Published online Dec 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i47.5133
Revised: February 4, 2011
Accepted: February 11, 2011
Published online: December 21, 2011
Primary liver cancer is the fifth most common malignancy in men and the eighth in women worldwide. The liver is also the second most common site for metastatic spread of cancer. To assist in the diagnosis of these liver lesions non-invasive advanced imaging techniques are desirable. Magnetic resonance (MR) is commonly used to identify anatomical lesions, but it is a very versatile technique and also can provide specific information on tumor pathophysiology and metabolism, in particular with the application of MR spectroscopy (MRS). This may include data on the type, grade and stage of tumors, and thus assist in further management of the disease. The purpose of this review is to summarize and discuss the available literature on proton, phosphorus and carbon-13-MRS as performed on primary liver tumors and metastases, with human applications as the main perspective. Upcoming MRS approaches with potential applications to liver tumors are also included. Since knowledge of some technical background is indispensable to understand the results, a basic introduction of MRS and some technical issues of MRS as applied to tumors and metastases in the liver are described as well. In vivo MR spectroscopy of tumors in a metabolically active organ such as the liver has been demonstrated to provide important information on tumor metabolism, but it also is challenging as compared to applications on some other tissues, in particular in humans, mostly because of its abdominal location where movement may be a disturbing factor.
-
Citation: ter Voert E, Heijmen L, van Laarhoven H, Heerschap A.
In vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy of liver tumors and metastases. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(47): 5133-5149 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i47/5133.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i47.5133
Primary liver cancer is the fifth most common malignancy in men and the eighth in women worldwide. In 2000, it was estimated that there were about 564 000 new cases of liver cancer worldwide, and a similar number of patients died as a result of this disease[1]. Also, the liver is the second most common site for metastatic spread of cancer[2]. In fact, liver lesions are more likely to represent a metastatic tumor than a primary liver tumor[3,4]. For further clinical management a proper diagnosis is crucial. Currently tissue sample analysis by histopathology is the golden standard for the diagnosis of suspected cancer in the liver. However, taking biopsies for histopathological analysis has some disadvantages. Besides patient discomfort, there is a change that the needle misses the cancer foci. Also, the needle might loosen cancerous cells which could result in tumor dissemination outside the liver along the needle track[5].
Thus, non-invasive advanced imaging techniques are desirable to assist in the diagnosis of liver lesions. A major modality to obtain anatomical information is magnetic resonance (MR). The MR technique is very versatile and it also offers many possibilities to acquire more functional information. Among these, MR spectroscopy (MRS) is particular interesting as it can provide specific information on tumor pathophysiology and metabolism. This may include data on the type, grade and stage of the tumor, which thus can assist in further management of the disease.
In this review, we will summarize and discuss the available literature on MRS of primary liver tumors and metastases. We will focus on the main nuclei employed in MRS, proton (1H), phosphorus-31 (31P) and carbon-13 (13C). Since knowledge of some technical background is indispensable to appreciate the impact of the results described in this paper we first give an introduction into the basics of MRS and some technical issues of MRS as applied to tumors and metastases in the liver.
In vivo MRS allows for the noninvasive measurement of the levels of some compounds in body tissues. It exploits the magnetic properties of certain atomic nuclei that are present in these molecules. The nuclei that are best accessible for in vivo MRS experiments are those of proton (1H), phosphorus (31P) and carbon-13 (13C) atoms.
The following sections present a short introduction of MR spectroscopy to provide the reader with sufficient background to understand the biological and clinical applications of MR spectroscopy. For more in-depth information the reader is referred to other publications, see for example[6].
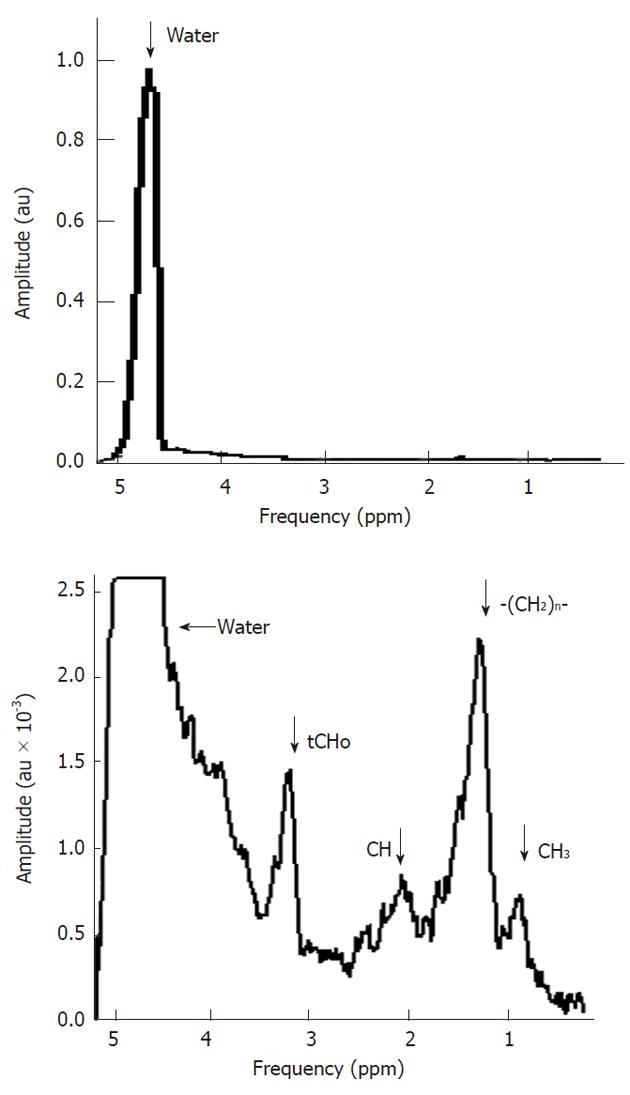
The key feature of MR spectroscopy is that certain biochemical compounds, mostly metabolites, can be identified in an MR spectrum by their specific spectral pattern, which is composed of one or more distinct signals. The intensity of the signal is proportional to the tissue amount of a certain nuclei and thus reflects the tissue levels of the compound in which it is present. An example of a typical in vivo1H MR spectrum of a healthy liver is shown in Figure 1. The horizontal axis of a spectrum represents the resonance frequency or chemical shift (both terms are explained below), the vertical axis represents the signal intensity. This spectrum is dominated by three main signals and in addition there are some smaller peaks, and broad underlying resonances. In the next few sections we explain in more detail how this spectrum is obtained and what particular information can be extracted from it.
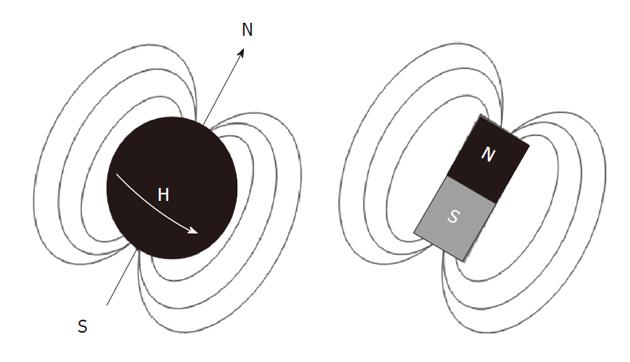
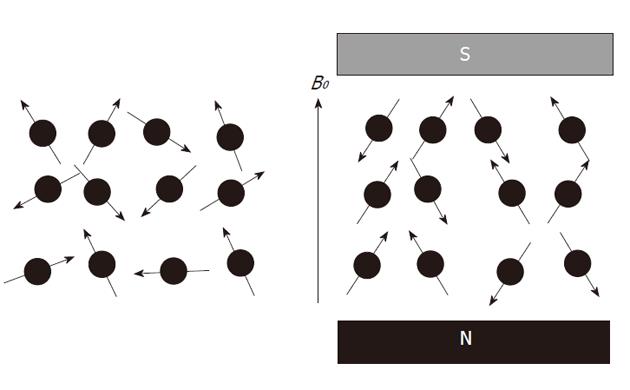
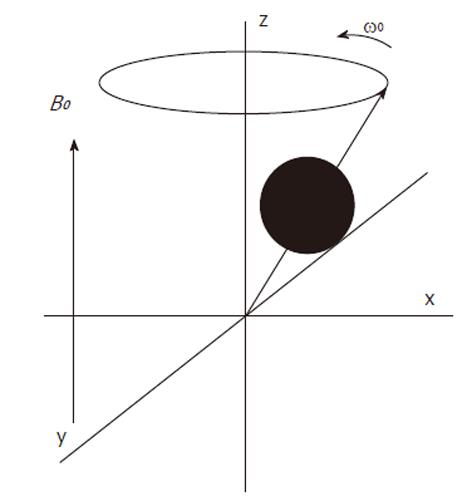
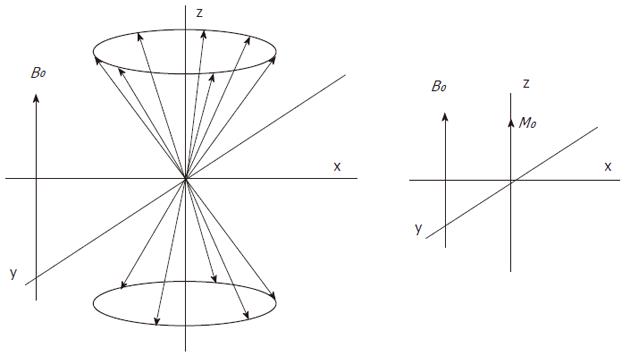
Atomic nuclei with unpaired neutrons and/or protons, are detectable by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). As the nucleus is spinning around its axes and bears an electric charge it is associated with a magnetic dipole that can be seen as a tiny bar magnet (Figure 2). Outside a magnetic field these nuclear spins or tiny magnets have a random orientation; however, when placed in a strong constant external magnetic field B0 they will become aligned (Figure 3). The nuclear spins of the atoms 1H, 31P and 13C can be oriented parallel or anti-parallel to B0. However, the spins do not exactly align but are at an angle to B0. This causes them to precess around the axis of B0 with the so-called Larmor frequency ν0 = ω0/2π = γB0/2π where the gyromagnetic ratio γ has a specific value for each nucleus (Figure 4). This implies that every type of nucleus has a different precession frequency, proportional to the B0 field strength. At a field strength of 3T, which is commonly used for human applications, these frequencies for 1H, 31P and 13C are: 127.7 MHz, 51.8 MHz and 32.1 MHz respectively, which is in the radiofrequency range.
