Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2011; 17(24): 2879-2889
Published online Jun 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i24.2879
Published online Jun 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i24.2879
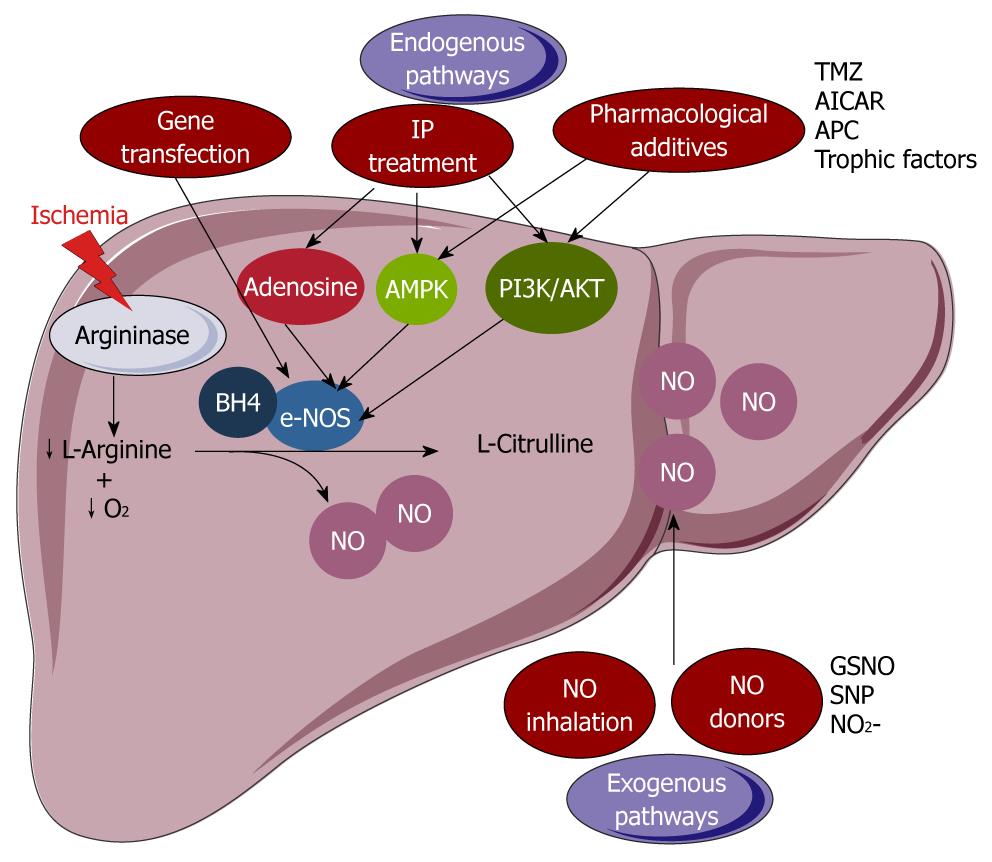
Figure 4 Modulation of the decline in endothelial nitric oxide synthase-derived nitric oxide production.
endothelial nitric oxide synthase (e-NOS)-derived nitric oxide (NO) bioavailability can be compromised either by a reduced L-arginine and cofactor (tetrahydrobiopterin, BH4) availability, or by a decreased e-NOS protein activity and level. Two ways seem to be able to overcome these obstacles: the use of exogenous sources of NO (NO donors or NO inhalation) and the induction of the endogenous downstream effectors of e-NOS (pharmacological treatment or ischemic preconditioning) or transfection by an adenovirus containing e-NOS enzyme. SNP: Sodium nitroprusside; GSNO: S-nitroso-L-glutathione; AICAR: 5-amino-4-imidazole carboxamide riboside; TMZ: Trimetazidine; APC: Activated protein C; AMPK: Adenosine monophosphate protein kinase; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase.
- Citation: Abdennebi HB, Zaoualí MA, Alfany-Fernandez I, Tabka D, Roselló-Catafau J. How to protect liver graft with nitric oxide. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(24): 2879-2889
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i24/2879.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i24.2879