Published online Dec 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i46.17352
Revised: April 14, 2014
Accepted: July 24, 2014
Published online: December 14, 2014
Processing time: 307 Days and 9.9 Hours
Abnormalities in liver function tests, including transient and self-limiting hypertransaminasemia, cholestatic disease and hepatitis, can develop during treatment with anti-tumour-necrosis-factor (TNF) therapy. The optimal management of liver injury related to anti-TNF therapy is still a matter of debate. Although some authors recommend discontinuing treatment in case of both a rise of alanine aminotransferase more than 5 times the upper limit of normal, or the occurrence of jaundice, there are no standard guidelines for the management of anti-TNF-related liver injury. Bibliographical searches were performed in PubMed, using the following key words: inflammatory bowel disease (IBD); TNF inhibitors; hypertransaminasemia; drug-related liver injury; infliximab. According to published data, elevation of transaminases in patients with IBD treated with anti-TNF is a common finding, but resolution appears to be the usual outcome. Anti-TNF agents seem to be safe with a low risk of causing severe drug-related liver injury. According to our centre experience, we found that hypertransaminasemia was a common, mainly self-limiting finding in our IBD cohort and was not correlated to infliximab treatment on both univariate and multivariate analyses. An algorithm for the management of liver impairment occurring during anti-TNF treatment is also proposed and this highlights the need of a multidisciplinary approach and suggests liver biopsy as a key-point in the management decision in case of severe rise of transaminases. However, hepatic injury is generally self-limiting and drug withdrawal seems to be an exception.
Core tip: Anti-tumour-necrosis-factor (TNF) agents appear to be safe with a low risk of causing severe liver injury. Standard guidelines for the management of anti-TNF-related liver injury are lacking. Our approach, based on evidence from literature and our centre experience, highlights the need of a multidisciplinary approach and suggests liver biopsy as a key-point in the management decision. We particularly highlight that continuation of the anti-TNF treatment is usually possible, in view of the rarity of severe liver injury and the lack of alternative medical options in case of severe active inflammatory bowel disease.
- Citation: Rossi RE, Parisi I, Despott EJ, Burroughs AK, O'Beirne J, Conte D, Hamilton MI, Murray CD. Anti-tumour necrosis factor agent and liver injury: Literature review, recommendations for management. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(46): 17352-17359
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i46/17352.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i46.17352
Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), including Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC), are a heterogenous group of chronic immune disorders of unclear aetiology. There are approximately 240000 patients with IBD in the United Kingdom (UC: 243/100000 = 146000 people; CD: 145/100000 = 87000 people)[1]. People affected by IBD show a life-time risk for surgery of 70%-80% and 20%-30% for CD and UC, respectively[2-6].
Therapy for IBD is a rapidly evolving field with many new biological agents that have shown promising results. Therapeutic options for IBD include corticosteroids, aminosalicylates, antibiotics (i.e., metronidazole and ciprofloxacin), thiopurines (i.e., azathioprine and mercaptopurine), methotrexate, ciclosporin, tacrolimus and anti-tumour necrosis factor (TNF) agents[1].
TNF-α is an integral pro-inflammatory cytokine, which is produced by macrophages and promotes the release of other inflammatory cytokines. It plays a key role in immune defense against infections and contributes to the development of certain cancers[7,8]. In view of its well known pro-inflammatory action, TNF-α has been identified as a key therapeutic target for treating inflammatory diseases including IBD[8].
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved several anti-TNF-α agents, such as infliximab (Remicade, Janssen), adalimumab (Humira, Abbott), etanercept (Enbrel, Amgen), certolizumab (Cimzia, UCB), and golimumab (Simponi, Janssen), for the treatment of several immunological conditions[9-13].
Some placebo-controlled trials have shown that infliximab[14,15], adalimumab[16-18] and certolizumab pegol[19] are efficacious in the treatment of moderate-to-severe CD, both when used as first-line therapy and in patients who did not respond to standard treatment. Anti-TNF agents have been reported to achieve disease remission, to maintain the treatment response[15,20-22], to allow tapering of glucocorticoids[15,16] and to promote mucosal healing[23]. Infliximab is also effective in the treatment of fistulizing CD[24] and, according to current data, early treatment with infliximab or adalimumab (within 4 wk after surgery) could prevent histologic and endoscopic recurrence after ileal resection[25,26].
As concerns UC, some randomized, controlled trials have shown that infliximab[27], adalimumab[28,29] and golimumab[30] can induce and maintain clinical remission in patients with moderate-to-severe disease activity who failed to respond to standard therapy. In particular, data suggest that infliximab reduces the rate of colectomy after one year from 17% in the placebo group to 10% in those treated with infliximab[31]. Adverse effects of anti-TNF agents include acute infusion reactions (10%), severe infusion reactions (less than 1%), including anaphylaxis, convulsions, erythematous rash, and hypotension, serum sickness and leukocytoclastic vasculitis (< 1 per 1000 patients), neurologic events (e.g., demyelinating neuropathy) (< 1 event per 1000 patients), risk of opportunistic infections, and reactivation of latent tuberculosis and/or hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection[32]. According to some studies, the risk of specific cancers (i.e., non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, lung cancer, skin cancer, and others) may be increased by the combinations of glucocorticoids, immunomodulators, and TNF inhibitors[32].