The parallel and anti-parallel orientations are associated with a low and a high energy state respectively. The energy difference between the two spin states equals
E = h γ B0 [Equation 1],
where h is Planck’s constant (h = 6.626 × 10-34 J/s). At room temperature, there are slightly more spins in the lower energy level, Nα, than in the upper level, Nβ. The distribution over these energy levels is given by Boltzmann statistics
Nβ/Nα= e-E/kT [Equation 2],
where k is Boltzmann’s constant (1.3805 × 10-23 J/K) and T is the temperature in Kelvin. The population difference results in a net macroscopic magnetization M0. This so-called longitudinal magnetization is aligned parallel to B0 (Figure 5). Only the net magnetization is detectable and its extent determines the achievable signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). At 1.5T and 37 °C (310 K), the population difference represents only a small fraction (about 10-6) of the total spin population, which explains why MR is a relatively insensitive technique. It follows from Equations 1 and 2 that sensitivity can be improved with a higher magnetic field B0 or a lower temperature.
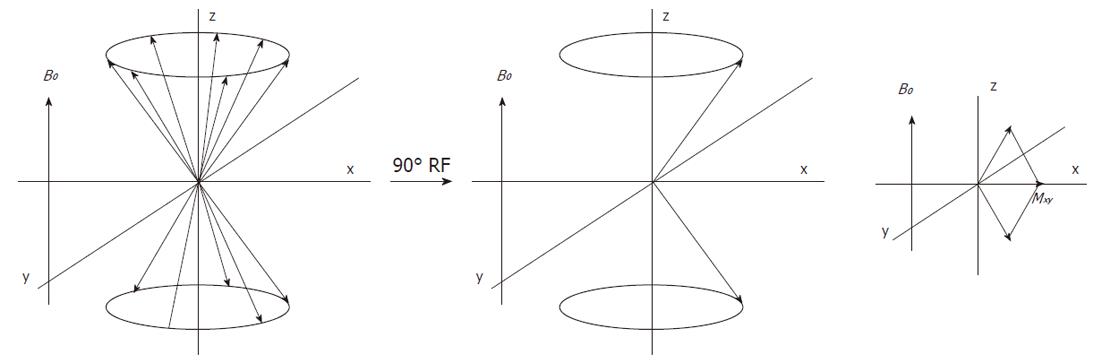
The direction of the main magnetic field B0, is commonly placed along the z-axis and the magnetization along this axis is Mz, which at equilibrium, equals M0 (Figure 5). The longitudinal magnetization however is not detectable as it is “overruled” by the main magnetic field B0. To detect the net macroscopic magnetization M0, an radio frequency (RF) pulse with a magnetic field perpendicular to the main magnetic field B0 and with a frequency equal to the precession frequency is sent with an RF transmitter coil. As a consequence of the applied RF pulse M0 magnetization will rotate away from the z-axis toward the transverse plane (x-y plane). The angle to which the net magnetization is rotated relative to the main magnetic field direction is called the flip angle. A so called 90° RF excitation pulse will therefore rotate M0 into the transverse plane. The spin population of the energy levels becomes equal and spins precess coherently (Figure 6). However, after the RF excitation pulse the spins start to return towards the original energy level distribution and towards incoherent precession (dephasing) and after a while the system will be in equilibrium again. The time constant which describes how the magnetization returns to the original longitudinal alignment is called the spin lattice relaxation time T1: Mz = M0(1-e-t/T1). The time constant which describes the return to incoherent precession is called the spin-spin relaxation time T2: Mxy = Mxy0 e-t/T2. By definition T1 is longer than T2.
After the RF pulse, the transverse component of the M0 magnetization precesses with the Larmor frequency at resonance and will induce a current in the RF coil which is now switched to receive mode. The decaying signal of this component is called the free-induction decay (FID) response signal. This digitally recorded FID signal is mathematically converted by a Fourier transform from the time to the frequency domain, which results in a so called MR spectrum, that may contain one or more resonances, signals or peaks at particular frequencies.
An MR spectrum of the liver would not be very interesting if all nuclei of a certain type resonate at the same frequency. Fortunately, each nucleus in a given molecule is shielded from the main field by a weak opposing field from the surrounding electrons, induced by and also proportional to B0. The amount of shielding by these electrons highly depends on the chemical environment of the nucleus. This shielding, which is generally unique for each chemically distinguishable site in a molecule, is expressed as the shielding constant σ, and the total effective field experienced by a given nucleus is: Beff = B0 (1-σ). The resulting change in resonance frequency νeff = ωeff/2π = γ B0 (1-σ)/2π relative to that of a chosen reference compound, νref, is generally referred to as the chemical shift σ = (νeff - νref )/νref expressed in units of ppm (1 ppm = 100 Hz at ν0 = 100 MHz). Thus the chemical shift is the key property of MR spectroscopy which enables detection of a wide variety of chemical groups and metabolites containing these groups. Special RF pulses are used to excite a band of frequencies covering the chemical shift range of a particular nucleus in a biological sample.
As shown in Figure 1 the 1H spectrum of the liver is dominated by 3 peaks. The peak on the right originates from the 1H nuclei in methylene groups (-CH2-) in lipids, the peak in the middle originates from the 1H nuclei in the three methyl groups (CH3) of choline containing compounds [(CH3)3N+CH2CH2O-], and the peak on the left originates from the 1H nuclei in water (H2O). The electronegative oxygen atom in the water molecule shifts the electron density away from the 1H nuclei, leading to a reduced shielding and thus to a higher resonance frequency compared to 1H nuclei in the methylene groups of lipids. Thus 1H nuclei in water have a higher chemical shift value then the 1H nuclei in the methylene groups from lipids (compared to 1H nuclei in a reference compound at 0 ppm) and appear on the left side. Note that the chemical shift scale on the horizontal axis increases from right to left.
The peak area rather than its amplitude is proportional to the amount of 1H nuclei in the same chemical environment and thus the tissue content of that chemical group or metabolite. Quantification of metabolite concentrations is performed by comparing peak areas with those of known substances and concentrations.
The content of water in the liver is much higher than that of metabolites. Hence, the proton signals of the latter have a much lower SNR (Figure 1). For this reason signal averaging is usually required and it is also needed to measure larger voxels than commonly done with MR imaging of water.
As the water resonance in 1H MR spectra is at least 200 times more intense than the resonances of hydrogen containing metabolites (Figure 1) it may hamper the proper detection of metabolite signals, e.g., by artifacts such as side bands of this huge signal[7], the suppression of the water signal is commonly performed. There are many ways to do this: a well-known sequence is chemical shift selective water suppression[8]. A frequency selective RF pulse excites the water spin magnetization into the transverse plane after which all coherences are dephased by magnetic field gradients. The spectrum shown in Figure 1 was obtained with only partial water signal suppression.
As the purpose of MR spectroscopy is to separate signals with different chemical shift it is crucial for its proper application that good magnetic field homogeneity is obtained over the object of interest. However, due to the many different tissue types and air containing compartments, the magnetic field in the human body is usually not very homogeneous, leading to broadened spectral lines, which may overlap. Therefore optimizing field homogeneity (a process called shimming) is usually a required step in an MR spectroscopy experiment. Good homogeneity is most important in 1H MRS as it has a relatively small chemical shift range and needs a well separated and defined water signal for proper suppression and to avoid artifacts. By selecting small volumes of interest, a limited amount of different tissues are included which will result in a more homogeneous magnetic field. The requirements for homogeneity are much less strict for 31P and 13C MRS because resonances in their spectra are more separated (larger spectral dispersion).
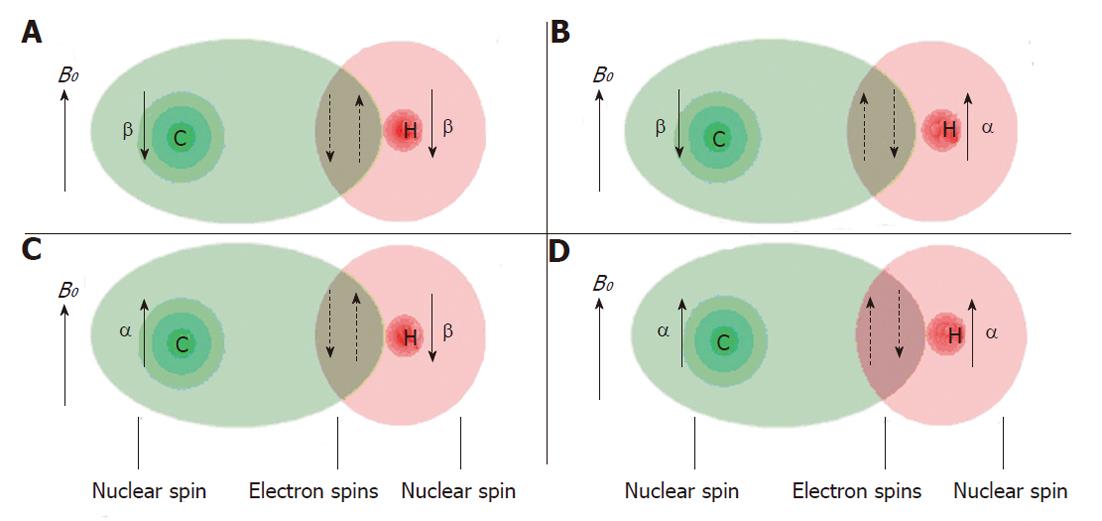
Nuclei which are close to one another exert an influence on each other’s effective magnetic field through electrons in chemical bonds (Figure 7). If the distance between non-equivalent nuclei is less than or equal to three bond lengths, this effect may be observable in the in vivo MR spectrum. Instead of one peak for a certain nucleus several smaller peaks are observed in the spectrum. This interaction of nuclei is often referred to as scalar coupling, J coupling or spin-spin coupling. Because of this splitting the signal to noise decreases and spectral interpretation may become more complicated. However, the specific pattern may also be helpful to identify specific molecular groups and with special pulse sequences the phenomenon of spin-spin coupling may be used to identify the resonances of these groups in the presence of other overlapping resonances (so-called editing).
Spin-spin couplings are expressed in Hz. A typical value for a three bond proton-proton coupling in metabolites is 7 Hz. For example this can be used to identify the methyl doublet resonance of lactate in 1H MR spectra. At magnetic fields above about 2T, line width broadening will obscure the direct visualization of this coupling. Two bond 31P - 31P couplings occur at about 17 Hz in adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Heteronuclear couplings commonly dealt with in in vivo MRS are between protons and 31P or 13C. To improve signal to noise and spectral resolution the spin-spin splitting can be removed by a technique called decoupling. Special RF pulses are used to irradiate selected resonance(s) of nuclear spins such that their field directionality is averaged out. As a result nearby spins in a molecule experience no field of these irradiated spins anymore and the resonance splitting disappears.
