Published online Jan 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i1.360
Peer-review started: June 2, 2014
First decision: June 27, 2014
Revised: August 19, 2014
Accepted: September 29, 2014
Article in press: September 30, 2014
Published online: January 7, 2015
Processing time: 220 Days and 13.7 Hours
AIM: To investigate the clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment of giant colonic diverticulum (GCD, by means of a complete and updated literature review). GCD is a rare manifestation of diverticular disease of the colon. Less than 200 studies on GCD were published in the literature, predominantly case reports or small patient series.
METHODS: A systematic review of the literature was performed using the Embase and PubMed databases to identify all the GCD studies. The following MESH search headings were used: “giant colonic diverticulum”; “giant sigmoid diverticulum”. The “related articles” function was used to broaden the search, and all of the abstracts, studies, and citations were reviewed by two authors. The following outcomes were of interest: the disease and patient characteristics, study design, indications for surgery, type of operation, and post-operative outcomes. Additionally, a subgroup analysis of cases treated in the last 5 years was performed to show the current trends in the treatment of GCD. A GCD case in an elderly patient treated in our department by a sigmoidectomy with primary anastomosis and a diverting ileostomy is presented as a typical example of the disease.
RESULTS: In total, 166 GCD cases in 138 studies were identified in the literature. The most common clinical presentation was abdominal pain, which occurred in 69% of the cases. Among the physical signs, an abdominal mass was detected in 48% of the cases, whereas 20% of the patients presented with fever and 14% with abdominal tenderness. Diagnosis is based predominantly on abdominal computed tomography. The most frequent treatment was colic resection with en-bloc resection of the diverticulum, performed in 57.2% of cases, whereas Hartmann’s procedure was followed in 11.4% of the cases and a diverticulectomy in 10.2%. An analysis of sixteen cases reported in the last 5 years showed that the majority of patients were treated with sigmoidectomy and en-bloc resection of the diverticulum; the postoperative mortality was null, morbidity was very low (1 patient was hospitalized in the intensive care unit for postoperative hypotension), and the patients were discharged 4-14 d after surgery.
CONCLUSION: Giant colonic diverticulum is a rare manifestation of diverticular diseases. Surgical treatment, consisting predominantly of colonic resection with en bloc resection of the diverticulum, is the preferred option for GCD and guarantees excellent results.
Core tip: This article presents a systematic and comprehensive review of all the studies concerning giant colonic diverticulum. The majority of the published studies are case reports on single cases. The authors performed an extensive literature search and a systematic review, with the aim of collecting and providing complete and updated information regarding the clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment of this rare disease. The results of the review indicate that surgical treatment, consisting predominantly of colonic resection with en bloc resection of the diverticulum, is the preferred option for giant colonic diverticulum and guarantees excellent results.
- Citation: Nigri G, Petrucciani N, Giannini G, Aurello P, Magistri P, Gasparrini M, Ramacciato G. Giant colonic diverticulum, clinical presentation, diagnosis and treatment: Systematic review of 166 cases. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(1): 360-368
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i1/360.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i1.360
Giant colonic diverticulum (GCD) is a rare manifestation of diverticular disease of the colon[1]. Fewer than 200 studies, predominantly case reports or small patient series, have been published[2]. In this study, we present a comprehensive and updated review of the literature and a GCD case in an elderly patient. We identified 166 GCD cases published in the literature, to extract and discuss the complete and updated information on the diagnosis and treatment of GCD.
We hypothesize that an updated and complete review is needed to clarify and summarize current knowledge on this subject. The information is fragmented and available only from case reports or small series, and the published systematic reviews are not recent. Changes in the diagnosis and treatment of GCD have occurred in recent years such as the widespread use of computed tomography for the diagnosis of GCD and the diminution of the use of barium enemas as well as the emerging role of laparoscopic surgery with the first cases treated by laparoscopic sigmoidectomy; these changes should be emphasized. We hypothesize that a comprehensive review might provide useful, relevant and updated information to help clinicians in the diagnosis and treatment of this rare disease. In this review, a subgroup analysis of the previous five years was conducted to analyze the current trends and emerging possibilities in the treatment of this disease.
Systematic review of the literature: A systematic literature search of the literature was performed using the Embase and PubMed databases to identify all the published studies on GCD. The following MESH search headings were used: “giant colonic diverticulum”; “giant sigmoid diverticulum”. The “related articles” function was used to broaden the search, and all the abstracts, studies, and citations were reviewed. The studies on pediatric patients were excluded.
Two reviewers independently extracted the following information from each study using standardized extraction tables developed a priori: the first author, year of publication, characteristics of the disease and patients, study design, indications for surgery, type of operation, and post-operative outcomes.
Additionally, a subgroup analysis of the cases treated in the previous 5 years was performed to show the current trends in the treatment of GCD.
A case of GCD in an elderly patient treated in our department by a sigmoidectomy with primary anastomosis and a diverting ileostomy is presented as a typical example of the disease.
One hundred and thirty-eight studies were identified[1-138], including 166 patients. The results of the systematic review are reported in Tables 1, 2, 3 and 4.
| Symptoms | Patients (n = 166) |
| Abdominal pain | 115 (69) |
| Constipation | 29 (17) |
| Diarrehea | 19 (11) |
| Vomiting | 20 (12) |
| Nausea | 16 (10) |
| Abdominal mass | 29 (17) |
| Rectal bleeding/melena | 15 (9) |
| Urinary problems | 11 (7) |
| Weight loss | 8 (5) |
| Asymptomatic | 7 (4) |
| Anorexia | 7 (4) |
| Vaginal bleeding | 2 (1) |
| Meteorism | 3 (2) |
| Dyspepsia | 1 (0.6) |
| Symptoms of bowel obstruction | 2 (1) |
| Difficulty in breathing | 1 (0.6) |
| Tenesmus | 1 (0.6) |
| Physicalsigns | Patients (n = 166) |
| Abdominal mass, non-tender | 47 (28) |
| Abdominal mass, tender | 34 (20) |
| Fever | 33 (20) |
| Abdominal tenderness | 24 (14) |
| Normal | 15 (9) |
| Acute abdomen | 10 (6) |
| Abdominal distension | 15 (9) |
| Operation | Patients (n = 166) |
| Resection, primary anastomosis | 95 (57.2) |
| Resection, primary anastomosis and drainage | 1 (0.6) |
| Diverticulectomy | 17 (10.2) |
| Resection, colostomy | 19 (11.4) |
| Conservative treatment | 13 (7.8) |
| Diverticulectomy,colostomy | 3 (1.8) |
| Drainage | 4 (2.4) |
| Not mentioned | 4 (2.4) |
| Laparoscopic colectomy | 5 (3) |
| Excision of the cyst | 3 (1.8) |
| Colectomy, ileostomy | 1 (0.6) |
| computed tomography-guided percutaneous intervention | 1 (0.6) |
| Ref. | Treatment | Type | Complications | Hospital stay |
| Kam et al[4] | Left colectomy with primary anastomosis and abscess drainage | 1,2 | No | NR |
| Kim et al[5] | Laparoscopic right colectomy | 3 | No | 7 d |
| Filippucci et al[6] | Sigmoid resection with primary anastomosis | NR | No | NR |
| Mahamid et al[7] | Laparoscopic sigmoidectomy | NR | Nr | NR |
| Khaikin et al[8] | Hartmann’s resection | 2 | No | NR |
| Anderton et al[9] | IV antibiotics (high-risk for laparotomy) | NR | No | 3 d |
| Olakowski et al[10] | Right colectomy | 3 | No | 7 d |
| Sasi et al[11] | Hartmann’s resection | NR | No | NR |
| Beddy et al[12] | Hartmann’s resection | 2 | Hypotension | 14 d |
| Collin et al[13] | Laparoscopic sigmoidectomy | 2 | No | 4 d |
| Hogan et al[14] | No treatment (asymptomatic patient) | NR | Nr | NR |
| Chatora et al[15] | Excision of the cyst | 1 | No | NR |
| laparoscopic sigmoidectomy | 1 | No | NR | |
| Abdelrazeq et al[16] | Sigmoidectomy | NR | No | NR |
| Guarnieri et al[17] | Left colectomy | NR | No | 9 d |
| Present study | Sigmoid resection with primary anastomosis and ileostomy | 2 | No | 7 d |
Regarding the clinical presentation, abdominal pain was the most common symptom (69% of the cases), followed by constipation (17%), sensation of an abdominal mass (17%), vomiting (12%), and diarrhea (11%). Rectal bleeding was present in 9% of the patients. Among the physical signs, an abdominal mass was detected in 48% of the cases, whereas 20% of the patients presented with fever and 14% with abdominal tenderness. Perforation was diagnosed at presentation or at the time of surgery in 44/166 patients (26.5%).
A computed tomography (CT) scan is the most accurate and recommended examination and permits a correct diagnosis in nearly all the cases. In the first cases, a barium enema was used. A colonoscopy is generally avoided because of the risk of perforation.
A colic resection with an en-bloc resection of the diverticulum was the most frequent treatment, performed in 57.2% of the cases. Hartmann’s procedure was used in 11.4% of the cases, and a diverticulectomy was performed in 10.2% of the cases. In emergency settings, Hartmann’s resection might be performed; its disadvantage is the need of a second complex surgical procedure to restore the intestinal continuity. The treatments used in the remnant cases are reported in Table 3.
A sub-group analysis of 16 patients treated in the previous five years (Table 4) showed that only one patient was treated with a simple diverticulum resection. In this case, the GCD did not communicate with the bowel lumen[15]; no information is reported regarding the postoperative course in this case. A laparoscopic colectomy has been reported to be safe[7], however, it was performed only in 4 patients and only in the previous 5 years. In the previous five years, no postoperative mortality was reported, and complications occurred only in 1 patient (postoperative hypotension requiring 24-h hospitalization in the intensive care unit), and the duration of hospital stay ranged from 4 to 14 d[4-17]. Only one case of recurrent GCD is reported in the literature, which occurred after a diverticulectomy[45]. No recurrences are reported after a colectomy and en bloc diverticulectomy.
Non-surgical treatments have been rarely used and are considered in patients refusing surgery and in high-risk patients to resolve acute inflammation and are typically followed by a delayed elective segmental colectomy.
Case presentation: An 80-year-old woman was admitted to the surgery department with a 2-d history of rectal bleeding, associated with left lower quadrant abdominal pain, abdominal swelling and nausea. The patient had reported episodic abdominal pain for 10-12 mo prior to admission. She did not report any changes in bowel habits. Her prior medical history included hypertension treated with beta-blockers. Previous surgeries included a hysterectomy 30 years before and an appendectomy in her childhood. The patient’s weight was 60 kg, and her height was 160 cm, with a BMI of 23.44.
