Published online Dec 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i46.8770
Revised: September 23, 2013
Accepted: September 29, 2013
Published online: December 14, 2013
Processing time: 125 Days and 15.6 Hours
AIM: To investigate the epidemiology and characteristics of Barrett’s esophagus (BE) in China and compare with cases in the west.
METHODS: Studies were retrieved from the China National Knowledge Infrastructure and PubMed databases using the terms “Barrett” and “Barrett AND China”, respectively, as well as published studies about BE in China from 2000 to 2011. The researchers reviewed the titles and abstracts of all search results to determine whether or not the literature was relevant to the current topic of this research. The references listed in the studies were also searched. Inclusion and exclusion criteria for the literature were appropriately established, and the data reported in the selected studies were analyzed. Finally, a meta-analysis was performed.
RESULTS: The current research included 3873 cases of BE from 69 studies. The endoscopic detection rate of BE in China was 1%. The ratio of male to female cases was 1.781 to 1, and the average age of BE patients was 49.07 ± 5.09 years. Island-type and short-segment BE were the most common endoscopic manifestations, accounting for 4.48% and 80.3%, respectively, of all cases studied. Cardiac-type BE was observed in 40.0% of the cases, representing the most common histological characteristic of the condition. Cancer incidence was 1.418 per 1000 person-years.
CONCLUSION: Average age of BE patients in China is lower than in Western countries. Endoscopic detection and cancer incidence were also lower in China.
Core tip: Barrett’s esophagus (BE) is a precursor of esophageal adenocarcinoma. Western countries have published more research on BE than China has. Thus, epidemiological knowledge of BE in China is inadequate. Diagnosis and treatment of BE in China is based on western criteria, therefore, diagnosis, monitoring, and treatment of BE require more data based on the unique characteristics of patients and clinics in China. The current research analyzed 69 clinical studies to obtain a comprehensive understanding of BE in China. Results provide important guidelines that can help improve the treatment and follow-up of BE patients in China.
- Citation: Dong Y, Qi B, Feng XY, Jiang CM. Meta-analysis of Barrett’s esophagus in China. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(46): 8770-8779
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i46/8770.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i46.8770
Barrett’s esophagus (BE) is a pathological phenomenon that occurs when the stratified squamous epithelium in the lower esophagus is replaced by a metaplastic simple columnar epithelium. In some cases, BE is accompanied by intestinal metaplasia, which is considered a precursor of esophageal adenocarcinoma[1]. Academics in Western countries have conducted more research on the subject than researchers in China. As such, despite the attention BE has drawn in recent years, epidemiological knowledge of BE in China is insufficient. The Digestive Disease Branch of the Chinese Medical Association drafted the Diagnosis and Treatment Consensus[2] of BE in 2005 and amended it in 2011, when a consensus amongst clinicians was finally achieved[1]. This consensus on BE, however, is based on western standards. Thus, the diagnosis, monitoring, and treatment of BE in China require more data based on Chinese clinics.
Although increasing numbers of researchers in China have focused on BE, the studies published thus far do not feature large samples or prospective designs. A systematic review[3] of the clinical characteristics of BE in China was published in 2008. However, in this review, studies that used metaplasia as a necessary standard were not excluded, which contradicts the consensus. In addition, the sample sizes of some included studies are rather small, with reports featuring only one or two cases. The present study aims to obtain a comprehensive understanding of the characteristics of BE in China by conducting a meta-analysis on BE in China and comparing findings with cases in Western countries. Results will help improve the treatment and follow-up of Chinese BE patients.
Information from the China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) and PubMed databases were used. Clinical studies on BE published in Chinese between 2000 and 2011 were retrieved from the CNKI database, and those published in English were obtained from the PubMed database using the keywords “Barrett” and “Barrett AND China”, respectively. The researchers reviewed the titles and abstracts of all search results to determine whether or not the study was relevant to the current topic. The references listed in the studies obtained were also reviewed to locate additional studies.
The selected studies met the following criteria: (1) all of the cases described were from China; (2) diagnosis of BE conformed to standards set by the Digestive Disease Branch of the Chinese Medical Association in 2011; (3) BE was diagnosed through endoscopy and pathology; and (4) the number of cases included in the sample was > 10.
Studies were excluded if they featured any of the following criteria: (1) only published as an abstract; (2) intestinal metaplasia was used as a necessary diagnostic criteria; (3) the clinical aspects of BE were insufficient; that is, the study lacked at least three of the following aspects: endoscopic detection rate, sex, age, endoscopic manifestations, or histological type; (4) only a short segment of the study focused on BE; or (5) duplicate publication.
Four researchers independently extracted data from every study, and any ensuing disagreements were resolved through discussion. The following data were extracted: name of the first author; year of publication; region of study; total number of cases; male to female ratio of the patients; average age, endoscopic detection rate; proportion of each endoscopic and histological type; follow-up cases and follow-up duration; and occurrence of esophageal adenocarcinoma during follow-up.
Data were analyzed using SPSS version 17.0. Proportions were evaluated using standard formulas. A mean difference demonstrating a 95% confidence rate was used for continuous data. The total number of person-years during follow-up was calculated by multiplying the number of follow-up cases with the follow-up duration. Cancer incidence was calculated by dividing the number of occurrences of esophageal adenocarcinoma among the follow-up cases by the total number of person-years.
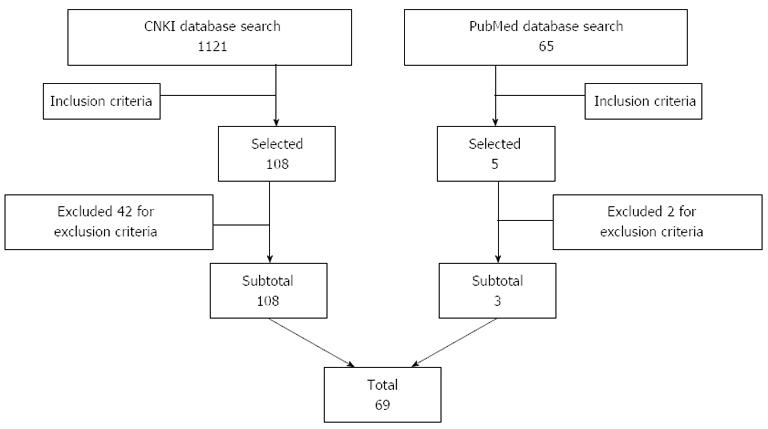
A total of 1121 studies were found in the CNKI database, and 108 of these studies met the inclusion criteria. Among these studies, 42 were rejected on the basis of the exclusion criteria; seven[4-10] for using intestinal metaplasia as a necessary diagnostic standard; 28[11-38] for having insufficient data on the clinical aspects of BE; four[39-42] for providing only a small study on BE; and one each for inconsistent data[43], doubts about plagiarism[44] and duplicate publication[45]. A total of 65 studies were found in the PubMed database; five of which met the inclusion criteria. Among these studies, one[46] was excluded because of its duplicate publication in Chinese, and another[47] was excluded for its use of intestinal metaplasia as a necessary diagnostic standard. A total of 69[48-116] studies were included in the present research. The screening process is summarized using the flow diagram shown in Figure 1.
The 69 studies included in the present research were conducted in 25 provinces. The total number of samples in these studied was 12404, and the total number of cases was 3873 (Table 1).
| Ref. | Year of publication | Region (province) | Cases | Male | Female | Mean age (yr) |
| Chen et al[48] | 2011 | Henan | 150 | 60 | 90 | 45.42 |
| Chen et al[49] | 2011 | Hubei | 52 | 31 | 21 | 49 |
| Guo et al[50] | 2011 | Hebei | 42 | 27 | 15 | 48 |
| Han et al[51] | 2011 | Jilin | 30 | 21 | 9 | 45 |
| Hao et al[52] | 2011 | Guangdong | 76 | 58 | 18 | 50.6 |
| Lin et al[53] | 2011 | Zhejiang | 41 | 28 | 13 | 58.9 |
| Lv et al[54] | 2011 | Zhejiang | 108 | 80 | 28 | 61 |
| Su et al[55] | 2011 | Hubei | 23 | 13 | 10 | 40.3 |
| Wang et al[56] | 2011 | Fujian | 113 | 67 | 46 | 54.5 |
| Zou et al[57] | 2010 | Guangxi | 23 | 16 | 7 | 50.3 |
| Xia et al[58] | 2010 | Hubei | 56 | 34 | 22 | 45.85 |
| Wu et al[59] | 2010 | Shanghai | 84 | 50 | 34 | 36.3 |
| Liu et al[60] | 2010 | Chongqing | 62 | 35 | 27 | 51 |
| Li et al[61] | 2010 | Anhui | 32 | 18 | 14 | 48.6 |
| Li et al[62] | 2010 | Guangdong | 45 | 18 | 27 | 43 |
| Hao et al[63] | 2010 | Henan | 144 | 98 | 46 | NA1 |
| Yao et al[64] | 2010 | Sichuan | 21 | 15 | 6 | 40.1 |
| Tang et al[65] | 2010 | Jiangxi | 63 | 43 | 20 | 45 |
| Shi et al[66] | 2010 | Fujian | 57 | 36 | 21 | 53 |
| Jia et al[67] | 2010 | Shanxi | 26 | 21 | 5 | 49 |
| Gao et al[68] | 2010 | Hubei | 32 | 21 | 11 | NA |
| Tian et al[69] | 2009 | Shandong | 59 | 43 | 16 | 49.14 |
| Li et al[70] | 2009 | Guangxi | 38 | 27 | 11 | 47.56 |
| Dai et al[71] | 2009 | Hunan | 23 | 18 | 5 | 50.3 |
| Bai et al[72] | 2009 | Chongqing | 67 | 41 | 26 | 50.7 |
| Yang et al[73] | 2009 | Shaanxi | 87 | 58 | 29 | 53.3 |
| Yang et al[74] | 2009 | Ningxia | 51 | 29 | 22 | 49.14 |
| Tan et al[75] | 2009 | Liaoning | 48 | 31 | 17 | 58.4 |
| Qiu et al[76] | 2009 | Fujian | 404 | 238 | 166 | 44.2 |
| Lu et al[77] | 2009 | Jiangsu | 12 | 9 | 3 | NA |
| Liu et al[78] | 2009 | Liaoning | 23 | 18 | 5 | 49 |
| Gao et al[79] | 2009 | Liaoning | 42 | 25 | 17 | NA |
| Peng et al[80] | 2009 | Guangdong | 27 | 14 | 13 | 48.18 |
| Wu et al[81] | 2008 | Henan | 25 | 16 | 9 | 48.3 |
| Wang et al[82] | 2008 | Henan | 12 | 10 | 2 | 49.5 |
| Wang et al[83] | 2008 | Ningxia | 109 | 64 | 45 | 50.11 |
| Lu et al[84] | 2008 | Guangxi | 32 | 22 | 10 | 52.5 |
| Gao et al[85] | 2008 | Shandong | 44 | 22 | 20 | 50 |
| Zhang et al[86] | 2008 | Jiangxi | 84 | 51 | 33 | 46 |
| Yang et al[87] | 2008 | Hebei | 74 | 40 | 34 | 52.6 |
| Jian et al[88] | 2008 | Yunnan | 68 | 51 | 17 | 52 |
| Ji et al[89] | 2008 | Jiangsu | 51 | 38 | 13 | 52.5 |
| Tseng et al[90] | 2008 | Taiwan | 12 | 9 | 3 | 61.6 |
| Zhang et al[91] | 2007 | Shandong | 30 | 24 | 6 | 52 |
| Meng et al[92] | 2007 | Liaoning | 21 | 13 | 8 | 54.6 |
| Duan et al[93] | 2007 | Henan | 54 | 38 | 16 | 51.6 |
| Zhou et al[94] | 2007 | Zhejiang | 13 | 7 | 6 | NA |
| Wang et al[95] | 2007 | Hubei | 88 | 61 | 27 | 47.46 |
| Li et al[96] | 2007 | Fujian | 75 | 45 | 30 | 45.42 |
| Jin et al[97] | 2007 | Zhejiang | 37 | 22 | 15 | 53 |
| Zhou et al[98] | 2006 | Hubei | 128 | 93 | 35 | NA |
| Yang et al[99] | 2006 | Shaanxi | 86 | 58 | 28 | 46 |
| Wu et al[100] | 2006 | Fujian | 13 | 10 | 3 | 48 |
| Wang et al[101] | 2006 | Shaanxi | 73 | 29 | 44 | 45.6 |
| Suo et al[102] | 2006 | Fujian | 37 | 24 | 13 | 50 |
| Li et al[103] | 2006 | Liaoning | 54 | 35 | 19 | 49 |
| Li et al[104] | 2006 | Tianjin | 37 | 25 | 12 | 58.3 |
| Dou et al[105] | 2006 | Guizhou | 89 | 57 | 32 | 46.3 |
| Wang et al[106] | 2006 | Hubei | 33 | 22 | 11 | 48 |
| Shu et al[107] | 2006 | Hubei | 13 | 12 | 1 | NA |
| Zheng et al[108] | 2005 | Hubei | 45 | 31 | 14 | NA |
| Liang et al[109] | 2005 | Xinjiang | 20 | 14 | 6 | NA |
| Zhang et al[110] | 2004 | Shaanxi | 69 | 54 | 15 | 56.2 |
| Zhao et al[111] | 2003 | Shandong | 55 | 38 | 17 | 46.8 |
| Dong et al[112] | 2003 | Zhejiang | 32 | 23 | 9 | 48.8 |
| Zhang et al[113] | 2001 | Anhui | 14 | 11 | 3 | NA |
| Wang et al[114] | 2001 | Guangdong | 21 | 16 | 5 | 67.3 |
| Zhao et al[115] | 2000 | Shandong | 35 | 26 | 9 | NA |
| Yang et al[116] | 2000 | Beijing | 29 | 22 | 7 | 50 |
A total of 15 studies reported the endoscopic detection rate of BE, which was obtained from all patients who had undergone endoscopy. However, the detection rate varied significantly, with rates ranging from 0.06% to 17.65%. The total endoscopic detection rate was 1.0% (95%CI: 0.1%-1.8%).
All studies reported the sex of BE patients (Table 1). One study[85] was not included in this analysis because the sum of male and female patients was inconsistent with the reported total number of cases. The remaining 68 studies showed a total of 3829 cases with 2452 male patients, accounting for 64.0% of the sample (95%CI: 61.1%-67.0%), and 1377 female patients, accounting for 36.0% of the sample (95%CI: 33.0%-38.9%). The male to female ratio was 1.781 (95%CI: 1.552-2.009).
A total of 58 studies reported the age of the BE patients (Table 1), and the average age of the patients was 49.07 ± 5.09 years.
The endoscopic patterns of BE in 49 studies could be categorized into several types based on Herlihy criteria[117]: island, tongue, circumferential, and mixed. On the basis of the columnar epithelial length reported in 29 studies, BE was divided into long-segment BE (LSBE) (i.e., columnar epithelial metaplasia cells were involved in the entire circumference of the esophagus and the length of the segment was ≥ 3 cm) and short-segment BE (SSBE) (i.e., columnar epithelial metaplasia cells were not involved in the entire circumference of the esophagus or the whole circumference of esophagus was involved but the length of the segment was < 3 cm)[1] (Table 2).
| Type | Proportion | 95%CI |
| Island | 0.448 | 0.375-0.521 |
| Tongue | 0.262 | 0.204-0.320 |
| Circumferential | 0.247 | 0.190-0.303 |
| Mixed | 0.043 | -0.006-0.093 |
| SSBE | 0.803 | 0.771-0.835 |
| LSBE | 0.197 | 0.165-0.229 |
The histological type of BE was divided into the gastric-fundic, cardiac, and intestinal metaplasia types[1] (Table 3).
| Type | Proportion | 95%CI |
| Cardiac | 0.400 | 0.310-0.491 |
| Gastric-fundic | 0.325 | 0.227-0.422 |
| Intestinal Metaplasia | 0.272 | 0.226-0.318 |
| Mixed type | 0.003 | -0.002-0.008 |
Thirty-one studies reported follow-up information. The total number of follow-up cases was 1283, with a follow-up duration ranging from 3 mo to 3 years. The mean follow-up duration was 1.099 years. Three studies[80,91,95] focused only on the follow-up of atypical hyperplasia of BE; thus, these studies were not included in this analysis. The total number of person-years during follow-up was 1410. Among 1283 cases, only two developed esophageal adenocarcinoma during the follow-up period; these cases were reported in two studies[91,103]. Four cases were also detected with esophageal adenocarcinoma during follow-up, but the number of follow-up cases and follow-up times were not provided. Studies with these cases were excluded from this analysis. The cancer incidence of BE was 1.418 per 1000 person-years.
The present research included 69 studies. The total endoscopic detection rate of BE was 1.0%, consistent with the total BE morbidity rate in Asia (0.9%-1.2%) reported by Hou et al[118]. The endoscopic detection rate of BE in the reviewed studies ranged from 0.06% to 17.65%. Tseng et al[90] reported that the endoscopic detection rate of BE in Taiwan was 0.06%, which is much lower than the total detection rate observed in China. This variation may be attributed to their inclusion of upper gastrointestinal tract endoscopy in routine health maintenance programs, which can yield more reliable data on the prevalence of BE in local populations. The endoscopic detection rate of BE in most studies is based on patients who have undergone upper gastrointestinal tract endoscopy in a local hospital. These patients mainly suffer from several gastrointestinal symptoms such as regurgitation, heartburn, epigastric discomfort, nausea, vomiting, and eructation. Reports of such symptoms increase the detection rate of BE, so this result cannot represent the prevalence of BE in the general population.
In this research, the total endoscopic detection rate was lower than that reported in a meta-analysis in 2008[3] (2.39%), likely because of the increasing number of patients accepting endoscopy in recent years as a means of diagnosing and treating upper gastrointestinal tract diseases. Some patients opt to undergo endoscopic examination when experiencing upper gastrointestinal tract symptoms, while others choose endoscopy for routine health maintenance. Thus, the data do not provide sufficient evidence to conclude that the incidence of BE has declined in China.
The detection rate of BE in Western countries is 3%-8%[119], which is higher than that in China. Variations observed may be due to the following reasons: (1) variations in genetic and environmental factors; (2) western lifestyle and diet-related factors, such as visceral obesity, high-fat diet, and tobacco and alcohol consumption, which are risk factors for BE[118,120-133]; and (3) delayed recognition of BE in China, considering that current diagnostic standards are based on western practices and some Chinese doctors experience difficulties when diagnosing patients with BE.
In this research, the number of male BE patients was higher than that of female patients, which is similar to western reports[133]. The average age of onset of BE in this study was 49.07 years, whereas the average age in Western countries is 60 years[134,135]. Variations observed may be attributed to differences in the Chinese and western lifestyles.
The main types of endoscopic manifestations of BE include the island type and SSBE, which is similar to western reports[136]. Experts in the United States believe that LSBE and SSBE represent two different pathological changes and that the former is related to severe gastroesophageal reflux disease, which is common in older people. Although LSBE tends to increase the risk of cancer, no evidence today correlates the length of BE and cancer risk[137].
The number of cases of cardiac type BE was higher than that of other histological types in this research. Jankowski et al[138] reported that intestinal metaplasia progresses to cancer, and the Diagnosis and Treatment Consensus of BE of China (2011) regards intestinal metaplasia as a precursor of esophageal adenocarcinoma. Unfortunately, the reviewed studies present limited clinical and pathological data on intestinal metaplasia related to BE, considering Chinese researchers’ lack of knowledge on the topic. Some researchers believe that cancer formation is related to atypia of the epithelial instead of columnar epithelial metaplasia[139].
An individual with BE is estimated to be at 25-30 times greater risk of developing esophageal adenocarcinoma[140-143] than the general population. Cancer incidence was found to be 1.418 per 1000 person-years in the present study, which is lower than that in England (7.0 per 1000 person-years), United States (6.4 per 1000 person-years), and other European countries (5.6 per 1000 person-years)[144]. Thus, the cancer incidence of BE in China is lower than that in Western countries. The spectrum of BE characteristics differs significantly between the two regions.
Barrett’s esophagus (BE) is a precursor of esophageal adenocarcinoma. The Diagnosis and Treatment Consensus of BE in China is based on Western criteria. Epidemiological knowledge of BE in China is inadequate.
A large number of clinical studies on BE have been conducted in China but they do not feature large sample sizes or prospective designs. A systematic review of the clinical characteristics of BE in China was published in 2008. However, in this review, studies that used metaplasia as a necessary standard were not excluded, which contrasts the consensus.
The Digestive Disease Branch of the Chinese Medical Association drafted the Diagnosis and Treatment Consensus of BE in 2005 and amended it in 2011, when a consensus amongst clinicians was achieved. Based on this consensus, the present research analyzed existing clinical studies with the aim of obtaining a comprehensive understanding of the characteristics of BE in China.
This research analyzed existing clinical studies with the aim of understanding the characteristics of BE in China. The results obtained will help improve the treatment and follow-up protocols of BE patients in China.
BE is a pathological phenomenon that occurs when the stratified squamous epithelium in the lower esophagus is replaced by a metaplastic simple columnar epithelium. In some cases, BE is accompanied by intestinal metaplasia, which is considered a precursor of esophageal adenocarcinoma.
This research has a high degree of significance. The meta-analysis presented here reviews the characteristics of the BE cases in China, including patient demographics, endoscopic and histological features, and risks for developing adenocarcinoma. The inclusion and exclusion criteria are appropriate, and the information obtained from selected reports is sufficiently analyzed.
P- Reviewers: Kastelein F, Sharma P S- Editor: Qi Y L- Editor: Kerr C E- Editor: Liu XM
| 1. | Digestive disease association, Chinese medical association. Diagnosis and Treatment Consensus of Barrett's Esophagus (June, 2011 Chongqing). Weichangbingxue He Ganbingxue Zazhi. 2011;29:1-2. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 2. | Digestive disease association, Chinese medical association. Diagnosis and Treatment Consensus of Barrett's Esophagus (2005). Weichangbingxue He Ganbingxue Zazhi. 2006;15:80-81. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 3. | Chen X, Zhu LR, Hou XH. Analysis of Clinical Characteristics of Chinese Barrett‘s Esophagus. Weichangbingxue He Ganbingxue Zazhi. 2008;17:102-105. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 4. | Wu YF, Liu H, Li YX, Hu W, Zhou XL, Mao DH, Shi ZH. Clinical Observation of Argon Plasma Coagulation in Treatment of Barrett's Esophagus by Staining Magnifying Endoscopy. Neike Jiwei Zhongzheng Zazhi. 2009;15:154-155. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 5. | Bai M, Liu ZH. Clinical Study of Argon Plasma Coagulation Combined with Omeprazole on Barrett's Esophagus. Chongqing Yixue Zazhi. 2009;38:415-416. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 6. | Xiong LS, Cui Y, Wang JP, Wang JH, Xue L, Hu PJ, Chen MH. The Study of Diagnostic Criteria of Barrett's Esophagus. Zhongguo Xiaohua Neijing. 2008;2:33-36. |
| 7. | Yu Y, Huang ZH, He GH. Endoscopic Finding and Clinical Analysis of Barrett's Esophagus. Nongken Yixue. 2006;28:152-153. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 8. | Xue HB, Ge ZZ, Chen XY, Hu YB, Xiao SD, Mo JZ, Gao YJ, Song Y, Liu Y. Effect of Argon Plasma Coagulation on the Barrett's Esophagus. Zhonghua Xiaohua Neijing Zazhi. 2006;23:3-6. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 9. | Wang Y, Liu XF. Discuss about Diagnosis of Barrett's Esophagus. Zhonghua Xiaohua Neijing Zazhi. 2003;20:339-340. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 10. | Zhang J, Zhang SS, Luo JY, Gong J, Wang XQ, Zuo AL. Barrett's Esophagus: Clinical Study. Zhonghua Xiaohua Neijing Zazhi. 2001;18:15-18. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 11. | Bao Y, Xia XH. Clinical Observation of Radio Frequency Combining Acid Suppression in Endoscopic Treatment of Barrett's Esophagus. Zhongguo Dangdai Yiyao Qikan. 2011;18:24-25. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 12. | Jin GF, Tang Y. The Value of Narrow-band Imaging (NBI) in the Diagnosis of Barrett's Esophagus. Zhongguo Shequ Yishi. 2011;27:204. |
| 13. | Ma AB. Study of Endoscopic Elastic Band in Treatment of Barrett's Esophagus. Yunnan Yiyao. 2011;32:496-497. |
| 14. | Sun L, Qiu M, Xu R, Li X. 35 Cases of Barrett's Esophagus Clinical Pathology. Jilin Yiyao. 2011;32:7080-7081. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 15. | Wen F, Zhu JL, Huang JZ, Qu L, Hu HT. Clinical Analysis of Argon Plasma Coagulation Combined with Rabeprazole for Barrett's Esophagus. Jujie Shoushu Zazhi. 2011;20:394-395. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 16. | Wu HH, Zou HP, Du J. The Effective of Argon Plasma Coagulation for Treatment of Patients with Barrett's Esophagus. Wujing Yixueyuan Xuebao. 2011;20:213-214. |
| 17. | Yan S. Clinical Study of Argon Plasma Coagulation Treatment of Barrett's Esophagus under Magnifying Endoscopy. Zhongguo Yiyao Zhinan. 2011;9:7-8. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 18. | Zheng SJ, Zhang L, Zhang M, Yang LF. Argon Plasma Coagulation and Narrow Band Imaging Combined with Proton Pump Inhibitors in Diagnosis and Treatment of Barrett‘s Esophagus. Jiaotong Yixue. 2011;25:373-375. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 19. | Zhong YF, Fan LH, Liu J. High Frequency Electrocoagulation Combined with Rabeprazole and Hydrotalcitum in Treatment of Island-type Barrett's Esophagus. Shiyong Yixue Zazhi. 2011;27:3176-3177. |
| 20. | Htaj T, Zgl A. Prognosis Analysis of Argon Plasma Coagulation Combined with Proton Pump Inhibitors in Treatment of Barrett's Esophagus. Xinjiang Yiyao. 2010;40:13-16. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 21. | Wang RL, Hou L, Yang WX, Gu P. Argon Plasma Coagulation Combined with Acid Suppression and Prokinetics in Treatment of Barrett's Esophagus. Xiandai Yixue Weisheng. 2010;26:3112. |
| 22. | Liu ZX, Huang YX, Wen QS, Wang JJ, Zhao BM, Wang XX, Qin M, Zhao SG, Yang Q, Zhang SL. Clinical Analysis of Argon Plasma Coagulation in Treatment of Barrett's Esophagus in 118 Cases. Zhongguo Shiyong Zhenduan Zhiliao. 2010;24:53-54. |
| 23. | Wang W, Liu HF, Wen XD, Wu QP. Prospective Study on Argon Plasma Coagulation Combined with Drugs for the Treatment of Barrett‘s Esophagus. Zhongguo Shiyong Zhenduan Zhiliao. 2009;23:538-540. |
| 24. | Tang Y, Long XQ, Chen YJ, Yao Y. Clinical Study of Endoscopic Argon Plasma Coagulation and Acid Suppression for Treatment of Barret's Esophagus. Huaxi Yixue. 2009;24:664-665. |
| 25. | Sheng JW, Fan HZ, Gao XH, Xie P. Radio Frequency Combined with Weifuchun in Treatment of Barret's Esophagus. Jiangxi Zhongyiyao Zazhi. 2009;8:27-28. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 26. | Lv HY, Li ZW, Yao DH, He JT. Short-term Clinical Study of Argon Alasma Coagulation in Treatment of Barret's Esophagus in 23 Cases. Xinan Guofang Yixue. 2009;19:598-599. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 27. | Lao YY, Chen Z. Endoscopic Argon Alasma Coagulation in Treatment of Barret's Esophagus in 23 Cases. Guangxi Yike Daxue Xuebao. 2009;26:808-809. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 28. | Li HR, Mi CF, Cai YJ. High Frequency Electric Combining PPI, Anti-reflux and Mucosa-protection in Endoscopic Treatment of Barret’s Esophagus. Zhongguo Yiyao Zhinan. 2008;6:8-9. |
| 29. | Chen W, Hang ZH, Zhou XG. Clinical Study of Argon Alasma Coagulation Combined with Rabeprazole in Treatment of Barret‘s Esophagus. Zhonghua Quanke Yixue. 2007;5:344-345. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 30. | Li QX, Yin HK, Chen LJ. Effects of Esophageal Motility Abnormalities in Barret's Esophagus by Argon Alasma Coagulation Combined with Proton Pump Inhibitor. Zhongguo Yishi Jinxiu Zazhi. 2006;29:41-43. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 31. | Zhao L, Wen JL, Wang WJ. Clinical Effect of Radio Frequency (RF) Combining Acid Suppression and Anti-reflux in Endoscopic Treatment of Barret‘s Esophagus (BE). Wannan Yixueyuan Xuebao. 2006;25:204-206. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 32. | Liu YH, Yang XM, Wen ZW. Clinical Analysis of Argon Alasma Coagulation in Treatment of Barret‘s Esophagus in 16 Cases. Zhongguo Yishi Zazhi. 2006;8:1374-1375. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 33. | Zhong DJ, Hao Y, Li XC, Zhou XM. Plasma Endothelin and Calcition in Gene-related Peptide in Barrett's Esophagus. Disi Junyi Daxue Xuebao. 2005;26:665-666. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 34. | Zhu J, Huang JF, Bao BJ, Zhang XY. Clinical Effect of Argon Plasma Coagulation in Endoscopic Treatment of Barrett's Esophagus. Linchuang Huicui. 2005;20:541-543. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 35. | Zhao M, Meng GX. Treatment of Barrett's Esophagus with Compound Ligation and Acid Suppression. Linchuang Yixue. 2005;25:1-2. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 36. | Cui SZ, Zhang ZM, Hou ZB, Guo BM, Li XL. Clinical Experience about Diagnosis of Reflux Esophagitis and Barrett's Esophagus. Qinghai Yiyao Zazhi. 2004;34:55. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 37. | Liu AL, He S, Zhang HY, Liu JH, Liu DW. Clinical Pathological Analysis of Barrett's Esophagus in 36 Cases. Zhonghua Xiaohua Neijing Zazhi. 2002;19:100-101. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 38. | Fang DL, Ma ZS, Cheng QY, Yang HQ, Lv Y, Li ZH. Clinical Study on Reversal of Barrett's Esophagus with Acid Suppression and Microwave. Zhonghua Xiaohua Neijing Zazhi. 2001;8:207-209. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 39. | Yuan S, Shu JC, Liu SX. Comparative Study of High Frequency Electrocoagulation versus Argon Plasma Coagulation in the Treatment of Short-segment Barrett's Esophagus. X. iandai Xiaohua Ji Jieru Zhiliao. 2009;14:77-79. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 40. | OuYang JD, Gao J, Cheng LF. Endoscopic and Pathological Characteristics of Barrett's Esophagus. Zhongguo Weisheng Baojian Yiyao. 2008;10:35-37. |
| 41. | Ding BJ, Xu Z. Clinical Effect of Radio Frequency in Treatment of Short-segment Barrett's Esophagus. Zhongguo Neijing Zazhi. 2006;12:1289-1290. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 42. | Xu XR, Li ZZ, Zou DW, Xu GM, Sun ZX, Yin N. A Clinical Study of Short-segment Barrett's Esophagus. Zhonghua Xiaohua Zazhi. 2004;24:326-328. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 43. | He M, Yang LL. Endoscopic Clinical Diagnosis and Pathological Characteristic Analysis of Barrett's Esophagus. Zhongguo Xiandai Yisheng. 2010;48:25-26. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 44. | Qin GD, Zhang F. Analysis of Endoscopic and Clinical Features of Barrett's Esophagus. Changzhi Yixueyuan Xuebao. 2002;16:120-121. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 45. | Chen T, Song WX, Wang HJ, Li DH. Analysis of Endoscopic Argon Alasma Coagulation Combined with Esomeprazole in Treatment of Barret‘s Esophagus. Xibao Fenzi Mianyixue Zazhi. 2011;27:227-228. |
| 46. | Wang W, Zhang ZJ, Lin KR, Li DZ, Wen XD, Wu QP. The Prevalence, Clinical and Endoscopic Characteristics of Barrett‘s Esophagus in Fujian. Zhonghua Neike Zazhi. 2006;45:393-395. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 47. | Xiong LS, Cui Y, Wang JP, Wang JH, Xue L, Hu PJ, Chen MH. Prevalence and risk factors of Barrett’s esophagus in patients undergoing endoscopy for upper gastrointestinal symptoms. J Dig Dis. 2010;11:83-87. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 30] [Cited by in RCA: 29] [Article Influence: 1.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 48. | Chen CJ, You XD, Wang YQ. Clinical Analysis of Argon Alasma Coagulation Combined with Esomeprazole in Treatment of Barret's Esophagus in 100 Cases. Xiandai Xiaohua Jieru Zhiliao. 2011;16:55-57. |
| 49. | Chen T, Song WX, Duan J. Early Therapeutic Observation on the Treatment of Barrett's Esophagus with Argon Plasma Coagulation Combined with Esomeprazole. Weichang Yixue. 2011;6:102-104. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 50. | Guo HM, Cui BJ, Liu Y, Su B. Analysis of Barrett's Esophagus by Diagnosis of Endoscopy in 42 Cases. Zhongguo Wuzhenxue Zazhi. 2011;11:2959. |
| 51. | Han YG, Lin Y. Clinical Symptom, Endoscopic Feature and Pothological Analysis of Barrett's Esophagus in 30 Cases. Zhongguo Shiyong Yiyao. 2011;6:102-103. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 52. | Hao LP, Lai JY, Si HQ, Liu Q, Zhang XL, Lin YP, Gong FY. Clinical and Follow-up Analysis of Endoscopic Argon Alasma Coagulation Combined with Omeprazole of Barret's Esophagus in 30 Cases. Weichangbingxue Ji Ganbingxue Zazhi. 2011;20:429-431. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 53. | Lin ZM. Clinical Analysis of Barret's Esophagus in 30 Cases. Zhongguo Zhongxiyi Jiehe Xiaohua Zazhi. 2011;19:178-179. |
| 54. | Lv J, Ying Q. Endoscopic Analysis of Barret's Esophagus in 108 Cases. Zhongguo xiangcun Yiyao Zazhi. 2011;18:64. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 55. | Su Y, Wu J, Wang P, Sun SB. Effect of Argon Plasma Coagulation on the Barrett’s Esophagus. Zhongguo Neijing Zazhi. 2011;17:53-56. |
| 56. | Wang W, Liu HF, Li DZ, Zhang ZJ, Wen XD, Wu QP. Argon Plasma Coagulation Combined with Drugs for the Treatment of Barrett's Esophagus: a Prospective Study. Fuzhou Zhongyiyuan Xuebao. 2011;18:85-87. |
| 57. | Zou YB, Rao GH, Wer SL. Endoscopic Argon Plasma Coagulation Combined with Rabeprazole in Treatment of Barret‘s Esophagus. Hainan Yixue. 2010;21:60-61. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 58. | Xia YN, Luo HS, Li WS, Jiang HW, Huang CY, Tan P. The Clinical Effect of Argon Plasma Coagulation in Endoscopic Treatment of Barrett's Esophagus. Weichangbingxue He Ganbingxue Zazhi. 2010;19:459-461. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 59. | Wu WC, Xu Lm, Zhang L, Zhou M, Qv CY, Zhang Y, Chen Y. Comparative Study of Two Different Treatment Methods on Barrett's Esophagus. Weichangbingxue He Ganbingxue Zazhi. 2010;1:818-820. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 60. | Liu BL, Wang J, Wang JH. Effects of Argon Plasma Coagulation under Endoscopic on Barrett‘s Esophagus. Chongqing Yixue. 2010;39:2342-2343. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 61. | Li X, Wang ZH, Yang SF, Shi ZW, He Y, Xiao Q, Dai DZ, Bao DM. Clinical Observation of Radio-frequency Ablation (RFA) Combined with Esomeprazole Magnesium and Almagate Suspension in Treatment of 32 Cases of Barrett's Esophagus (BE). Anhui Yixue. 2010;31:1491-1493. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 62. | Li JS. Endoscopic Argon Plasma Coagulation in the Treatment of 45 Cases of Barrett's Esophagus. Xiandai Yiyuan. 2010;10:45-46. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 63. | Hao RC, Fang P, Feng LX, Song SJ, Liang J. Experience on the Endoscopic Diagnosis of Barrett's Esophagus in 144 Cases. Wujing Yixueyuan Xuebao. 2010;19:816-817. |
| 64. | Yao Y, Xu JY, Long XQ. Endoscopic Argon Plasma Coagulation for Barrett’s Esophagus: A Clinical Observation. Xinan Junyi. 2010;12:1057-1058. |
| 65. | Tang SL, Shi QH. Endoscopic and Clinical Analysis of Barrett's Esophagus in 63 Cases. Shiyong Linchang Yixue. 2010;11:29-30. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 66. | Shi H, Jiang SJ, Wang YG, Zhou D, Chen G, Cai H. Band Ligation-assisted Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for Barrett's Esophagus Killing Two Birds with One Stone. Zhonghua Linchuang Yishi Zazhi. 2010;4:410-413. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 67. | Jia YM, Zhang AZ. Clinical Endoscopic and Pathological Analysis of Barrett's Esophagus in 26 Cases. Changzhi Yixueyuan Xuebao. 2010;24:366-367. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 68. | Gao S, Chen X, Ding XW, Xu DQ, Chen XJ, Wang HX. Effects of Argon Plasma Coagulation Combined with Proton Pump Inhibitor on Barrett's Esophagus in 32 Cases. Zhonghua Shiyong Zhenduan Yu Zhiliao. 2008;22:726-728. |
| 69. | Tian Y, Li YQ. The Relationship of Pathology and Clinical, Endoscopic Characteristics in Barrett's Esophagus. Weichangbingxue He Ganbingxue Zazhi. 2009;18:728-731. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 70. | Li HQ, Bei GM, Yu TZ, Zhou Y, Zhang B, Zhang DQ. Clinical Observation of Argon Alasma Coagulation Combined with Plum Soup in Treatment of Barret's Esophagus. Sichan Zhongyi. 2009;27:69-71. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 18] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 71. | Dai J, Tang JX, Xie N, Xiong XL, Liu CY. Clinical Observation of Argon Plasma Coagulation or Radio Frequency Combining Acid Suppression in Endoscopic Treatment of Barrett's Esophagus. Linchuang Huicui. 2009;24:120-122. |
| 72. | Bai JY, Wang YQ, Zhao XY. Effect of Argon Plasma Coagulation on the Barrett's Esophagus. Jujie Shoushuxue Zazhi. 2009;18:165-166. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 73. | Yang Q, Wang JJ, Yang Y. Clinical Study of Argon Plasma Coagulation Treatment of Barrett's Esophagus Under Endoscopy. Weichangbingxue He Ganbingxue Zazhi. 2009;18:355-356. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 74. | Yang XM, Zhao CJ, Yu YH, Wang Y, Zhao J, Shen H, Hu SJ. Relationship Among Endoscopic Characteristics, Clinical Features and Pathologic Epithelial Types of Barrett's Esophagus. Ningxia Yixue Zazhi. 2009;31:605-606. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 75. | Tan JX. Clinical Experience of Argon Plasma Coagulation in Treatment of Barrett's Esophagus. Zhongguo Yiyao Zhinan. 2009;7:30-31. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 76. | Qiu QW, Lin CZ. Analysis on 404 Cases of Barrett's Esophagus. Xiandai Zhenduan Yu Zhliao. 2009;20:123-124. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 77. | Lu W, Zhang W. Effect of Argon Plasma Coagulation on the Barrett's Esophagus. Binzhou Yixueyuan Xuebao. 2009;32:44-46. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 78. | Liu XY, Zhang J. Clinical Analysis of 23 Cases of Barrett's Esophagus. Hebei Yixue. 2009;15:503-504. |
| 79. | Gao N, Wang CX, Liu MH, Wang MC. Correlation Between Magnifying Chromoendoscopic Classification and Histological Type of Barrett‘s Esophagus: a Clinical Study. Zhonguo Yike Daxue Xuebao. 2009;38:465-467. |
| 80. | Peng S, Cui Y, Xiao YL, Xiong LS, Hu PJ, Li CJ, Chen MH. Prevalence of erosive esophagitis and Barrett’s esophagus in the adult Chinese population. Endoscopy. 2009;41:1011-1017. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 66] [Cited by in RCA: 73] [Article Influence: 4.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 81. | Wu YW, Guo XK. Endoscopic Argon Alasma Coagulation Combined with Acid Suppression in Treatment of Barret's Esophagus. Shiyong Yiyao Zazhi. 2008;25:424. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 82. | Wang ZN. Clinical Observation of Esomeprazole Combined with Domperidone in Treatment of 12 Cases of Barret's Esophagus. Linchuang He Shiyan Yixue Zazhi. 2008;7:77. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 83. | Wang QH, Guo XN. Clinical Research of Barrett's Esophagus. Ningxia Yixue. 2008;30:202-204. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 84. | Lu Q. Clinical and Pathological Analysis of Barrett's Esophagus. Shiyong Zhenduan yu Zhiliao Zazhi. 2008;22:100-102. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 85. | Gao J, OuYang JD, Zhao ZD, Zhang XY. Analysis Endoscopic and Pathological Characteristics of Barrett's Esophagus. Xiandai Yixue. 2008;36:290-292. |
| 86. | Zhang C, Shi QH. Endoscopic and Pathological Analysis of 84 Cases of Barrett's Esophagus. Shiyong Linchuang Yixue. 2008;9:35-36. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 87. | Yang J, Zhao J. Analysis of Endoscopic and Pathological Characteristics of 74 Cases of Barrett's Esophagus. Zhongguo Wuzhenxue Zazhi. 2008;8:5440-5441. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 88. | Jian MS. Endoscopic Diagnosis of Barrett's Esophagus. Yunnan Yiyao. 2008;29:355. |
| 89. | Ji G, Yan ZP, Chen J, Wang XQ, Yu WZ, Tai SL. Clinical Observation of Endoscopic in Treatment of Barret's Esophagus. Linchuang Huicui. 2008;23:880-881. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 90. | Tseng PH, Lee YC, Chiu HM, Huang SP, Liao WC, Chen CC, Wang HP, Wu MS, Lin JT. Prevalence and clinical characteristics of Barrett’s esophagus in a Chinese general population. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2008;42:1074-1079. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 66] [Cited by in RCA: 60] [Article Influence: 3.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 91. | Zhang ZQ, Xu XJ. Clinical Analysis of 30 Cases of Barrett's Esophagus. Gongqi Yikan. 2007;20:26-27. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 92. | Meng XG, Wang ZY, Zhu DM. Analysis of 21 Cases of Barrett‘s Esophagus. Zhongguo Wuzhenxue Zazhi. 2007;7:605-606. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 93. | Duan SF, Gao CG. Analysis of Clinical Endoscopic and Pathological 54 Cases of Barrett's Esophagus. Zhongguo Wuzhenxue Zazhi. 2007;7:1072-1073. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 94. | Zhou XB, Ye LP, Ding JX, Lin MH. Clinical Observation of Endoscopic Argon Alasma Coagulation in Treatment of Barret's Esophagus in 13 Cases. Xinyixue. 2007;38:749-750. |
| 95. | Wang DR, Xu JY, Hou XH. The Clinical and Pathological Analysis of Barrett‘s Esophagus. Linchuang Xiaohuabing Zazhi. 2007;19:306-308. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 96. | Li DZ, Wang W, Zhang ZJ, Lin KR, Zhu JZ, Wen XD. Effect of Different Treatments on Barrett's Esophagus. Shandong Yiyao. 2007;47:16-18. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 97. | Jin ZC, Cai MY, Nie MW, Chen WX. Short-term Observation of Endoscopic Argon Alasma Coagulation in Treatment of Barret‘s Esophagus. Linchuang Yixue. 2007;27:42-43. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 98. | Zhou J, Shen ZY, Luo HS, Shen L, Liu J, Yang YM, Zou LP. Comparisons of Endoscopic and Pathological Characteristics Between Long and Short Segment Barret’s Esophagus. Zhonghua Xiaohua Zazhi. 2006;26:440-443. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 99. | Yang HY, Lei JK, Zhang MG, Han CL, Lu JX, Shi GM. Clinical Study of Barrett's Esophagus (BE). Xiandai Linchuang Yixue. 2006;32:168-170. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 100. | Wu YL. Clinical Analysis of 13 Cases of Barrett's Esophagus. Xiandai Xiaohua Ji Jieru Zhiliao. 2006;11:40-41. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 101. | Wang SL, Zhou Y, Ge FL. Clinical Analysis of Endoscopic Radio Frequency in Treatment of Barret's Esophagus in 73 Cases. Xibei Guofang Yixue Zazhi. 2006;27:138-139. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 102. | Suo B, Su PL. Analysis of Clinical and Endoscopic Characteristics of Barrett's Esophagus. Zhonghua Xiaohua Neijing Zazhi. 2006;23:291-292. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 103. | Li RK, Jiang CM. Clinical Analysis of 54 Cases of Barrett's Esophagus. Zhonghua Quanke Yishi Zazhi. 2006;5:304-306. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 104. | Li FL, Hu JZ, Han YS. Clinical Analysis of Barrett’s Esophagus in 37 Cases. Zhongguo Neijin Zazhi. 2006;12:1172-1173. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 105. | Dou XL, Chen WW, Du HT. Analysis of Endoscopic and Pathological Characteristics of Barrett’s Esophagus. Guizhou Yiyao. 2006;30:1011-1012. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 106. | Wang P, He XF. Clinical Analysis of 33 Cases of Endoscopic Barrett's Esophagus. Xianning Xueyuan Xuebao. 2006;20:132. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 107. | Shu Z. Stusy of Omeprazole in Treatment of Barret's Esophagus in 13 Cases. Linchuang He Shiyan Yixue Zazhi. 2006;5:915. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 108. | Zheng LD, Yang XP, Liu JS, Hou XH. Clinical Pathological Characteristics of Barrett’s Esophagus. Zhonghua Xiaohua Zazhi. 2005;25:496-497. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 109. | Liang Y. Clinical Analysis of 20 Cases of Barrett's Esophagus. Nongken Yixue. 2005;27:193-194. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 110. | Zhang J, Chen XL, Wang KM, Guo XD, Zuo AL, Gong J. Barrett’s esophagus and its correlation with gastroesophageal reflux in Chinese. World J Gastroenterol. 2004;10:1065-1068. [PubMed] |
| 111. | Zhao WD, Zhang WQ, Cui ZQ, Niu HZ. Analysis of Clinical, Endoscopic Characteristics and HP Detection Rate of 55 Cases of Barrett's Esophagus. Linchuang Neike Zazhi. 2003;20:305. |
| 112. | Dong LH, Chen LG, Wang WY. Link of Barrett‘s Esophagus and Helicobacter Pylori Infection. Yishi Jinxiu Zazhi. 2003;26:24-25. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 113. | Zhang GM. Clinical Analysis of 14 Cases of Barrett's Esophagus. Zhongguo Yejin Gongye Yixue Zazhi. 2001;18:211-212. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 114. | Wang YM, Xu HL, Xiong YM, Zheng GR. Endoscopic and Clinical Analysis of Barrett's Esophagus. Zhonghua Xiaohua Neijing Zazhi. 2001;18:363-364. |
| 115. | Zhao WD, Zhang WQ, Niu HZ, Niu Q. Analysis of Endoscopic Shape and HP Detection of 35 Cases of Barrett's Esophagus. Binzhou Yixueyuan Xuebao. 2000;23:349-350. |
| 116. | Yang HY, Zhang MG, Zhao HC. Analysis of 29 Patients with Barrett's Esophagus. Zhongri Youhao Yiyuan Xuebao. 2000;14:33-35. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 117. | Herlihy KJ, Orlando RC, Bryson JC, Bozymski EM, Carney CN, Powell DW. Barrett’s esophagus: clinical, endoscopic, histologic, manometric, and electrical potential difference characteristics. Gastroenterology. 1984;86:436-443. [PubMed] |
| 118. | Hou XH, Zheng LD, Wang DR. Pathogeny and Epidemiology of Barrett‘s Esophagus. Zhonghua Xiaohua Zazhi. 2006;26:114-115. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 119. | Casson AG, Williams L, Guernsey DL. Epidemiology and molecular biology of Barrett esophagus. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2005;17:284-291. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 120. | Fujiwara Y, Higuchi K, Watanabe Y, Shiba M, Watanabe T, Tominaga K, Oshitani N, Matsumoto T, Nishikawa H, Arakawa T. Prevalence of gastroesophageal reflux disease and gastroesophageal reflux disease symptoms in Japan. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005;20:26-29. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 75] [Cited by in RCA: 66] [Article Influence: 3.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 121. | Kuo CJ, Lin CH, Liu NJ, Wu RC, Tang JH, Cheng CL. Frequency and risk factors for Barrett’s esophagus in Taiwanese patients: a prospective study in a tertiary referral center. Dig Dis Sci. 2010;55:1337-1343. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 27] [Cited by in RCA: 29] [Article Influence: 1.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 122. | Park JJ, Kim JW, Kim HJ, Chung MG, Park SM, Baik GH, Nah BK, Nam SY, Seo KS, Ko BS. The prevalence of and risk factors for Barrett’s esophagus in a Korean population: A nationwide multicenter prospective study. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2009;43:907-914. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 54] [Cited by in RCA: 53] [Article Influence: 3.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 123. | Wong BC, Kinoshita Y. Systematic review on epidemiology of gastroesophageal reflux disease in Asia. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;4:398-407. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 148] [Cited by in RCA: 151] [Article Influence: 7.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 124. | Wu JC. Gastroesophageal reflux disease: an Asian perspective. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;23:1785-1793. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 70] [Cited by in RCA: 79] [Article Influence: 4.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 125. | Ma XQ, Cao Y, Wang R, Yan X, Zhao Y, Zou D, Wallander MA, Johansson S, Liu W, Gu Z. Prevalence of, and factors associated with, gastroesophageal reflux disease: a population-based study in Shanghai, China. Dis Esophagus. 2009;22:317-322. [PubMed] |
| 126. | Lagergren J. Etiology and risk factors for oesophageal adenocarcinoma: possibilities for chemoprophylaxis? Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2006;20:803-812. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 127. | Cook MB, Kamangar F, Whiteman DC, Freedman ND, Gammon MD, Bernstein L, Brown LM, Risch HA, Ye W, Sharp L. Cigarette smoking and adenocarcinomas of the esophagus and esophagogastric junction: a pooled analysis from the international BEACON consortium. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2010;102:1344-1353. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 247] [Cited by in RCA: 223] [Article Influence: 14.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 128. | Cook MB, Greenwood DC, Hardie LJ, Wild CP, Forman D. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the risk of increasing adiposity on Barrett’s esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol. 2008;103:292-300. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 101] [Cited by in RCA: 91] [Article Influence: 5.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 129. | Corley DA, Kubo A, Levin TR, Block G, Habel L, Zhao W, Leighton P, Quesenberry C, Rumore GJ, Buffler PA. Abdominal obesity and body mass index as risk factors for Barrett’s esophagus. Gastroenterology. 2007;133:34-41; quiz 311. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 263] [Cited by in RCA: 259] [Article Influence: 14.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 130. | Cook MB, Wild CP, Forman D. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the sex ratio for Barrett’s esophagus, erosive reflux disease, and nonerosive reflux disease. Am J Epidemiol. 2005;162:1050-1061. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 163] [Cited by in RCA: 165] [Article Influence: 8.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 131. | Kubo A, Levin TR, Block G, Rumore G, Quesenberry CP, Buffler P, Corley DA. Cigarette smoking and the risk of Barrett’s esophagus. Cancer Causes Control. 2009;20:303-311. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 41] [Cited by in RCA: 41] [Article Influence: 2.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 132. | Kubo A, Block G, Quesenberry CP, Buffler P, Corley DA. Effects of dietary fiber, fats, and meat intakes on the risk of Barrett’s esophagus. Nutr Cancer. 2009;61:607-616. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 45] [Cited by in RCA: 44] [Article Influence: 2.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 133. | Cameron AJ, Lomboy CT. Barrett’s esophagus: age, prevalence, and extent of columnar epithelium. Gastroenterology. 1992;103:1241-1245. [PubMed] |
| 134. | Caygill CP, Watson A, Reed PI, Hill MJ. Characteristics and regional variations of patients with Barrett’s oesophagus in the UK. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2003;15:1217-1222. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 21] [Cited by in RCA: 24] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 135. | Falk GW. Barrett’s esophagus. Gastroenterology. 2002;122:1569-1591. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 260] [Cited by in RCA: 253] [Article Influence: 11.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 136. | Csendes A, Smok G, Quiroz J, Burdiles P, Rojas J, Castro C, Henríquez A. Clinical, endoscopic, and functional studies in 408 patients with Barrett’s esophagus, compared to 174 cases of intestinal metaplasia of the cardia. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002;97:554-560. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 42] [Cited by in RCA: 49] [Article Influence: 2.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 137. | Sharma P, McQuaid K, Dent J, Fennerty MB, Sampliner R, Spechler S, Cameron A, Corley D, Falk G, Goldblum J. A critical review of the diagnosis and management of Barrett’s esophagus: the AGA Chicago Workshop. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:310-330. [PubMed] |
| 138. | Jankowski JA, Wright NA, Meltzer SJ, Triadafilopoulos G, Geboes K, Casson AG, Kerr D, Young LS. Molecular evolution of the metaplasia-dysplasia-adenocarcinoma sequence in the esophagus. Am J Pathol. 1999;154:965-973. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 300] [Cited by in RCA: 288] [Article Influence: 11.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 139. | Zhang YL. Endoscopic Biopsy Diagnosis of Barrett's Esophagus. Zhonghua Xiaohua Neijing Zazhi. 2006;23:69-71. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 140. | Solaymani-Dodaran M, Logan RF, West J, Card T, Coupland C. Risk of oesophageal cancer in Barrett’s oesophagus and gastro-oesophageal reflux. Gut. 2004;53:1070-1074. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 196] [Cited by in RCA: 207] [Article Influence: 9.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 141. | Cossentino MJ, Wong RK. Barrett’s esophagus and risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma. Semin Gastrointest Dis. 2003;14:128-135. [PubMed] |
| 142. | Wong A, Fitzgerald RC. Epidemiologic risk factors for Barrett’s esophagus and associated adenocarcinoma. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005;3:1-10. [PubMed] |
| 143. | Van der Veen AH, Dees J, Blankensteijn JD, Van Blankenstein M. Adenocarcinoma in Barrett’s oesophagus: an overrated risk. Gut. 1989;30:14-18. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 161] [Cited by in RCA: 148] [Article Influence: 4.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 144. | Yousef F, Cardwell C, Cantwell MM, Galway K, Johnston BT, Murray L. The incidence of esophageal cancer and high-grade dysplasia in Barrett’s esophagus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Epidemiol. 2008;168:237-249. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 287] [Cited by in RCA: 288] [Article Influence: 16.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |