Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2011; 17(19): 2357-2364
Published online May 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i19.2357
Published online May 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i19.2357
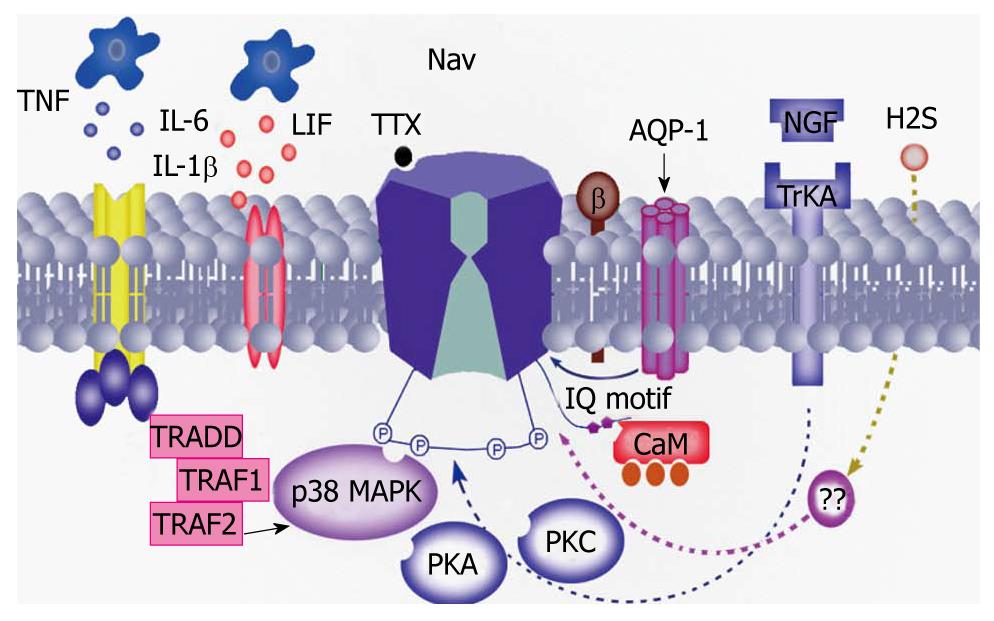
Figure 3 Possible mechanisms underlying the modulation of voltage-gated sodium channel activity.
Inflammatory mediators such as nerve growth factor (NGF), prostaglandin (PG) E2, interleukin (IL)-1β may sensitize sodium channels by different intracellular signal transduction pathways such as protein kinase A (PKA), protein kinase C (PKC), mitogen-activated protein kinase and calmodulin (CaM). In addition, a recent study showed that aquaporin (AQP)-1 directly interacted with the sodium channel, thus contributing to the perception of pain[48]. TTX: Tetrodotoxin; LIF: leukemia inhibitory factor; Trk: Tyrosine receptor kinase; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; TRAF: Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor; TRADD: TNF receptor-associated death domain protein.
- Citation: Qi FH, Zhou YL, Xu GY. Targeting voltage-gated sodium channels for treatment for chronic visceral pain. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(19): 2357-2364
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i19/2357.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i19.2357