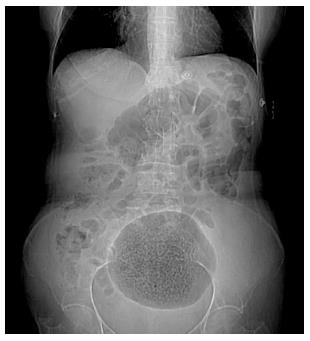
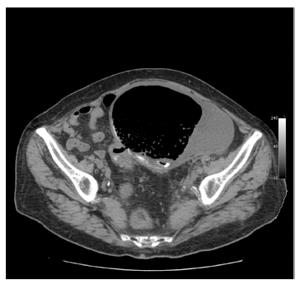
On clinical examination the abdomen was distended, soft, and mildly tender on the lower abdominal quadrants, where a large mass was palpable. The blood tests revealed a hemoglobin level of 7.7 g/dL, a white blood cell count of 11.42 × 103/uL and neutrophil level of 79.9%. The C-reactive protein level was 9.94 mg/dL. An abdominal X-ray showed a large gas-filled cavity in the lower abdomen (Figure 1). An axial non-contrast CT scan showed a 15.5 cm × 10.5 cm cystic lesion containing air and fluid, with a thick wall (Figure 2). A large cyst, adherent to the antimesenteric border of the sigmoid colon, was found during a laparotomy. Resection of the cyst en-bloc with the sigmoid colon, primary colonic anastomosis and loop ileostomy were performed. The postoperative course was uneventful and the patient was discharged on post-operative day 7. The pathology examination showed a giant colonic diverticulum containing blood and feces, with acute and chronic inflammation and foreign-body giant-cells, with no evidence of malignancy. The GCD was classified as type 2 according to McNutt et al[3].
Giant colonic diverticula are colic diverticula greater than 4 cm in size, by definition; approximately 90% of the cases involve the sigmoid colon[2]. They might be isolated, but in 85% of the cases, GCDs are associated with concomitant diverticular disease[19].
Different hypotheses might explain the development of GCD. One theory asserts that it is caused by a unidirectional ball-valve mechanism through a tiny communicating diverticular neck, which causes air entrapment and gradual enlargement of the diverticulum[20]. Another hypothesis is that GCD is secondary to the action of gas forming organisms[21].
McNutt et al[3] classified GCD in three types. Type 1 diverticula (22% of the cases, according to Steenvoorde et al[2]) are pulsion diverticula, which enlarge gradually (pseudo-diverticula such as small colonic diverticula), with remnants of muscularis mucosa and true muscularis, which ends at the colonic border of the diverticulum. Chronic inflammatory cells and granulation and fibrous tissue are present in its wall. Type 2 diverticula (inflammatory diverticula, 66% of the cases[2]) are secondary to a subserosal perforation, leading to a walled off abscess cavity communicating with the bowel lumen and gradually enlarging. Their wall is composed of fibrous scar tissue, without a normal intestinal layer.
Type 3 (true diverticula, 12% of the cases[2]) contains all the bowel layers with a well-developed smooth muscle wall and is in continuity with the gut lumen. Type 3 diverticula most likely have a congenital origin. The etiology of the true giant diverticulum is possibly related to anomalous embryologic development and is sometimes referred to as a congenital diverticulum.
The clinical presentation is variable, ranging from an acute presentation with severe complications to no symptoms. An acute presentation (30%-35% of the patients) is characterized by an acute onset of abdominal pain, eventually associated with fever, nausea, vomiting, and rectal bleeding[1,22,23]. In two thirds of the patients, a palpable mass is noticed at the physical examination[22]. Complications occur in 15%-35% of the cases[24]. The most common complication is peritonitis, caused by the perforation of the GCD, followed by abscess formation, intestinal obstruction, volvulus, and infarction[22]. Rarely, a carcinoma might develop from the diverticular mucosa[25]. Chronic presentation (30%-35% of the patients) is characterized by intermittent abdominal discomfort, bloating, and constipation, which might be associated with a palpable and soft abdominal mass, with variations in size[22]. Approximately 10% of the patients are asymptomatic; the mass is typically detected on examination or from radiological or endoscopic exams.
As shown in Tables 1 and 2, our review of 166 patients[1-138] showed that abdominal pain was the most common symptom (69% of cases), followed by constipation (17%), and a sensation of an abdominal mass (17%). Among the physical signs, an abdominal mass was detected in 48% of the cases, whereas 20% of the patients presented with fever.
An abdominal X-ray typically shows a large gas-filled cyst (Ballon sign), with an air-fluid level and regular and smooth walls[26]. A CT scan is the most accurate exam, and it permits a correct diagnosis in nearly all the cases, demonstrating a smooth-walled gas-containing structure[27]. Barium enemas might show communication between the bowel lumen and the GCD in 60%-70% of the cases; a rare complication of an enema is a GCD perforation requiring emergency surgical treatment. A colonoscopy is rarely performed because it might cause GCD perforation[28].
The preferred treatment of uncomplicated GCD is resection of the diverticulum and adjacent colon with primary colonic anastomosis[4], with or without a temporary diverting ileostomy. A simple diverticulectomy has been rarely reported[29] and should be avoided in case of concomitant diverticular disease. When a diverticulectomy and colonic suture are performed, there is a consistent risk of dehiscence because the diverticular neck is frequently wide and the surrounding tissue is inflammatory. The analysis of the literature showed that colic resection with an e-bloc resection of the diverticulum was the most frequent treatment and was performed in 57.2% of the cases. Hartmann’s procedure was used in 11.4% of the cases, and a diverticulectomy was performed in 10.2% of the cases. In emergency settings, Hartmann’s resection might be performed; its disadvantage is the need of a second complex surgical procedure to restore the intestinal continuity. The treatment of the remaining cases is reported in Table 3.
A sub-group analysis of the previous 5 years (Table 4) showed that in that time period only one patient was treated with a simple diverticulum resection. In this case, the GCD did not communicate with the bowel lumen[15]; no information is reported regarding the postoperative course. A laparoscopic colectomy has been reported to be safe[7], but it was performed only in 4 patients and only in the previous 5 years, most likely because most authors felt that open surgery is safer in this setting, in consideration of the large size of the GCD and the risk of diverticular perforation and fecal peritoneal contamination. Surgical treatment guarantees excellent results. In the previous five years, no postoperative mortality was reported, complications occurred only in 1 patient (postoperative hypotension requiring a 24-h hospitalization in the intensive care unit), and the hospital stay ranged from 4 to 14 d[4-17]. No recurrences are reported after colectomy and en bloc diverticulectomy.
Non-surgical treatments have been rarely used, and include percutaneous drainage[1], stent placement in the diverticular neck with drainage in the colic lumen[19], and antibiotics[9]. These options are considered in patients refusing surgery, and in high-risk patients, to resolve GCS acute inflammation, and are typically followed by delayed elective segmental colectomy.
GCD is a rare but potentially dangerous pathological entity. A correct diagnosis is predominantly based on an abdominal CT scan. A segmental colectomy with en-bloc diverticular resection and primary anastomosis with or without a diverting ileostomy is the preferred and most frequent treatment, and it is indicated in asymptomatic patients as well, to prevent potential dangerous complications (primarily, peritonitis from diverticular perforation). In emergency settings or in high-risk patients, Hartmann’s procedure might be performed. Laparoscopic surgery has been reported to be safe; however, it has been performed only in 4 patients in the previous five years. Surgical treatment guarantees excellent results. In the previous 5 years, the mortality was null, morbidity very low (1 patient was hospitalized in the intensive care unit for postoperative hypotension), and the patients were discharged 4-14 d after surgery.
Giant colonic diverticulum (GCD) is a rare manifestation of diverticular disease of the colon. In the literature, fewer than 200 studies were published, predominantly case reports or small patient series. In this study, we present a comprehensive and updated systematic review of the literature and a case of GCD in an elderly patient.
The pathogenesis and best treatment options of GCD are important areas of research on the subject.
This article provides a complete systematic review of the literature on GCD, summarizing the current evidence on the clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment options of this rare disease. Additionally, an example case is presented.
To guide the clinical management of patients presenting with GCD.
Giant colonic diverticula are colic diverticula greater than 4 cm in size, by definition; approximately 90% of the cases involve the sigmoid colon. They might be isolated, however, in 85% of the cases, GCDs are associated with concomitant diverticular disease.
This manuscript describes a case of an 80-year-old lady presenting with rectal bleeding in whom a giant diverticulum of the sigmoid colon was diagnosed and surgically treated. Also a review of this rare variant of colonic diverticular disease is reported. It is a useful overview of this pathological condition, its clinical manifestations and treatment options.
P- Reviewer: Cologne KG, Lorenzo-Zuniga V, Perakath B, Stanghellini V, Steele SR S- Editor: Ma YJ L- Editor: A E- Editor: Wang CH
| 1. | Praveen BV, Suraparaju L, Jaunoo SS, Tang T, Walsh SR, Ogunbiyi OA. Giant colonic diverticulum: an unusual abdominal lump. J Surg Educ. 2007;64:97-100. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 2. | Steenvoorde P, Vogelaar FJ, Oskam J, Tollenaar RA. Giant colonic diverticula. Review of diagnostic and therapeutic options. Dig Surg. 2004;21:1-6; discussion 6. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 49] [Cited by in RCA: 53] [Article Influence: 2.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 3. | McNutt R, Schmitt D, Schulte W. Giant colonic diverticula--three distinct entities. Report of a case. Dis Colon Rectum. 1988;31:624-628. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 38] [Cited by in RCA: 46] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (2)] |
| 4. | Kam JC, Doraiswamy V, Spira RS. A rare case presentation of a perforated giant sigmoid diverticulum. Case Rep Med. 2013;2013:957152. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 0.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 5. | Kim HJ, Kim JH, Moon OI, Kim KJ. Giant ascending colonic diverticulum presenting with intussusception. Ann Coloproctol. 2013;29:209-212. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 6. | Filippucci E, Pugliese L, Pagliuca V, Crusco F, Pugliese F. Giant sigmoid diverticulum: a rare cause of common gastrointestinal symptoms. Intern Emerg Med. 2012;7 Suppl 2:S149-S151. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 7. | Mahamid A, Ashkenazi I, Sakran N, Zeina AR. Giant colon diverticulum: rare manifestation of a common disease. Isr Med Assoc J. 2012;14:331-332. [PubMed] |
| 8. | Khaikin M, Zbar AP, Mezhibovsky V, Gutman M, Weidenfeld J, Aviel-Ronen S. Perforated giant sigmoid diverticulum. Tech Coloproctol. 2013;17:251-252. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (2)] |
