Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2014; 20(6): 1602-1607
Published online Feb 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i6.1602
Published online Feb 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i6.1602
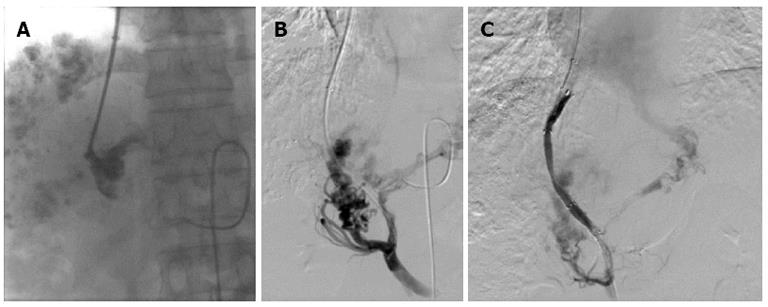
Figure 2 Portal venograms in a 41-year-old man with hepatocellular carcinoma and lymphatic metastasis, who was treated with transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for severe varicosis and vomiting blood for 5 d.
A: Injection of a small amount of contrast agent demonstrated tubular and slow blood flow with no dissipation and the portal vein was clearly defined; B: After a catheter was introduced, the portal vein image was confirmed by 30° right anterior oblique angiography; C: After two Fluency stent grafts with a length of 80 mm and diameter of 8 mm were implanted, the shunt was shown to have smooth blood flow by postoperative angiography.
- Citation: Zhao JB, Feng C, Zhu QH, He XF, Li YH, Chen Y. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt with covered stents for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(6): 1602-1607
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i6/1602.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i6.1602