Decoupling is important in MRS of 31P and 13C as these atoms often show split resonances due to nearby hydrogen atoms. Irradiation of these protons for decoupling increases the signal to noise ratio and impro-ves spectral resolution. Irradiation also induces a throu-gh space effect called nuclear overhauser enhancement (NOE), which can increase signal intensity even more[9-11]. Typical enhancement values reached in vivo by NOE are 1.3-2.9 and 1.4-1.8 for 13C-1H and 31P-1H interactions respectively[6].
13C labeled (enriched) substrates combined with 13C MRS have traditionally been used to monitor metabolic conversions during steady-state conditions and even has been used to assess active metabolism in human tumors[12-14]. The relative low sensitivity of 13C MRS prevented imaging of these processes. However, with polarization transfer techniques sensitivity can be enhanced[14-16].
Recently a new method has been introduced in bio-medical MR, dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP), that mostly makes use of 13C MRS, to image metabolic conversions at reduced acquisition times (in an order of minutes or less). Inspection of Equation 2 (above) reveals that decreasing the temperature also will increase the population differences between energy levels. DNP is a hyperpolarization technique that increases the spin polarization obtained at room or body temperature in traditional MR, by orders of magnitude by cooling the sample to very low temperatures and using selective microwave irradiation for efficient transfer of spin polarization from electron spin to nuclear spin[6,17,18]. The substrate is then rapidly transferred to body temperature for administration. The major disadvantage of DNP is that the polarization decay is determined by the spin-lattice relaxation time T1 of the nucleus (20-40 s for a 13C nucleus in a carboxyl group). The consequence is that only conversions in which substrates are rapidly taken up by tissues and metabolized within minutes can be imaged successful. With efficient uptake usually one or two metabolic steps can be imaged, before the signal has decayed away.
To analyze different regions of interest in the liver with healthy tissue or tumor lesions by in vivo MRS it is required that only signals that originate from these locations appear in the spectra. This can be achieved in different ways. The most rudimentary one is to use only a surface coil on the body adjacent to the liver with a simple pulse sequence globally selecting the area next to the coil. However, in most cases a better localization is desired. More advanced spatial localization is possible with single voxel or multi-voxel methods.
The most common single voxel localization techniques are Image Selected In Vivo Spectroscopy (ISIS)[19], Stimulated Echo Acquisition Mode (STEAM)[20] and Point Resolved Spectroscopy (PRESS)[21].
ISIS uses three frequency-selective inversion pulses, in the presence of three orthogonal magnetic field gradients. By turning on and off the inversion pulses, according to an encoding scheme, eight different scans are recorded. Adding and subtracting the different scans will add signal from the desired location while canceling signal from other locations. A disadvantage of ISIS is its sensitivity to motion as eight scans need to be obtained for a full 3D localization. ISIS is rarely used for 1H MRS, because of potential artifacts such as those arising from incomplete water signal suppression. However, it is the favored method in 31P MRS localization as effects due to relatively rapid T2 decay and to J-coupling are avoided.
For 1H MRS the most common single voxel localization techniques are STEAM and PRESS, which both use three spatially slice selective RF pulses to produce an echo signal from a well-defined region. STEAM uses 90°-90°-90° pulses and PRESS 90°-180°-180° pulses to define three orthogonal slices. Only signal from the volume of interest remains in the final echo. In STEAM 50% of the original signal is lost as the second 90° pulse only rotates half of the transverse magnetization to the longitudinal axis, while the other half is dephased by crushers. The PRESS technique retains full signal intensity, but the minimal possible TE is commonly larger than for STEAM.
Multi voxel localization allows the detection of localized spectra from a multidimensional array of locations. Disadvantages compared to single voxel localization concerns some more magnetic field inhomogeneities due to the many different tissue types in the field of view, intervoxel contamination, and the minimally required number of scans that may end up in long acquisition times. Spectroscopic imaging techniques acquire the signal from multiple voxels by using phase encoding gradients[22], analogous to the phase encoding technique used in MR imaging. The nominal voxel size is the field of view divided by the number of phase encoding gradient steps. The actual voxel size can deviate substantially from the nominal value as the signal is sampled only over a finite time. This introduces intervoxel contamination due to the characteristics of the Fourier transform. This voxel bleeding can be decreased by apodization functions like those with Gaussian or Hamming shapes, however at the expense of decreased spatial resolution.
Conventional encoding of N1× N2× N3 volume elements (voxels) requires N1× N2× N3 acquisitions. A typical 16 × 16 × 16 dataset obtained with a repetition time of 2000 ms and 4 averages would require a measuring time of (16 × 16 × 16 × 2000 × 4/3600 = 9 h). Therefore techniques are developed that increase the temporal resolution, e.g., by special k-space trajectories. For example “circular 2D or spherical 3D k-space sampling with k-space apodization during acquisition”. This also reduces the total acquisition time by spending less time acquiring the high k-space coordinates and more time acquiring the low k-space coordinates. Other methods are based on fast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) sequences, e.g., EPI, RARE, spiral and steady-state sequences[6].
Although the tissue level of metabolites is proportional to the area under its signal curve in the spectrum, it commonly requires some corrections and calibration with a signal of known concentration to obtain an absolute number (e.g., in mmol/L).
Such a reference signal maybe that of water or of another metabolite in the liver assuming a stable and known value for its tissue level. In the liver, the unsuppressed water signal is often used as an internal reference after correction for T1 and T2 relaxation. However, dietary regimes and liver pathologies may affect the amount of water. Li et al[23] reported a 1.8 fold difference in five normal liver studies between the largest and smallest water signal intensity obtained from localized liver tissues. In four hepatocellular carcinoma studies, they observed a 3.2-fold difference between the largest and smallest water signal intensities obtained from the localized liver tumors. Lipid peaks exhibited even larger variations than did the water peaks.
External phantoms with known concentrations sometimes are also used for calibration purposes, but this may be not so practical in a clinical environment. In addition differences in coil loading have to be taken into account in this approach. To avoid correction and calibration issues spectral quantities are sometimes also assessed as ratio’s between integrals of signals of different compounds.
Motion can lead to voxel misregistration and outervoxel contamination. Motion of tissue through inhomogeneous fields (e.g., air in the lungs) results in broadening of the spectral resonances. Broadening of the resonances increases the risk of signal overlap and also lowers the signal to noise ratio. Compared to other organs like brain and skeletal muscle, MR spectroscopy of the liver is challenging as there are potential field inhomogeneities and artifacts caused by respiratory movement, cardiac and aortic pulsations[24-26]. Although often applied, breath-hold acquisitions may be problematic. Long acquisition times are needed to increase the SNR and, since a breath-hold period can only last for about 15 s in patients, the acquisition will require multiple breath-hold periods. Even when the acquisition is performed at end-expiration, there is no guarantee that the tissue is at exactly the same position, leading to outervoxel contamination. Respiratory and cardiac gating can be applied to reduce motion artifacts at the cost of an increased scan time. Another option is to align individual spectra and/or exclude bad spectra before averaging during post processing. Some liver pathologies, e.g., due to long-term total parenteral nutrition may induce iron accumulation in the liver, which will result in field inhomogeneities and broadening of the spectral resonances.
In order to predict treatment outcome or monitor therapy, differences in in vivo MR spectroscopy outcome para-meters should reflect true differences in tumor biology and not differences induced by variations in the MRS protocol or interfering body physiology. This issue is relevant, since the time of MR scanning during the day (e.g., before or after a meal) or differences in eating patterns might already influence the metabolic activity and thus the concentrations of metabolites in the liver. Large inter- and intrapatient variability of MRS outcome parameters have been described[23].
In MR, hydrogen (proton) is the most commonly studied nucleus. Compared to other MR sensitive nuclei it has the highest sensitivity and occurs at 100% isotopic abundance. Almost all metabolites in the human body contain protons. Therefore, in principle a large amount of metabolites can be investigated. However, in practice, sensitivity restrictions set the in vivo detection limit of metabolites to a minimum tissue concentration of about 0.1 mmol/L. An advantage of 1H MRS is that it uses the same nucleus as MRI techniques. Therefore, it can be performed with the same hardware and there is no need for special equipment. The major drawback of 1H MRS is the relatively small chemical shift range (about 10 ppm) for the many resonances of in vivo detectable compounds, resulting in limited spectral resolution. Moreover, these have to be resolved from a dominating water peak, in certain cases a large lipid peak, and at short echo times a high baseline due to macro-molecules.
Lipids: Outside the brain 1H MR spectra of tissues usually show large signals of mobile lipids, mostly triglycerides: in particular a methylene peak at 1.2 ppm with smaller methylene peaks between 2.1 and 2.4 ppm and a peak for methyl protons at 0.9 ppm (Figure 1). Triglycerides occur in fatty liver, but also may be a marker of membrane breakdown and can be seen in tumors, abscesses and other pathological processes[27].
Lactate: Due to the Warburg effect tumor cells obtain relative less energy than normal cells from oxidative phosphorylation and have a more glycolytic character[28,29]. Pyruvate, the end product of glycolysis, is converted into lactate, which is further promoted by hypoxic conditions. Therefore MR spectra of tumor tissue often show signals for lactate. The three equivalent methyl protons of lactate give rise to a resonance at 1.31 ppm, which is a doublet due to coupling with the methylene proton, while the single methylene proton resonates as a quartet at 4.10 ppm due to coupling with the methyl protons. In liver and tumor tissue, the lactate signal at 1.3 ppm will overlap with large lipid resonances. However, with so-called spectral editing techniques it is possible to separate the lactate signal from the lipid signals.
Creatine: Creatine (Cr) and phosphorylated creatine (PCr) play an important role in energy metabolism of many tissues. PCr serves as a spatio-temporal energy buffer, maintaining a constant level of ATP, facilitated by the creatine kinase reaction. The methyl protons of Cr and PCr resonate at about 3.03 ppm and the methylene protons resonate at approximately 3.9 ppm. Under normal conditions, the concentration of total creatine is relatively constant in muscle and brain and therefore often used as an internal reference. However, decreased Cr levels have been observed in tumors and other pathologies. Furthermore, hepatocytes do not express creatine kinase under normal circumstances[30], and therefore no creatine peak will be visible in the spectrum of healthy liver tissue. In vitro experiments at 9.4T have shown 5-10 times increased levels of Cr in liver metastasis compared to normal liver tissue[31].
