain CT scanning); B: Increased FDG uptake at the lesion with the SUVmax of 10.6. This disease was diagnosed as pancreatic cancer (depicted by a PET/CT image)]; C-D: CECT and PET/CECT fusion image: splenic artery invasion was clearly displayed; the splenic artery was thinner with irregular vascular edges. This case was pathologically diagnosed as a moderately differentiated pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma with splenic artery invasion. PET/CT: Positron emission tomography/computed tomography; CECT: Contrast-enhanced CT; FDG: Fluorodeoxyglucose.
- Citation: Zhang J, Zuo CJ, Jia NY, Wang JH, Hu SP, Yu ZF, Zheng Y, Zhang AY, Feng XY. Cross-modality PET/CT and contrast-enhanced CT imaging for pancreatic cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(10): 2988-2996
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i10/2988.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i10.2988