All of the TNF-antagonists currently marketed have been associated with drug-induced liver injury (DILI)[33,34]. According to a FDA post-marketing surveillance program, more than 130 reports of hepatic damage resulting from either infliximab or etanercept treatment have been reported. Among these, seven cases showed a strong association with the anti-TNF agents[35]. Of relevance, the use of TNF inhibitors has been associated with the risk of reactivation of viral hepatitis B, although the exact underlying mechanism is still far from being fully elucidated. Accordingly, pre-treatment screening for hepatitis B is required prior to start anti-TNF therapy and vaccination should be encouraged in the non-immune high-risk patients[36]. In addition, TNF inhibitor therapy may result in a wide range of liver abnormalities, including transient and self-limiting hypertransaminasemia, cholestatic disease and hepatitis.
The optimal management of liver injury related to anti-TNF therapy is still a matter of debate. Although some authors recommend discontinuation of treatment in case of both a rise of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) of more than five times the upper limit of normal (ULN), or the occurrence of jaundice[37-39], at present there are no standard guidelines for the management of anti-TNF-related liver injury. Herein, we propose an algorithm for the management of liver impairment occurring during anti-TNF treatment, according to both current evidence from literature and our own centre experience.
Bibliographical searches were performed in PubMed, using the following key words: inflammatory bowel disease; TNF inhibitors; hypertransaminasemia; drug-related liver injury; infliximab. Reference lists from studies selected by the electronic search were manually searched to identify further relevant reports. Reference lists from all available review articles, primary studies and proceedings of major meetings were also considered. No language restriction was applied.
Regarding our own centre experience, 305 patients with a histologically confirmed diagnosis of IBD were retrospectively evaluated. Laboratory and clinical data were retrieved from a database at Department of Gastroenterology, Royal Free Hospital, London. Patients with known liver related disease were excluded. Of these 305 patients, 176 consecutive patients were treated with infliximab, between 2008 and 2013, at the standard regimen dose of 5 mg/kg at weeks 0, 2, 6 and every 8 wk thereafter. Baseline laboratory parameters were obtained the day before infliximab induction and full blood count and liver biochemistry were monitored every 8 wk thereafter. Liver enzymes were recorded until each patient’s last follow-up. The same parameters were recorded from a control group of IBD patients, who did not receive any anti-TNF agent and were matched by gender, type of IBD and duration of follow-up to the study group.
Elevation of ALT/AST, usually between 2 and 3xULN is not uncommon during anti-TNF treatment with a reported prevalence of 37%-42% compared with 29%-36% in control groups[40], but rarely results in liver failure[41]. However, liver damage including hepatitis or cholestasis might be a complication of anti-TNF treatment[42-53] and cases of acute liver failure[54-58], fulminant hepatitis B infection[36,57,58] as well as severe liver injury requiring emergency liver transplantation have been reported[39,59]. Induction of auto-immune/immuno-mediated hepatitis in patients with IBD[60-71] has also been reported. Anti-TNF hepatitis, although rare, might be a life-threatening complication, which needs to be promptly recognized and treated. However, according to a recent systematic review, these agents are generally considered to be safe in the majority of patients, including those with underlying liver disease (i.e., chronic hepatitis C), whereas the risk of activation of hepatitis B needs to be taken into account[72,73].
The underlying mechanism for liver toxicity associated with anti-TNF remains to be elucidated. Pre-existing liver disease and concomitant potentially hepatotoxic drugs may increase the risk. Infliximab hepatitis seems to be sustained by an immuno-mediated mechanism, mimicking the characteristics of autoimmune hepatitis type I, although a direct liver damage cannot be ruled out[48,50]. Additionally, anti-TNF treatment is known to induce lipid profile changes[74-77], which may be reflected in a increased risk of liver steatosis, although the importance of these alterations needs to be clarified in future studies. Furthermore, whether infliximab immuno-mediated liver injury may lead to chronic disease, or ultimately resolve with treatment withdrawal remains to be fully elucidated.
According to our centre experience, 176 IBD patients were treated with infliximab between 2008 and 2013, with a mean duration of treatment of 23.1 ± 21.7 mo, and ALT increase was observed in 69 (39.2%) of them, with spontaneous resolution in 76% of cases. Approximately 50% of these patients were taking immunomodulators. When comparing the 67 patients who had elevated transaminases with the 107 patients on infliximab who showed persistent normal ALT, there were no statistically significant differences in terms of age, gender, diagnosis (UC or CD) and use of immunomodulators, aminosalicylates or steroids. 36.2% of patients with abnormal ALT during follow-up had elevated transaminases up to one year before infliximab induction, compared to 15% of those with normal liver enzymes (P = 0.002). The mean duration of anti-TNF treatment was significantly longer in patients with abnormal liver enzymes than in the subgroup of patients with normal transaminases (29.5 mo vs 11.5 mo, P < 0.0005). In multivariate analysis, abnormal ALT in the subgroup of patients treated with infliximab was significantly associated with elevated ALT prior to infliximab induction (OR = 3.854, 95%CI: 1.800-8.251, P = 0.001) and longer duration of infliximab treatment (OR = 1.030, 95%CI: 1.013-1.047, P = 0.001).