| 9. | Anderton M, Griffiths B, Ferguson G. Giant sigmoid diverticulitis mimicking acute appendicitis. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2011;93:e89-e90. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 10. | Olakowski M, Jabłońska B, Lekstan A, Szczęsny-Karczewska W, Pilch-Kowalczyk J, Kohut M. Gastrointestinal image: a true giant transverse colon diverticulum. J Gastrointest Surg. 2011;15:1289-1291. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 11. | Sasi W, Hamad I, Quinn A, Nasr AR. Giant sigmoid diverticulum with coexisting metastatic rectal carcinoma: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2010;4:324. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 12. | Beddy D, DeBlacam C, Mehigan B. An unusual cause of an acute abdomen--a giant colonic diverticulum. J Gastrointest Surg. 2010;14:2016-2017. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 13. | Collin JE, Atwal GS, Dunn WK, Acheson AG. Laparoscopic-assisted resection of a giant colonic diverticulum: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2009;3:7075. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 22] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 14. | Hogan RB, Phillips P, Boyd SA, Williams JC. Two-year retention of Bravo capsule in a giant colonic diverticulum. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104:1062. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 15. | Chatora GT, Kumaran M. Giant colonic pseudo-diverticula importance of, and aids to radiological diagnosis: a case series. Cases J. 2009;2:9314. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 16. | Abdelrazeq AS, Owais AE, Aldoori MI, Botterill ID. A giant colonic diverticulum presenting as a ‘phantom mass’: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2009;3:29. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 17. | Guarnieri A, Cesaretti M, Tirone A, Francioli N, Piccolomini A, Vuolo G, Verre L, Savelli V, Di Cosmo L, Carli AF. Giant Sigmoid Diverticulum: A Rare Presentation of a Common Pathology. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2009;3:5-9. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 18. | Zeina AR, Nachtigal A, Matter I, Benjaminov O, Abu-Gazala M, Mahamid A, Kessel B, Amitai M. Giant colon diverticulum: clinical and imaging findings in 17 patients with emphasis on CT criteria. Clin Imaging. 2013;37:704-710. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 14] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 19. | Singh AK, Raman S, Brooks C, Philips D, Desai R, Kandarpa K. Giant colonic diverticulum: percutaneous computed tomography-guided treatment. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2008;32:204-206. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 20. | Toiber-Levy M, Golffier-Rosete C, Martínez-Munive A, Baquera J, Stoppen ME, D’Hyver C, Quijano-Orvañanos F. Giant sigmoid diverticulum: case report and review of the literature. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 2008;32:581-584. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 21. | Salazar-Ibargüen J, Escárcega RO, Pérez Chávez G. Giant sigmoid colon diverticulum. Dig Surg. 2007;24:17-18. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 22. | de Oliveira NC, Welch JP. Giant diverticula of the colon: a clinical assessment. Am J Gastroenterol. 1997;92:1092-1096. [PubMed] |
| 23. | Choong CK, Frizelle FA. Giant colonic diverticulum: report of four cases and review of the literature. Dis Colon Rectum. 1998;41:1178-1185; discussion 1185-1186. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 71] [Cited by in RCA: 70] [Article Influence: 2.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (2)] |
| 24. | Majeski J, Durst G. Obstructing giant colonic diverticulum. South Med J. 2000;93:797-799. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 25. | Abou-Nukta F, Bakhos C, Ikekpeazu N, Ciardiello K. Ruptured giant colonic diverticulum. Am Surg. 2005;71:1073-1074. [PubMed] |
| 26. | Thomas S, Peel RL, Evans LE, Haarer KA. Best cases from the AFIP: Giant colonic diverticulum. Radiographics. 2006;26:1869-1872. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 25] [Cited by in RCA: 25] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (2)] |
| 27. | Sassani P, Singh HM, Gerety D, Abbas MA. Giant colonic diverticulum: endoscopic, imaging, and histopathologic findings. Perm J. 2008;12:47-49. [PubMed] |
| 28. | Paoluzi OA, Tosti C, Andrei F, Stroppa I, Pallone F. Look out before polypectomy in patients with diverticular disease--a case of a large, inverted diverticulum of the colon resembling a pedunculated polyp. Can J Gastroenterol. 2010;24:61-63. [PubMed] |
| 29. | Gendy RK, Jeffery PJ. Giant diverticulum of colon treated by diverticulectomy. Hosp Med. 2000;61:362. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 30. | Mohammad AI, Ben-Nakhi AM, Khoursheed M. Giant sigmoid diverticulum: a case report. Med Princ Pract. 2009;18:70-72. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 31. | Shetty K, Selvam LA. Electronic clinical challenges and images in GI: image 2. Giant sigmoid diverticular abscess. Gastroenterology. 2008;135:e3-e4. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 32. | Scott DA, Glancy S. Spontaneous resolution of a giant colonic diverticulum. Clin Radiol. 2008;63:833-835. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 33. | McQuade KL, Foreman ML. Giant colonic diverticulum. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2008;21:25-26. [PubMed] |
| 34. | Hurreiz H, Mayes R, Humphreys G. A giant sigmoid diverticulum presenting as an upper abdominal mass. Ir J Med Sci. 2008;177:409-411. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 35. | Yoon SE, Lee YH, Yoon KH, Kim EA, Choi SS, Juhng SK, Yun KJ, Park WC. Complicated giant diverticulum of the transverse colon accompanied by right inguinal hernia of the greater omentum. Br J Radiol. 2007;80:e201-e204. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 36. | Al-Jaroof AH, Al-Zayer F, Meshikhes AW. A case of sigmoid colon duplication in an adult woman. BMJ Case Rep. 2014;2014:bcr2014203874. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 37. | Chaiyasate K, Yavuzer R, Mittal V. Giant sigmoid diverticulum. Surgery. 2006;139:276-277. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 14] [Cited by in RCA: 16] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 38. | Altaf N, Geary S, Ahmed I. Giant colonic diverticulum. J R Soc Med. 2005;98:169-170. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 39. | Neary P, Kurli V, Nicholson A, MacDonald AW, Monson JR. Giant colonic diverticulum. Ir J Med Sci. 2004;173:38-39. [PubMed] |
| 40. | Hughes WL, Greene RC. Solitary air cyst of peritoneal cavity. AMA Arch Surg. 1953;67:931-936. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 36] [Cited by in RCA: 39] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 41. | Kricun R, Stasik JJ, Reither RD, Dex WJ. Giant colonic diverticulum. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1980;135:507-512. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 32] [Cited by in RCA: 34] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 42. | Boijsen E. [Giant diverticulum of the sigmoid]. Fortschr Geb Rontgenstr Nuklearmed. 1956;84:760-761. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 43. | CASE RECORDS of the Massachusetts General Hospital; case 43402. N Engl J Med. 1957;257:677-680. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 44. | Frankenfeld RH, Waters CH, Schepeler TV. Giant air cyst of the abdomen; an unusual manifestation of diverticulitis of the sigmoid: report of a case. Gastroenterology. 1959;37:103-106. [PubMed] |
| 46. | Macbeth WA, Riddle PR. Gas-Filled Abscess Cavity As A Manifestation Of Diverticulitis Of The Colon. Br J Radiol. 1964;37:861-862. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 14] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 47. | Moore JM, Gold C. Giant Diverticulum Of Sigmoid Colon. Br J Surg. 1964;51:876-878. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 16] [Cited by in RCA: 18] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 48. | Bergeron RB, Hanley PH. Giant Sigmoid Diverticulum. Am J Surg. 1965;109:660-662. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 18] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 49. | Ferguson WH, Boinis GA. A giant diverticulum of the colon. Report of a case. Med Ann Dist Columbia. 1966;35:66-68. [PubMed] |
| 50. | Fontaine R, Warter P, Bridier JJ, Philippe E. [Giant abdominal gas cyst in a patient with sigmoidal diverticulosis]. J Radiol Electrol Med Nucl. 1966;47:657-662. [PubMed] |
| 51. | Beauchant J, Debelut J, Payard J, Fontaine A, Breuil J. [Sigmoid cyst]. Sem Hop. 1968;44:1967-1968. [PubMed] |
| 52. | Finby N, Begg CF. Pneumocyst of colon. N Y State J Med. 1968;68:2941-2943. [PubMed] |
| 53. | Piper JV, Thornley BA. Solitary giant diverticulum of the sigmoid colon. Br J Surg. 1968;55:398-400. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 54. | Vanapruks S, Fuhrman M. Giant solitary gas cyst of the sigmoid colon. A case report. Radiology. 1969;92:1533-1534. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 55. | Asch T, Milikow E, Gump F. Giant gas cyst of the sigmoid. Report of a case and review of the literature. Radiology. 1970;96:409-410. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 56. | Barratt JG. Giant cyst of the sigmoid colon. Australas Radiol. 1971;15:38-40. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 57. | Mainzer F, Minagi H. Giant sigmoid diverticulum. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1971;113:352-354. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 18] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 58. | Swann JC, Giles KW. Giant diverticulum of the sigmoid colon. Br J Radiol. 1971;44:551-553. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 59. | Saha SP, Roesch CB. A giant sigmoid diverticulum: report of a case. Dis Colon Rectum. 1972;15:63-65. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 60. | Schenken JR, Cochran R. An intestinal-gas cyst, a rare complication of diverticulitis: report of a case. Dis Colon Rectum. 1972;15:448-452. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 61. | Sibson DE, Edwards AJ. Giant gas-filled cyst of sigmoid colon. Report of a case and review of the literature. Postgrad Med J. 1972;48:180-184. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 62. | Sagar S. Giant solitary diverticulum of the transverse colon with diverticulosis. Br J Clin Pract. 1973;27:145-146. [PubMed] |
| 63. | Joubaud F, Plane P, Bouali AB, Ronceray J, Barthe JP. [Giant diverticulum of the colon]. Sem Hop. 1974;50:2536-2537. [PubMed] |
| 64. | Kempczinski RF, Ferrucci JT. Giant sigmoid diverticula: a review. Ann Surg. 1974;180:864-867. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 27] [Cited by in RCA: 30] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 65. | Rabinowitz JG, Farman J, Dallemand S, Twerskey J, Rosen Y. Giant sigmoid diverticulum. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1974;121:338-343. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 66. | Smulewicz JJ, Govoni AF. Giant air cysts of the colon. J Can Assoc Radiol. 1974;25:245-250. [PubMed] |
| 67. | Sutorius DJ, Bossert JE. Giant sigmoid diverticulum with perforation. Am J Surg. 1974;127:745-748. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 18] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 68. | Barlow B, Goodhue WW, Schullinger JN. Giant congenital diverticulum of the sigmoid colon. J Pediatr Surg. 1975;10:549-550. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 0.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 69. | Harris RD, Anderson JE, Wolf EA. Giant air cyst of the sigmoid complicating diverticulitis: report of a case. Dis Colon Rectum. 1975;18:418-424. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 70. | Moss AA. Giant sigmoid diverticulum: clinical and radiographic features. Am J Dig Dis. 1975;20:676-683. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 16] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 71. | Johns ER, Hartley MG. Giant gas filled cysts of the sigmoid colon: a report of two cases. Br J Radiol. 1976;49:930-931. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 72. | Beal JM. Case report: giant diverticulum of sigmoid. IMJ Ill Med J. 1977;151:272-273. [PubMed] |
| 73. | Camprodon R, Guerrero JA, Mendoza CG, Crespo C. Giant diverticula of the colon. Br J Surg. 1977;64:628-629. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 74. | Foster DR, Ross B. Giant sigmoid diverticulum: clinical and radiological features. Gut. 1977;18:1051-1053. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 14] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 75. | Macleod DA, Jacques J. Solitary, paracolic gas cyst. Md State Med J. 1977;26:74-77. [PubMed] |
| 76. | Ingram NP, Holford CP, Ellis WR. Two cases of giant intestinal gas cyst. Br J Surg. 1978;65:214. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 77. | Wetrich RM, Sidhu DS. Giant sigmoid diverticulum. West J Med. 1978;128:539-541. [PubMed] |
| 78. | Wetstein L, Camera A, Trillo RA, Zamora BO. Giant sigmoidal diverticulum: report of a case and review of the literature. Dis Colon Rectum. 1978;21:110-112. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 79. | Arianoff AA, Vielle C, Arianoff V, Nouzaradan J. [Giant diverticulum of the sigmoid]. Acta Chir Belg. 1979;78:223-229. [PubMed] |
| 80. | Gallagher JJ, Welch JP. Giant diverticular of the sigmoid colon: a review of differential diagnosis and operative management. Arch Surg. 1979;114:1079-1083. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 26] [Cited by in RCA: 26] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 81. | Teyssou H, Bureau M, Torras P, Ruiz R, Ter-Davtian M, Tessier JP. [Giant diverticulum of the sigmoid: A report on one case and review of the literature (author’s transl)]. J Radiol. 1979;60:439-443. [PubMed] |
| 82. | Cameron CR. Giant sigmoid diverticulum. J R Coll Surg Edinb. 1980;25:457-459. [PubMed] |
| 83. | Ona FV, Salamone RP, Mehnert PJ. Giant sigmoid diverticulitis. A cause of partial small bowel obstruction. Am J Gastroenterol. 1980;73:350-352. [PubMed] |
| 84. | Slomic A, Saunders GM, Khor CY. [Giant diverticulum of the sigmoid]. J Can Assoc Radiol. 1980;31:168-170. [PubMed] |
| 85. | Castagnone D, Ranzi T. Giant sigmoid diverticula. Case report and review. Panminerva Med. 1981;23:203-206. [PubMed] |
| 86. | Cronin TG, Tway MS, Boraca CT. Recurrent giant air cyst of the colon. IMJ Ill Med J. 1981;160:40-42. [PubMed] |
| 87. | Heimann T, Aufses AH. Giant sigmoid diverticula. Dis Colon Rectum. 1981;24:468-470. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 88. | Maresca L, Maresca C, Erickson E. Giant sigmoid diverticulum: report of a case. Dis Colon Rectum. 1981;24:191-195. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 89. | Muhletaler CA, Berger JL, Robinette CL. Pathogenesis of giant colonic diverticula. Gastrointest Radiol. 1981;6:217-222. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 20] [Cited by in RCA: 21] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 90. | Rosenberg RF, Naidich JB. Plain film recognition of giant colonic diverticulum. Am J Gastroenterol. 1981;76:59-69. [PubMed] |
| 91. | Wallers KJ. Giant diverticulum arising from the transverse colon of a patient with diverticulosis. Br J Radiol. 1981;54:683-688. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 92. | Pinsolle J, Riviere J, Boisseau C, Videau J. [Giant diverticulum of the sigmoid colon. A rare complication of colonic diverticulosis. Review of the literature apropos of a case]. J Chir (Paris). 1982;119:583-587. [PubMed] |
| 93. | Al-Jurf AS, Foucar E. Uncommon features of giant colonic diverticula. Dis Colon Rectum. 1983;26:808-813. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 94. | Moesgaard J, Felding C. Giant diverticulum of the sigmoid colon. Acta Chir Scand. 1983;149:445-447. [PubMed] |
| 95. | Patel D, Diab W. Giant colonic diverticulum. N Y State J Med. 1983;83:750-754. [PubMed] |
| 96. | Ricci MA, Cady D. Giant colonic diverticulum. N Y State J Med. 1983;83:1153. [PubMed] |
| 98. | van Vugt AB, Sleeboom C, Dekker LA, Mallens WM, ten Velde J. Giant cysts in diverticular disease of the sigmoid colon. Neth J Surg. 1985;37:183-186. [PubMed] |
| 99. | Siskind BN, Burrell MI, Richter JO, Radin DR. CT appearance of giant sigmoid diverticulum. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1983;10:543-544. [PubMed] |
| 100. | Fields SI, Haskell L, Libson E. CT appearance of giant colonic diverticulum. Gastrointest Radiol. 1987;12:71-72. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 101. | Smith TR, Tyler IM. CT demonstration of a giant colonic diverticulum. Gastrointest Radiol. 1987;12:73-75. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 102. | Lapeyrie H, Balmes P, Loizon P, Delhoume JY. [Giant diverticulum of the transverse colon]. J Chir (Paris). 1988;125:717-720. [PubMed] |
| 103. | Maréchal A, Brousse P, Rousseau J. [Giant diverticulum of the colon. Apropos of 2 cases]. J Radiol. 1989;70:43-46. [PubMed] |
| 104. | van Niekerk AJ, Fourie PA. Giant colonic diverticulum--a radiological diagnostic problem. A case report. S Afr Med J. 1989;75:447-448. [PubMed] |
| 105. | Scerpella PR, Bodensteiner JA. Giant sigmoid diverticula. Report of two cases. Arch Surg. 1989;124:1244-1246. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 106. | Fontanelle L, Le Goff JY, Convard JP. [Giant diverticulum of the colon. Apropos of a case disclosed by complication]. Ann Radiol (Paris). 1991;34:398-400. [PubMed] |
| 107. | Ritchie AJ, Carson JG, Humphreys WG. Encysted pneumatocele: a complication of diverticular disease. Br J Surg. 1991;78:683. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 108. | Agarwal DK, Choudhuri G, Dhiman RK, Kapoor VK. Giant colonic diverticulae presenting as painless abdominal lump. Indian J Gastroenterol. 1992;11:90. [PubMed] |
