Published online May 7, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i17.2190
Revised: January 24, 2010
Accepted: January 31, 2010
Published online: May 7, 2010
Lipoma within jejunal duplication presenting as abdominal bloating and partial intestinal obstruction is an exceptional clinical entity. We report a case of 68-year-old man complaining of abdominal bloating for 10 d due to multiple lipomas arising from jejunal duplication cysts. Only a few cases of a single lipoma within a Meckel’s diverticulum giving rise to this clinical scenario have been reported in the English language literature. However, no case of multiple lipomas within jejunal duplication cysts has been reported. We present a case in which double-balloon endoscopy revealed a small intestinal structure changed into Meckel’s diverticulum-like cavities containing several lipomas. This case highlights intestinal lipoma as an uncommon cause of adult intussusceptions, which should be included in the differential diagnosis of small intestinal obstruction and appropriate examinations should be chosen.
- Citation: Wan XY, Deng T, Luo HS. Partial intestinal obstruction secondary to multiple lipomas within jejunal duplication cyst: A case report. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(17): 2190-2192
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i17/2190.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i17.2190
Lipoma of the small intestine is a benign tumor of mesenchymal origin which is mostly found by chance during gastrointestinal investigation. Invaginations account for 2/3 of small bowel occlusion caused by up to 80% of tumors and the lipoma is the most frequent benign tumor that causes invagination in its submucous polypoid and it is in more or less scissile form[1].
However, multiple lipomas within the intestinal duplication canal as a predominant cause of partial intestinal obstruction is an exceptional clinical scenario. We report a case of a 68-year-old man with a 10-d history of abdominal bloating after meals caused by intussusception due to a small intestine lipomatous lesion located in the jejunal duplication cyst. Although the same complications such as intestinal obstruction and intussusception may crop up in the duplication patients, we still consider the multiple lipomas as the main cause of the symptom.
A 68-year-old man was referred to our department complaining of gradual abdominal bloating after meals for the last 10 d, but without abdominal pain and vomiting. He had a bowel movement every 2 d despite a history of chronic constipation for 6 years. The patient refused eating for 2 d and lost approximately 5 kg. There was no more relevant past medical, family or surgical histories. Physical examination revealed abdominal bulge with visible intestinal peristalsis, and active bowel sounds. Abdominal palpation revealed a firm, round and fixed mass of 7 cm × 4 cm over the left umbilical region. Examination of other systems was unremarkable with insignificant laboratory results.
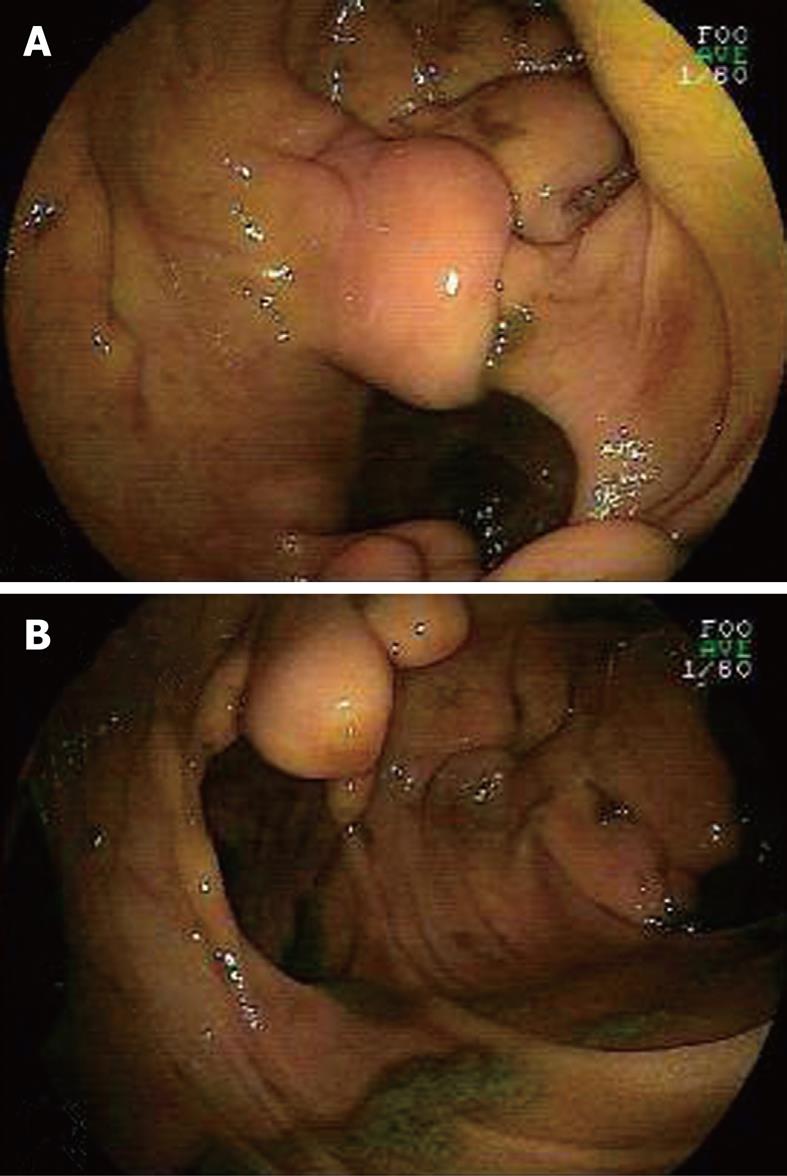
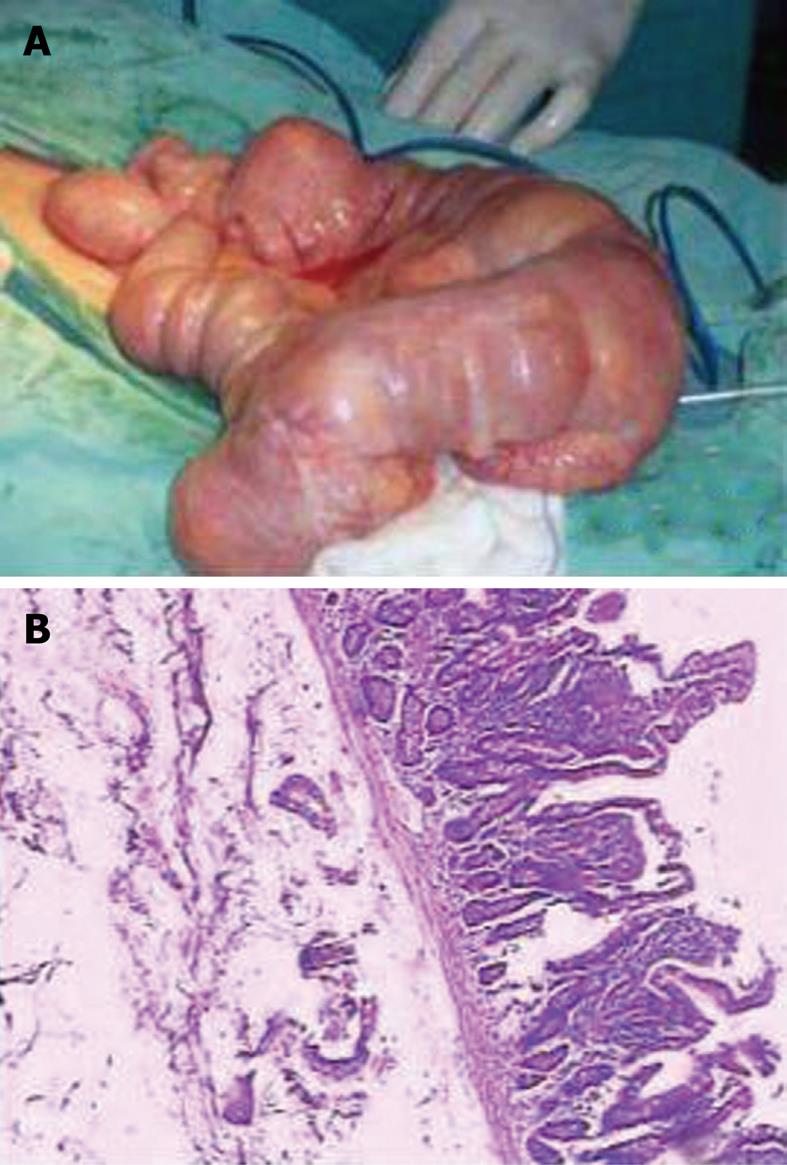
Abdominal plain X-ray film showed air-fluid levels while colonoscopy failed to reveal any lesions which might be responsible for the symptoms. However, double-balloon endoscopy (DBE) revealed small intestinal structures which changed into Meckel’s diverticulum-like cavities at 30 cm beyond the ligament of Treitz from the oral route (Figure 1A). Several yellow spherical or stalactite-like protuberances of unequal size rose into the jejunal cavity in these cystic formations with smooth surface (Figure 1B). We also found scar tissues in the partial jejunal cavity (Figure 1A). A possible diagnosis of jejunal duplication with multiple lipomas was established and the patient underwent exploratory laparotomy. One remarkably dilated intestinal canal with seven duplication cysts of about 7.5 cm × 6 cm on the mesenteric aspect of the jejunum of around 55 cm was found intraoperatively (Figure 2A). All the cyst-like dilatation had independent vascular supply, some of them were connected to the intestinal cavity while some did not. The end of intestinal tract invaginating into the low intestinal canal appeared dark red and edematous, while the upper segment was dilated significantly. Excision of the cystic lesion and an end-to-end anastomosis of the jejunum were performed. Pathological examination of the resected specimen revealed jejunal duplications having seven cysts ranging from 5.5 cm × 6 cm to 8.5 cm × 7.5 cm, with multiple submucosal lipomas lining on its wall (Figure 2B). The biggest lipoma was 32 mm in diameter. The patient had an uneventful postoperative recovery and was discharged on the seventh post-operative day. He remained well 14 mo after surgery without any symptoms of recurrence.
Alimentary tract duplications are rare congenital malformations, which in most of cases are diagnosed in infancy and childhood, although they can remain undetected until older age[2]. In contrast to Meckel’s diverticulum, duplication cysts are located on the mesenteric aspect and share a common smooth muscle wall and vascular supply[2,3]. Most of the patients are asymptomatic and remain undiagnosed for years. When symptomatic, they manifest as bleeding, constipation and obstruction as a result of direct compression, volvulus or intussusception[4,5]. Our patient had a history of chronic constipation as a presenting symptom of jejunal duplication. Although it seemed to be the complication of duplication cyst, the right diagnosis was only made after 6 years.
Lipoma is a benign tumor of mesenchymal origin which is uncommon to be localized in the small bowel. It is mostly encountered incidentally during the investigation of the gastrointestinal tract for other reasons, since they are usually asymptomatic[6]. Generally, lipoma is defined to originate in the submucosal layer and usually solitary (85%-90%), with variable sizes ranging from 1 to 30 cm[7]. Zografos et al[8] reported that lesions smaller than 1 cm are generally unable to cause symptoms, while 75% of those > 4 cm might give rise to gastrointestinal symptoms. Intestinal occlusion is one of the major results, which is caused by direct pressure by the lipoma or due to intestinal intussusception. Duplication cysts and lipomas can both lead to intussusception or obstruction, but in this case, we speculated that the small bowel lipomas should be the main reason. Firstly, more than 60% of the gastrointestinal duplications are diagnosed prenatally or in the first 2 years of life[9], making it rare to be symptomatic in adults. Ileocecal valve makes cystic duplications easier to cause obstruction of the colon than jejunal duplication. Secondly, several lipomas in the lesion are greater than 3 cm in diameter which might be the cause of intussusception and partial intestinal obstruction in our patient. Direct compression of cystic duplication led to intestinal stenosis, prolonging the time for chyme passage. Consequently, jejunal lipomas continued to be under progressive inflammatory stimulation.
Preoperative diagnosis of duplication cyst or small intestinal lipoma is difficult. Data from our hospital shows that, from 1998 to 2008, only 14.3% of duplication cysts have been correctly diagnosed before surgery. Abdominal computed tomography and ultrasonography were helpful in identifying large lesions but not in small intestinal lesions. However, the availability of DBE[10] and wireless capsule endoscopy made it possible to directly examine the whole digestive tract. In this case, we found multiple small intestinal lipomas arising from the spherical type duplication cysts of the jejunum using DBE. From April 2007 to May 2009, 214 enteroscopic studies were carried out, and 165 patients underwent entire digestive tract examinations. We found other two cases of tubular duplications of the ileum.
Although it is a rare entity, malignant transformation has been reported, mostly to adenocarcinoma[11]. From our patient, we have found out that jejunal duplication may induce the growth of lipoma, hence causing symptoms of intestinal obstruction. We consider that surgical removal of the lesion in asymptomatic cases is necessary because of the risk of malignant degeneration.
Multiple lipomas within jejunal duplication cysts are rare and difficult to diagnose before surgery. This case highlights intestinal lipoma as an uncommon cause of adult intussusceptions, which should be included in the differential diagnosis of small intestinal obstruction. Such a case found by DBE is an example to remind doctors to be vigilant in diagnosing patients with intestinal obstruction and in choosing appropriate examinations.
Peer reviewer: Roberto de Franchis, Professor of Medicine (Gastroenterology), Department of Medical Siences, University of Milan, Head, Gastroenterology 3 Unit, IRCCS Ospedale Maggiore Policlinico, Mangiagalli and Regina Elena Foundation, Via Pace 9, 20122 Milano, Italy
S- Editor Wang YR L- Editor Ma JY E- Editor Zheng XM
| 1. | Nincheri Kunz M, Evaristi L, Spadoni R, Cozzani R, Valle O, Bacigalupo B. [Lipoma of the small intestine as a rare cause of intestinal occlusion]. Minerva Chir. 1994;49:859-865. |
| 2. | Yokoyama J. [Duplications of the alimentary canal]. Nippon Rinsho. 1994;Suppl 6:408-410. |
| 3. | Bissler JJ, Klein RL. Alimentary tract duplications in children: case and literature review. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 1988;27:152-157. |
| 4. | Otter MI, Marks CG, Cook MG. An unusual presentation of intestinal duplication with a literature review. Dig Dis Sci. 1996;41:627-629. |
| 5. | Puligandla PS, Nguyen LT, St-Vil D, Flageole H, Bensoussan AL, Nguyen VH, Laberge JM. Gastrointestinal duplications. J Pediatr Surg. 2003;38:740-744. |
| 7. | Weiss A, Mollura JL, Profy A, Cohen R. Two cases of complicated intestinal lipoma. Review of small intestinal lipomas. Am J Gastroenterol. 1979;72:83-88. |
| 8. | Zografos G, Tsekouras DK, Lagoudianakis EE, Karantzikos G. Small intestinal lipoma as a cause of massive gastrointestinal bleeding identified by intraoperative enteroscopy. A case report and review of the literature. Dig Dis Sci. 2005;50:2251-2254. |
| 9. | D'Journo XB, Moutardier V, Turrini O, Guiramand J, Lelong B, Pesenti C, Monges G, Giovannini M, Delpero JR. Gastric duplication in an adult mimicking mucinous cystadenoma of the pancreas. J Clin Pathol. 2004;57:1215-1218. |
| 10. | Yamamoto H, Sekine Y, Sato Y, Higashizawa T, Miyata T, Iino S, Ido K, Sugano K. Total enteroscopy with a nonsurgical steerable double-balloon method. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001;53:216-220. |
| 11. | Kuraoka K, Nakayama H, Kagawa T, Ichikawa T, Yasui W. Adenocarcinoma arising from a gastric duplication cyst with invasion to the stomach: a case report with literature review. J Clin Pathol. 2004;57:428-431. |