When considering a whole cohort of 305 IBD patients (176 patients treated with infliximab and 129 IBD patients matched for gender, type of IBD and length of follow-up as a control group), hypetransaminasemia was found in 36.4% of the patients and spontaneous resolution occurred in 73% of cases. Univariate and multivariate analysis showed that the treatment with immunomodulators was correlated to increased transaminases (OR = 2.666, 95%CI: 1.576-4.511, P < 0.001), whilst the use of infliximab, steroids or aminosalicylates, age, gender and diagnosis were not (P = NS).
Twelve patients treated with infliximab developed severe hypertransaminasemia (ALT > 3 x ULN). They were all screened for hepatitis A, B, C, for HIV and CMV serology and found negative. Immunoglobulin G, ferritin, alpha1- antitrypsin, copper, ceruloplasmin levels and coeliac screening were also normal. Alcohol intake was excluded. Three patients had positive antinuclear antibodies: one patient had concomitant lupus erythematosus (titer 1:80) and the remaining two showed a very low titer (1:40). Additionally, as they all had normal immunoglobulins, normal other autoantibodies and only transient hypertransaminasemia, they were not further investigated. A liver ultrasound was performed in all the patients, showing fatty liver in 4 patients. A liver biopsy was done in 3 out of 12 infliximab patients with persistent severe hypertransaminasemia and liver histopathology was suggestive of DILI in 2 patients and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in the remaining one. Of the two patients with established DILI one was on infliximab monotherapy (which was discontinued) and one on combination of infliximab and 6-mercaptopurine (6-MP, which was subsequently discontinued). The 12 patients were carefully monitored and hypertransaminasemia spontaneously resolved in 11/12 patients without discontinuation of anti-TNF treatment, whilst infliximab was stopped only in the patient with a confirmed diagnosis of DILI on liver biopsy.
The optimal management of liver injury related to anti-TNF therapy is still a matter of debate and a multidisciplinary management is required.
According to previous case reports and a recent consensus statement[39,62], it was recommended that infliximab therapy should be avoided or discontinued in patients with a raise of aminotransferases more than three times the ULN and that liver function tests should be determined prior to anti-TNF treatment, after induction treatment and at least every four months while on maintenance treatment. However, the application of the above mentioned precautions failed in systematic prevention of the development of severe liver injury[54]. Furthermore, such stringent criteria might deny anti-TNF to many patients who might benefit from it due to the lack of alternative therapeutic options.
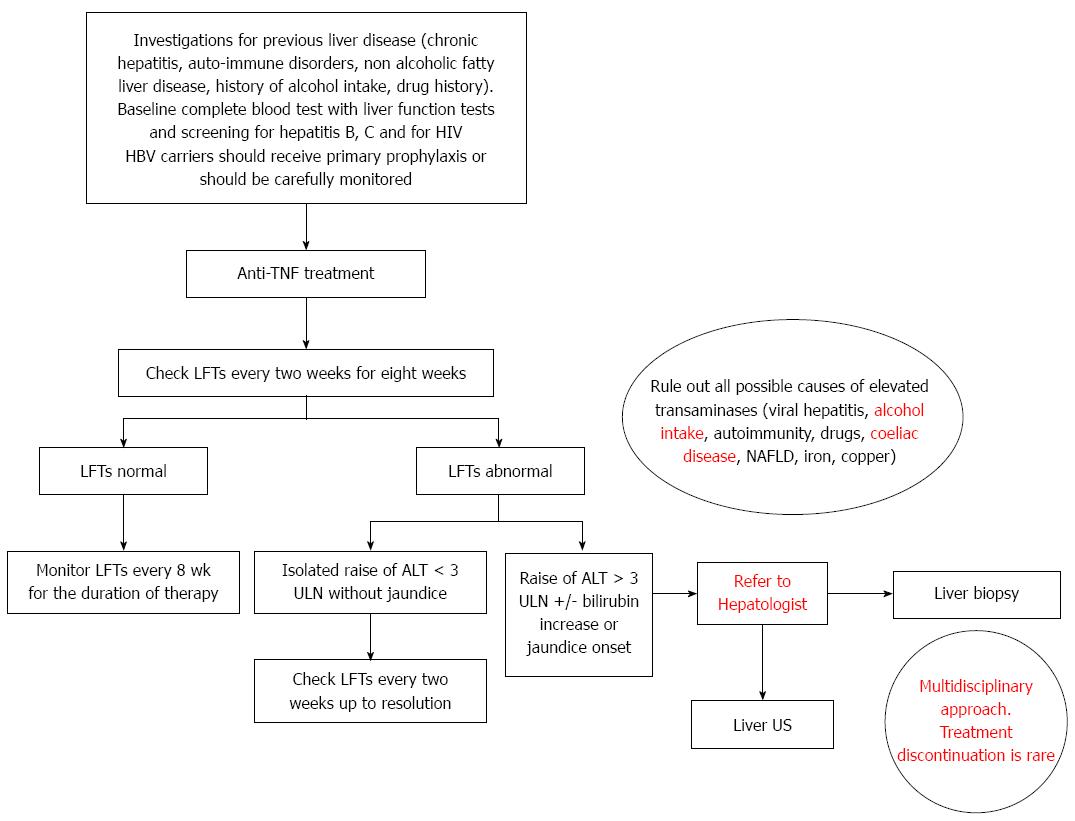
In view of the available literature and our own centre’s experience we suggest the following algorithm for the management of liver impairment occurring during anti-TNF treatment (Figure 1).
All patients should be aware of the potential problem of hepatotoxicity and should seek urgent medical advice in case they feel unwell or notice the presence of jaundice. Moreover, alcohol intake should be reduced, as per current recommendations[78].
Before starting anti-TNF treatment, all the patients should be investigated for previous liver disease including viral chronic hepatitis, auto-immune disorders, non alcoholic fatty liver disease, history of alcohol intake/abuse and/or of illicit drug use. A baseline complete blood test including liver function tests and screening for hepatitis B, C and for HIV is advisable. Risk of reactivation of hepatitis B should be taken into account and HBV carriers should receive primary prophylaxis or should be carefully monitored[79].
Liver function tests should be regularly performed after starting anti-TNF therapy, every two weeks for the first eight weeks, and eight weekly thereafter.
In those patients receiving anti-TNF therapy and with abnormal transaminase levels, the first step is to rule out all other possible causes of hypetransaminasemia, including viral hepatitis, history of alcohol abuse, auto-immune disorders, coeliac disease, non alcoholic fatty liver disease and drug history.
When facing with an increase of ALT < 3 x ULN repeated monitoring is advisable, even if further action might not be required. On the contrary, in case of marked elevation of ALT levels (> 3 x ULN) or alarm signs (e.g., rapid onset of jaundice), a multidisciplinary approach is required. Further tests, including a liver ultrasound scan, should be requested and in case of persistent elevated transaminases, a liver biopsy might be useful to confirm the diagnosis of DILI or to exclude other potential aetiologies, possibly suitable for specific treatment. Of course, DILI represents a relevant cause of liver impairment with significant morbidity and mortality[80]. Early diagnosis of DILI might be difficult[81,82] and is usually by exclusion[83]. Liver histology is considered helpful in strengthening the diagnosis or excluding other potential causes of liver injury and a recent study provided a standardized framework for systematic review and classification of pathological changes in liver biopsies[84]. Discontinuation of the treatment might be considered, but the decision should be tailored to each single patient, given the rarity of severe liver injury and the possibility of a spontaneous resolution of the elevation of transaminase levels. According to our centre experience, the spontaneous resolution of hypetransaminasemia despite continuing anti-TNF treatment, might suggest that severe liver injury due to anti-TNF therapy, although possible, is rare.
In conclusion, we have highlighted the lack of standard guidelines for the management of anti-TNF-related liver injury and, differently from previous reviews, we have proposed a possible algorithm for its management according to both evidence from literature and our own centre’s experience. Innovative aspects of our approach, which are not present in the algorithm previously suggested by Mancini et al[62], include: (1) a multidisciplinary approach for this subgroup of patients, which requires a close interaction between Hepatologists and Gastroenterolgists; (2) the continuation of the anti-TNF treatment which is usually possible, in view of the rarity of severe liver injury, the high percentage of spontaneous regression of the hypertransaminasemia and the lack of alternative medical options in case of severe active IBD. The decision should be tailored to each single patient; (3) a liver biopsy which is advisable prior to stopping treatment because it might be useful to confirm the diagnosis of DILI or to exclude other possible aetiologies which might benefit from specific therapy; and (4) the exclusion of other possible causes of hypetransaminasemia which should also include history of alcohol intake, coeliac disease screening[85] and careful evaluation of drug intake (other than anti-TNF treatment).
In summary, elevation of ALT in patients with IBD treated with anti-TNF is a common finding, but, even in case of moderate or severe ALT abnormalities, resolution appears to be the usual outcome. Anti-TNF agents appear to be safe with a low risk of causing severe DILI. In case of severe hypertransaminasemia a multidisciplinary approach is recommended but drug withdrawal seems to be an exception due to the rarity of severe liver injury.
P- Reviewer: Desai DC, Goossens N, Yuksel I S- Editor: Ma N L- Editor: A E- Editor: Ma S
| 1. | Mowat C, Cole A, Windsor A, Ahmad T, Arnott I, Driscoll R, Mitton S, Orchard T, Rutter M, Younge L. Guidelines for the management of inflammatory bowel disease in adults. Gut. 2011;60:571-607. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1045] [Cited by in RCA: 946] [Article Influence: 67.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Munkholm P, Langholz E, Davidsen M, Binder V. Disease activity courses in a regional cohort of Crohn’s disease patients. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1995;30:699-706. [PubMed] |
| 3. | Langholz E, Munkholm P, Davidsen M, Binder V. Course of ulcerative colitis: analysis of changes in disease activity over years. Gastroenterology. 1994;107:3-11. [PubMed] |
| 4. | Munkholm P, Langholz E, Davidsen M, Binder V. Intestinal cancer risk and mortality in patients with Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology. 1993;105:1716-1723. [PubMed] |
| 5. | Lennard-Jones JE, Shivananda S. Clinical uniformity of inflammatory bowel disease a presentation and during the first year of disease in the north and south of Europe. EC-IBD Study Group. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1997;9:353-359. [PubMed] |
| 6. | Winther KV, Jess T, Langholz E, Munkholm P, Binder V. Survival and cause-specific mortality in ulcerative colitis: follow-up of a population-based cohort in Copenhagen County. Gastroenterology. 2003;125:1576-1582. [PubMed] |
| 7. | Park HJ, Ranganathan P. TNF-alpha antagonism and cancer risk in rheumatoid arthritis: is continued vigilance warranted? Discov Med. 2012;13:229-234. [PubMed] |
| 8. | Mariette X, Matucci-Cerinic M, Pavelka K, Taylor P, van Vollenhoven R, Heatley R, Walsh C, Lawson R, Reynolds A, Emery P. Malignancies associated with tumour necrosis factor inhibitors in registries and prospective observational studies: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70:1895-1904. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 327] [Cited by in RCA: 300] [Article Influence: 21.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Humira (adalimumab) [U.S. package insert and full prescribing information]. Abbott Laboratories. Last revised December 2011. Accessed January 28, 2013. Available from: http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2011/125057s0276lbl.pdf.. |
| 10. | Enbrel (etanercept) [U.S. package insert and full prescribing information]. Amgen Wyeth, manufactured by Immunex. Last revised September 2011. Accessed January 28, 2013. Available from: http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2009/103795s5415lbl.pdf.. |
| 11. | Remicade (infliximab) [U.S. package insert and full prescribing information]. Janssen Biotech, Inc. Last revised October 2011. Accessed January 28, 2013. Available from: http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2011/103772s5295lbl.pdf.. |
| 12. | Cimzia (certolizumab) [U.S. package insert and full prescribing information].UCB Inc. Last revised April 2012. Accessed January 28, 2013. Available from: http://www.accessdata. fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2012/125160s0174lbl.pdf.. |
| 13. | Simponi (golimumab) [U.S. package insert and full prescribing information]. Janssen Biotech, Inc. Last revised December 2011. Accessed January 28, 2013. Available from: http: //www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2011/125289s0064lbl.pdf.. |
| 14. | Targan SR, Hanauer SB, van Deventer SJ, Mayer L, Present DH, Braakman T, DeWoody KL, Schaible TF, Rutgeerts PJ. A short-term study of chimeric monoclonal antibody cA2 to tumor necrosis factor alpha for Crohn’s disease. Crohn’s Disease cA2 Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1997;337:1029-1035. [PubMed] |
| 15. | Hanauer SB, Feagan BG, Lichtenstein GR, Mayer LF, Schreiber S, Colombel JF, Rachmilewitz D, Wolf DC, Olson A, Bao W. Maintenance infliximab for Crohn’s disease: the ACCENT I randomised trial. Lancet. 2002;359:1541-1549. [PubMed] |
| 16. | Colombel JF, Sandborn WJ, Rutgeerts P, Enns R, Hanauer SB, Panaccione R, Schreiber S, Byczkowski D, Li J, Kent JD. Adalimumab for maintenance of clinical response and remission in patients with Crohn’s disease: the CHARM trial. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:52-65. [PubMed] |
| 17. | Hanauer SB, Sandborn WJ, Rutgeerts P, Fedorak RN, Lukas M, MacIntosh D, Panaccione R, Wolf D, Pollack P. Human anti-tumor necrosis factor monoclonal antibody (adalimumab) in Crohn’s disease: the CLASSIC-I trial. Gastroenterology. 2006;130:323-333; quiz 591. [PubMed] |
| 18. | Sandborn WJ, Rutgeerts P, Enns R, Hanauer SB, Colombel JF, Panaccione R, D’Haens G, Li J, Rosenfeld MR, Kent JD. Adalimumab induction therapy for Crohn disease previously treated with infliximab: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2007;146:829-838. [PubMed] |
| 19. | Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, Stoinov S, Honiball PJ, Rutgeerts P, Mason D, Bloomfield R, Schreiber S. Certolizumab pegol for the treatment of Crohn’s disease. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:228-238. [PubMed] |
| 20. | Schreiber S, Khaliq-Kareemi M, Lawrance IC, Thomsen OØ, Hanauer SB, McColm J, Bloomfield R, Sandborn WJ. Maintenance therapy with certolizumab pegol for Crohn’s disease. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:239-250. [PubMed] |
| 21. | Lichtenstein GR, Thomsen OØ, Schreiber S, Lawrance IC, Hanauer SB, Bloomfield R, Sandborn WJ. Continuous therapy with certolizumab pegol maintains remission of patients with Crohn’s disease for up to 18 months. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;8:600-609. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 80] [Cited by in RCA: 82] [Article Influence: 5.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Sandborn WJ, Hanauer SB, Rutgeerts P, Fedorak RN, Lukas M, MacIntosh DG, Panaccione R, Wolf D, Kent JD, Bittle B. Adalimumab for maintenance treatment of Crohn’s disease: results of the CLASSIC II trial. Gut. 2007;56:1232-1239. [PubMed] |
| 23. | Neurath MF, Travis SP. Mucosal healing in inflammatory bowel diseases: a systematic review. Gut. 2012;61:1619-1635. [PubMed] |
| 24. | Sands BE, Anderson FH, Bernstein CN, Chey WY, Feagan BG, Fedorak RN, Kamm MA, Korzenik JR, Lashner BA, Onken JE. Infliximab maintenance therapy for fistulizing Crohn’s disease. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:876-885. [PubMed] |
| 25. | Aguas M, Bastida G, Cerrillo E, Beltrán B, Iborra M, Sánchez-Montes C, Muñoz F, Barrio J, Riestra S, Nos P. Adalimumab in prevention of postoperative recurrence of Crohn’s disease in high-risk patients. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18:4391-4398. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 66] [Cited by in RCA: 73] [Article Influence: 5.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Yoshida K, Fukunaga K, Ikeuchi H, Kamikozuru K, Hida N, Ohda Y, Yokoyama Y, Iimuro M, Takeda N, Kato K. Scheduled infliximab monotherapy to prevent recurrence of Crohn’s disease following ileocolic or ileal resection: a 3-year prospective randomized open trial. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2012;18:1617-1623. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 123] [Cited by in RCA: 122] [Article Influence: 9.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Rutgeerts P, Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, Reinisch W, Olson A, Johanns J, Travers S, Rachmilewitz D, Hanauer SB, Lichtenstein GR. Infliximab for induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:2462-2476. [PubMed] |
| 28. | Reinisch W, Sandborn WJ, Hommes DW, D’Haens G, Hanauer S, Schreiber S, Panaccione R, Fedorak RN, Tighe MB, Huang B. Adalimumab for induction of clinical remission in moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis: results of a randomised controlled trial. Gut. 2011;60:780-787. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 588] [Cited by in RCA: 671] [Article Influence: 47.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Sandborn WJ, van Assche G, Reinisch W, Colombel JF, D’Haens G, Wolf DC, Kron M, Tighe MB, Lazar A, Thakkar RB. Adalimumab induces and maintains clinical remission in patients with moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 2012;142:257-65.e1-3. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 817] [Cited by in RCA: 943] [Article Influence: 72.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, Marano C, Zhang H, Strauss R, Johanns J, Adedokun OJ, Guzzo C, Colombel JF, Reinisch W. Subcutaneous golimumab induces clinical response and remission in patients with moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 2014;146:85-95; quiz e14-5. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 563] [Cited by in RCA: 683] [Article Influence: 62.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Sandborn WJ, Rutgeerts P, Feagan BG, Reinisch W, Olson A, Johanns J, Lu J, Horgan K, Rachmilewitz D, Hanauer SB. Colectomy rate comparison after treatment of ulcerative colitis with placebo or infliximab. Gastroenterology. 2009;137:1250-1260; quiz 1520. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 332] [Cited by in RCA: 338] [Article Influence: 21.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Nielsen OH, Ainsworth MA. Tumor necrosis factor inhibitors for inflammatory bowel disease. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:754-762. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 231] [Cited by in RCA: 251] [Article Influence: 20.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 33. | Bezabeh S, Flowers CM, Kortepeter C, Avigan M. Clinically significant liver injury in patients treated with natalizumab. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2010;31:1028-1035. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 32] [Article Influence: 2.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 34. | Davern T. Hepatotoxicity of immunomodulator agents and the transplant situation. Drug-induced liver injury. New York: Informa Helathcare 2007; . |
| 35. | FDA. Briefing document: Arthritis Advisory Committee. Accessed November 2011. Available from: http://www.fda.gov/ohrms/dockets/ac/03/transcripts/3930T1.htm. |
| 36. | Esteve M, Saro C, González-Huix F, Suarez F, Forné M, Viver JM. Chronic hepatitis B reactivation following infliximab therapy in Crohn’s disease patients: need for primary prophylaxis. Gut. 2004;53:1363-1365. [PubMed] |
| 37. | Hoentjen F, van Bodegraven AA. Safety of anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy in inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2009;15:2067-2073. [PubMed] |
| 38. | Orlando A, Armuzzi A, Papi C, Annese V, Ardizzone S, Biancone L, Bortoli A, Castiglione F, D’Incà R, Gionchetti P. The Italian Society of Gastroenterology (SIGE) and the Italian Group for the study of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IG-IBD) Clinical Practice Guidelines: The use of tumor necrosis factor-alpha antagonist therapy in inflammatory bowel disease. Dig Liver Dis. 2011;43:1-20. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 107] [Cited by in RCA: 100] [Article Influence: 7.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 39. | Miehsler W, Novacek G, Wenzl H, Vogelsang H, Knoflach P, Kaser A, Dejaco C, Petritsch W, Kapitan M, Maier H. A decade of infliximab: The Austrian evidence based consensus on the safe use of infliximab in inflammatory bowel disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2010;4:221-256. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 68] [Cited by in RCA: 74] [Article Influence: 4.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 40. | FDA, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, Arthritis Advisory Committee. Safety of TNF Inhibitors, 4 March 2003 (Transcript). Accessed 18 September 2007. Available from: http://www.fda.gov/ohrms/dockets/ac/03/transcripts/3930T1.htm. |
| 41. | FDA. Guidelines for Industry-drug Induced Liver Injury: Premarketing Clinical Evaluation. Accessed 24 Oct 2007. Available from: http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/GuidanceComplianceRegulatoryInformation/Guidances/UCM174090.pdf. |
| 42. | Ierardi E, Valle ND, Nacchiero MC, De Francesco V, Stoppino G, Panella C. Onset of liver damage after a single administration of infliximab in a patient with refractory ulcerative colitis. Clin Drug Investig. 2006;26:673-676. [PubMed] |
| 43. | Menghini VV, Arora AS. Infliximab-associated reversible cholestatic liver disease. Mayo Clin Proc. 2001;76:84-86. [PubMed] |
| 44. | García Aparicio AM, Rey JR, Sanz AH, Alvarez JS. Successful treatment with etanercept in a patient with hepatotoxicity closely related to infliximab. Clin Rheumatol. 2007;26:811-813. [PubMed] |
| 45. | Soto-Fernández S, González-Carro P, De Pedro-Esteban A, Legaz-Huidobro ML, Pérez-Roldán F, Roncero García-Escribano O, Valbuena-González M, Ruiz-Carrillo F. [Infliximab-induced hepatitis in a patient with Crohn’s disease]. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;29:321-322. [PubMed] |
| 46. | Wahie S, Alexandroff A, Reynolds NJ. Hepatitis: a rare, but important, complication of infliximab therapy for psoriasis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2006;31:460-461. [PubMed] |
| 47. | Becker H, Willeke P, Domschke W, Gaubitz M. Etanercept tolerance in a patient with previous infliximab-induced hepatitis. Clin Rheumatol. 2008;27:1597-1598. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 20] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 48. | Kluger N, Girard C, Guillot B, Bessis D. Efficiency and safety of etanercept after acute hepatitis induced by infliximab for psoriasis. Acta Derm Venereol. 2009;89:332-334. [PubMed] |
| 49. | Thiéfin G, Morelet A, Heurgué A, Diebold MD, Eschard JP. Infliximab-induced hepatitis: absence of cross-toxicity with etanercept. Joint Bone Spine. 2008;75:737-739. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 47] [Cited by in RCA: 45] [Article Influence: 2.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 50. | Carlsen KM, Riis L, Madsen OR. Toxic hepatitis induced by infliximab in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis with no relapse after switching to etanercept. Clin Rheumatol. 2009;28:1001-1003. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 42] [Cited by in RCA: 36] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 51. | Ghabril M, Bonkovsky HL, Kum C, Davern T, Hayashi PH, Kleiner DE, Serrano J, Rochon J, Fontana RJ, Bonacini M. Liver injury from tumor necrosis factor-α antagonists: analysis of thirty-four cases. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;11:558-564.e3. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 173] [Cited by in RCA: 155] [Article Influence: 12.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 52. | Moum B, Konopski Z, Tufteland KF, Jahnsen J. Occurrence of hepatoxicicty and elevated liver enzymes in a Crohn’s disease patient treated with infliximab. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2007;13:1584-1586. [PubMed] |
| 53. | Poulin Y, Thérien G. Drug-induced hepatitis and lupus during infliximab treatment for psoriasis: case report and literature review. J Cutan Med Surg. 2010;14:100-104. [PubMed] |
| 54. | Kinnunen U, Färkkilä M, Mäkisalo H. A case report: ulcerative colitis, treatment with an antibody against tumor necrosis factor (infliximab), and subsequent liver necrosis. J Crohns Colitis. 2012;6:724-727. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 55. | Haennig A, Bonnet D, Thebault S, Alric L. Infliximab-induced acute hepatitis during Crohn’s disease therapy: absence of cross-toxicity with adalimumab. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 2010;34:e7-e8. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 16] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 56. | Caussé S, Bouquin R, Wylomanski S, Flamant M, Joubert M, Dréno B, Quéreux G. [Infliximab-induced hepatitis during treatment of vulvar Crohn’s disease]. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2013;140:46-51. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 57. | Ostuni P, Botsios C, Punzi L, Sfriso P, Todesco S. Hepatitis B reactivation in a chronic hepatitis B surface antigen carrier with rheumatoid arthritis treated with infliximab and low dose methotrexate. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003;62:686-687. [PubMed] |
| 58. | Michel M, Duvoux C, Hezode C, Cherqui D. Fulminant hepatitis after infliximab in a patient with hepatitis B virus treated for an adult onset still’s disease. J Rheumatol. 2003;30:1624-1625. [PubMed] |
| 59. | Tobon GJ, Cañas C, Jaller JJ, Restrepo JC, Anaya JM. Serious liver disease induced by infliximab. Clin Rheumatol. 2007;26:578-581. [PubMed] |
| 60. | Cravo M, Silva R, Serrano M. Autoimmune hepatitis induced by infliximab in a patient with Crohn’s disease with no relapse after switching to adalimumab. BioDrugs. 2010;24 Suppl 1:25-27. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 39] [Cited by in RCA: 38] [Article Influence: 2.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 61. | Arai O, Omoto K, Notohara K, Shibata N, Kuboki M, Ikeda H. [A case of infliximab-related liver damage -case report and literature review]. Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi. 2013;110:104-111. [PubMed] |
| 62. | Mancini S, Amorotti E, Vecchio S, Ponz de Leon M, Roncucci L. Infliximab-related hepatitis: discussion of a case and review of the literature. Intern Emerg Med. 2010;5:193-200. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 90] [Cited by in RCA: 75] [Article Influence: 5.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 63. | Saleem G, Li SC, MacPherson BR, Cooper SM. Hepatitis with interface inflammation and IgG, IgM, and IgA anti-double-stranded DNA antibodies following infliximab therapy: comment on the article by Charles et al. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44:1966-1968. [PubMed] |
| 64. | Germano V, Picchianti Diamanti A, Baccano G, Natale E, Onetti Muda A, Priori R, Valesini G. Autoimmune hepatitis associated with infliximab in a patient with psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005;64:1519-1520. [PubMed] |
| 65. | Ozorio G, McGarity B, Bak H, Jordan AS, Lau H, Marshall C. Autoimmune hepatitis following infliximab therapy for ankylosing spondylitis. Med J Aust. 2007;187:524-526. [PubMed] |
| 66. | Marques M, Magro F, Cardoso H, Carneiro F, Portugal R, Lopes J, Costa Santos C. Infliximab-induced lupus-like syndrome associated with autoimmune hepatitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2008;14:723-725. [PubMed] |
| 67. | Fairhurst DA, Sheehan-Dare R. Autoimmune hepatitis associated with infliximab in a patient with palmoplantar pustular psoriaisis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009;34:421-422. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 33] [Cited by in RCA: 30] [Article Influence: 1.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 68. | Doyle A, Forbes G, Kontorinis N. Autoimmune hepatitis during infliximab therapy for Crohn’s disease: a case report. J Crohns Colitis. 2011;5:253-255. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 30] [Cited by in RCA: 28] [Article Influence: 2.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 69. | Goldfeld DA, Verna EC, Lefkowitch J, Swaminath A. Infliximab-induced autoimmune hepatitis with successful switch to adalimumab in a patient with Crohn’s disease: the index case. Dig Dis Sci. 2011;56:3386-3388. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 30] [Cited by in RCA: 29] [Article Influence: 2.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 70. | Subramaniam K, Chitturi S, Brown M, Pavli P. Infliximab-induced autoimmune hepatitis in Crohn’s disease treated with budesonide and mycophenolate. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2011;17:E149-E150. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 24] [Cited by in RCA: 25] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 71. | Goujon C, Dahel K, Bérard F, Guillot I, Gunera-Saad N, Nicolas JF. Autoimmune hepatitis in two psoriasis patients treated with inflixmab. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;63:e43-e44. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 25] [Cited by in RCA: 26] [Article Influence: 1.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 72. | Viganò M, Degasperi E, Aghemo A, Lampertico P, Colombo M. Anti-TNF drugs in patients with hepatitis B or C virus infection: safety and clinical management. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2012;12:193-207. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 69] [Cited by in RCA: 69] [Article Influence: 4.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 73. | Carroll MB, Bond MI. Use of tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitors in patients with chronic hepatitis B infection. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2008;38:208-217. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 90] [Cited by in RCA: 93] [Article Influence: 5.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 74. | Antoniou C, Dessinioti C, Katsambas A, Stratigos AJ. Elevated triglyceride and cholesterol levels after intravenous antitumour necrosis factor-alpha therapy in a patient with psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis vulgaris. Br J Dermatol. 2007;156:1090-1091. [PubMed] |
| 75. | Spanakis E, Sidiropoulos P, Papadakis J, Ganotakis E, Katsikas G, Karvounaris S, Bizaki A, Kritikos H, Boumpas DT. Modest but sustained increase of serum high density lipoprotein cholesterol levels in patients with inflammatory arthritides treated with infliximab. J Rheumatol. 2006;33:2440-2446. [PubMed] |
| 76. | Castro KR, Aikawa NE, Saad CG, Moraes JC, Medeiros AC, Mota LM, Silva CA, Bonfá E, Carvalho JF. Infliximab induces increase in triglyceride levels in psoriatic arthritis patients. Clin Dev Immunol. 2011;2011:352686. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 14] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 77. | Koutroubakis IE, Oustamanolakis P, Malliaraki N, Karmiris K, Chalkiadakis I, Ganotakis E, Karkavitsas N, Kouroumalis EA. Effects of tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibition with infliximab on lipid levels and insulin resistance in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;21:283-288. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 35] [Cited by in RCA: 42] [Article Influence: 2.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 78. | European Association for the Study of Liver. EASL clinical practical guidelines: management of alcoholic liver disease. J Hepatol. 2012;57:399-420. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 454] [Cited by in RCA: 456] [Article Influence: 35.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 79. | European Association For The Study Of The Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines: Management of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol. 2012;57:167-185. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2323] [Cited by in RCA: 2401] [Article Influence: 184.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 80. | Fontana RJ, Seeff LB, Andrade RJ, Björnsson E, Day CP, Serrano J, Hoofnagle JH. Standardization of nomenclature and causality assessment in drug-induced liver injury: summary of a clinical research workshop. Hepatology. 2010;52:730-742. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 234] [Cited by in RCA: 235] [Article Influence: 15.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 81. | Lee WM, Senior JR. Recognizing drug-induced liver injury: current problems, possible solutions. Toxicol Pathol. 2005;33:155-164. [PubMed] |
| 82. | Shapiro MA, Lewis JH. Causality assessment of drug-induced hepatotoxicity: promises and pitfalls. Clin Liver Dis. 2007;11:477-505, v. [PubMed] |
| 83. | Chalasani N, Fontana RJ, Bonkovsky HL, Watkins PB, Davern T, Serrano J, Yang H, Rochon J. Causes, clinical features, and outcomes from a prospective study of drug-induced liver injury in the United States. Gastroenterology. 2008;135:1924-1934, 1934.e1-4. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 624] [Cited by in RCA: 612] [Article Influence: 36.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 84. | Kleiner DE, Chalasani NP, Lee WM, Fontana RJ, Bonkovsky HL, Watkins PB, Hayashi PH, Davern TJ, Navarro V, Reddy R. Hepatic histological findings in suspected drug-induced liver injury: systematic evaluation and clinical associations. Hepatology. 2014;59:661-670. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 262] [Cited by in RCA: 292] [Article Influence: 26.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 85. | Volta U. Liver dysfunction in celiac disease. Minerva Med. 2008;99:619-629. [PubMed] |