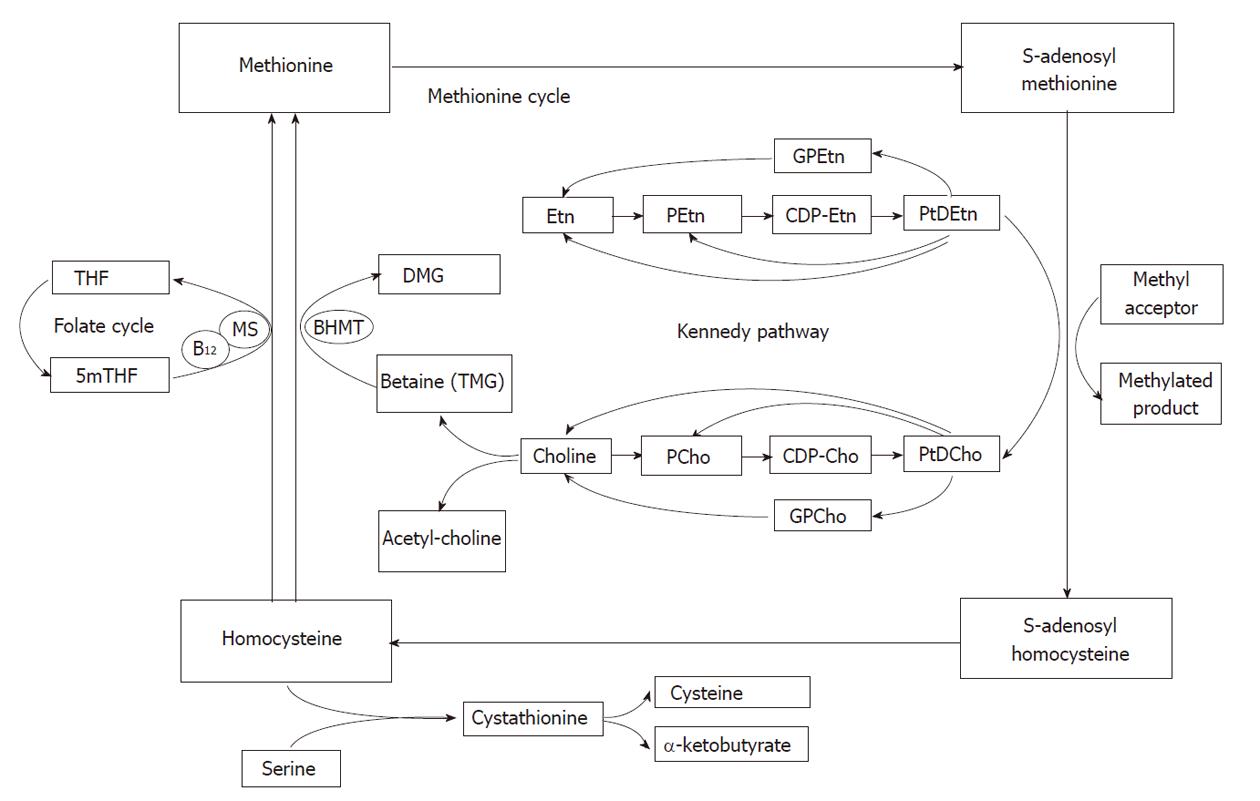
The signals of choline containing compounds in MR spectra have been used as key biomarkers to identify malignant tumors[32-34]. In vivo1H MR spectra of the liver show the N-trimethyl [+N(CH3)3] resonances of choline compounds at about 3.2 ppm. This resonance is also known as the total choline (tCho) peak as it may originate from several different choline compounds. The relative increase in the tCho signal seen in human tumors is due to an abnormal choline uptake and/or metabolism related to cell membrane turnover. However, metabolism of choline containing compounds in tissue cells is complex. Although far less prominent in 1H MR spectra than choline, ethanolamine signals may also contribute to a characteristic spectral profile of tumor tissue. Therefore some important biochemical pathways involving choline metabolism and the closely related metabolism of ethanolamine in the liver are briefly described (Figure 8).
Choline is a key precursor molecule in several metabolic pathways. It can be acetylated, oxidized, phosphorylated or hydrolyzed. Choline oxidation plays a major role in the provision of methyl groups via its metabolite, trimethylglycine (betaine) that participates in the synthesis of S-adenosylmethionine (SAM). Methylation reactions are involved in the biosynthesis of lipids, the regulation of several metabolic pathways, and detoxification in the body. Choline phosphorylation results in compounds such as phosphatidylcholine (PtdCho), lysophosphatidylcholine, choline plasmalogen, and sphingomyelin which are essential for structural integrity and signaling in cell membranes[35-38].
PtdCho, the major phospholipid component of cells is derived from the Kennedy pathway[39], which has two branches, one via cytidine 5’diphospho (CDP)-choline and the other via CDP-ethanolamine (Figure 8). In the CDP-choline branch choline is initially converted to phosphorylcholine (PCho) and after some steps to PtdCho which can be converted into choline or into PCho again[36]. Alternatively, phosphatidylethanolamine (PtdEtn) is generated via the CDP-ethanolamine branch, employing similar biochemical reaction steps. The resulting PtdEtn can be methylated, using SAM as the methyl donor, to PtdCho[36-38,40]. The methylation pathway is, however, only relevant in liver. In rat hepatocytes it accounts for 20%-40% of PtdCho synthesis[41]. Besides entering the CDP-choline branch of the Kennedy pathway, choline can also enter another major pathway in the liver in which it is oxidized into betaine[42-44].
The contribution of the nine methyl protons of free choline, which resonate at 3.19 ppm, to the tCho peak is limited as the concentration of free choline is usually low. Another potential contribution to the tCho peak may come from PtdCho, which makes up a very high proportion of the cell plasma membrane. However, it is a large molecule with a relatively short T2 relaxation time that becomes even shorter by being incorporated into a membrane. Therefore, it is almost invisible in the in vivo1H MR spectrum. Nevertheless, some evidence suggests that PtdCho may contribute to the tCho signal[45]. Precursors of PtdCho such as PCho and phosphorylethanolamine (PEtn) are more likely to contribute to 1H MR spectra as these are small molecules with long T2 relaxation times. Experimental evidence suggests that the tissue levels of PCho and PEtn increase during cell proliferation and tCho levels also have been correlated with tumor aggressiveness[46]. In addition to PCho and PEtn [together called phosphomonoesters (PME)] their glycerol derivatives glycerol-3-phosphorylcholine (GPCho) and glycerol-3-phosphorylethanolamine (GPEtn) [together called phosphodiesters (PDE)] also contribute to the tCho signal. Besides protons of choline and ethanolamine containing compounds, protons from other metabolites might also resonate around 3.2 ppm, e.g., glucose at 3.23 ppm, myo-inositol at 3.27 ppm, and taurine at 3.25 ppm. In liver and kidney the resonance at about 3.26 ppm is almost entirely composed of proton signals of betaine (trimethylglycine)[6].
In vitro high field 1H MR spectra of the liver: Soper et al[47] performed a diagnostic correlation between MR spectra and histopathology. They analyzed liver tissue specimens from 54 patients undergoing partial or total hepatectomy. The samples included 31 normal, 59 cirrhotic and 32 hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) histologically confirmed tissues and were analyzed by 1H MRS at 8.5 Tesla. They found reduced amounts of lipids and carbohydrate residues and increased tCho in HCC compared to all normal and all cirrhotic liver tissue. Cirrhotic liver tissue and HCC were distinguished with a sensitivity and specificity of 95.8% and 88.9%, respectively. Lactate signals of variable intensity were found at 1.3 ppm, probably resulting from anaerobic metabolism after excision.
In vivo liver 1H MR spectrum:In vivo1H MRS is characterized by a much poorer spectral resolution and SNR than in vitro1H MRS (see above, technical issues). Kuo et al[48] investigated the value of in vivo1H MRS in the assessment of large focal hepatic lesions. They included 43 consecutive patients and 8 normal volunteers in a prospective MRS study. MRS was performed at 3.0T with shallow and regular breathing. Single voxel PRESS with TE = 30 ms, TR = 1500 ms, 256 averages, was used to select a volume of 2 cm × 2 cm × 3 cm. The voxel of interest was located in the largest solid portion of hepatic tumors in patients. Healthy liver data was collected from an area at the centre of the right hepatic lobe for normal volunteers, or in an uninvolved area of the right hepatic lobe in patients. Patients with diffuse-type HCC, with focal nodular hyperplasia and obvious fatty infiltration, and histological unconfirmed lesions were excluded. Thirty-three lesions (21 HCC, 2 angiosarcomas, 1 lymphoma and 9 hemangiomas) were included. They found that malignant tumors had elevated tCho resonances compared to uninvolved liver or benign tumors, but the difference in mean tCho/lipid ratio between malignant tumors or uninvolved liver did not reach statistical significance. Several factors may have contributed to these results. First of all, the tumors in this study may have contained significant necrotic areas with less viable cells. This may have diluted more prominent changes observed in areas of rapid cell turnover, within viable tumor tissue and may have caused low signal to noise for metabolite signals leading to larger errors. Physiological motion due to breathing and cardiac movement will have contributed, especially if the tumor was located in the left lobe or at the extreme end of the right hepatic lobe. Finally, three different tumor types were included in the malignant group, which may have resulted in a variation of different metabolites in phospholipid metabolism, and thus in a more variable tCho resonance. Thus, in vivo1H MRS is technically feasible at 3.0T for the evaluation of focal hepatic lesions, but the clinical application of the measurement protocol used by Kuo et al[48] is limited as normal liver, benign and malignant tumors cannot be clearly differentiated.
In the second part of their study Kuo et al[48] attempted to measure metabolic changes in HCC after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE). Eight HCC were evaluated before and two to five days after TACE. The tCho peak at 3.2 ppm was significantly decreased while the lipid and water signals at 1.3 and 4.7 ppm respectively, were increased. The mean tCho/lipid ratio significantly decreased from 0.23 ± 0.11 before to 0.01 ± 0.00 after TACE treatment. One of the post-TACE lesions showed recurrence three months later and MRS also revealed an elevated tCho/lipid ratio at that stage. Therefore, 1H MRS at 3.0T may be used for treatment monitoring.
Fishbach et al[49] improved the MRS acquisition and processing protocol compared to previous studies by introducing a control of respiratory motion using breath-hold acquisitions and an abdominal compression belt. They also applied dedicated pre- and post-processing including automatic phase and frequency correction based on the residual and the unsuppressed water signal in order to remove potential distortions mainly introduced by motion. Apart from 39 volunteers, they included 55 patients with advanced cancer with lesions of more than 3 cm in diameter in their study (22 metastases of colorectal cancer, 11 hepatocellular carcinomas, 9 metastases of breast cancer, 3 metastases of pancreatic cancer and 1 metastasis of prostate cancer). Liver spectra were acquired at 3.0T using a body transmit/receive coil. Breath-hold at end-expiration spectra were acquired with the single voxel (2 cm × 2 cm × 2 cm) PRESS technique with TE=35 ms, TR=2000 ms, 128 averages and 16 additional unsuppressed water reference lines. The intra-individual reproducibility of this 1H MRS acquisition in the liver was tested in 25 patients and volunteers and judged to be satisfactory. In total 186 spectra were acquired and 27 spectra had to be discarded because they did not meet the predefined quality specifications. The remaining 113 spectra were measured in normal-appearing parenchyma of 37 patients and 39 volunteers.
Although, remarkably, tCho signals relative to those of water seemed to be lower in metastatic lesions compared to normal liver tissue, no significant differences were observed between malignant liver tumors and normal liver parenchyma for any of the parameters analyzed, in particular tCho signals relative to water and lipid signals. This was attributed to the large variability of normal values.
The divergent results observed in the above mentioned studies might also be due to the multiple contributions from the unresolved tCho signal. In normal liver tissue low concentrations of PMEs and high concentrations of PDEs have been shown while in tumor tissue elevated levels of PMEs and decreased levels of PDEs have been observed[50]. This implies that in tumor tissue increased levels of PMEs may be canceled out by decreased PDEs, resulting in an unchanged overall tCho level. Different tumor types might also have divergent contributions to the unresolved tCho signal. In addition, alterations of the metabolite concentrations might not be due to malignancy, but due to proliferating healthy tissue such as a regenerating liver, benign tumors, and even some degenerative pathologies. With 31P MRS PME and PDE signals can be studied separately as discussed below.
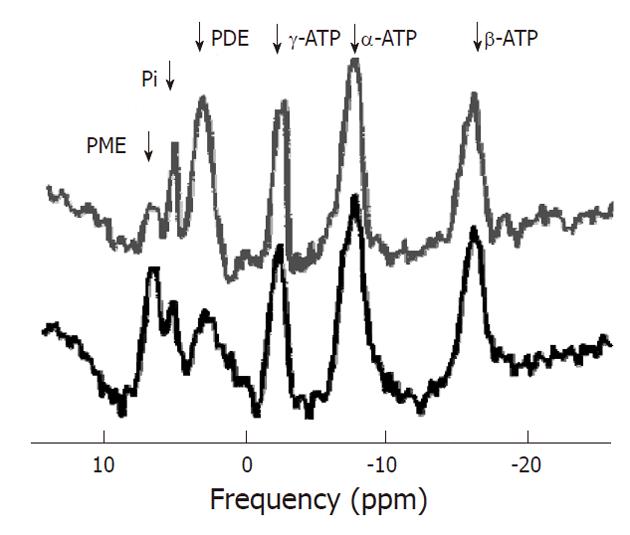
After 1H MRS, phosphorus-31 MR spectroscopy is the most commonly used MRS technique to study tumors in vivo. Phosphorus has an MR sensitivity of 6.6% compared to proton. However, the chemical shift dispersion of its signals observed in vivo is larger (about 30 ppm vs about 10 ppm), resulting in a better spectral resolution. Also, 31P MRS is capable of detecting some key metabolites in tissue energy metabolism such as ATP, PCr, and inorganic phosphate (Pi). In addition some important metabolites involved in membrane metabolism such as PCho and PEtn (together called PME) and their glycerol derivatives GPCho and GPE (together called PDE) may be resolved. In this respect 31P spectra (Figure 9) are more informative than 1H MR spectra in which signals of all choline compounds (tCho) usually are observed unresolved at about 3.2 ppm. Furthermore, from 31P MR spectra physiological parameters like intracellular pH can be deduced from the chemical shift of the Pi resonance. The phosphoryl resonances from large and membrane bound compounds may only show up in a phosphorous-31 MR spectrum as broad underlying baseline signals due to their very short T2 values[51].
Unfortunately, due to a lower sensitivity and less favorable spin relaxation the spatial resolution of 31P MR spectra is an order of magnitude less than that of 1H MRS. Higher magnetic fields provide improved experimental conditions for 31P MRS.
Phosphocreatine: The largest peak in 31P MR spectra of muscle, brain and other tissues originates from PCr. Its spectral position is used as an internal chemical shift reference and commonly has been assigned a chemical shift of 0.00 ppm. PCr is, however, not detectable in spectra of healthy liver since hepatocytes do not express creatine kinase under normal circumstances[30]. Tumors, however, might express creatine kinase and show some PCr.
Adenosine triphosphate: ATP is the main direct energy supply within cells. ATP consists of adenosine and three phosphate groups. The phosphoryl groups, starting with those closest to the adenosine moiety, are referred to as α, β, and γ phosphates. ATP is produced by ATP synthase from inorganic phosphate and adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or adenosine monophosphate (AMP). Multiple processes in the cell can split ATP into ADP or AMP and inorganic phosphate, and use the energy that is released. At a pH of 7.2, with full magnesium complexation, the resonances of ATP appear at -7.52 ppm (α), -16.26 ppm (β), and -2.48 ppm (γ). The ATP resonances may overlap with the signals of other nucleotides: uridine triphosphate (UTP), guanosine triphosphate (GTP) and cytidine triphosphate (CTP). Therefore these resonances are sometimes referred to as nucleoside triphosphate (NTP), although the others usually occur at much lower concentrations.
Inorganic phosphate: Like the level of ATP that of inorganic phosphate (Pi) reflects the cellular phosphorylation potential. The chemical shift of Pi and some other phosphorus containing compounds is dependent on the intracellular pH (pHi) and magnesium concentrations[52]. The protonation or complexation with magnesium of phosphate affects the chemical environment of the 31P nucleus and hence its chemical shift. As proton exchange is fast on the NMR timescale, the resonance frequency is indicative of the relative amount of protonated and unprotonated molecules, and hence the pH can be deduced. The shift in resonance of Pi relative to PCr is most commonly used as it has a large dependence in the physiological pH range whereas the chemical shift of PCr is constant in this range. At a pH of 7.2 and normal magnesium level it occurs at 5.02 ppm. The accuracy of pH determination from the Pi-PCr shift is typically 0.05 pH units[6]. However, as PCr is not detectable in the normal liver the α-ATP resonance is used instead as a reference.
Tumor pH: Due to the Warburg effect and/or hypoxic conditions tumor cells preferentially convert glucose to lactic acid. Lactic acid is largely dissociated in vivo to H+ and lactate-. Normal, as well as tumor cells, have multiple systems to continuously export H+ ions to maintain a constant pHi, as well as a system for exporting lactic acid (but not lactate). This results in a neutral, or a slightly alkaline pHi of intact (tumor) cells. However, since tumors may be poorly vascularized the extracellular tumor pH (pHe) of tumors is more commonly acidic[53-59].
Phosphodiesters: Signals of PDE occur around 3 ppm in 31P MR spectra. Tumor tissue sometimes contains significantly lower concentrations of PDE than healthy liver tissue. Some in vitro studies show that the PDE levels increase with decreasing growth fraction of the tumor. This suggest that PDE signals may be dominated by breakdown products of phospholipids[60], and the concentration may be an indicator of the necrotic fraction in tumors associated with phospholipid catabolism[61]. The phospholipid derivatives, particularly GPCho and GPEtn, were found to contribute to the PDE resonance[61]. Their phosphor spins resonate at 2.76 ppm and 3.20 ppm respectively.
Phosphomonoesters: Resonances of PME occur at about 6 ppm in 31P MR spectra. Increased levels of PME have been hypothesized to be associated with intensified cell membrane synthesis, cellular growth, cell nutritional state and rate of cell replication. Several studies identified increased PME signals as a possible diagnostic marker for tumors. PME/PDE ratios were suggested to represent altered relative rates of membrane synthesis, catabolism and metabolic turnover[36,60,61]. Phospholipid derivatives, particularly PCho and PEtn, contribute to the PME resonance[61]. PCho and PEtn resonate at 5.88 ppm and 6.78 ppm respectively.
In vitro high field 31P MR spectroscopy of liver: Many in vitro31P MRS animal studies and several in vitro31P MRS studies on human hepatic tumor tissues have been performed. Obtaining a fully representative human hepatic tissue sample for 31P MRS is difficult as the surgical removal and extraction usually results in a period of ischemia/hypoxia, which affects metabolic processes resulting in decreased ATP and increased Pi levels. Nevertheless, in vitro31P MRS may be used to study signals in the PME and PDE peaks that are still unresolved in in vivo31P MR spectra, as these are less affected by short periods of hypoxia.
Bell et al[50] investigated the metabolic changes arising in hepatic tumors and the possible systemic effects of these tumors on the liver as a whole. Ten biopsy specimens were obtained from hepatic tumors (one cystadenoma, four hepatocellular carcinomas, four metastatic colonic adenocarcinomas and one metastatic squamous cell carcinoma from the lungs). Five histologically proven normal tissue samples from the same tumor-bearing hepatic lobe were obtained immediately after the blood supply had been clamped and before partial hepatectomy. Six control samples were obtained from morphologically normal liver tissue from patients with histologically proven chronic pancreatitis and known to be free of any hepatic malignancy. Both 31P spectra with proton decoupling and 1H MR spectra with partially water suppression were acquired using high-resolution 11.7T systems. Betaine is the most prominent resonance in the in vitro rat liver 1H spectrum but no resonance for betaine was observed in any of the human biopsy samples, suggesting that its presence is species related. The in vitro31P MRS spectrum showed that over 10 different compounds contributed to the PME resonance. The five principal resonances were: PCho, PEtn, glucose-6-phosphate, AMP, and glycerol-3-phosphate. The PDE region included at least 3 different compounds. The two main components were: GPCho and GPEtn. Compared to control tissue, tumor tissue showed significantly lower concentrations of GPCho (0.59 ± 0.15 vs 2.46 ± 0.37) and GPEtn (0.57 ± 0.17 vs 2.25±0.46), and elevated levels of PCho (1.36 ± 0.50 vs 0.17 ± 0.11) and PEtn (2.47 ± 0.84 vs 0.16 ± 0.10). It was suggested that the increase in PME/NTP observed in in vivo spectra of HCC and liver metastasis (see next section) is due to increased levels of PCho and PEtn. The decrease in concentration in GPC and GPE observed in this study might be responsible for the change in PDE/NTP seen in in vivo spectra. However, the underlying cause of these changes remains partially unknown and requires further study.
Bell et al[50] also observed that spectra from histologically normal tissue from the liver tumor-bearing hepatic lobe contained more PCho (0.32 ± 0.18 vs 0.17 ± 0.06) and PEtn (0.34 ± 0.12 vs 0.16 ± 0.07) than spectra obtained from control tissue. The levels of GPC and GPE showed no significant change.
Previously, in 1993 Dagnelie et al[62] studied liver metabolic changes in rats bearing subcutaneous Dunning prostate tumors by in vivo and in vitro31P MRS. Although absence of metastatic tumor cells in the liver of all tumor-bearing animals was confirmed by histological examination, hepatic phosphorylation status, phospholipid metabolism, and gluconeogenesis was significantly affected in the tumor-bearing animals. Dagnelie et al[63] also investigated liver metabolism in humans with metastatic cancer without evidence of liver metastases by 31P in vivo MRS. They included 23 cancer patients and 12 healthy subjects and found markedly elevated PME and reduced PDE levels in the non-metastatic liver compared to controls.
Thus this may complicate the use of increased PME (PCho and PEtn) levels as a sole diagnostic biomarker to detect (metastatic) liver cancer. In addition, as no significant differences between HCC and liver metastasis were observed in biopsy samples by in vitro31P MRS[50,64], the use of in vivo31P MRS seems limited in this differentiation.
In vivo31P MRS of the liver: In 1985 Maris et al[65] combined the results of in vivo and in vitro31P MR spectroscopy studies to compare the spectral characteristics of the liver of 2 children, one infant with neuroblastoma stage IV-S and the other with neuroblastoma stage IV disease. The 31P MR spectra from the primary tumor in the latter infant, and the spectra from the infiltrated liver regions in both the infants showed substantially elevated PME/β-NTP ratios compared with a spectrum from a normal control. The ratio increased during periods of rapid progression and persisted until treatment became effective. The PME/β-NTP ratio decreased to normal values, during either spontaneous or therapy-induced regression of the disease[66]. It was suggested that the increased PME (corresponding to PEtn and PCho) was due to the need for increased phospholipid synthesis in these tissues. This study demonstrated that 31P MRS could be used to detect tumors and to monitor their response to treatment.
Dixon et al[67,68] studied whether hepatic involvement in lymphoma produced biochemical changes that could be detected by in vivo31P MRS of the liver. Twenty-two patients were included. Lymph node biopsies showed that eight patients had Hodgkin’s disease and 14 non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Eleven patients of these 14 had high grade lymphoma and three low grade disease. Six patients, diagnosed with lymphomatous infiltration of the liver on the basis of liver function tests and either ultrasound or CT imaging, had a significantly higher PME/Pi ratio (1.43 ± 0.37) or PME/ATP ratio (0.94 ± 0.27) compared to 25 controls (ages 20-50 years) (0.58 ± 0.11 and 0.37 ± 0.10, respectively) with normal livers. The PME/Pi ratio decreased following chemotherapy to an average of 66% of the initial value (range 40%-82%). In two patients the ratio fell to the normal range and these patients showed clinical remission. Four patients whose liver spectra showed persistently high ratios after therapy died subsequently of progressive disease. In vitro31P MRS studies of extracts of lymphomatous lymph nodes suggested that PEtn was largely responsible for the increased PME signal. In this study, however, no difference was observed between Hodgkin’s and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma and between histological grades.
Meyerhoff et al[69] used 31P MRS to assess the metabolic state of hepatic cancers and their metabolic response to chemoembolization. Their preliminary report described studies on five patients (two with colon cancer metastasis, two with HCC, and one with adenocarcinoma of unknown primary) and thirteen healthy volunteers. Untreated hepatic tumors showed elevated PME/ATP ratios, reduced ATP and Pi content, and normal PDE levels compared to normal controls. ATP, PME, and/or PDE levels diminished as an acute response to chemoembolization, whereas Pi content increased or stayed relatively constant. This could point to tumor regression and/or necrosis. Long-term follow-up after treatment showed decreased PME/ATP and increased ATP levels, even in the absence of changes on standard imaging. This could be the result of returning normal liver tissue and thus recovery.
Negendank[70] reviewed hundreds of cancer cases in 31P and/or 1H MRS studies that were published up to early 1992. In general he found that human cancers, other than brain, of different types in different locations had similar metabolic characteristics: 173 of 194 cases had high PME and levels, 121 of 166 cases had high PDE levels, 59 of 125 cases had high Pi levels and 96 of 117 cases had low PCr. Table 1 lists the cases with HCC, metastatic liver cancer and lymphoma in the liver. The most frequently used characteristic that differentiated healthy liver tissue from liver lymphoma was an increased PME level, and an increased PME/Pi and increased PME/Pi for HCC, and increased PME/NTP and increased PDE/NTP ratios for metastasis in the liver. Also, an early decrease in PME (or in the PME/PDE ratio) was a good predictor of response to whatever treatment.
| High PME | High PDE | High Pi | Low PCr | |
| HCC | 91% (of 11 cases) | 75% (of 4 cases) | 0% (of 4 cases) | 100% (of 11 cases) |
| Liver metastasis | 100% (of 7 cases) | 33% (of 6 cases) | 17% (of 6 cases) | 100% (of 4 cases) |
| Liver lymphoma | 100% (of 6 cases) | 17% (of 6 cases) | 100% (of 6 cases) | 100% (of 6 cases) |
From these studies it appears that the increase of PME levels is associated with tumor progression and that successful treatment is associated with its decrease. Therefore 31P MRS seems very suitable for treatment response monitoring. Since 2003, however, only a limited number of in vivo31P MRS studies on liver tumors and metastasis have been reported. The reason for this could be the low spatial and time resolution of in vivo31P MRS on 1.5T MR systems. Currently, 3T MR systems have become widely available, dual tuned multi-channel 31P/1H coils have been developed and several techniques, e.g., 1H decoupling, nuclear overhauser enhancement, polarization transfer, have been demonstrated[16] to improve 31P MRS sensitivity and spectral resolution. Finally, high field in vitro31P MRS of cell cultures might establish new markers to distinguish different tumor types and to separate benign from malignant tumors.
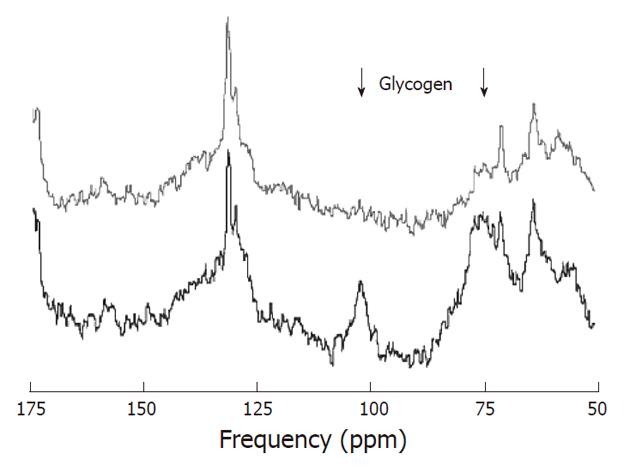
As carbon-12 has no net nuclear spin it cannot be detected by MR spectroscopy. In contrast, 13C can be detected by MRS but it has a natural abundance of only 1.11%. Therefore 13C has a relatively low MR sensitivity. In addition, the signal to noise ratio may be negatively affected by 1H coupling. To obtain spectra with acceptable signal to noise it is needed to apply averaging, polarization transfer, and 1H decoupling. The chemical shift dispersion of 13C MRS in vivo is large (about 200 ppm) and is also characterized by narrow line widths, resulting in a very good spectral resolution (Figure 10). Although 13C MR spectroscopy is primarily known for MRS of 13C-labeled substrates (e.g., glucose), natural abundance 13C MRS can also be applied.
Almost all metabolites in the human body contain carbon and therefore in principle a large amount of metabolites can be investigated with 13C MRS, but because of the 1.11% natural abundance this is restricted to only a few highly concentrated compounds such as lipids. Chemical shifts above 150 ppm are indicative of carbonyl groups; carbons adjacent to hydroxyl groups typically resonate in the 60-100 ppm range; CH, CH2, CH3 groups resonate in the 45-60 ppm, 25-45 ppm and < 25 ppm ranges, respectively. The resonances of -CH = CH- groups are located around 125 ppm. Dominant lipid resonances are usually found in non-brain tissue. Two distinct resonances at 63 and 73 ppm originate from the glycerol backbone[6].
13C MRS with labeled substrates is the only way to study metabolic conversions in the living intact body. Substrates enriched with 13C are usually administrated intravenously to reach a high and stable level in the blood. One of the most commonly used enriched substrate in humans is [1-13C]glucose. Other known substrates are [1,2-13C2]-choline, [1,2-13C2]-ethanolamine, [3-13C]pyruvate and lactate, [2-13C]acetate, [2-13C]glucose and [1,6-13C2]glucose. The latter, often used in studies involving rats and mice, results in two labeled [3-13C]-pyruvate molecules, and thus more signal. Pyruvate is an intermediate common to three major metabolic and catabolic pathways. After i.v. injection, pyruvate is rapidly distributed in the body and taken up by most cells, and then converted into alanine, lactate, or carbon dioxide, depending on the intracellular energy status.
Natural abundance 13C MR liver spectrum: In 1983 Bottomley et al[71] demonstrated the feasibility of natural abundance 13C MRS at 1.5T. The low sensitivity and the fact that most information could also be obtained from 1H and 31P MRS spectra has prevented widespread application of natural abundance 13C MRS. However, there are areas where it has some advantages such as in the detection of glycogen. Carbohydrate reserves are mainly stored as glycogen in animals and humans, in particular in muscle and liver. Natural abundance 13C MRS detection of glycogen is typically performed via the glycogen-C1 resonance at 100.5 ppm[72]. Some studies on rats have indicated that glycogen levels in hepatic tumors were markedly less than those observed in livers of control animals[73,74].
13C-labeled glucose: Infusion of enriched 13C-labeled glucose in combination with 13C MRS can provide highly specific information on metabolites and metabolic rates involved in energy metabolism. The 13C-labeled glucose is transported into the cell in the same way as 18FDG used in PET[75]. Where the derivative of 18FDG is trapped inside the cell, indicating areas of high glucose transport and thus indirectly indicating glycolytic activity, the 13C-labeled glucose will enter metabolic pathways like glycolysis and the TCA cycle. This allows the direct study of glucose uptake, the flux through labeled metabolites, relative contributions of glycolytic pathways and oxidative phosphorylation, as well as oxygen consumption[12,76].
13C labeled glucose combined with 13C MRS in human liver tissue is, however, not without difficulties and the number of studies with this technique is still very limited. In 2008 Tomiyasu et al[77] monitored liver glycogen synthesis in diabetic patients using 13C MRS on a 3.0T system. The MR signals of liver [1-13C]-glucose and glycogen were assessed and a correlation between the quantity of liver glycogen and the fasting plasma glucose levels was found. To investigate glucose metabolism of liver tumors would be of great interest, but such studies are still lacking.
13C-labeled ethanolamine and choline in experimental tumors: Dixon et al[67,78] administrated [13C2]-ethanolamine to mice with lymphomatous liver to study the kinetics of PtdEtn synthesis[79]. The newly synthesized PEtn and PtdEtn could be distinguished from naturally-abundant compounds by their 13C label. The results showed that PtdEtn synthesis in the normal liver largely follows the Kennedy pathway. The data extracted from the 13C MR spectra were fitted to a kinetic model representing this pathway, which allowed them to determine the approximate rates of the various enzymes in the synthetic pathway in vivo. They also showed that the overall rate of PtdEtn synthesis from Etn was not increased in lymphomatous liver.
Katz-Brull et al[35] investigated the distribution of metabolites following infusion of [1,2-13C]-choline by 13C MRS in mice. In their study MCF7 human breast cancer cells were inoculated s.c. in the right flank of CD-1 female athymic mice. In the tumors significantly more PCho (labeled and unlabeled) was observed than in normal liver and kidney tissue. Therefore, 13C MRS combined with modeling can be used to study choline and ethanolamine metabolism and enzymes rates in mice.
Hyperpolarization and tumor metabolism: Gallagher et al[80] performed a 13C MRS in vitro study of glutaminase activity in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells using DNP hyperpolarized 13C-labeled glutamine. They showed that the conversion of hyperpolarized [5-13C]glutamine to glutamate senses intramitochondrial glutaminase activity in hepatoma cells. These results represented the first step in the development of an imaging technique for the detection of glutamine metabolism in vivo. The rate of glutamine uptake and metabolism to glutamate in HCC cells was shown to be up to 30-fold higher than in normal hepatocytes. And thus this approach has clinical potential such as in the detection of small HCC in the presence of a cirrhotic liver. This study also suggests a new technique to detect changes in tumor cell proliferation in response to cytotoxic treatment since glutamine utilization has been correlated with cell proliferation.
Golman et al[75] conducted a metabolic imaging study in P22 tumors implanted on the back of rats. The high signal, due to DNP hyperpolarization, allowed mapping of pyruvate, lactate and alanine in a 5 mm × 5 mm × 10 mm imaging voxel using a 1.5T scanner. Tumor tissue showed a significantly higher lactate content than normal tissue, possibly explained by the Warburg effect. The results indicate that fast noninvasive quantification may be possible. To show that the DNP technique can be used both in small and larger animals, Golman et al[81] also conducted nearly similar real-time metabolic imaging studies in rats and pigs. The pig study would provide important information as to whether [1-13C] enriched hyperpolarized dynamics also could be visualized in a more clinically relevant setting. They showed that in both species, where pharmacokinetic parameters widely differ, it is possible to map pyruvate and some of its metabolites in resting skeletal muscle within a clinically useful time frame of about 10 seconds. This indicates the technique may work in humans as well.
Hyperpolarization is a promising technique in MR cancer research. Similar images as those in 18FDG-PET can be obtained, but with the further advantages that, without radiation, real (glucose) metabolism is observed. Although this new MR method is far more sensitive than conventional 13C MRS it only allows measurement of single step metabolic conversions associated with rapid cellular uptake of the administered substrate. Therefore, conventional 13C MRS studies will remain valuable to understand and complement results from hyperpolarized 13C MR imaging.
Hydrogen is the most commonly studied nucleus, as it has the highest sensitivity compared to 31P and 13C, and essentially can be performed with the same hardware as for standard MR imaging. In liver tumor studies the lactate resonance is related to energy metabolism (Warburg effect) of the tumor. Proton resonances of mobile lipids and the peak of total choline (tCho) have been explored as biomarkers to identify malignant tumors. However, the tCho peak is composed of several unresolved resonances of different choline containing compounds, which makes changes in this signal difficult to interpret.
With 31P MRS phosphorylated choline and ethanolamine containing compounds can be resolved. From several studies it is known that the increase of PME is associated with tumor progression and that successful treatment is associated with a decrease of PME levels. Therefore 31P MRS could very well be used for treatment response monitoring. Besides the signals from phospholipid metabolism, 31P MR spectra of liver also show signals of ATP and Pi which can be used to investigate tumor energy metabolism.
MRS with 13C as label is a unique method to measure the dynamics of metabolic conversions in vivo, but it has hardly been used to examine human liver metabolism due to its technical complexity and relatively low sensitivity. However, developments such as hyperpolarization may open new ways of liver assessment and imaging.
In vivo MR spectroscopy provides a number of adequate research tools to study metabolism in liver tumors and metastasis. However, they are not yet applied often in a clinical setting for diagnosis and treatment monitoring. This may be due to technical challenges associated with the body location of the liver, relatively long scan times needed for a good signal to noise ratio, the need for additional hardware (except 1H MRS) and the need for expertise in spectral interpretation. With higher magnet fields becoming available, new multi-element detection probes, new acquisition techniques for improved spatial and time resolution, better postprocessing, and with new biomarkers it is expected that the research and clinical usefulness of MRS of liver and tumors therein will increase.
Peer reviewer: Xiao-Peng Zhang, Professor, Department of Radiology, Peking University School of Oncology, Beijing Cancer Hospital and Institute, No.52 Haidian District, Beijing 100142, China
S- Editor Tian L L- Editor O’Neill M E- Editor Li JY
| 1. | Bosch FX, Ribes J, Díaz M, Cléries R. Primary liver cancer: worldwide incidence and trends. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:S5-S16. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 2. | Khan AN. Liver, Metastases: eMedicine Radiology. 2009; Available from: URL: http: //emedicine.medscape.com/article/369936-overview. |
| 3. | Gilbert H, Kagan A, Hintz B, Nussbaum H. Patterns of metastases. Liver metastases. Boston, Mass: GK Hall Medical Publishers 1982; 19-39. |
| 4. | Pickren J, Tsukada Y, Lane W. Analysis of Autopsy Data. Liver metastases. Boston, Mass: GK Hall Medical Publishers 1982; 2-18. |
| 5. | Silva MA, Hegab B, Hyde C, Guo B, Buckels JA, Mirza DF. Needle track seeding following biopsy of liver lesions in the diagnosis of hepatocellular cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gut. 2008;57:1592-1596. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 6. | de Graaf RA. In Vivo NMR Spectroscopy. Chichester, UK: John Wiley and Sons, Ltd 2007; Available from: URL:http: //www3.interscience.wiley.com/cgi-bin/bookhome/116835983. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 7. | Clayton DB, Elliott MA, Lenkinski RE. In vivo proton spectroscopy without solvent suppression. Concepts in Magnetic Resonance. 2001;13:260-275. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 8. | Haase A, Frahm J, Hänicke W, Matthaei D. 1H NMR chemical shift selective (CHESS) imaging. Phys Med Biol. 1985;30:341-344. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 10. | Freeman DM, Hurd R. Decoupling: theory and practice. II. State of the art: in vivo applications of decoupling. NMR Biomed. 1997;10:381-393. [PubMed] |
| 12. | Gruetter R, Adriany G, Choi IY, Henry PG, Lei H, Oz G. Localized in vivo 13C NMR spectroscopy of the brain. NMR Biomed. 2003;16:313-338. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 13. | Ross B, Lin A, Harris K, Bhattacharya P, Schweinsburg B. Clinical experience with 13C MRS in vivo. NMR Biomed. 2003;16:358-369. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 14. | Wijnen JP, Van der Graaf M, Scheenen TW, Klomp DW, de Galan BE, Idema AJ, Heerschap A. In vivo 13C magnetic resonance spectroscopy of a human brain tumor after application of 13C-1-enriched glucose. Magn Reson Imaging. 2010;28:690-697. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 15. | Klomp DW, Kentgens AP, Heerschap A. Polarization transfer for sensitivity-enhanced MRS using a single radio frequency transmit channel. NMR Biomed. 2008;21:444-452. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 16. | Klomp DW, Wijnen JP, Scheenen TW, Heerschap A. Efficient 1H to 31P polarization transfer on a clinical 3T MR system. Magn Reson Med. 2008;60:1298-1305. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 17. | Ardenkjaer-Larsen JH, Fridlund B, Gram A, Hansson G, Hansson L, Lerche MH, Servin R, Thaning M, Golman K. Increase in signal-to-noise ratio of & gt; 10,000 times in liquid-state NMR. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:10158-10163. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 18. | Golman K, Ardenkjaer-Larsen JH, Petersson JS, Mansson S, Leunbach I. Molecular imaging with endogenous substances. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:10435-10439. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 19. | Ordidge RJ, Connelly A, Lohman JAB. Image-selected in Vivo spectroscopy (ISIS). A new technique for spatially selective nmr spectroscopy. Journal of Magnetic Resonance (1969). 1986;66:283-294. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 20. | Frahm J, Merboldt K, H�nicke W. Localized proton spectroscopy using stimulated echoes. Journal of Magnetic Resonance (1969). 1987;72:502-508. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 21. | Bottomley PA. United States Patent: 4480228 - Selective volume method for performing localized NMR spectroscopy. 1984; Available from: URL: http: //patft.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?patentnumber=4480228. |
| 22. | Brown TR, Kincaid BM, Ugurbil K. NMR chemical shift imaging in three dimensions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1982;79:3523-3526. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 23. | Li CW, Kuo YC, Chen CY, Kuo YT, Chiu YY, She FO, Liu GC. Quantification of choline compounds in human hepatic tumors by proton MR spectroscopy at 3 T. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 2005;53:770-776. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 24. | Hanley J, Debois MM, Mah D, Mageras GS, Raben A, Rosenzweig K, Mychalczak B, Schwartz LH, Gloeggler PJ, Lutz W. Deep inspiration breath-hold technique for lung tumors: the potential value of target immobilization and reduced lung density in dose escalation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1999;45:603-611. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 25. | Kitamura K, Shirato H, Seppenwoolde Y, Shimizu T, Kodama Y, Endo H, Onimaru R, Oda M, Fujita K, Shimizu S. Tumor location, cirrhosis, and surgical history contribute to tumor movement in the liver, as measured during stereotactic irradiation using a real-time tumor-tracking radiotherapy system. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003;56:221-228. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 26. | Shirato H, Seppenwoolde Y, Kitamura K, Onimura R, Shimizu S. Intrafractional tumor motion: lung and liver. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2004;14:10-18. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 27. | Kuesel AC, Sutherland GR, Halliday W, Smith IC. 1H MRS of high grade astrocytomas: mobile lipid accumulation in necrotic tissue. NMR Biomed. 1994;7:149-155. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 28. | Vander Heiden MG, Cantley LC, Thompson CB. Understanding the Warburg effect: the metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Science. 2009;324:1029-1033. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 29. | Warburg O, Posener E, Negelein E. Ueber den Stoffwechsel der Tumoren. Biochem Z. 1924;152:319-344. |
| 30. | Fischbach F, Bruhn H. Assessment of in vivo 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy in the liver: a review. Liver Int. 2008;28:297-307. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 31. | Moreno A, López LA, Fabra A, Arús C. 1H MRS markers of tumour growth in intrasplenic tumours and liver metastasis induced by injection of HT-29 cells in nude mice spleen. NMR Biomed. 1998;11:93-106. [PubMed] |
| 32. | Glunde K, Ackerstaff E, Mori N, Jacobs MA, Bhujwalla ZM. Choline phospholipid metabolism in cancer: consequences for molecular pharmaceutical interventions. Mol Pharm. 2006;3:496-506. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 33. | Glunde K, Serkova NJ. Therapeutic targets and biomarkers identified in cancer choline phospholipid metabolism. Pharmacogenomics. 2006;7:1109-1123. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 34. | Glunde K, Jacobs MA, Bhujwalla ZM. Choline metabolism in cancer: implications for diagnosis and therapy. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2006;6:821-829. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 35. | Katz-Brull R, Margalit R, Degani H. Differential routing of choline in implanted breast cancer and normal organs. Magn Reson Med. 2001;46:31-38. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 36. | Podo F. Tumour phospholipid metabolism. NMR Biomed. 1999;12:413-439. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 37. | Zeisel SH. Choline: an essential nutrient for humans. Nutrition. 2006;16:669-671. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 38. | Zeisel SH, da Costa KA. Choline: an essential nutrient for public health. Nutr Rev. 2009;67:615-623. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 39. | Kennedy EP, Weiss SB. The function of cytidine coenzymes in the biosynthesis of phospholipides. J Biol Chem. 1956;222:193-214. [PubMed] |
| 40. | Bremer J, Greenberg DM. Methyl transfering enzyme system of microsomes in the biosynthesis of lecithin (phosphatidylcholine). Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 1961;46:205-216. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 41. | Sundler R, Akesson B. Regulation of phospholipid biosynthesis in isolated rat hepatocytes. Effect of different substrates. J Biol Chem. 1975;250:3359-3367. [PubMed] |
| 42. | Barak AJ, Tuma DJ. Betaine, metabolic by-product or vital methylating agent? Life Sci. 1983;32:771-774. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 43. | Finkelstein JD. Methionine metabolism in mammals. J Nutr Biochem. 1990;1:228-237. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 44. | Finkelstein JD. Methionine metabolism in liver diseases. Am J Clin Nutr. 2003;77:1094-1095. [PubMed] |
| 45. | Richards TL. Proton MR spectroscopy in multiple sclerosis: value in establishing diagnosis, monitoring progression, and evaluating therapy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1991;157:1073-1078. [PubMed] |
| 46. | Herminghaus S, Pilatus U, Möller-Hartmann W, Raab P, Lanfermann H, Schlote W, Zanella FE. Increased choline levels coincide with enhanced proliferative activity of human neuroepithelial brain tumors. NMR Biomed. 2002;15:385-392. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 47. | Soper R, Himmelreich U, Painter D, Somorjai RL, Lean CL, Dolenko B, Mountford CE, Russell P. Pathology of hepatocellular carcinoma and its precursors using proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy and a statistical classification strategy. Pathology. 2002;34:417-422. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 48. | Kuo YT, Li CW, Chen CY, Jao J, Wu DK, Liu GC. In vivo proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of large focal hepatic lesions and metabolite change of hepatocellular carcinoma before and after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization using 3.0-T MR scanner. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2004;19:598-604. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 49. | Fischbach F, Schirmer T, Thormann M, Freund T, Ricke J, Bruhn H. Quantitative proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the normal liver and malignant hepatic lesions at 3.0 Tesla. Eur Radiol. 2008;18:2549-2558. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 50. | Bell JD, Cox IJ, Sargentoni J, Peden CJ, Menon DK, Foster CS, Watanapa P, Iles RA, Urenjak J. A 31P and 1H-NMR investigation in vitro of normal and abnormal human liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993;1225:71-77. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 51. | Bates TE, Williams SR, Gadian DG. Phosphodiesters in the liver: the effect of field strength on the 31P signal. Magn Reson Med. 1989;12:145-150. [PubMed] |
| 52. | Moon RB, Richards JH. Determination of intracellular pH by 31P magnetic resonance. J Biol Chem. 1973;248:7276-7278. [PubMed] |
| 53. | Griffiths JR. Are cancer cells acidic? Br J Cancer. 1991;64:425-427. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 54. | Griffiths JR, Stevens AN, Iles RA, Gordon RE, Shaw D. 31P-NMR investigation of solid tumours in the living rat. Biosci Rep. 1981;1:319-325. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 55. | Griffiths JR, Cady E, Edwards RH, McCready VR, Wilkie DR, Wiltshaw E. 31P-NMR studies of a human tumour in situ. Lancet. 1983;1:1435-1436. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 56. | Iles RA, Stevens AN, Griffiths JR. NMR Studies of metabolites in living tissue. Progress in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. 1982;15:49-200. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 57. | Oberhaensli RD, Hilton-Jones D, Bore PJ, Hands LJ, Rampling RP, Radda GK. Biochemical investigation of human tumours in vivo with phosphorus-31 magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Lancet. 1986;2:8-11. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 58. | Vaupel P, Kallinowski F, Okunieff P. Blood flow, oxygen and nutrient supply, and metabolic microenvironment of human tumors: a review. Cancer Res. 1989;49:6449-6465. [PubMed] |
| 59. | Stubbs M, Veech RL, Griffiths JR. Tumor metabolism: the lessons of magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1995;35:101-115. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 60. | Ruiz-Cabello J, Cohen JS. Phospholipid metabolites as indicators of cancer cell function. NMR Biomed. 1992;5:226-233. [PubMed] |
| 61. | Evanochko WT, Sakai TT, Ng TC, Krishna NR, Kim HD, Zeidler RB, Ghanta VK, Brockman RW, Schiffer LM, Braunschweiger PG. NMR study of in vivo RIF-1 tumors. Analysis of perchloric acid extracts and identification of 1H, 31P and 13C resonances. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984;805:104-116. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 62. | Dagnelie PC, Bell JD, Williams SC, Bates TE, Abel PD, Foster CS. Altered phosphorylation status, phospholipid metabolism and gluconeogenesis in the host liver of rats with prostate cancer: a 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Br J Cancer. 1993;67:1303-1309. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 63. | Dagnelie PC, Sijens PE, Kraus DJA, Planting AST, Dijk PV. Abnormal liver metabolism in cancer patients detected by 31P MR spectroscopy. NMR in Biomedicine. 1999;12:535-544. |
| 64. | Bell JD, Bhakoo KK. Metabolic changes underlying 31P MR spectral alterations in human hepatic tumours. NMR Biomed. 1998;11:354-359. [PubMed] |
| 65. | Maris JM, Evans AE, McLaughlin AC, D'Angio GJ, Bolinger L, Manos H, Chance B. 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopic investigation of human neuroblastoma in situ. N Engl J Med. 1985;312:1500-1505. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 66. | Vaidya SJ, Payne GS, Leach MO, Pinkerton CR. Potential role of magnetic resonance spectroscopy in assessment of tumour response in childhood cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2003;39:728-735. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 67. | Dixon RM, Angus PW, Rajagopalan B, Radda GK. Abnormal phosphomonoester signals in 31P MR spectra from patients with hepatic lymphoma. A possible marker of liver infiltration and response to chemotherapy. Br J Cancer. 1991;63:953-958. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 68. | Dixon RM. NMR studies of phospholipid metabolism in hepatic lymphoma. NMR Biomed. 1998;11:370-379. [PubMed] |
| 69. | Meyerhoff DJ, Karczmar GS, Valone F, Venook A, Matson GB, Weiner MW. Hepatic cancers and their response to chemoembolization therapy. Quantitative image-guided 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Invest Radiol. 1992;27:456-464. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 70. | Negendank W. Studies of human tumors by MRS: a review. NMR Biomed. 1992;5:303-324. [PubMed] |
| 71. | Bottomley PA, Hart HR, Edelstein WA, Schenck JF, Smith LS, Leue WM, Mueller OM, Redington RW. NMR imaging/spectroscopy system to study both anatomy and metabolism. Lancet. 1983;2:273-274. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 72. | Roser W, Beckmann N, Wiesmann U, Seelig J. Absolute quantification of the hepatic glycogen content in a patient with glycogen storage disease by 13C magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Magn Reson Imaging. 1996;14:1217-1220. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 73. | Lea MA, Murphy P, Morris HP. Glycogen metabolism in regenerating liver and liver neoplasms. Cancer Res. 1972;32:61-66. [PubMed] |
| 74. | Sweeney MJ, Ashmore J, Morris HP, Weber G. Comparetive biochemistry hepatomas IV isotope studies of glucose and fructose metabolism in liver tumors of different growth rates. Cancer Res. 1963;23:995-1002. [PubMed] |
| 75. | Golman K, Zandt RI, Lerche M, Pehrson R, Ardenkjaer-Larsen JH. Metabolic imaging by hyperpolarized 13C magnetic resonance imaging for in vivo tumor diagnosis. Cancer Res. 2006;66:10855-10860. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 76. | Nielsen FU, Daugaard P, Bentzen L, Stødkilde-Jørgensen H, Overgaard J, Horsman MR, Maxwell RJ. Effect of changing tumor oxygenation on glycolytic metabolism in a murine C3H mammary carcinoma assessed by in vivo nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Cancer Res. 2001;61:5318-5325. [PubMed] |
| 77. | Tomiyasu M, Obata T, Nishi Y, Nakamoto H, Nonaka H, Takayama Y, Autio J, Ikehira H, Kanno I. Monitoring of liver glycogen synthesis in diabetic patients using carbon-13 MR spectroscopy. Eur J Radiol. 2010;73:300-304. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 78. | Dixon RM, Tian M. Phospholipid synthesis in the lymphomatous mouse liver studied by 31P nuclear magnetic resistance spectroscopy in vitro and by administration of 14C-radiolabelled compounds in vivo. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease. 1993;1181:111-121. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 79. | Dixon RM. Phosphatidylethanolamine synthesis in the normal and lymphomatous mouse liver; a 13C NMR study. Anticancer Res. 1996;16:1351-1356. [PubMed] |
| 80. | Gallagher FA, Kettunen MI, Day SE, Lerche M, Brindle KM. 13C MR spectroscopy measurements of glutaminase activity in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells using hyperpolarized 13C-labeled glutamine. Magn Reson Med. 2008;60:253-257. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 81. | Golman K, in 't Zandt R, Thaning M. Real-time metabolic imaging. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:11270-11275. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |