Published online Nov 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i44.7830
Revised: September 12, 2013
Accepted: October 19, 2013
Published online: November 28, 2013
Processing time: 173 Days and 4.3 Hours
AIM: To understand the changes and development of World Journal of Gastroenterology (WJG) in recent years.
METHODS: The Journal Citation Report (JCR) and SCI-E database of the ISI Web of Knowledge were used to search the articles and data of related indices in WJG during 2008-2012. Bibliometric methods were used for statistical analysis of the author’s degree of collaboration, collaboration rate, the first author’s publications, high-productivity authors, the authors’ origins in each year; the distribution of the countries and journals of the authors citing WJG papers was also analyzed. In addition, the indices related to this journal in each year were compared with the data from 6 SCI journals in the field of gastroenterology in the 2012 volume.
RESULTS: A total of 4409 papers in WJG were examined in this study. For the period 2008-2012, the self-citation rate was 8.59%, 6.02%, 5.50%, 4.47% and 5.21%. Of a total of 3898 first authors, 3526 published 1 paper, 291 published 2 papers, 59 published 3 papers, and 22 published 4 or more papers. The origin of WJG authors covered the six continents, and the majority came from Asia, Europe and North America. The number of countries of origin of WJG authors was 65, 66, 61, 65 an 60 for the period 2008-2012. Authors from 66 countries cited a total of 3194 of the 4409 papers, and these citations were found in 1140 journals.
CONCLUSION: The results suggest that WJG has stayed on the track of normal international publication and all the indices of this journal are stable and reasonable.
Core tip: A total of 4409 articles were examined to explore the development of World Journal of Gastroenterology (WJG) during 2008-2012. Based on analysis of the relevant indices, this study not only discussed the development and changes of WJG in recent years, but also the characteristics of the published papers and the authors’ origins. Furthermore, we performed analyses involving several journals of gastroenterology. The results show that all the indexes of this journal are stable and reasonable, and WJG has developed into one of the important journals in the field of gastroenterology.
-
Citation: Yang H, Chen YX. Improvement analysis of article quality in
World Journal of Gastroenterology during 2008-2012. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(44): 7830-7835 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i44/7830.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i44.7830
Journal quality evaluation is an important subject of concern to both editors and readers. Although the evaluation indexes are frequently the citation data of the papers in a given journal such as the total citation frequency, impact factor and so on, paper publication data for the journal, such as the number of papers and authors’ origins can also reflect the journal’s academic status in the relevant disciplines. World Journal of Gastroenterology (WJG) is an English journal founded in 1995 and published by Baishideng Publishing Group. In 2005 and 2008, 2 papers analyzed the multiple indexes of WJG for the periods of 1998-2004 and 2001-2007, respectively[1,2]. Following the above 2 papers, this study compared and analyzed the various indexes of the papers published in WJG in each year from 2008-2012 and the citations of these papers. We also selected 6 internationally renowned journals of gastroenterology including American Journal of Gastroenterology, BMC Gastroenterology, Gastroenterology, Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology, Journal of Gastroenterology and Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology for comparative analysis of the relevant indexes with WJG. Based on analysis of the above indexes, this study intended to determine not only the development and changes of WJG in the past several years, but also the characteristics of the published papers and the origins of the authors of this journal.
The Journal Citation Report (JCR) of ISI Web of Knowledge[3] and SCI-E[4] database were employed. The JCR database was searched to identify the number of references, the number of self-citations, the self-citation rate, and other indicators in WJG during 2008-2012. The SCI-E database was retrieved to identify the papers included in WJG every single year from 2008 to 2012; in addition, the relevant items including Title, Author, Source, Document Type, Times Cited, and Addresses were analyzed. Bibliometric methods were utilized for statistical analysis of the author’s degree of collaboration, the collaboration rate, the first author’s productivity, high-production authors, the authors’ geographic areas and/or country related to this journal in each year; the distribution of the countries and journals for the authors citing WJG papers was also analyzed. In the meantime, the 2012 issues of American Journal of Gastroenterology, BMC Gastroenterology, Gastroenterology, Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology, Journal of Gastroenterology, Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology and WJG were retrieved and compared. The comparative indexes included the number of annual publications, the author’s degree of collaboration, the collaboration rate, the number of countries of origin for all the authors, the proportion of papers written by native authors, the impact factor in 2012, discipline ranking and self-citation rate. Meanwhile, comparative analysis with WJG was carried out to determine the relative performance of various indexes of WJG.
