Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2011; 17(16): 2080-2085
Published online Apr 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i16.2080
Published online Apr 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i16.2080
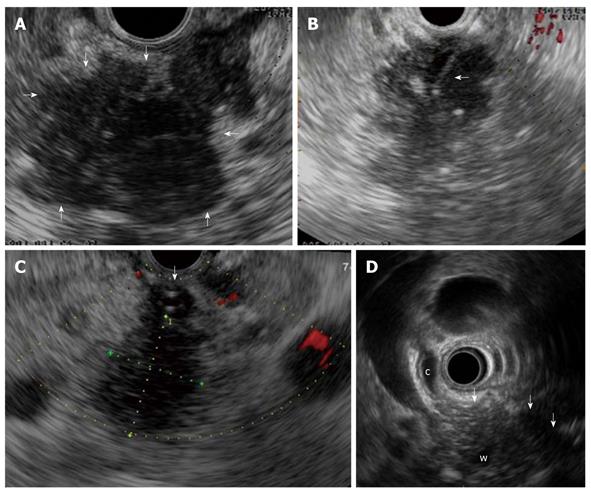
Figure 2 Focal form of autoimmune pancreatitis.
A: Endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) shows a focal lesion (arrows) of pancreatic head which is echopoor with hyperechoic strands; B: A EUS-guided fine needle aspiration is performed (arrow) for tissue characterization; C: Another case of focal autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) with echopoor lesion of pancreatic head (between callipers) and marked echopoor thickening of the choledochal wall (arrow); D: In this case of focal AIP EUS shows a echopoor lesion (arrows) of pancreatic head, with upstream dilatation of both common bile duct (c) and pancreatic duct (w); notice the thickened choledochal wall.
- Citation: Buscarini E, Lisi SD, Arcidiacono PG, Petrone MC, Fuini A, Conigliaro R, Manfredi G, Manta R, Reggio D, Angelis CD. Endoscopic ultrasonography findings in autoimmune pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(16): 2080-2085
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i16/2080.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i16.2080