Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2012; 18(42): 6005-6017
Published online Nov 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i42.6005
Published online Nov 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i42.6005
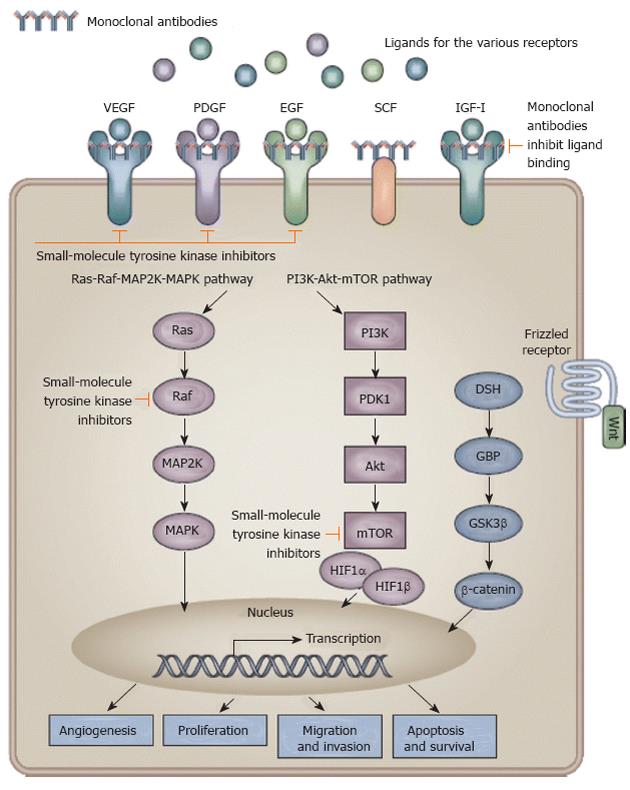
Figure 2 Signaling pathways and potential drug targets to inhibit hepatocarcinogenesis.
Activation of receptor tyrosine kinases by their ligands activates downstream signaling pathways with effects on angiogenesis, proliferation, migration and invasion, and apoptosis or survival of cells. Monoclonal antibodies inhibit ligand binding to the receptor and small-molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitors inhibit propagation of the downstream signal. (Cited from Spangenberg et al[11] with permission.) IGF: Insulin-like growth factor; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; EGF: Epidermal growth factor; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; PDGF: Platelet-derived growth factor; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; HIF: Hypoxia-inducible factor; SCF: Stem cell factor.
- Citation: Kudo M. Signaling pathway/molecular targets and new targeted agents under development in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(42): 6005-6017
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i42/6005.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i42.6005