| 109. | Levi DM, Levi JU, Rogers AI, Bergau DK, Wenger J. Giant colonic diverticulum: an unusual manifestation of a common disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 1993;88:139-142. [PubMed] |
| 110. | Slawson SH, Sykes MW, Binkovitz LA. Giant pseudodiverticulum of the sigmoid colon. Mayo Clin Proc. 1993;68:707-708. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 111. | Nagler-Reus M, Guhl L, Arlart IP. [Giant diverticulum of the sigmoid colon]. Rofo. 1994;161:171-173. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 112. | Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital. Weekly clinicopathological exercises. Case 19-1994. A 47-year-old woman with long-standing intermittent abdominal pain, vomiting, and marked weight loss. N Engl J Med. 1994;330:1376-1381. [PubMed] |
| 113. | Naber A, Sliutz AM, Freitas H. Giant diverticulum of the sigmoid colon. Br J Surg. 1995;82:985. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 114. | Naber A, Sliutz AM, Freitas H. Giant diverticulum of the sigmoid colon. Int J Colorectal Dis. 1995;10:169-172. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 14] [Cited by in RCA: 16] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 115. | Nano M, De Simone M, Lanfranco G, Bronda M, Lale-Murix E, Aimonino N, Anselmetti GC. Giant sigmoid diverticulum. Panminerva Med. 1995;37:44-48. [PubMed] |
| 116. | Ueda P, Hall D. Images in clinical medicine. Giant colonic diverticulum. N Engl J Med. 1995;333:228. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 117. | D’Almeida MJ, McQuiston JH. Giant sigmoid diverticulum. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 1996;96:309-313. [PubMed] |
| 118. | Mehta DC, Baum JA, Dave PB, Gumaste VV. Giant sigmoid diverticulum: report of two cases and endoscopic recognition. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996;91:1269-1271. [PubMed] |
| 119. | Roger T, Rommens J, Bailly J, Vollont GH, Belva P, Delcour C. Giant colonic diverticulum: presentation of one case and review of the literature. Abdom Imaging. 1996;21:530-533. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 16] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 120. | Grover H, Nair S, Hertan H. Giant true diverticulum of sigmoid colon. Am J Gastroenterol. 1998;93:2267-2268. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 121. | Kuganeswaran E, Fisher JK. Giant sigmoid diverticulum: a rare manifestation of diverticular disease. South Med J. 1998;91:952-955. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 122. | Custer TJ, Blevins DV, Vara TM. Giant colonic diverticulum: a rare manifestation of a common disease. J Gastrointest Surg. 1999;3:543-548. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 28] [Cited by in RCA: 31] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 123. | Díaz Candamio MJ, Pombo F, Yebra MT. Amyloidosis presenting as a perforated giant colonic diverticulum. Eur Radiol. 1999;9:715-718. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 124. | Havenstrite KA, Harris JA, Rivera DE. Giant colonic diverticulum: report of a case. Am Surg. 1999;65:578-580. [PubMed] |
| 125. | Naing T, Ray S, Loughran CF. Giant sigmoid diverticulum: a report of three cases. Clin Radiol. 1999;54:179-181. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 126. | Roth T, Demartines N, Gavelli A, Huguet C. [Giant diverticula of the colon. Apropos of 2 cases]. Chirurgie. 1999;124:307-312. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 127. | Arima N, Tanimoto A, Hamada T, Sasaguri Y, Sasaki E, Shimokobe T. MALT lymphoma arising in giant diverticulum of ascending colon. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000;95:3673-3674. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 128. | Brouland JP, Poupard B, Nemeth J, Valleur P. Lipomatous polyposis of the colon with multiple lipomas of peritoneal folds and giant diverticulosis: report of a case. Dis Colon Rectum. 2000;43:1767-1769. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 129. | Philip J, Whittlestone TH, Hamilton SG. An unusual case of acute urinary retention. BJU Int. 2000;85:557–554. |
| 130. | Rosen NG, Gibbs DL, Soffer SZ, Valderrama E, Lee TK. Uroepithelium in a colonic diverticulum. J Pediatr Surg. 2000;35:1375-1376. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 131. | Steenvoorde P, Tollenaar RA. Gastrointestinal: giant inflammatory colonic diverticulum. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002;17:805. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 132. | Silberman EL, Thorner MC. Volvulus of giant sigmoidal diverticulum. JAMA. 1961;177:782-784. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 133. | Elfrink RJ, Miedema BW. Colonic diverticula. When complications require surgery and when they don’t. Postgrad Med. 1992;92:97-98, 101-102, 105, 108 passim. [PubMed] |
| 134. | Bonvin MMP, Bonte G. Diverticules géants du sigmoide. Arch Mal Dig Mal Nutr. 1946;35:353–355. |
| 135. | Casas DJ, Tenesa M, Alastrué A, Hidalgo F, Barranco LC, Olazabal A. Case report: uncommon radiological and pathological features of giant colonic diverticula. Clin Radiol. 1991;44:125-127. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 136. | Silen W, Sheiman RG. Giant colonic diverticulum. N Engl J Med. 1995;333:1645. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 137. | Painter NS, Burkitt DP. Diverticular disease of the colon: a deficiency disease of Western civilization. Br Med J. 1971;2:450-454. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 571] [Cited by in RCA: 536] [Article Influence: 9.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 138. | Gooszen AW, Gooszen HG, Veerman W, Van Dongen VM, Hermans J, Klien Kranenbarg E, Tollenaar RA. Operative treatment of acute complications of diverticular disease: primary or secondary anastomosis after sigmoid resection. Eur J Surg. 2001;167:35-39. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 65] [Cited by in RCA: 68] [Article Influence: 2.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |