Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 21, 2012; 18(35): 4934-4943
Published online Sep 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i35.4934
Published online Sep 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i35.4934
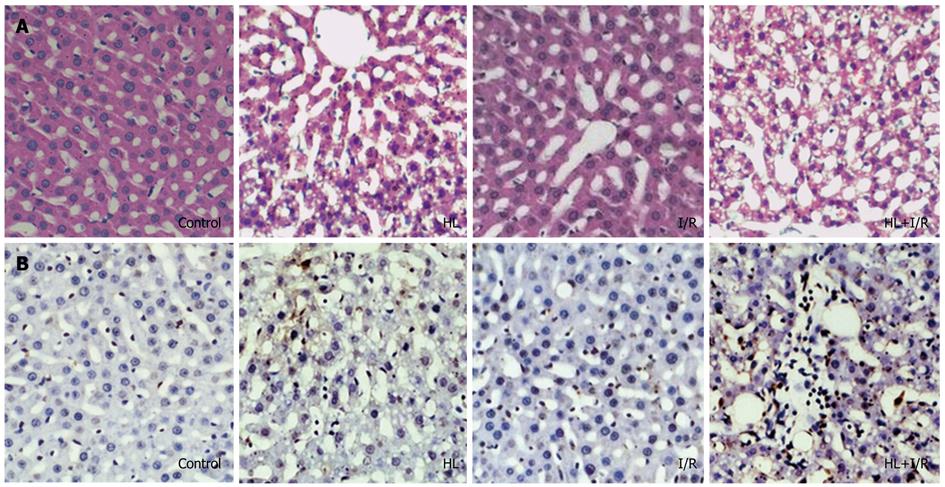
Figure 1 Histology and in situ apoptosis of liver sections from rats after high-fat diet treatment for 18 wk and/or 2 h transient focal cerebral ischemia followed by 24 h reperfusion.
A: HE staining showed liver damage in the hyperlipemia (HL) group and especially in the HL+ ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) group (× 200); B: Transferase dUTP nick-end labeling (TUNEL) staining showed TUNEL-positive apoptotic hepatocytes in the HL+I/R group are significantly greater than those in control, HL or I/R groups (× 200). Slides are representative of 6-10 animals per group.
- Citation: Gong WH, Zheng WX, Wang J, Chen SH, Pang B, Hu XM, Cao XL. Coexistence of hyperlipidemia and acute cerebral ischemia/reperfusion induces severe liver damage in a rat model. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(35): 4934-4943
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i35/4934.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i35.4934