WJG published 48 issues yearly in 2008-2012, and during the period SCI-E indexed 1200, 964, 916, 762 and 1008 WJG items in the respective years, giving a total inclusion of 4850 items; the included 5 types of items were article, review, editorial, letter and biography. The number of indexed articles and reviews was 1112, 863, 813, 677 and 944 in the respective years, a total of 4409 papers. The results and conclusion of our research are from the analysis of these 4409 papers. Table 1 lists the number of references, the average number of references in each paper, the number of self-citations in the journal, the average number of self-citations and the self-citation rate.
| Year | No. of papers | No. of references | Average No. of references | No. of self-citations in the journal | The mean No. of self-citations in each paper | Self-citation rate |
| 2008 | 1112 | 40485 | 36.41 | 930 | 0.84 | 8.59% |
| 2009 | 863 | 29458 | 34.13 | 767 | 0.89 | 6.02% |
| 2010 | 813 | 29624 | 36.44 | 832 | 1.02 | 5.50% |
| 2011 | 677 | 25878 | 38.22 | 758 | 1.12 | 4.47% |
| 2012 | 944 | 37947 | 40.20 | 918 | 0.97 | 5.21% |
There were 26600 authors from 4409 papers. Table 2 lists the distribution of the number of co-authors (mono-authorship and co-authorship), and 3898 were first authors; 3526 (90.46% of 3898 first authors) published 1 paper, 291 (7.47%) 2 papers, 59 (1.51%) 3 papers, 11 (0.28%) 4 papers, and 11 (0.28%) 5 or more papers. Table 3 shows the authors who published 5 or more papers.
| Year | Distribution of number of co-author articles | Total (articles) | Authors | Cooperation degree | Cooperation rate | ||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | ≥11 | |||||
| 2008 | 49 | 96 | 91 | 147 | 154 | 167 | 111 | 121 | 63 | 42 | 71 | 1112 | 6501 | 5.85 | 95.59% |
| 2009 | 28 | 66 | 100 | 102 | 139 | 107 | 107 | 74 | 46 | 38 | 56 | 863 | 5072 | 5.88 | 96.76% |
| 2010 | 28 | 62 | 77 | 84 | 113 | 108 | 108 | 74 | 53 | 46 | 106 | 813 | 5037 | 6.20 | 96.56% |
| 2011 | 21 | 46 | 63 | 77 | 103 | 87 | 100 | 96 | 29 | 25 | 30 | 677 | 4034 | 5.96 | 96.90% |
| 2012 | 31 | 67 | 86 | 122 | 95 | 137 | 111 | 91 | 57 | 57 | 90 | 944 | 5956 | 6.31 | 96.72% |
| Total | 157 | 337 | 417 | 532 | 604 | 606 | 537 | 456 | 248 | 208 | 353 | 4409 | 26600 | 6.03 | 96.44% |
| Author | Institute | No. of papers of first authors | No. of papers of the communicating authors | No. of cited papers | Citation frequency |
| Freeman, Hugh James | Univ British Columbia Hosp, Canada | 22 | 22 | 22 | 133 |
| Tarantino, Giovanni | Univ Naples Federico II, Med Sch Naples, Italy | 7 | 9 | 7 | 42 |
| Ishikawa, Toru | Saiseikai Niigata Daini Hosp, Japan | 7 | 7 | 5 | 20 |
| Akbulut, Sami | Diyarbakir Educ and Res Hosp, Turkey | 7 | 8 | 5 | 18 |
| Hirasaki, Shoji | Sumitomo Besshi Hosp,and Kubo Hosp, Japan | 7 | 8 | 6 | 27 |
| Sporea, Ioan | Univ Med and Farm Timisoara, Romania | 5 | 5 | 5 | 52 |
| Katsinelos, Panagiotis | Cent Hosp, Greece | 5 | 5 | 4 | 19 |
| Lohsiriwat, Varut | Mahidol Univ, Siriraj Hosp, Thailand | 5 | 5 | 5 | 48 |
| Terada, Tadashi | Shizuoka City Shimizu Hosp, Japan | 5 | 5 | 3 | 41 |
| Sun, Long | Xiamen Univ, Affiliated Hosp 1, China | 5 | 0 | 4 | 37 |
| Lee, Tae Hoon | Soon Chun Hyang Univ, Coll Med, Cheonan Hosp, South Korea | 5 | 2 | 4 | 9 |
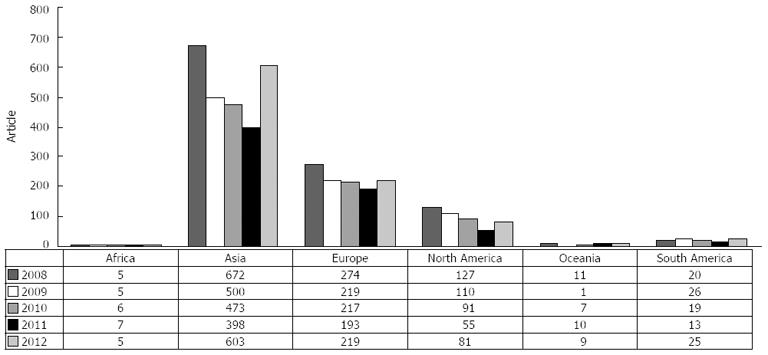
According to the 6 continents geographically, the authors’ addresses were mainly located in Asia, Europe and North America (Figure 1). Table 4 lists the number of papers published by authors of the top 15 countries. Of the top 15 countries, there were 5 countries in Asia, 7 in Europe, 2 in North America and 1 in South America.
| Country name | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | Total | Percentage |
| China | 361 | 276 | 290 | 240 | 365 | 1532 | 34.75% |
| Japan | 121 | 74 | 80 | 52 | 107 | 434 | 9.84% |
| United States | 94 | 79 | 74 | 49 | 69 | 365 | 8.28% |
| South Korea | 60 | 62 | 45 | 51 | 74 | 292 | 6.62% |
| Italy | 54 | 53 | 53 | 60 | 56 | 276 | 6.26% |
| Germany | 34 | 26 | 28 | 28 | 20 | 136 | 3.08% |
| Turkey | 48 | 33 | 19 | 19 | 12 | 131 | 2.97% |
| Spain | 31 | 35 | 13 | 16 | 21 | 116 | 2.63% |
| Greece | 30 | 15 | 18 | 15 | 7 | 85 | 1.93% |
| England | 23 | 18 | 16 | 9 | 17 | 83 | 1.88% |
| France | 20 | 12 | 14 | 8 | 13 | 67 | 1.52% |
| Brazil | 15 | 12 | 12 | 8 | 19 | 66 | 1.50% |
| Canada | 23 | 13 | 9 | 3 | 11 | 59 | 1.34% |
| Netherlands | 17 | 9 | 12 | 7 | 9 | 54 | 1.22% |
| Thailand | 13 | 5 | 11 | 6 | 11 | 46 | 1.04% |
| Total | 1305 | 998 | 984 | 811 | 1176 | 3742 | 84.87% |
Authors from 66 countries cited 3194 of the papers (72.44%), with a total of 19872 citations. The authors from the United States of America were the top and responsible for 4716 citations (23.73% of the total); authors from China ranked second and were responsible for 3088 citations (15.54%); the third was Japan with 1617 citations (8.14%). The top 15 countries were responsible for 18889 citations (95.06% of the total cited) (Figure 2). These citations were from 2083 journals, and the top 15 of these journals gave 3373 citations (16.97% of the total) (Table 5).
| No. | Name of the citing journals | Quantity |
| 1 | World J Gastroenterol | 1131 (5.69) |
| 2 | PLoS One | 430 (2.16) |
| 3 | Dig Dis Sci | 198 (1.00) |
| 4 | Gastrointest Endosc | 180 (0.91) |
| 5 | J Gastroenterol Hepatol | 171 (0.86) |
| 6 | Aliment Pharmacol Ther | 147 (0.74) |
| 7 | Inflamm Bowel Dis | 147 (0.74) |
| 8 | J Hepatol | 138 (0.70) |
| 9 | Hepatogastroenterology | 137 (0.69) |
| 10 | Endoscopy | 122 (0.62) |
| 11 | Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol | 120 (0.60) |
| 12 | Hepatology | 120 (0.60) |
| 13 | Gastroenterology | 114 (0.57) |
| 14 | Am J Gastroenterol | 110 (0.55) |
| 15 | Scand J Gastroenterol | 108 (0.54) |
| Total | 3373 (16.97) |
The data of the JCR database can be used to analyze the citation status of journals, we can evaluate the quality of the journals in each discipline. The Gastroenterology and Hepatology category of JCR 2012 Science Edition included 74 journals, and mean value of impact factor of these journals was 3.115. The 7 representative journals are American Journal of Gastroenterology, Gastroenterology, BMC Gastroenterology, Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology, Journal of Gastroenterology, Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology, and WJG; of these, 3 journals are from North America, 2 from Europe, and 2 from Asia. Table 6 lists the number of papers, author’s degree of collaboration, author’s collaboration rate, geographical distribution of the authors, proportion of articles contributed by domestic authors, 2012 impact factor (IF), discipline ranking of the journal by IF, and self-citation rate for these 7 journals in 2012.
| Journal name | Articles published in 2012 | Cooperation degree in 2012 | Cooperation rate in 2012 | Geographical distribution of authors | Ratio of articles contributed by domestic authors | 2012 impact factor | Ranking of discipline impact factors | Self-citation rate in 2012 |
| Am J Gastroenterol | 190 | 7.50 | 94.74 | 32 | United States 45.16 | 7.553 | 7 | 3.36 |
| BMC Gastroenterol | 165 | 7.35 | 98.79 | 36 | China 21.21 | 2.11 | 42 | 2.6 |
| Gastroenterology | 278 | 10.55 | 97.48 | 44 | United States 44.25 | 12.821 | 1 | 2.2 |
| J Clin Gastroenterol | 154 | 6.41 | 96.10 | 24 | United States 38.96 | 3.203 | 23 | 3.1 |
| J Gastroenterol | 140 | 9.53 | 98.57 | 22 | Japan 76.43 | 3.788 | 17 | 3.34 |
| Scand J Gastroenterol | 179 | 6.40 | 98.88 | 35 | Sweden 21.79 | 2.156 | 40 | 3.29 |
| World J Gastroenterol | 944 | 6.31 | 96.72 | 58 | China 35.67 | 2.547 | 34 | 5.21 |
The publishing frequency of WJG was stable during 2008-2012, without significant changes in the annual number of papers published and the average number of papers in each issue. The average number of references in each paper increased gradually while the self-citation rate decreased gradually year by year. When compared with 2004, the average number of references in each paper in 2012 increased by 8.9[1], while the self-citation rate per article decreased by 0.73[1] in 2012; all the indexes were in a satisfactory state.
The degree of collaboration increased slightly while the collaboration rate decreased slightly during 2008-2012. The collaboration degree for each respective year was 5.85, 5.88, 6.20, 5.96 and 6.31; the mean collaboration degree was 6.03 and increased by 0.15 when compared with 5.88 during 2001-2007[2]. The collaboration rate for each year was 95.59%, 96.76%, 96.56%, 96.90% and 96.72%; the mean collaboration rate was 96.44%. In contrast with the slight increase in collaboration degree during 2008-2012, the collaboration rate during this period decreased by 1.22% when compared with the 97.66% during 2001-2007.
The origin of the authors diversified and the proportion of authors with 1 paper increased, but the high-productivity authors did not increase. During 2008-2012, 3526 authors published 1 paper in WJG accounting for 90.46% of the total authors, and 22 authors published 4 papers or more accounting for 0.56%. The core author group of this journal has yet to increase.
The number of author geographic areas increased: the origin of WJG authors became increasingly diversified; the authors came from 87 countries across the 6 continents of the world. Asia, Europe and North America were the main origins of the authors; and the proportion of authors from Asia was relatively stable; the number of papers contributed by authors from Asia was 672 (60.60%), 500 (58.07%), 473 (58.18%), 398 (58.88%) and 603 (63.88%) in respective years. The number of authors from Europe and North America changed little in each year and only decreased slightly in 2012. The number of papers contributed by authors from North America was slightly higher when compared with the data during 2006-2007[2] but the number was slightly lower during 2011-2012. The number of author countries exceeded 60 in each year; these authors came from a total of 87 countries and/or regions. The origin of the first authors of WJG became increasingly diversified and the number of originating countries increased when compared with the data of the period of 2001-2007.
The distribution of the author countries tended to be balanced: authors from the top 15 countries published 3742 (84.87%) papers. The proportion of papers published by Chinese authors showed an annual incremental trend, which coincided with an overall increase in the number of scientific publications in China. The ranking of the top 15 countries have changed; the contemporary top 5 countries were China, Japan, United States, South Korea and Italy. The international trend in the origin of WJG authors increased significantly.
During 2008-2012, 72.44% of all WJG papers were cited; although the time factor of 2012 may be responsible for the relatively lower number of citations, and therefore affected the citation rate of WJG, but the rate reflected the fairly satisfactory quality of WJG papers. The authors citing these papers were distributed among 66 countries or regions; American authors were ranked first and accounted for 23.73%, while Chinese authors were ranked second and accounted for 15.54%. The significant impact of WJG around the world was evidenced by the fact that 1140 journals cited WJG papers, and the distribution of the citing journals was dispersed widely.
The changes in WJG in the past 5 years were compared with another 6 journals of gastroenterology at the same time. WJG had the highest number of annual publications; authors’ degree of collaboration in WJG was slightly lower than that of the other 6 journals, while the collaboration rate was within a reasonable range; the origin of WJG authors was the most diversified, and has gradually expanded from the predominant Chinese author group at the early stage to Asia and even the entire world across the 6 continents. Based on the data in JCR 2012, WJG ranked fifth of the 7 journals of gastroenterology; its self-citation rate declined and all other indexes were fairly reasonable.
In summary, WJG is attracting the attention of gastroenterologists globally, with authors scattered among 87 countries across the 6 continents. It has become a stage for gastroenterologists around the world to demonstrate their research findings. The author’s geographic areas and countries are widely distributed, and all the indexes of this journal are stable and reasonable. WJG has embarked onto the track of normal internationalized publication, although it is still necessary to cultivate the core author group for the journal to establish its stable research characteristics.
The paper publication data of a journal can reflect a journal’s academic status in the relevant disciplines, and the evaluation of journal quality is paid more and more attention by both editors and readers. In 2005 and 2008, two papers analyzed the multiple indices of World Journal of Gastroenterology (WJG) for the periods 1998-2004 and 2001-2007. Therefore, it was necessary to analyze the relevant indexes and make an objective evaluation of journal quality in recent years.
Although the evaluation indexes are frequently the citation data of the papers in a given journal such as the total citation frequency, impact factor and so on, the paper’s publication data of the journal such as the number of papers and author’s origin can also reflect the journal’s academic status in the relevant disciplines.
Based on analysis of the relevant indexes, the authors only studied the development and changes of WJG during 2008-2012, but also the characteristics of the published papers and the origin of the authors of this journal.
The results indicate that WJG has become an international publication, and gastroenterologists around the world can report their research findings in this journal.
The impact factor of a journal is a measure of the citations to science and social science journals, and is frequently used as a proxy for the importance of a journal to its field, with journals with higher impact factors deemed to be more important than those with lower ones.
Commendable effort. Much needed analysis to establish the position of WJG in the field of gastroenterology and hepatology. In this interesting paper, authors performed analyses involving several journals of gastroenterology. All aspects of comparison are presented sufficiently. Statistical analysis of the study made clear and demonstrate that WJG has developed into one of the important journals in the field of gastroenterology.
P- Reviewers: Gara N, Pavlovic M S- Editor: Wen LL L- Editor: Cant MR E- Editor: Zhang DN
| 1. | Ma LS, Pan BR, Li WZ, Guo SY. Improved citation status of World Journal Gastroenterology in 2004: Analysis of all reference citations by WJG and citations of WJG articles by other SCI journals during 1998-2004. World J Gastroenterol. 2005;11:1-6. [PubMed] |
| 2. | Yang H, Zhao YY. Variations of author origins in World Journal of Gastroenterology during 2001-2007. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14:3108-3111. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |